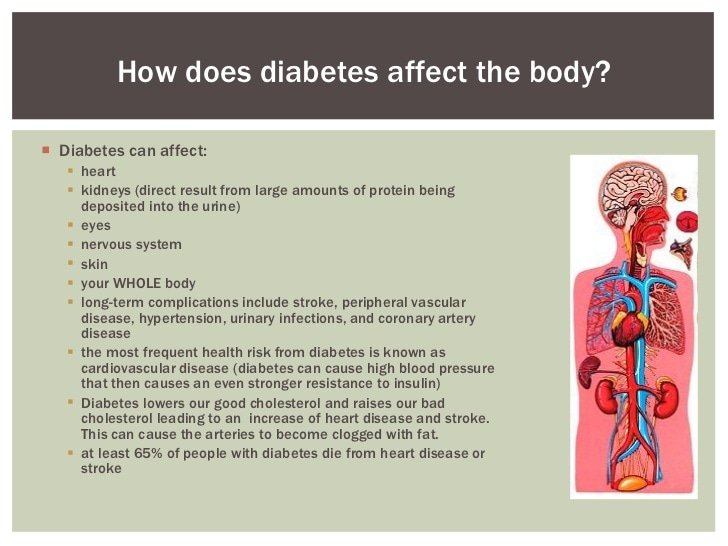
When You Have Diabetes You’re More At Risk Of Heart Disease This Is Also Called Cardiovascular Disease Or Coronary Disease And Can Lead To Heart Attacks And Strokes
Cardiovascular disease affects your circulation too. And poor circulation makes other diabetes complications worse – like problems with your eyes and feet.
That’s why it’s even more important to take good care of your heart when you have diabetes. We’re here to explain why diabetes increases your risk of heart problems, and how you can reduce this risk.
Every week diabetes causes 530 heart attacks and 680 strokes in the UK
Aside From Blood Pressure Meds And Statins Are There T2d Drugs A Person With T1d Can Take To Improve Heart Health
There are a few type 2 diabetes medications that are designed both to help with blood sugar management and protect the heart.
While those drugs aren’t currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in treatment of type 1 diabetes, a significant number of people with T1D use them “off-label” under the care of a healthcare provider.
Here are the various type 2 diabetes medications that may also be prescribed, in some cases, to help with heart health:
Naturally, any new medication can come with risks. For example, GLP-1 receptor agonists can cause increased risk of diabetic ketoacidosis , and SGLT2 drugs may increase the risk of a serious but rare infection around the genitals.
If you’re using a type 2 diabetes medication off-label, be sure to monitor for unusual symptoms and discuss the risks with your doctor.
Overall healthy lifestyle habits are your best bet, according to Basina. That includes:
- eating healthy and avoiding saturated fat
- keeping a moderate weight
- getting at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity exercise
- getting regular good sleep
Is There A Link Between The Autoimmune Response That Triggers T1d And Increased Heart Risk
People with type 1 diabetes have an increased risk for having one or more other autoimmune conditions. This can include autoimmune issues that can affect heart health.
In some people with type 1 diabetes, blood glucose swings that can cause repeated injury to the heart can, in turn, cause the body’s own immune system to attack the heart, much as it attacks the pancreas. This process is called cardiac autoimmunity .
A study conducted by researchers with the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston and other institutions found that blood sugar management that significantly fails to meet glycemic targets can lead to increased risk of cardiac autoimmunity in people with type 1 diabetes.
Their research also found that cardiac autoimmunity was associated with long-term, increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Dont People With T1d Have More Hdl Cholesterol And Isnt That Protective Of The Heart
Research shows that people with type 1 diabetes do generally have more HDL cholesterol, which can help protect heart health in the general population.
But alas, not all HDL is created equal. People with T1D are more likely to have the type of HDL that can convert to a molecule that promotes inflammation, and chronic inflammation is associated with cardiovascular disease.
A U.K. study of teens with type 1 diabetes, for example, found that many participants had elevated HDL, and that those levels could negatively affect the membrane that controls how the heart muscles squeeze and relax.
