Blood Sugar Chart: Summary
The fasting blood sugar, 2-hour post-meal blood sugar, and HbA1C tests are important ways to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, as well as indicate how well a persons diabetes is being managed. If you think you have diabetes, its important to not try and diagnose yourself by doing a finger-stick with a home blood glucose meter. There are strict standards and procedures that laboratories use for diagnosing diabetes therefore, you should get tested at your doctors office or at a laboratory.
Its also important to talk with your doctor to make sure you understand a) how often you should have certain tests, such as a fasting blood glucose or HbA1C test b) what your results mean and c) what your blood sugar and HbA1C targets are.
If you have not been previously diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes but your results are above normal, your doctor may recommend other tests and should discuss a plan of treatment with you. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, a healthy eating plan, and regular physical activity. You may need to start taking diabetes medications, including insulin. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, its recommended that you learn how to check your blood sugars with a meter so that you and your healthcare team can determine how your treatment plan is working for you.
What Are The Recommended Targets For Blood Glucose Levels
Many people with diabetes aim to keep their blood glucose at these normal levels:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL
- About 2 hours after a meal starts: less than 180 mg/dL
Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. Be sure to tell your health care professional if your glucose levels often go above or below your target range.
Target A Range Not A Single Number
Note that the CPGs recommend a realistic range for blood glucose levels, rather than a single number at any particular point in time. This is an important concept to grasp since diabetes management is far from a perfect science, and blood glucose levels can be expected to swing occasionally. Sometimes this can be for no seeming reason at all. On this topic, you may find it interesting to read our article Not all blood glucose levels need to be perfect.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Metformin To Lower Blood Sugar
Levels In The Morning
The best time to check blood sugar levels in the morning is right when you wake up and before you eat anything. This gives you a glimpse of what may be happening overnight, and it gives you a baseline for the day.
These are goal levels, according to The Joslin Diabetes Center:
- Under 70 mg/dl if you do not have diabetes.
- 70 to 130 mg/dl if you have diabetes.
The dawn effect can often lead to a high morning measurement in diabetes. This is your bodys tendency to get ready for the day by raising blood sugar by increasing levels of counter-regulatory hormones the ones that counteract insulin as in normal blood sugar. For people with diabetes, you do not have the capacity to counterbalance this rise in blood sugar, so levels can be dangerously high.
Ways to lower your morning blood sugar value include:
- Eating dinner earlier
- Checking your medications making sure you are taking them properly and asking your doctor if they are correct
- Going for a walk after dinner
- Including protein with your dinner
Do You Have To Fast For An A1c Blood Test
![25 Printable Blood Sugar Charts [Normal, High, Low] á? TemplateLab 25 Printable Blood Sugar Charts [Normal, High, Low] á? TemplateLab](https://www.livingwithdiabetes.info/wp-content/uploads/25-printable-blood-sugar-charts-normal-high-low-a-templatelab-scaled.jpeg)
Unlike the fasting plasma glucose and the OGTT tests, there is no need to fast before having the A1C test. If A1C test results indicate a person has or might have diabetes, a healthcare provider might suggest one of these tests to confirm the results. Another test, the random plasma glucose test, which does not require fasting, can also be used. If the results are borderline or if the results of the different tests do not match, a doctor might suggest repeating the test in several weeks or months.
Also Check: Can Metformin Cause Sweating
Diabetes Tracking And Treatment
- Follow your diabetes treatment plan: Understand the treatment plan before leaving the healthcare providers office and discuss barriers that could prevent you from following the program. Attend all follow-up visits.
- Consistently take prescribed medications: If a healthcare provider has prescribed medications to reduce blood sugar levels, take them regularly. Some people only take medication when they arent feeling well, but these medications dont work unless taken consistently.
- Monitor and track blood sugar: Regular blood sugar monitoring is the most important step in diabetes management, according to the CDC. Healthcare providers can inform patients of different types of meters and help patients find the best one for them. Providers can also tell patients how often to check their blood sugar and what their target blood sugar range is.Keep a log of your blood sugar levels to look for patterns and triggers for blood sugar spikes and lows. If you wear a continuous glucose monitor, you can use the data. Learning what causes blood sugar to rise or decrease can help you create a plan to keep it consistent.
