What Types Of Health Care Professionals Treat Diabetes
Most primary care providers have experience managing diabetes, including internists, gynecologists, and family practitioners. Specialists in diabetes care are called endocrinologists or diabetologists. You can locate endocrinologists using the “Find an Endocrinologist” search engine online at the Hormone Health Network. You can locate a pediatric endocrinologist for diabetic youth using the “Find a Doctor” search engine of the Pediatric Endocrine Society.
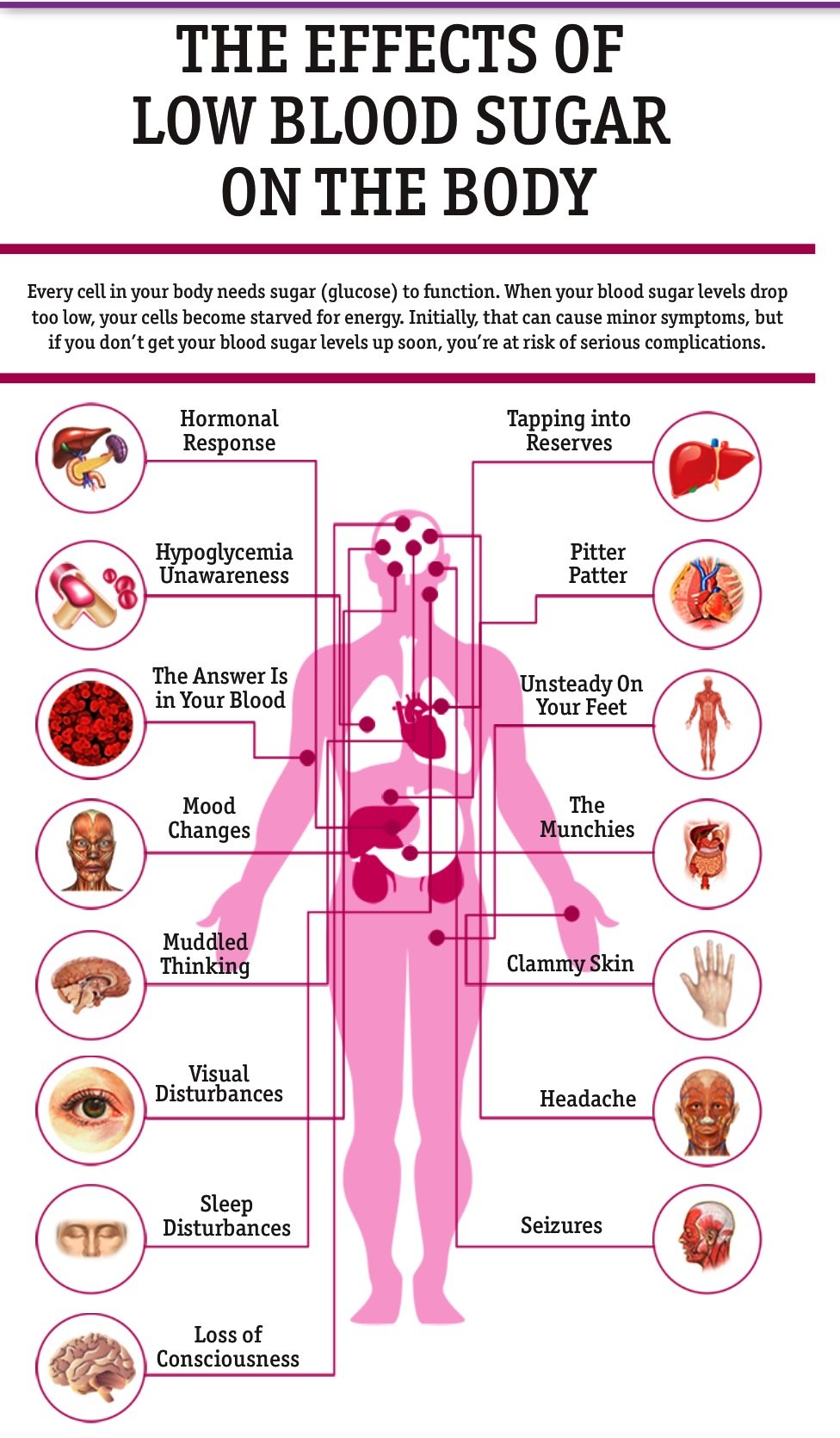
Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar You Need To Pay Attention To