Basina adds that efforts to create medication that could raise HDL failed to show a decrease in the likelihood of heart disease. Meanwhile, she says there’s actually more evidence on the flip side, showing that low HDL is a risk factor of heart disease.
Svs: Why Diabetes Can Damage Your Blood Vessels And How To Know If Youre At Risk
ROSEMONT, Ill., Nov. 25, 2019 – When patients meet vascular surgeon Dr. William Jordan, there is a 30 to 40 percent chance they have diabetes, whether they know it or not.
Dr. Jordan is a vascular surgeon at the Emory University School of Medicine Program, and in his profession, diabetes sends a steady stream of patients his way. That’s because untreated diabetes increases the levels of glucose, or sugar, in the blood, and high levels of glucose are dangerous for the arteries. Roughly one in four Americans with diabetes are unaware that they have the disease.
“Diabetes is a relatively silent disease,” he explained. “You don’t notice it until complications start, but then it can lead to kidney failure, peripheral artery disease, blindness and other problems so serious they can eventually kill.”
Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes cause high blood sugar. The sugar, also called glucose, damages the inner linings of both big and small arteries. The arteries respond by layering on plaque, a substance that fills in the arteries so that oxygen-rich blood has a hard time getting through to the eyes, kidneys, legs and feet.
That condition is called atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries. Anyone can have hardening of the arteries, but according to the Society for Vascular Surgery, it gets more common in older people. It can cause heart attacks, strokes and prevent oxygen from getting to the legs and feet.
###
Are Otherwise Healthy People With T1d Really At High Risk For Heart Disease
Unfortunately, yes. People with T1D are more likely to experience cardiovascular disease, and to receive a diagnosis of it at an earlier age, than the general population.
Research has shown that the annual rate of major coronary artery disease in young adults with type 1 diabetes was 0.98 percent, while the same rate for a similar-aged population without diabetes was just 0.1 percent.
“Cardiovascular disease continues to be the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in individuals with type 1 diabetes,” says Dr. Marina Basina of the Stanford Health Care Endocrinology Clinic.
“Remarkable improvements in management and survival have been observed during the past century, allowing people to live longer and healthier lives, but life expectancy still remains 8 to 13 years shorter comparing to the individuals without diabetes,” Basina says.
What Are The Heart Health Recommendations For Good Glucose Control
As the research on cardiovascular disease and type 1 diabetes continues to evolve, so do the specific guidelines for prevention and treatment.
Not surprisingly, there’s research suggesting that tight blood glucose management may reduce the risk of heart disease in people with T1D.
However, what the goals of that management might look like is evolving, especially as we more fully understand the effects of hypoglycemia on the body.
In the past, goals often focused on lowering A1C, as higher A1C has been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
However, another indicator of glycemic management is gaining importance. In 2019, the American Diabetes Association unveiled new recommendations that suggest that healthcare providers should consider Time-in-Range as a key indicator of blood glucose management.
This is defined as time spent with blood glucose levels between 70 mg/dL and 180 mg/dL. Evidence suggests a strong correlation between TIR and risk of vascular issues among people with type 1 diabetes.
How Can I Prevent Kidney Disease And Other Problems From Diabetes
Controlling blood sugar is the best way to protect your eyes, heart, nerves, feet, and kidneys. It lowers your risk for all health problems from diabetes. This is true for all people with diabetes— with or without kidney damage. Ask your healthcare provider what you need to do to control your blood sugar.
Learn The Warning Signs Of Serious Complications And Have A Plan
Coronary heart disease can lead to heart attack or stroke. If you think that you are or someone else is having the following symptoms, Every minute matters.
Heart attack
The signs and symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Prolonged or severe chest pain or discomfort not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin. This involves uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center or left side of the chest that can be mild or strong. This pain or discomfort often lasts more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back.
- Nausea, vomiting, light-headedness or fainting, or breaking out in a cold sweat. These symptoms of a heart attack are more common in women.