Treatment For Low Blood Sugar Levels
For those with low blood sugar levels, management and treatment is a little easier to do yourself. If you find your blood sugar is too low and you notice symptoms, always seek medical attention. They will aid you with what necessary precautions to take if the reading is extremely low.
Most of the time, the following treatment methods are advised to do at home yourself. Having a sugary drink or snack can help increase blood sugar levels and balance out and improve any symptoms. Even a small juice of juice or sweets can improve weakness and similar symptoms.
After youve consumed a sugary drink or snack, it is recommended to test your blood sugar level again. If it has increased and you feel better then you should consume a carbohydrate containing meal, such as bread, biscuits or milk. It is advised to eat a small meal to prevent any further drop in blood sugar.
For normal people without diabetes, it is sometimes advised to consume daily supplements that are beneficial for increasing insulin sensitivity and balancing your blood, its sugars and pressures. You can seek medical advice for those from a doctor. Some options may include supplements such as Garcinia Cambogia, which has shown results for increasing insulin sensitivity.
You may be wondering exactly how you can read and calculate your blood sugar level, as it advised to do so for both treatments. If you wish to calculate your blood sugar level, here is how to do so:
Don’t Miss: Signs Of High Or Low Blood Sugar
How Much Is Ozempic Without Insurance
Is Ozempic covered by insurance | How much does Ozempic cost without insurance? | How to get Ozempic without insurance
Ozempic is a brand-nameprescription drug that lowers blood sugar levels in people diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. It is also prescribed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems such as heart attack in people diagnosed with both Type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Ozempic is not used to treat Type 1 diabetes. Belonging to a family of drugs called GLP-1agonists, semaglutide reduces blood sugar by enhancing insulin release in the body and decreasing the bodys production of glucose.
Ozempic is administered once per week as a subcutaneous injection. Doses will start low and could rise to as high as 1 mg per week. Common side effects include constipation, diabetic retinopathy, and injection site or allergic reactions. Rarely, it may cause low blood sugar or hypoglycemia. There is no generic version of Ozempic yet available, so uninsured patients may need to pay the full retail price for the drug.
High Blood Sugar Level Causes
Several types of diabetes and medical conditions are the primary cause of high blood sugar levels. Most of which are unpreventable issues but are the reason for a spike in high blood sugar. The causes for high blood sugar levels are as follows:
Causes of low blood sugar levels are very different and are as important to be aware of, as they are in fact easier to control.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Why Elevated Glucose May Lead To Weight Gain
According to an article published in the journal Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity and other research, high-glycemic carbs promote fat storage through their effect on insulin productionâespecially when carbohydrates and fats are eaten together. Elevated insulin levels result from both hypersecretion and hyperinsulinemia .
High insulin levels can occur both at baseline and after a meal. Even slightly elevated insulin levels past your normal promote fat storage and play a âkey roleâ in obesity for many.
High-glycemic foods result in quick spikes in glucose and insulin production as your body tries to return your blood glucose back to a normal level. Examples of high-glycemic foods include:
- White bread, bagels, white rice, pasta, white potatoes
- Muffins, croissants, doughnuts, flavored instant oatmeal, most cereals
- Cakes, candy, cookies, most desserts
- Corn
When your glucose spikes and you donât burn the excess energy, your body converts the extra glucose to glycogen that gets stored in your muscle tissue and liver and, with the help of insulin, gets converted into fat stored in your adipose cells. Meanwhile, the fat that you ate at the same time is pushed straight into fat cells, since your body loves to burn carbohydrates for quick energy.
Summary Of Normal Glucose Ranges
In summary, based on ADA criteria, the IDF guidelines, a persons glucose values are normal if they have fasting glucose < 100 mg/dl and a post-meal glucose level < 140 mg/dl. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:
- Fasting glucose levels between 80-86 mg/dl
- Glucose levels between 70-120 mg/dl for approximately 90% of the day
- 24-hour mean glucose levels of around 89-104 mg/dl
- Mean daytime glucose of 83-106 mg/dl
- Mean nighttime glucose of 81-102 mg/dl
- Mean post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99.2 ± 10.5 to 137.2 ± 21.1 mg/dl
- Time to post-meal glucose peak is around 46 minutes 1 hour
These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in nondiabetic individuals.
