Are Diabetic Eye Exams Covered By Insurance
Most health insurance plans cover the cost of a diabetic eye exam in full. Although it is important to remember that health insurance is different from vision insurance.
Health insurance provides coverage on eye care that relates to a medical condition like glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy. Vision insurance provides coverage for vision needs such as glasses or contacts, which health insurance does not cover. Your doctor or a benefits representative may be able to help you better understand what will be covered.
Eye exams are important for everybody, but they are especially important for those with diabetes. Schedule an eye exam if you have not had one within the last year.
Revere Health Ophthalmology offers patients the best in eye care from the treatment of eye-related diseases and conditions to prescribing glasses and contacts.
CT scan . The Mayo Clinic.
Positron emission tomography scan . The Mayo Clinic.
MRI . The Mayo Clinic.
The Live Better Team
A Clear Picture Of Diabetic Risks
Town Eye Care uses modern fundus photography to get a complete picture of your ocular health. It helps us understand what is happening at the back of your eye and better manage eye diseases linked to diabetes.
The fundus is the inside, back surface of the eye that includes the retina and macula. Fundus photography allows us to see through a dilated pupil with clarity. This digital retinal imaging provides high-definition images of the optic nerve, giving us details on potential eye conditions caused by diabetes.
When Do I Need A Diabetic Eye Exam
According to the American Diabetes Association , people with diabetes should follow strict precautions to ensure ongoing eye health:
-
Adults with Type 1 diabetes should schedule an eye exam within five years of their diagnosis and every year thereafter.
-
Adults with Type 2 diabetes should schedule an exam as soon after their diagnosis as possible.
-
When possible, women with diabetes who are planning to get pregnant should consult with their eye doctor beforehand. An eye exam should also be scheduled within the first three months of pregnancy. Another exam should be scheduled a year after giving birth.
After an initial exam, the ADA recommends getting annual diabetic exams to monitor the health of your eyes. Its important to specifically schedule a diabetic eye exam a typical routine eye exam for people with no health problems may not focus enough on the specific needs of a diabetic patient.
Depending on the findings of your diabetic eye exam, your optometrist or ophthalmologist may recommend more frequent exams or may refer you to a retinal specialist.
The eyes can be among the first parts of your body affected by diabetes. But maintaining a regular routine of diabetic eye exams will ensure any problems are diagnosed and treated early to protect your eyesight.
Schedule an exam
Don’t Miss: What To Do If A Diabetic Feels Dizzy
What Is Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic eye disease is a group of eye problems that can affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Over time, diabetes can cause damage to your eyes that can lead to poor vision or even blindness. But you can take steps to prevent diabetic eye disease, or keep it from getting worse, by taking care of your diabetes.
The best ways to manage your diabetes and keep your eyes healthy are to
- manage your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, sometimes called the diabetes ABCs
- If you smoke, get help to quit smoking
- have a dilated eye exam once a year
Often, there are no warning signs of diabetic eye disease or vision loss when damage first develops. A full, dilated eye exam helps your doctor find and treat eye problems earlyoften before much vision loss can occur.
Diabetes And Your Eyes
The best way to handle eye problems related to diabetes is through early detection of retinal abnormalities, regular monitoring, and prompt treatment. Early detection and treatment typically begin with the retinal exam.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with type 1 diabetes have their first eye exam within the first five years after diagnosis. If you have type 2 diabetes, the ADA recommends that you have your first eye exam shortly after you receive a diagnosis. This is because type 2 diabetes often goes undetected and undiagnosed for years. Retinopathy may have already begun during that time. An eye exam will help your doctor determine if you already have damage.
The ADA recommends you have an eye exam each year after your first exam. If you wear glasses or contacts, you probably need an annual eye exam to keep your prescription up to date. During that exam, your doctor will conduct a few minor tests to see if your vision has changed as a result of diabetes.
You may develop retinopathy and find that your symptoms dont progress or stall entirely. If that happens, the likelihood youll be monitoring your eyes for changes for the rest of your life is high. If your doctor diagnoses you with retinopathy and treats you for it, they may request exams several times per year. The number of eye exams you need each year will depend largely on the severity of the retinopathy.