- Shortness of breath. This may accompany chest discomfort or happen before it.
- Upper body discomfort.This can be felt in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or upper part of the stomach.
Jan 21 2016diabetes And Its Impact On The Cardiovascular System
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 29 million Americans have diabetes, with one in four of those people completely unaware. Type 2 diabetes, the most commonly diagnosed form of the disease, is a result of the pancreas slowly losing its ability to produce insulin and a result of the body developing insulin resistance, causing inefficient use of the insulin created.
Even though it is primarily diagnosed in adults, more and more teens and adolescents are developing type 2 diabetes due to the increased rates of obesity and physical inactivity in the United States. When symptoms are mild, type 2 diabetes can go undiagnosed for years – putting the individual at-risk for serious medical conditions. Heart-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, stroke and peripheral arterial disease, are more common in diabetic individuals than those without diabetes.
Cardiovascular Disease
At least 68 percent of people with diabetes die from some form of cardiovascular disease, which is a result of the co-morbidities that are associated with diabetes. People with diabetes who experience hypertension, high cholesterol and triglycerides, obesity and lack of physical activity are at a very high risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Stroke
Peripheral Arterial Disease
Blood Glucose Management
For a referral to a Barnabas Health endocrinologist or primary care physician, call 888-724-7123.
What Are Clinical Trials For Diabetes Heart Disease And Stroke
Clinical trials—and other types of clinical studies—are part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, such as
- risk factors for heart disease and stroke in specific populations, such as Black Americans with diabetes
- improved imaging techniques and tests to help diagnose and treat conditions that lead to heart attacks and stroke
- the role of genetics in diabetes, heart disease, and stroke
How Can Heart Disease Be Prevented In A Person With Diabetes
The best way to prevent heart disease is to take good care of yourself and your diabetes.
- Keep your blood sugar as normal as possible.
- Control your blood pressure, with medication if necessary. The target for people with diabetes is under 130/80.
- Get your cholesterol numbers under control. You may need to take medication to do this.
- Lose weight if you are obese.
- Ask your doctor if you should take an aspirin a day.
Cardiovascular Risk Can Occur Earlier In Women With Diabetes
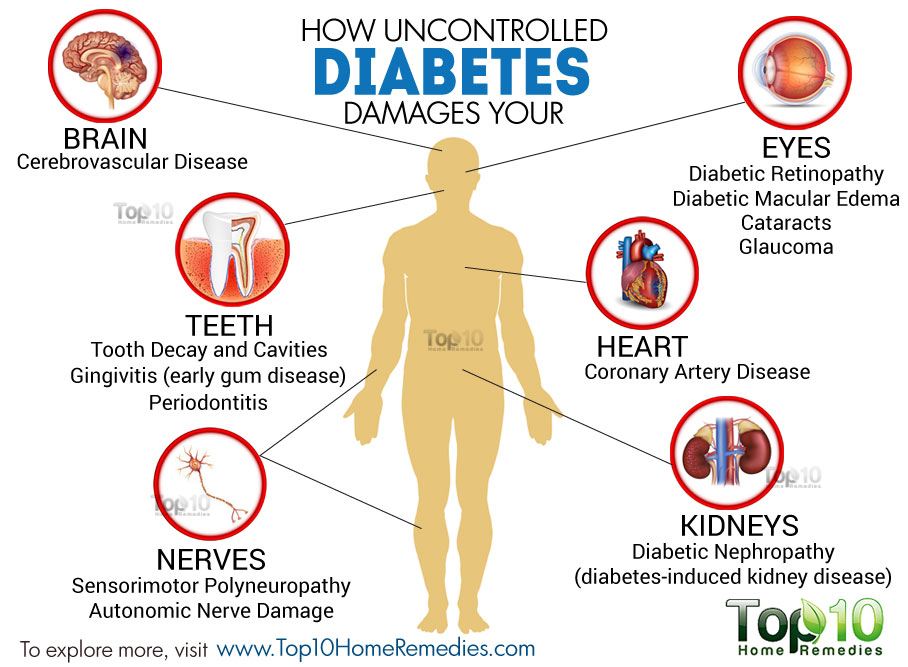
Among both men and women, diabetes is one of the strongest cardiovascular risk factors. Epidemiological studies have shown that people with diabetes have more than two times the chance of getting cardiovascular disease than people without diabetes. This includes premenopausal women, a group normally at lower risk for cardiovascular disease.