Also Check: Metformin Max Dose Per Day
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
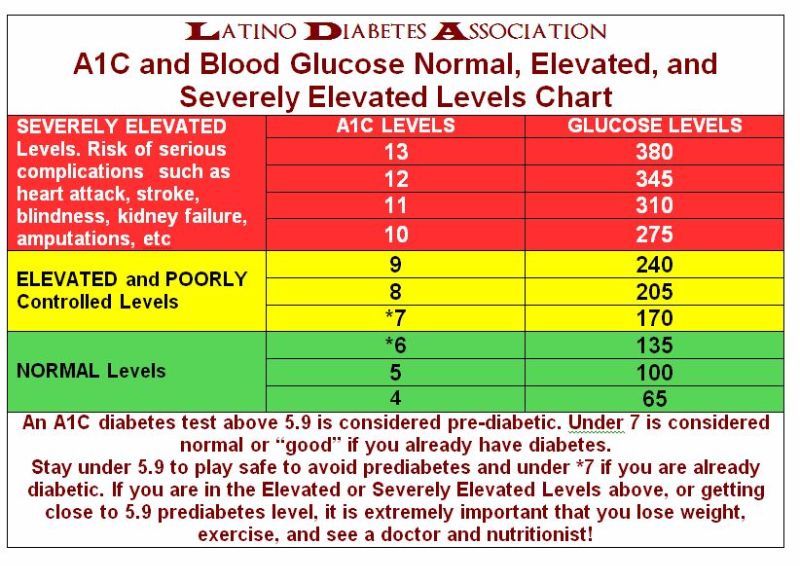
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
There are two types of blood sugar levels that may be measured. The first is the blood glucose level we get from doing finger prick blood glucose tests. These give us a reading of how high our levels are at that very point in time.
The second is the HbA1c reading, which gives a good idea of our average control over a period of 2 to 3 months. The target blood glucose levels vary a little bit depending on your type of diabetes and between adults and children.
Where possible, try to achieve levels of between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and under 8.5 mmol/L after meals. The target level for HbA1c is under 48 mmol/mol .
Research has shown that high blood glucose levels over time can lead to organ and circulation damage.
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous.
Your doctor may give you different targets. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets.
FREE blood glucose level chart
Also Check: Does Black Coffee Raise Your Blood Sugar
Fasting Glucose Goal: 72
Why? Previously we discussed that the ADA considers normal fasting glucose as anything < 100 mg/dl. However, multiple research studies show that as fasting glucose increases, there is an increased risk of health problems like diabetes and heart disease even if it stays within the normal range. The highlights of some of the study results include:
- Men whose fasting blood glucose was greater than 85 mg/dl had a significantly higher mortality rate from cardiovascular diseases than men with blood sugars less than 85 mg/dl.
- People with fasting glucose levels in the high normal range had significantly increased cardiovascular disease risk than people whose levels remained below 80 mg/dl.
- Children with fasting glucose levels 86-99 mg/dl had more than double the risk of developing prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes as adults when compared with children whose levels were less than 86 mg/dl.
- People with fasting glucose levels between 91-99 mg/dl had a 3-fold increase in Type 2 diabetes risk compared to those with levels less than 83 mg/dl.
- Among young, healthy men, higher fasting plasma glucose levels within the normal range constitute an independent risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. This means that as fasting glucose increases, even if the level is still considered normal, it could indicate a significantly higher risk of developing diabetes, and this is particularly pronounced if BMI is greater than 30. .
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner than age 45.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 and then every 3 years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
Recommended Reading: The Side Effect Of Metformin
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels vary based on when you last ate. For example, if you just ate a meal, your blood sugar levels will be higher than if you haven’t eaten in a while.
The normal blood glucose range is 70-99 mg/dL before meals, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. If you are fasting , your blood sugar should be below 95 mg/dL.
Normal Postmeal Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood glucose one to two hours after eating can help you understand how your blood sugar reacts to the food you consume. It can also offer insight into whether you’re taking the right dose of insulin or if you need to follow up with your healthcare provider to discuss medication and diet or lifestyle adjustments.
There are two ways you can measure your blood glucose levels: by pricking your fingertip using a glucometer or by using continuous glucose monitoring. How often you should check your glucose levels varies from a few times per week to four to six times each day. As a general rule, the American Diabetes Association recommends keeping blood sugar below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating.
However, your target blood sugar range will depend on the following:
- Duration of diabetes
Read Also: Side Effects Metformin Er
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.

