Will Gestational Diabetes Go Away After Pregnancy
Most womens blood sugar levels come down after they give birth and hormone levels return to normal. But about 50% of women with gestational diabetes develop Type 2 diabetes later in life. Diet and exercise can help lower your risk. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood glucose tests every six to 12 weeks after pregnancy to watch for diabetes.
Are You At Risk For Gestational Diabetes
You may be more likely than other women to develop gestational diabetes if:
- Youre older than 25.
- Youre overweight or obese and not physically active.
- You had gestational diabetes or a baby with macrosomia in a past pregnancy.
- You have high blood pressure or youve had heart disease.
- You have polycystic ovarian syndrome . This is a hormone imbalance that can affect a womens reproductive and overall health.
- You have prediabetes. This means your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diabetes.
- You have a parent, brother or sister who has diabetes.
Even women without any of these risk factors can develop gestational diabetes. This is why your health care provider tests you for GDM during pregnancy.
Who Is Most At Risk For Gestational Diabetes
While researchers aren’t certain why some women get gestational diabetes while others dont, they do know that you may be at an increased risk if:
In the U.S., about 90 percent of pregnant women have at least one risk factor for gestational diabetes, which is why universal screening is thought to be the most practical approach.
Recommended Reading: Lower Blood Sugar Fast
If I Am Pregnant How Do I Know If I Have Gestational Diabetes
Most doctors and midwives will screen women for gestational diabetes at 24-28 weeks. This screening involves taking a blood test for sugar before eating in the morning, then drinking 50-grams of a pure sugar drink, and having your sugar tested again. If the sugar level in the blood is high, this indicates that you need to be tested further for gestational diabetes.
Learn more about pregnancy and baby care.
What’s Causing The Confusion

Heather Davis Mahoney, from Hertfordshire, had gestational diabetes while carrying her second child, and was monitored closely during her third pregnancy.
She has not been told to shield, but says it’s worrying when others from similar backgrounds have been told they should.
“There’s been an explosion of confusion. People don’t know what’s going on and are worried about putting themselves and their babies at risk,” she says.
Vicky, from Melton Mowbray, had gestational diabetes two years ago and at first thought her shielding letter was a hoax.
She works as a supermarket store manager and has carried on throughout the pandemic.
“I rang the GP but I couldn’t get an answer as to why it was . I haven’t fully decided what I’m going to do,” she told the Jeremy Vine show on BBC Radio 2.
But GP Dr David Triska said just because someone has gestational diabetes or had it in the past, doesn’t mean they should be shielding.
“I think the major point of confusion is that people are expecting that this is a binary ‘yes’ or ‘no’ per condition algorithm – and it is not,” he said.
“The reason why people are getting different answers from various sources is because this is an individual risk assessment.”
Don’t Miss: What Are The Most Common Side Effects Of Metformin
Antepartum And Perinatal Considerations
Overt maternal diabetes mellitus can adversely influence intrauterine development. Spontaneous abortions and major congenital anomalies may be induced in the first trimester. Excessive foetal growth, neonatal hypoglycaemia, jaundice, polycythaemia and stillbirth may be induced during the second and third trimesters. As noted above, excess birth defects are generally limited to cases of gestationally diagnosed hyperglycaemia that meets criteria for overt diabetes mellitus. The frequency of the other adverse outcomes across the full range of maternal glycaemia that defines true GDM is difficult to determine. The reason is simpleâwomen in the upper part of that range almost always receive some form of treatment.
Why Are Bedtime Snacks Good For Gestational Diabetes
A high-protein, low-fat snack before bed may help people with diabetes stabilize their blood sugar levels overnight. Everyones blood sugar levels change throughout the night. In people with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes, these fluctuations can cause high blood sugar levels, or hyperglycemia, in the morning.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Too Much Metformin
What Can I Do To Make Living With Gestational Diabetes Easier
Make diabetes management part of your daily routine. Create a schedule and stick to it. Try to:
- Check your blood glucose levels at the same time each day.
- Choose three days each week to get 30 minutes of light exercise.
- Plan small, balanced meals ahead of time.
- Talk with your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator about other tips for daily diabetes management.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women when theres too much glucose in their blood. GD is usually diagnosed during the middle stage of pregnancy with a few simple blood tests. If left untreated, GD can cause health complications for the mother and the baby. Most women can manage gestational diabetes with diet and exercise. Some will need medication. Gestational diabetes increases your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to reduce your risk of diabetes before, during and after pregnancy.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/14/2021.
References
What Is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes in which the body does not produce adequate amounts of insulin to regulate sugar during pregnancy. It may also be called glucose intolerance or carbohydrate intolerance.In women with gestational diabetes, blood sugar usually returns to normal soon after delivery. But if youve had gestational diabetes, you have a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Youll need to be tested for changes in blood sugar more often.
Don’t Miss: Can Metformin Cause Sweating
Prevention Of Gestational Diabetes
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent gestational diabetes, there are some steps you can take to lower your risk.