Don’t Miss: Does Bananas Raise Blood Sugar
Diabetic Retinal Exam Faqs
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that causes changes to the blood vessels in the back part of your eye, called the retina. Left undetected, these changes can cause vision loss and even blindness.
What is a diabetic retinal exam?
Diabetic retinal exams can occur at the office of your ophthalmologist, optometrist, or primary healthcare provider. When the diabetic retinal exam is performed in primary care, a photograph of the retina is captured in your physicians office and sent to an ophthalmologist for review. The exam is quick and comfortable. Results from the ophthalmologist are returned to your physician in about one business day.
Why is my physician recommending a retinal exam for me?
It is recommended that all patients living with diabetes have a retinal exam at least once per year. Your physician is committed to providing quality preventative care and has made this potentially vision-saving technology available to help keep watch for signs of diabetic retinopathy in the early stageswhen treatments to preserve vision are most effective.
What if I have diabetic retinopathy?
If diabetic retinopathy is identified, your physician will discuss next steps with you, including potential referral to an eye specialist, as needed.
Do I need to have my eyes dilated for this exam?
What Can I Do To Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
Managing your diabetes is the best way to lower your risk of diabetic retinopathy. That means keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. You can do this by getting regular physical activity, eating healthy, and carefully following your doctors instructions for your insulin or other diabetes medicines.
To make sure your diabetes treatment plan is working, youll need a special lab test called an A1C test. This test shows your average blood sugar level over the past 3 months. You can work with your doctor to set a personal A1C goal. Meeting your A1C goal can help prevent or manage diabetic retinopathy.
Having high blood pressure or high cholesterol along with diabetes increases your risk for diabetic retinopathy. So controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol can also help lower your risk for vision loss.
Also Check: What Are The First Signs Of Diabetes
Causes & Risk Factors
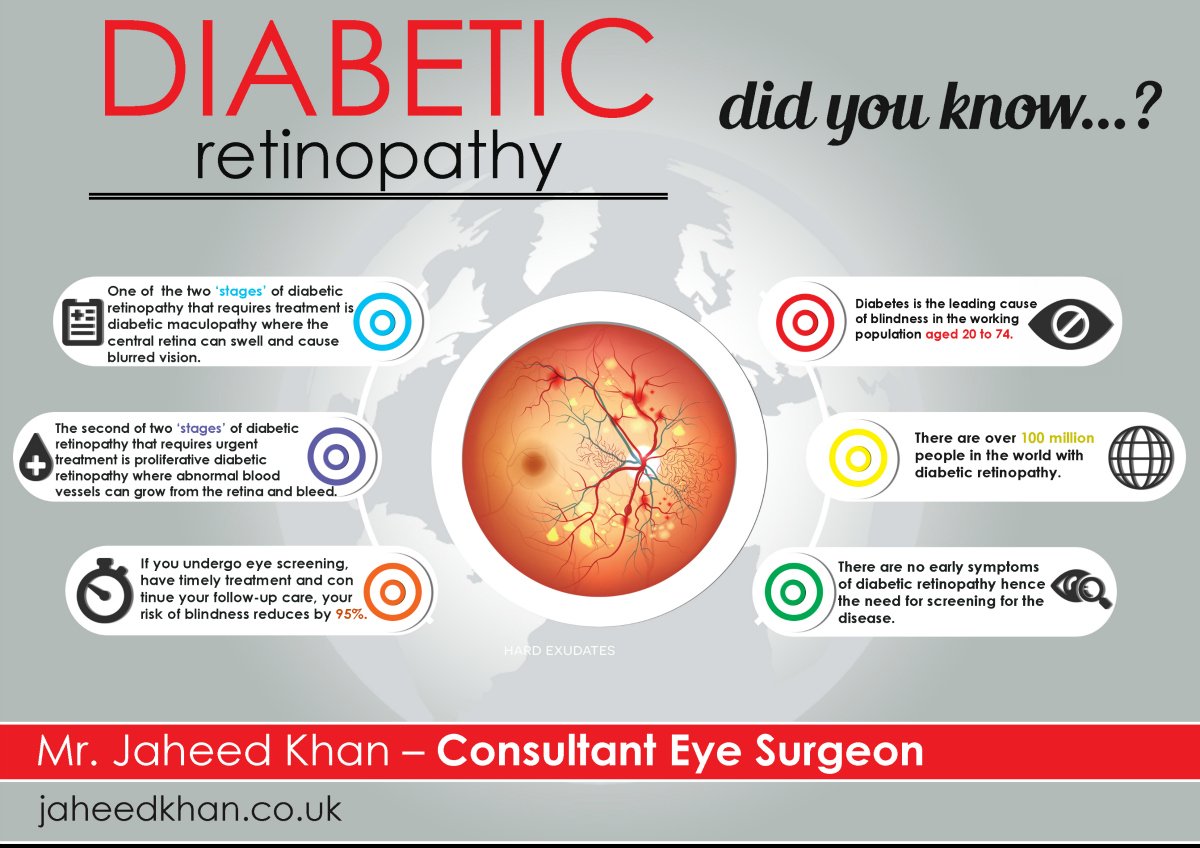
Diabetic retinopathy results from the damage diabetes causes to the small blood vessels located in the retina. These damaged blood vessels can cause vision loss:
- Fluid can leak into the macula, the area of the retina responsible for clear central vision. Although small, the macula is the part of the retina that allows us to see colors and fine detail. The fluid causes the macula to swell, resulting in blurred vision.
- In an attempt to improve blood circulation in the retina, new blood vessels may form on its surface. These fragile, abnormal blood vessels can leak blood into the back of the eye and block vision.