Men generally have heart disease in their 40’s and 50’s, about a decade before women. But this is generally not true for diabetic women. For diabetic women, the cardiovascular risk occurs earlier. Diabetes takes away much of the protection premenopausal women would normally get from estrogen.
Does Low Blood Sugar Also Play A Role In Heart Health Risks
While hyperglycemia is often the focus of studies on heart health and type 1 diabetes, researchers also know that hypoglycemia can stress the heart and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease as well. That’s because hypoglycemia can disrupt electrical signals that are vital for heart function.
However, researchers haven’t yet been able to isolate exactly how large a role hypoglycemia may play, independent of other factors, in causing cardiovascular events.
research does seem to suggest that the blood glucose fluctuations common in type 1 diabetes make people with T1D more vulnerable to heart disease than people with type 2 diabetes.
It’s a stubborn problem, in that research even demonstrates that people with T1D who take the traditional steps to lower cardiovascular risk still have a higher risk of death from cardiovascular issues than the general population.
In contrast, people with type 2 diabetes who underwent similar interventions had a more substantially reduced risk for death from cardiovascular issues, one that aligned closely with the risk faced by the general population.
But Stanford’s Basina points out that the research may be confounded because the study groups and control groups for T1D versus T2D heart health trials were very different.
“The bottom line is that we cannot directly compare if the risk is more or less. We can just say that it is different,” she says.
Another factor at play for both types of diabetes may be damage to the kidneys.
What Is The Link Between Diabetes Heart Disease And Stroke
High blood glucose from diabetes can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart and blood vessels. Over time, this damage can lead to heart disease.1
People with diabetes tend to develop heart disease at a younger age than people without diabetes. Adults with diabetes are nearly twice as likely to have heart disease or stroke as adults without diabetes.2,3
The good news is that the steps you take to manage your diabetes also help lower your chances of having heart disease or stroke.
How You Can Reduce Your Risk Of Developing Heart Disease
To manage or reduce your chances of developing heart disease if you’re living with diabetes, it’s important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage your diabetes effectively. Ways to do this include:
- Taking your medication to control diabetes as prescribed by your doctor
- Eating a varied diet of healthy foods
- Being physically active
- Managing your blood cholesterol and blood pressure levels
- Being smoke-free
Why Does Coronary Heart Disease Affect Women Differently
Coronary heart disease is different for women than men because of hormonal and anatomical differences.
- Hormonal changes affect a woman’s risk for coronary heart disease. Before menopause, the hormone estrogen provides women with some protection against coronary artery disease. Estrogen raises levels of HDL cholesterol and helps keep the arteries flexible so they can widen to deliver more oxygen to the tissues of the heart in response to chemical and electrical signals. After menopause, estrogen levels drop, increasing a woman’s risk for coronary heart disease.
- The size and structure of the heart is different for women and men. A woman’s heart and blood vessels are smaller, and the muscular walls of women’s hearts are thinner.
- Women are more likely to have nonobstructive coronary heart disease or coronary microvascular disease. These types are harder to diagnose than obstructive coronary artery disease, which can be harder to diagnose. This can cause delays in getting diagnosed and treated.