- NDTV Food
Plos One
2. Taking a higher dose of the medicine prescribed.
3. Sedentary lifestyle or no physical activity.
4. Kidney disease which reduces the excretion of drugs taken to manage diabetes.
5. Fever or similar illness that increases catabolism and the diabetes drug becomes too effective.
2. Drink a solution of sugar and water or some sweet juice.
3. Grab a quick snack that is rich in carbohydrates.
4. Eating a small snack before you sleep helps in reducing the frequency and severity of sleep disturbances.
Why Does Sweetness Cause Such Pain
Shakespeare probably pondered this as he was writing Romeo and Juliet. And just as he was perplexed by the joyous agony of true love, we wanna know why sugar is such a wiley b*tch sometimes.
First of all, when we say sugar as in, Good god, this sugar headache makes me regret my choice to eat a sleeve of Oreos in one sitting were talking about added sugar. Added sugar is just what it sounds like, its sugar thats added to foods.
Why does this matter? Well, many foods have naturally occurring sugars, like fruits and dairy. When you eat a piece of fruit or some plain Greek yogurt, youre getting some sugar, but the fiber or protein in the food helps balance the effects of the glucose.
When you eat something with lots of added sugar , the lack of fiber, protein, or other good stuff with nutritional value means the sugar hits your bloodstream, causes a spike in glucose, also known as blood sugar, and off you go to headache town.
Radical dips and spikes in blood sugar are the main cause of sugar headaches. Your body actually runs, not on Dunkin, but on sugar .
We need a steady supply of glucose for energy and our brains in particular need glucose to make sure the body can function. When theres a sudden change in glucose levels, our brains are the first to feel the effects.
You May Like: Diabetics And Cheese
Check Your Blood Sugar Regularly
Checking your blood sugar regularly is the only way to better understand how your body is responding to your illness. It is generally advised that you check your blood sugar with an at-home glucometer at least four times per day. Be sure to record your numbers and keep this information readily available so you can share it with your healthcare team.
For people with type 1 diabetes who may be more concerned about DKA, you can check your blood sugar levels every two hours. Again, record these measurements and keep them close so you can share them with your healthcare team when the time comes.
What Are Risk Factors For Hyperglycemia
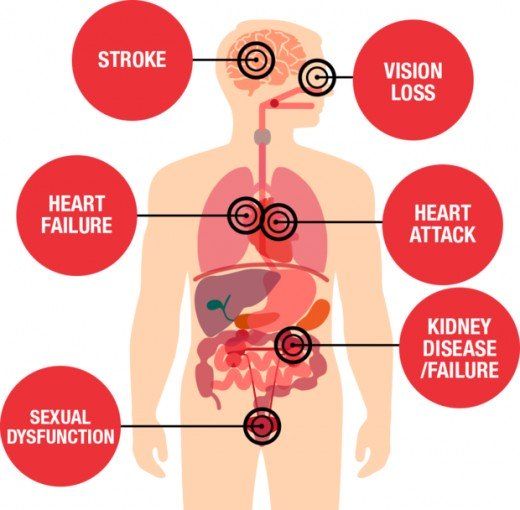
Major risk factors for hyperglycemia are:
- You have a family history of type 2 diabetes.
- You are African American, Native American, Hispanic or Asian American.
- You are overweight.
- You have high blood pressure or cholesterol.
- You have polycystic ovarian syndrome .
- You have a history of gestational diabetes.