The best way to reduce your risk of developing gestational diabetes is to maintain a proper diet and body weight prior to and during the pregnancy, as well as increasing physical activity, Borst says.
Focus your diet on healthy foods that are high in fiber and low in fat like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Try to get at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity each day. These healthy habits can make lasting changes that will help you through your pregnancy.
However, sometimes women who are of normal weight, who exercise and have a healthy diet, still may develop gestational diabetes, Fay says. In these cases, it is likely to occur because of the effects of placental hormones. Genetics may also play a role, as there is a higher risk of gestational diabetes in patients who have a first-degree relative with diabetes, Fay says.
What It Is: High Blood Pressure And Protein In The Urine That Afflicts Up To 8 Percent Of Pregnant Women It Can Cause Blood Clotting And Impaired Kidney And Liver Function
What causes it: One study suggests preeclampsia may be caused by a protein that halts the growth of blood vessels in the placenta, while another study suggests the odds for it increase with a woman’s prepregnancy body-mass index. At highest risk: moms carrying more than one fetus, women over 40, or those who have a close relative who’s had preeclampsia.
Symptoms: High blood pressure, swelling in the hands and feet, severe headaches, blood in the urine, or extreme nausea.
Treatment: If symptoms are mild, most physicians suggest bed rest. Vitamins E and C may also help. Delivery usually ends the condition.
Can you prevent preeclampsia? You can decrease the likelihood by staying at a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, and getting regular exercise.
You May Like: Can A Diabetic Get Tattoos
How Can I Prevent Gestational Diabetes
There are no guarantees when it comes to prevention, but the more healthy habits you can adopt before pregnancy, the better. If youve had gestational diabetes, these healthy choices may also reduce your risk of having it again in future pregnancies or developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
- Eat healthy foods Choose foods high in fiber and low in fat and calories. Focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Strive for variety to help you achieve your goals without compromising taste or nutrition. Watch portion sizes.
- Keep active exercising before and during pregnancy can help protect you from developing gestational diabetes. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity on most days of the week. Take a brisk daily walk. Ride your bike. Swim laps. Short bursts of activity such as parking further away from the store when you run errands or taking a short walk break all add up too.
- Start pregnancy at a healthy weight if youre planning to get pregnant, losing extra weight beforehand may help you have a healthier pregnancy. Focus on making lasting changes to your eating habits that can help you through pregnancy, such as eating more vegetables and fruits.
- Dont gain more weight than recommended gaining some weight during pregnancy is normal and healthy. But gaining too much weight too quickly can up your risk of gestational diabetes. Ask your doctor what a reasonable amount of weight gain is for you.
How Long After Waking Up Should I Check My Blood Sugar

Blood sugar testing at home
In most cases, doctors ask people to measure fasting blood sugar immediately upon waking and before they have anything to eat or drink. It may also be appropriate to test blood sugar before eating or sometimes 2 hours after a meal when blood sugar has returned to normal levels.
Also Check: Low Blood Sugar Disease
How Does Gd Affect Your Baby After Birth
Babies who are born to mothers with gestational diabetes should be tested for low blood sugar , even if they have no symptoms, with a simple blood test after birth. This happens immediately after delivery, while you and baby are still in the hospital.
After birth, its essential to keep the focus you had during pregnancy on a healthy lifestyle for your whole family you may find that it helps you stick to your resolutions as well.
Teach your child good eating and exercise habits early on: If you had gestational diabetes, your baby could be at a higher risk for health problems, including obesity as a child or teen and an increased risk for type 2 diabetes later in life, according to the CDC.
To help avoid a type 2 diabetes diagnosis for your child, aim to ensure that he or she:
- Eats nutritious meals. The same diet you follow during pregnancy and beyond is good for your child, too. When he gets old enough, have him help you in the kitchen children who help prepare dishes are more likely to eat them.
- Gets plenty of exercise as he grows. Start by taking walks. As he gets older, toddler soccer and other activities are a great way to get him interested in healthy movement.
- Maintains a healthy weight. Talk to his pediatrician to make sure his BMI is on target, and talk openly to him about healthy weight and the increase in obesity he might notice in school.
How Has The Shielding List Changed
Anyone considered to be clinically extremely vulnerable is advised to stay at home at all times and only go out to exercise or for medical appointments.
In England, the new way of calculating who is most at risk from Covid-19, called ‘QCovid’, has been introduced based on data gathered during the first wave of coronavirus in spring 2020.
- the postcode they live in and how deprived it is
- their weight
Anyone added to the list will now be made a priority when it comes to getting the Covid vaccine.
Don’t Miss: Is Metformin Bad For Kidneys
Favorite App For Gestational Diabetes
This app acts as a reliable companion to aid management of gestational diabetes. It can help you analyze dips and rises in your blood sugar readings, offers education about blood sugar management, and facilitates connecting you virtually with a certified diabetes care and education specialist. MySugr is free on Android and iOS with in-app purchases available.