Diabetic retinopathy is classified into two types.
Diabetic Eye Exam Vs Regular Eye Exam
Whether you visit the optometrist for a regular eye exam or a diabetic eye exam, they will ask basic questions about your medical history and vision. You will also read an eye chart at both exams. Next, the doctor will give you a retinal exam using an ophthalmoscope.
Some features of diabetic retinopathy cant be seen during a regular eye exam and require special exams. For a better look at the inside of your eye, the doctor may use drops to dilate your pupils. They may also look at your retina with lenses and a specialized microscope called a slit lamp. The fluorescein angiography test will reveal changes in the structure and function of the retinal blood vessels.
Diabetic eye exams are a lot more specialized and complex than regular eye exams, but they are a necessary part of diabetes care.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Type 1 Diabetes Go Untreated
Diabetic Eye Exam: What To Expect At Your Eye Exam
If you are fortunate enough to have excellent eyesight, you might be surprised when your diabetes care team advises that you make an appointment with an optometrist. If your vision is steady, and your eyes do not trouble you, why should you have your eyes inspected?
Contents
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetic Retinopathy
The early stages of diabetic retinopathy usually dont have any symptoms. Some people notice changes in their vision, like trouble reading or seeing faraway objects. These changes may come and go.
In later stages of the disease, blood vessels in the retina start to bleed into the vitreous . If this happens, you may see dark, floating spots or streaks that look like cobwebs. Sometimes, the spots clear up on their own but its important to get treatment right away. Without treatment, the bleeding can happen again, get worse, or cause scarring.
Read Also: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Mountain Ice Pain Relief Gel For People With Diabetic Neuropathy
Many patients with neuropathy apply topical pain relievers to relieve localized pain. Mountain Ice is an ideal choice for that, but can also do so much more. The ingredients contained in Mountain Ice have anti-inflammatory as well as anti-oxidant properties, both of which help to increase blood flow. Poor circulation is a common factor in neuropathy, and increasing the body’s ability to deliver blood and oxygen to damaged nerves can speed up regeneration.
Many neuropathy cases also stem from inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, which cause painful inflammation and swelling as the body’s immune system attacks itself. Mountain Ice contains a number of ingredients with anti-inflammatory properties, such as menthol, hyaluronic acid, Vitamin E, and glucosamine that can reduce that swelling.