The Impact Of Hypoglycemia On The Cardiovascular System
Intensive glycemic control may increase cardiovascular risk and mortality due to hypoglycemia. The pathophysiology of glucose counter-regulation in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes for over 15 years is characterized by impairment of the defense mechanisms against hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia causes pronounced physiological and pathophysiological effects on the CV system as consequences of autonomic system activation and counter regulatory hormones release. These effects provoke a series of hemodynamic changes that include an increase in heart rate and peripheral systolic blood pressure, a decrease in central blood pressure, reduced peripheral arterial resistance, and increased myocardial contractility and cardiac output. Cardiac electrophysiological changes including flattening or inversion of T waves, QT prolongation, and ST segment depression were observed in both insulin-induced and spontaneous hypoglycemia. Sympathoadrenal activation is the main cause of these changes through mechanisms that involve, but are not limited to, catecholamine-mediated hypokalemia. Hypoglycemia is also involved in platelet activation. There is growing concern about the long-term effects of hypoglycemia, especially as related to inflammation and atherogenesis.Continue reading >>
Impact Of Diabetes On Cardiovascular Disease: An Update
Alessandra Saldanha de Mattos Matheus
1Department of Internal Medicine, Diabetes Unit, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Avenida 28 de Setembro 77, Terceiro Andar, Vila Isabel, 20551-030 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
2Department of Internal Medicine, Bauru’s Diabetics Association, Rua Saint Martin 27-07, 17.012-433 Bauru, SP, Brazil
Academic Editor:
Abstract
1. Introduction
Diabetes is an important chronic disease which incidence is globally increasing and though considered as an epidemic . The World Health Organization estimated there were 30 million people who had diabetes worldwide in 1985. This number increased to 135 million by 1995 and reached 217 million in 2005. By the year 2030 WHO predicts this number will increase to at least 366 million . This growth in diabetes prevalence, driven principally by an increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes , is occurring in both developing and developed countries . The incidence of type 1 diabetes is also increasing in parallel to that of T2D worldwide .
The underlying mechanisms that cause accelerated atherosclerosis in patients with diabetes and consequently an increased prevalence of CVD are poorly understood. The purpose of this paper is to describe the association between poor glycemic control, oxidative stress, markers of insulin resistance, and of low-grade inflammation that have been suggested as putative factors linking these two conditions.
2. The Role of Glycemic Control
3. Obesity
4. Dyslipidemia
Does Age Of Onset With T1d Have An Impact On The Heart
Research is just beginning to provide some possible answers to this question, but there appears to be evidence that the age of diagnosis is tied to risk of heart complications.
A large study in Sweden that tracked 27,000 people with type 1 diabetes found that those who were diagnosed earlier in life had a greater number of cardiovascular complications than those who got their diagnosis later in life.
For example, those who were diagnosed before the age of 10 had a 30 times greater risk for serious cardiovascular outcomes than those diagnosed after that age.
Dr. Araz Rawshani from the University of Gothenburg in Sweden, who co-led the study, said in a statement that such findings “warrant consideration of earlier treatment with cardioprotective drugs” for those who were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes in childhood.
Diabetes And Its Effects On The Cardiovascular System

These include retinopathy, or damage to the retinas of the eyes, that can lead to blindness; neuropathy, or nerve damage; kidney failure, which can lead to dialysis; and cardiovascular disease. The term cardiovascular disease generally refers to diseases that include the heart and blood vessels. The latest statistics from the Texas Department of Health Services places diabetes as the sixth leading cause of death in Texas. The first and third leading causes of death in Texas are from heart attacks and strokes . In the Rio Grande Valley the death rate from diabetes is higher than in many other parts of Texas.
Why Does Diabetes Increase Your Risk Of Heart Disease
If you have high blood sugar levels for a period of time, even slightly high, your blood vessels can start to get damaged and this can lead to serious heart complications.
This is because your body can’t use all of this sugar properly, so more of it sticks to your red blood cells and builds up in your blood. This build-up can block and damage the vessels carrying blood to and from your heart, starving the heart of oxygen and nutrients.
So keeping as close as possible to your target HbA1c level will help protect your blood vessels and in turn your heart. Even mildly raised blood sugar levels can, over time, put you more at risk.
Be in the know about your HbA1c and how to lower it if it’s too high.