For more of our favorite diabetes apps, check out our list.
How Do You Know If You Have Gestational Diabetes
Your health care provider tests you for gestational diabetes with a prenatal test called a glucose tolerance test. You get the test at 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. If your provider thinks youre at risk for GDM, you may get the test earlier.
If your glucose screening test comes back positive, you get another test called a glucose tolerance test to see for sure if you have gestational diabetes.
Also Check: High Diabetes Symptoms
Favorite Orgs For Essential Info On Gestational Diabetes
ACOG is the leading group of obstetricians and gynecologists dedicated to improving womens health. Learn about ways to manage gestational diabetes, how to track blood sugar levels, and steps you can take to have a healthy pregnancy from the experts who diagnose and treat the condition every day.
This project from the International Diabetes Federation , an umbrella organization of more than 240 diabetes associations in 168 countries, offers articles, as well as video guides on insulin, healthy eating, and blood glucose monitoring. You can also test your knowledge with interactive quizzes on topics such ashow to reduce your risk and how to manage gestational diabetes with diet and exercise.
Treatment And Medication Options For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes can be managed with close blood sugar monitoring, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, medication.
Monitor your blood sugar. If you have gestational diabetes, your doctor may ask you to monitor your blood sugar levels several times a day.
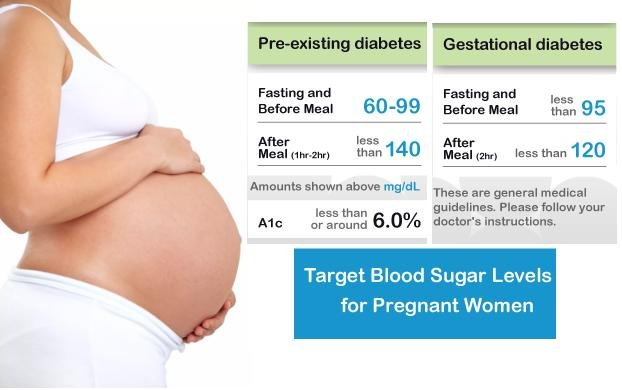
- Before a meal: 95 mg/dL or less
- One hour after a meal: 140 mg/dL or less
- Two hours after a meal: 120 mg/dL or less
Maintain a healthy diet. Unfortunately, gestational diabetes will not go away while still pregnant, because all those metabolic changes are still occurring that drive the insulin resistance, Fay explains. However, it can sometimes be controlled with diet alone.
She typically recommends a diet of 30 to 40 percent carbohydrates, and choosing those carbohydrates that are more slowly digested and less likely to cause blood sugar spikes. These foods tend to be high in fiber. For example, having whole wheat bread instead of white bread, or having whole fruit instead of fruit juice, Fay says. A certified diabetes care and education specialist and registered dietitian nutritionist, which you can find via the Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists, can help you build a diabetes-friendly diet.
Get exercise. Talk to your doctor about the amount and level of physical activity that is right for you during your pregnancy. Faye typically recommends 30 minutes of exercise at least five days a week for all her patients. Adding in a walk after meals can also help lower blood sugars, she says.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Dangerous Side Effects
How Gestational Diabetes Can Affect Your Pregnancy
Most women with gestational diabetes have otherwise normal pregnancies with healthy babies.
However, gestational diabetes can cause problems such as:
- your baby growing larger than usual this may lead to difficulties during the delivery and increases the likelihood of needing induced labour or a caesarean section
- polyhydramnios too much amniotic fluid in the womb, which can cause premature labour or problems at delivery
- premature birth giving birth before the 37th week of pregnancy
- pre-eclampsia a condition that causes high blood pressure during pregnancy and can lead to pregnancy complications if not treated
- your baby developing low blood sugar or yellowing of the skin and eyes after he or she is born, which may require treatment in hospital
- the loss of your baby though this is rare
Having gestational diabetes also means you’re at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
After Your Baby Is Born
Gestational diabetes can cause problems for you and your baby after labour and in the long term. If youve had gestational diabetes, you are also at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes during your life. Babies of mothers with gestational diabetes may also be at greater risk of developing obesity or diabetes in later life.
You can reduce your risk of health issues in the future by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet and taking regular exercise.
Find out more about the long-term implications of gestational diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Oatmeal Good For Diabetics
Prognosis Of Gestational Diabetes
However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of getting it again during future pregnancies and are also at an increased risk of type 2 diabetes later in life. For this reason, its important for women who have had gestational diabetes to have their blood glucose levels regularly checked even after pregnancy.
What Foods Will Lower Blood Sugar Quickly
Some of the foods that help keep your blood sugar levels in the healthy range include:
- Vegetables: Green peas. Onions. Lettuce.
- Certain fruits: Apples. Pears. Plum.
- Whole or minimally processed grains: Barley. Whole wheat. Oat bran and rice bran cereals.
- Dairy and dairy-substitute products: Plain yogurt. Cheese. Cottage cheese.
Read Also: Long Term Side Effects Of Metformin