Be sure to speak with your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before stopping or starting any medication, taking any supplements, or beginning a new healthcare regimen.
How Often Should You Get An Eye Exam
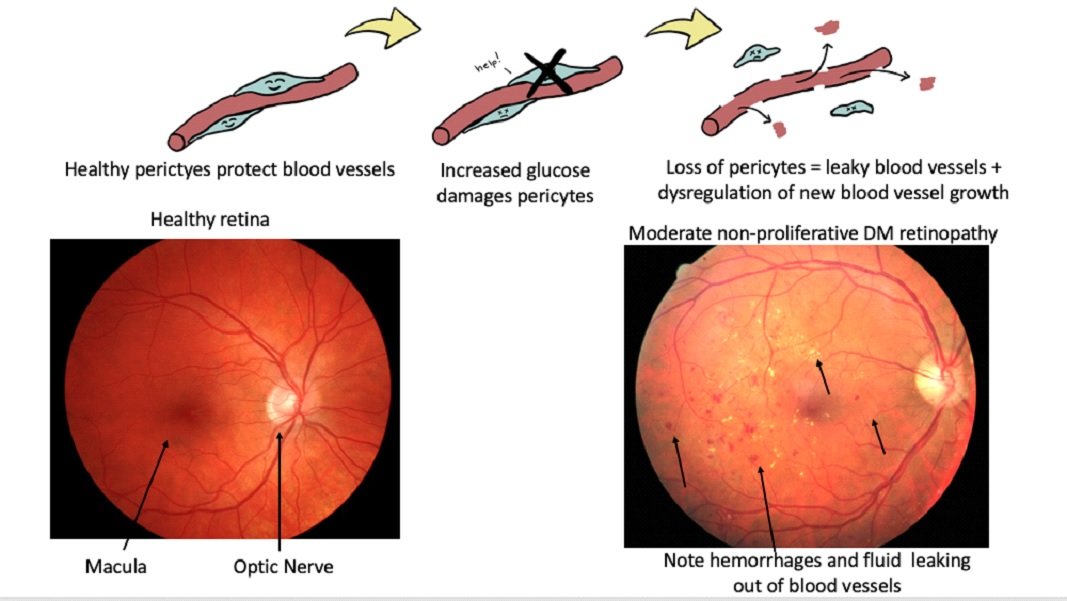
Because you have diabetes, you need a comprehensive eye exam every year from an ophthalmologist or optometrist who knows about the eye problems that are a risk with diabetes.
For adults with type 1 diabetes, itâs recommended that you have a dilated eye exam within 5 years of being diagnosed, and then shift to an annual exam.
About 1 in 5 people with type 2 diabetes have some eye problems when theyâre diagnosed. So getting an eye exam right after your type 2 diagnosis is key. After that, you would get your eyes screened every year. If your results are normal, some eye doctors might suggest moving your exams to every 2 or 3 years.
For women with diabetes who become pregnant, youâll need an eye exam during your first trimester. Youâll also need to be checked again a year after you give birth. Talk to your eye doctor about the effects pregnancy can have on your eyes.
Recommended Reading: Common Side Effects Of Insulin
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by high blood sugar due to diabetes. Over time, having too much sugar in your blood can damage your retina the part of your eye that detects light and sends signals to your brain through a nerve in the back of your eye .
Diabetes damages blood vessels all over the body. The damage to your eyes starts when sugar blocks the tiny blood vessels that go to your retina, causing them to leak fluid or bleed. To make up for these blocked blood vessels, your eyes then grow new blood vessels that dont work well. These new blood vessels can leak or bleed easily.
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetic Eye Disease
Often there are no early symptoms of diabetic eye disease. You may have no pain and no change in your vision as damage begins to grow inside your eyes, particularly with diabetic retinopathy.
When symptoms do occur, they may include
- blurry or wavy vision
- frequently changing visionsometimes from day to day
- dark areas or vision loss
- poor color vision
- spots or dark strings
- flashes of light
Talk with your eye doctor if you have any of these symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Is Ginger Ale Good For Diabetics
Diabetic Eye Exam And Diagnosis
It is important to note that these eye changes are not always symptomatic. Early to moderate diabetic eye disease can be picked up before the patient notices visual changes, and we want to catch these issues and fix them before they become severe and to the point where they can cause irreversible vision loss.