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Are Medical Treatments For Diabetes
Treatment of diabetes is highly individualized. Treatment depends on the specific type of diabetes, co-existing medical problems, presence of diabetes-related complications, and the physical and mental skills of the affected person.
- A health care team helps set healthy and feasible goals for lifestyle changes, blood sugar control, and treatment.
- Together, the affected person and his or her health care team formulate a plan to help meet these goals.
Education about diabetes and its treatment is essential.
- At the initial diagnosis of diabetes, the health care team will spend much time educating the patient about the condition, treatment, and practical skills for daily self-care.
- The diabetes care team includes the health care professional and support staff. A professional dietitian and a diabetes educator are usually part of the team. The team may include specialists in hormone health , foot care , neurology, kidney diseases , eye diseases , and behavioral health .
- Among reputable sources, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease provides information on diabetes and related research including clinical trials.
The health care team will encounter the patient at appropriate intervals to monitor progress and evaluate goals.
Type 1 diabetes treatments
Treatment of T1D involves multiple daily injections of insulin or continuous insulin delivery by a pump. Daily injections usually combine short-acting insulin and a long-acting insulin .
Fungal Skin Infections And Nail Infections
People with diabetes are also more likely to get fungal infections or yeast infections, many of which affect the skin and nails. Our skin is naturally covered with fungi that are there to protect us from bad germs. But having too much of that fungi can be a problem. Fungi, especially yeast, feed on sugar, so the more sugar your body has, the more likely it is that you will develop more fungi or yeast than you should.
Examples of common fungal skin and nail infections are athletes foot, ringworm, vaginal yeast infections, and fungal nail infections.
You May Like: Regular Insulin Adverse Effects
What Tests Do Health Care Professionals Use To Diagnose Diabetes
Doctors use common tests to diagnose diabetes and monitor blood sugar control.
The health care professional will take a history including information about the patient’s symptoms, risk factors for diabetes, past medical problems, current medications, allergies to medications, family history of diabetes, or other medical problems , and personal habits and lifestyle.
Various laboratory tests can confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
Fingerstick blood glucose at the point of care. This rapid test may be performed anywhere, including community-based screening programs.
- Although not as accurate as testing blood in a hospital laboratory, a fingerstick blood glucose test is easy to perform, and the adequate result is available quickly.
- The test involves sticking the patient’s finger for a tiny blood sample. The blood drop is placed on a strip to be inserted into a machine that reports the blood sugar level. These portable machines are accurate to within about 10%-20% of true laboratory values.
- Fingerstick blood glucose values tend to be most inaccurate at very high or very low levels. Abnormally low or high results should be confirmed by repeat testing. Point-of-care testing is how most people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels at home.
Oral glucose tolerance test. After fasting for at least six hours, the health care professional draws blood to measure plasma glucose before and at two hours after drinking a specific sweet drink .
Does High Blood Sugar Make You Sleepy
High Blood Sugar Causes Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of high blood sugar. In people with diabetes, it is referred to as diabetes fatigue. Many people with the condition feel tired all the time regardless of how well they sleep, how healthily they eat, or how much they exercise on a regular basis.
Also Check: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
How Do I Prevent Hyperglycemia
- Exercise to help lower blood sugar. Work with your healthcare provider to make a daily activity plan.
- Follow your meal plan if you have one. Learn how carbohydrates impact your blood sugar, and work with your diabetes care team to find the best meal plan for you.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Dont smoke.
- Limit drinking alcohol. Alcohol can raise blood sugar levels, but can also cause dangerously low blood sugar levels. Work with your provider to determine how much is safe to drink.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/12/2020.
References
What High Blood Sugar Feels Like
The symptoms can include:
- Breath that smells like fruit
- Confusion
These are symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis . Your body burns glucose for energy. When your cells donât get enough of it, they burn fat. That produces chemicals called ketones. When these build up, your blood becomes more acid-like. This can be life-threatening if itâs not treated.