What Are The Warning Signs Of Heart Attack And Stroke
- pain or pressure in your chest that lasts longer than a few minutes or goes away and comes back
- pain or discomfort in one or both of your arms or shoulders, or your back, neck, or jaw
- shortness of breath
- indigestion or nausea
- feeling very tired
Treatment works best when it is given right away. Warning signs can be different in different people. You may not have all the listed symptoms.
Women may experience chest pain, nausea, and vomiting; feel very tired ; and have pain that spreads to the back, neck, throat, arms, shoulders, or jaw. People with diabetes-related nerve damage may not notice any chest pain.
If you have angina, it’s important to know how and when to seek medical treatment.
- weakness or numbness of your face, arm, or leg on one side of your body
- confusion, or trouble talking or understanding
- dizziness, loss of balance, or trouble walking
- trouble seeing out of one or both eyes
- sudden, severe headache
If you have any one of these warning signs, call 9-1-1. You can help prevent permanent damage by getting to a hospital within an hour of a stroke.
How Exactly Does T1d Affect The Cardiovascular System
Basina says the exact cause of how type 1 diabetes affects the cardiovascular system isn’t known. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetic kidney disease can all play a role, if present.
Hyperglycemia itself is considered to be a leading reason for elevated risk, as it can damage blood vessels and nerves essential for circulation and heart health.
This can lead to neuropathy , which can lead to abnormalities in the vascular system as well.
It helps to remember that your cardiovascular system isn’t that different than plumbing pipes, says Gary Scheiner, a well-known Diabetes Care and Education Specialist , author, and clinical director of Integrated Diabetes Services in Pennsylvania.
“The way I explain it to patients is this: Sugar is a very sticky substance. Imagine dumping maple syrup down your kitchen sink every time you do the dishes. Eventually, that syrup is going to combine with all the other leftover food that we dump out to form blockages in the pipes,” Scheiner tells DiabetesMine.
The Challenge And Importance Of Living A Healthy Life
High-sugar, high-calorie, high-salt packaged food is relatively inexpensive, extremely accessible, and very tempting for people with very little free time. But it’s essential to take the time to learn your genetic risks and recognize your individual condition, and make the effort to cut portion sizes, follow a healthy diet, and make physical activity part of daily life.
It’s important to be proactive and speak with a primary care physician about diabetes and its associated conditions, like hypertension and cholesterol disorder.
Johns Hopkins Women’s Cardiovascular Health Center
The Johns Hopkins Women’s Cardiovascular Health Center provides education, comprehensive treatment and diagnostic services to prevent and manage heart disease in women.
How Is Heart Disease Treated In Those With Diabetes
There are several treatment options for heart disease in those with diabetes, depending on the severity of the heart disease, including:
- Aspirin therapy* to reduce the risks of clots that lead to heart attacks and strokes.
- Diet.
- Exercise not only for weight loss, but to improve blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, cholesterol levels and to decrease abdominal fat, a risk factor of heart disease.
- Medicines.
Reducing Your Risk Of Heart Attack Or Heart Disease
The good news is, you can reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing heart disease.
Here’s how:
- Get your HbA1c, blood pressure and blood cholesterol measured at least once a year as part of your annual diabetes review – make sure you get advice and support from your healthcare team to keep them within your target range. Your care might look a bit different due to the coronavirus pandemic.
- Don’t smoke. Smoking makes it harder for blood to flow around your body, especially to your heart. If you need help stopping, ask your healthcare team for more help or check out our information to help you quit.
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to protect your heart – reducing how much saturated fat you have is a good place to start.
- Be physically active and do some regular exercise.
- If you are living with obesity or overweight, get support to help you lose some weight. Even losing a small amount can make a real difference. Being a healthy weight range reduces the strain on your heart.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Some medicines help to protect your heart by reducing high blood pressure or blood fats and you may take these even if you don’t have any blood pressure problems or high blood fats.
And if you have any chest pain or pain when walking – call 999 straight away. These could be signs of a heart attack.
We’ve got more information about reducing your risk of a stroke too – it’s all very similar advice as they’re closely linked.