Ophthalmologists Eye Surgeons And Optometrists Located In Bellmore Great Neck Huntington And Little Neck New York
If you have diabetes and experience eye pain, vision changes, or other unpleasant symptoms, see the caring team at Long Island Ophthalmic Concepts. They can complete a diabetic eye exam to detect and treat eye diseases and prevent blindness. Call the office nearest you in Bellmore, Great Neck, Huntington, or Little Neck, New York, to schedule an appointment or book one online.
- Request Appointment
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Pasta Can Diabetics Eat
How Diabetes Affects Your Eyes
Throughout your body, two of the key problems diabetes can cause are damage to the nerves and blood vessels. Both of those problems can affect your eyes, and your eye exam can help flag any damage.
Diabetes affects the retina, which is at the back of the eye. It turns light signals into electrical signals. Those signals travel through the optic nerve to the brain, which turns the signals into images you see. A part of the retina called the macula lets you see fine details clearly. The macula depends on blood vessels in and behind the retina to keep it working.
Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can damage those blood vessels and cause a condition called diabetic retinopathy. How much of your macular function and vision are affected can vary.
People with diabetes are also more likely to develop glaucoma. The longer youâve been living with diabetes, the more common this eye condition is. Uncontrolled diabetes is a major risk.
Glaucoma happens when thereâs a buildup of pressure in the eye. The extra pressure can damage the optic nerve, causing your vision to slowly get worse. You could eventually lose your vision completely.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Eye Problems From Diabetes
Having a full, dilated eye exam is the best way to check for eye problems from diabetes. Your doctor will place drops in your eyes to widen your pupils. This allows the doctor to examine a larger area at the back of each eye, using a special magnifying lens. Your vision will be blurry for a few hours after a dilated exam.
Your doctor will also
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
If You Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes Annual Eye Exams Will Help To Protect Your Eyes From Serious Sight
Diabetes is a condition that prevents the body from using and storing sugar properly. As a result, excessive amounts of sugar remain in the bloodstream and if uncontrolled, can cause damage to the tiny blood vessels all over the body, including those in your eyes.
Diabetic retinopathy affects 30 percent of people with diabetes.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when the blood vessels inside the eye start to leak blood and fluid into the retina, causing damage and permanent vision loss. Early detection and treatment is crucial for preserving your eyesight.
Diabetic macular edema is a complication of diabetic retinopathy, and occurs when the macula, the center of the retina, begins to swell. The macula is responsible for your central and color vision. When the macula swells, it damages the blood vessels, causing them to leak resulting in vision loss.
While patients with uncontrolled blood sugar levels have a higher risk of diabetic retinopathy, those with controlled diabetes are still at risk.
For this reason, eye doctors recommend annual eye exams for early detection of the disease, and increased optimal treatment results. By regularly monitoring your ocular health, you are ensuring that any changes that occur will be detected early, before they can cause any harm.
Whats The Treatment For Diabetic Retinopathy And Dme
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, your eye doctor will probably just keep track of how your eyes are doing. Some people with diabetic retinopathy may need a comprehensive dilated eye exam as often as every 2 to 4 months.
In later stages, its important to start treatment right away especially if you have changes in your vision. While it wont undo any damage to your vision, treatment can stop your vision from getting worse. Its also important to take steps to control your diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Injections. Medicines called anti-VEGF drugs can slow down or reverse diabetic retinopathy. Other medicines, called corticosteroids, can also help.
Recommended Reading: Thin Type 2 Diabetes
What Is The Outlook For People With Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatments for diabetic retinopathy are often very successful, but theyre not a cure. Diabetes is a chronic condition, which means youll likely experience complications of the condition for the rest of your life. This includes vision problems.
If you develop diabetic retinopathy, you may find relief with treatment, but youll need regular eye exams to monitor for worsening issues. You may eventually need more treatment for retinopathy.