Don’t Miss: Normal Dose Of Metformin
Normal Blood Sugar Range
Normal ranges for blood sugars depends on the fact that the patient is in fasting condition or had meal recently.
Also, as in this situation, the patient have been given an intravenous glucose infusion, so his sugar can be higher than the normal blood sugar range, even though the patient dont have sugar.
Normal blood sugar ranges are :
What Are The Causes Of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes causes
T1D is an autoimmune disease. The body’s immune system specifically destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- A predisposition to develop T1D may run in families. However, genetic causes are much more common for T2D.
- Common and unavoidable viral infections are among the environmental factors which contribute to T1D by triggering autoimmunity.
- T1D is most common among people of non-Hispanic, Northern European descent , followed by African Americans, and Hispanic Americans. It is relatively rare among Asian Americans.
- T1D is slightly more common in men than in women.
- T1D most often presents before age 21 but can occur at any age.
Type 2 diabetes causes
T2D is strongly linked to genetics, so T2D tends to run in families. Several genes have been linked to T2D, and many more are under study. Risk factors for developing T2D include:
Type 1 diabetes symptoms
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are often dramatic and come on very suddenly.
- T1D is usually recognized in childhood or early adolescence, often in association with an injury or illness .
- The extra stress can cause diabetic ketoacidosis .
- Symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea and vomiting. Dehydration and often serious disturbances in blood levels of potassium and other factors follow.
- Without treatment, ketoacidosis can lead to coma and death.
Type 2 diabetes symptoms
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes are often subtle and may be attributed to aging or obesity.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Causes Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The main cause of DKA is not enough insulin. A lack of insulin means sugar cant get into your cells. Your cells need sugar for energy. This lack of insulin causes your bodys glucose levels to rise. To get energy, your body starts to burn fat. This process causes ketones to build up. Ketones can poison the body.
High blood glucose levels can also cause you to urinate often. This leads to a lack of fluids in the body .
DKA can be caused by missing an insulin dose, eating poorly, or feeling stressed. An infection or other illness can also lead to DKA. If you have signs of infection , contact your doctor. You will want to make sure you are getting the right treatment. For some people, DKA may be the first sign they have diabetes.
What Causes High Blood Sugar
A variety of things can trigger an increase in blood sugar level in people with diabetes, including:
- stress
- missing a dose of your diabetes medicine or taking an incorrect dose
- overtreating an episode of low blood sugar
- taking certain medicines, such as steroids
Occasional episodes of hyperglycaemia can also occur in children and young adults during growth spurts.
You May Like: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Diabetic Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome is a potentially life threatening condition involving extremely high blood sugar levels.
When your blood sugar gets too high, the kidneys try to compensate by removing some of the excess glucose through urination.
If you dont drink enough fluids to replace the fluid youre losing, your blood sugar levels spike. Your blood also becomes more concentrated. This can also occur if you drink too many sugary beverages.
This condition is called hyperosmolarity. Blood thats too concentrated begins to draw water out of other organs, including the brain.
Any illness that makes you dehydrated or reduces your insulin activity can lead to HHS. Its commonly a result of unmanaged or undiagnosed diabetes. An illness or infection can trigger HHS.
Failure to monitor and manage blood glucose levels can also lead to HHS.
Symptoms may develop slowly and increase over a period of days or weeks. Possible symptoms include:
- fluids given through your veins to prevent or reverse dehydration
- insulin to lower and stabilize your blood sugar levels
- potassium, phosphate, or sodium replacement if necessary to help return your cells to their normal function
Treatment will also address any complications from HHS, such as shock or coma.
Factors that can increase your risk of complications with HHS include:
- advanced age
- severity of dehydration when youre treated
- the presence of other illnesses when youre diagnosed
Take the following steps to help prevent HHS:
What Are The Types Of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
The body produces little or no insulin to regulate blood glucose level.
- T1D affects about 10% of all people with diabetes in the United States.
- T1D is typically diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. In the past T1D was called juvenile-onset diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Insulin deficiency can occur at any age due to destruction of the pancreas by alcohol, disease, or removal by surgery.
- T1D results from progressive destruction by the immune system of the pancreatic beta cells, the only cell type that produces significant amounts of insulin.
- People with T1D require daily insulin treatment to sustain life.
Type 2 diabetes
Although the pancreas still secretes insulin in someone with T2D, the bodyâs tissues are partially or completely incapable of responding to insulin. This is often referred to as insulin resistance. The pancreas tries to overcome this resistance by secreting more and more insulin. People with insulin resistance develop T2D when they fail to secrete enough insulin to cope with their body’s demands.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs during the second half of pregnancy.
- Although gestational diabetes typically resolves after delivery of a baby, a woman who develops gestational diabetes is more likely than other women to develop T2D later in life.
- Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to have large babies, complicated pregnancies, and complicated deliveries.
Prediabetes
Recommended Reading: How Do U Get Diabetes
First Up How To Tell If Its A Diabetes
When youre not staying on top of your diabetes, it can cause your blood sugar to drop too low or climb too high. Both of these problems are triggers for headaches. Having a headache itself isnt harmful, but it could be a sign that your blood sugar isnt where it should be.
How exactly do blood sugar levels lead to head pain, though? Lets take a closer look at the culprits.
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, happens when your blood glucose levels drop below where they need to be. It can happen if you skip a meal or if you inject too much insulin.
Its also possible for your blood glucose to dip if you eat something with too many carbs, since the sudden spike in blood sugar can lead to an unhealthy drop after the body tries to compensate.
Usually hypoglycemia-related headaches come on quickly as your blood sugar takes a nosedive. Basically, the brain needs a steady supply of glucose to function. If you dont have enough glucose in your bloodstream to give the brain what it needs, you can end up with a throbbing headache.
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, may occur when your blood glucose levels get too high usually at least over 180 mg/dL or 10 mmol/L.
If you have diabetes and are insulin-resistant or arent producing or injecting enough insulin, the glucose from your food cant be absorbed by your cells for energy. That causes the glucose to build up in your bloodstream, which then leads to high blood sugar.
Which Type Of Diabetes
Both hypo- and hyperglycemia can trigger headaches and migraines. They can be super painful, with a throbbing or pulsing sensation on in your head. You might also feel weak, nauseous, and sensitive to light or sound.
Diabetes-related headaches can cause other symptoms too, depending on whether your blood sugar is too low or too high.
- Low blood sugar headaches can leave you feeling faint, shaky, nauseous, or sweaty.
- High blood sugar headaches may be accompanied by feeling super thirsty or having to pee more than usual, fatigue, or blurred vision.
First up, when you notice that throbbing pain coming on, start by checking your levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends aiming for these targets:
- Between 80 and 130 mg/dL before meals
- Less than 180 mg/dL 2 hours after meals
If your blood sugar is below the target range, try having 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting carbs like glucose tablets or gel, juice, regular soda, or sugary candy.
If you dont start to feel any better within 15 minutes, have another 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting carbs. This can help bring your blood sugar back up and start to ease your headache. After, have a healthy meal or snack to keep your levels stable.
If your blood sugar is above the target range, you may need to adjust your insulin levels or take a supplement of short-acting insulin.
Say it with us: Extreme blood sugar swings can be life-threatening. No bueno.
Recommended Reading: Can Diabetic Eat Cheese
Surprising Things That Can Spike Your Blood Sugar
When you first found out you had diabetes, you tested your blood sugar often to understand how food, activity, stress, and illness could affect your blood sugar levels. By now, youve got it figured out for the most part. But thenbam! Something makes your blood sugar zoom up. You try to adjust it with food or activity or insulin, and it dips really low. Youre on a rollercoaster no one with diabetes wants to ride.
Do you know all of these blood sugar triggers?
Knowledge is power! Look out for these surprising triggers that can send your blood sugar soaring:

