What Happens To The Pancreas
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas, a large gland behind the stomach, stops making insulin because the cells that make the insulin have been destroyed by the bodys immune system. Without insulin, the bodys cells cannot turn glucose , into energy.
People with type 1 diabetes depend on insulin every day of their lives to replace the insulin the body cannot produce. They must test their blood glucose levels several times throughout the day.
The onset of type 1 diabetes occurs most frequently in people under 30 years, however new research suggests almost half of all people who develop the condition are diagnosed over the age of 30. About 10-15 per cent of all cases of diabetes are type 1.
What Is Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
Many doctors consider LADA the adult form of type 1 diabetes because its also an autoimmune condition.
As in type 1 diabetes, the islet cells in the pancreas of people with LADA are destroyed. However, this process occurs much more slowly. Once it starts, it can take several months up to several years for the pancreas to stop being able to make insulin.
Other experts consider LADA somewhere in between type 1 and type 2 and even call it type 1.5 diabetes. These researchers believe that diabetes can occur along a spectrum.
Researchers are still trying to figure out the details, but in general, LADA is known to:
- develop in adulthood
- have a slower course of onset than type 1 diabetes
- often occur in people who arent overweight
- often occur in people who dont have other metabolic issues, such as high blood pressure and high triglycerides
- result in a positive test for antibodies against the islet cells
The symptoms of LADA are similar to those of type 2 diabetes, including:
- excessive thirst
The Goals Of Treatment
The elements of treatment from the time the diagnosis is made include insulin therapy, individual self-monitoring of blood sugar, age-adapted and structured patient education, and the psychosocial care of the family . The target HbA1c value is < 7.5% without simultaneous hypoglycemia . It is currently being discussed whether the target should be lowered to HbA1c< 7.0% , because modern treatment methods are associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia .
Further parameters for the assessment of metabolic control that have recently come into wide use are the so-called time in range and other measures of glycemic variability .
Read Also: Diabetes Meal Planning Involves Having The Person
What Can I Do To Make Living With Gestational Diabetes Easier
Make diabetes management part of your daily routine. Create a schedule and stick to it. Try to:
- Check your blood glucose levels at the same time each day.
- Choose three days each week to get 30 minutes of light exercise.
- Plan small, balanced meals ahead of time.
- Talk with your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator about other tips for daily diabetes management.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women when theres too much glucose in their blood. GD is usually diagnosed during the middle stage of pregnancy with a few simple blood tests. If left untreated, GD can cause health complications for the mother and the baby. Most women can manage gestational diabetes with diet and exercise. Some will need medication. Gestational diabetes increases your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to reduce your risk of diabetes before, during and after pregnancy.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/14/2021.
References
What Is The Long
Over a period of many years, high glucose levels can cause damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Lifelong insulin treatment is essential for people with type 1 diabetes. Maintaining healthy glucose levels over the long term greatly reduces your childs risk of developing diabetes complications later in life. Your diabetes team will teach you how to balance insulin, food, and exercise to maintain safe and healthy blood glucose levels.
Also Check: Dex4 Fast Acting Glucose
What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
Risk Factors For Type 1 Diabetes:
Any combination of the following factors may put people at a higher risk for type 1 diabetes:
- Self-allergy : The immune system usually protects us from disease, but in the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system turns against the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin . If you have any type of autoimmune disease, your risk of developing diabetes increases. Doctors can test for diabetes antibodies, specifically one called GAD65. Measuring this antibody early in the disease can help your medical team determine if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- Genes: People with type 1 diabetes are more likely to have inherited genes putting them at risk. Over 50% of those diagnosed with type 1 diabetes also have a close relative with the disease.
Also Check: Meds To Lower A1c
Are You Experiencing The Signs And Symptoms Of Di
Diabetes insipidus can affect anyone of any age. Age is a risk factor for development, but the genetic variations that create the disease can be present from birth. The biggest risks of DI are becoming too dehydrated and having excessive urination that interrupts daily living activities. Children may also experience pain, diarrhea, and vomiting when DI is present.
Some people can manage their diabetes insipidus symptoms on their own just by making sure there are enough fluids around. They may pack a backpack full of water bottles, be near convenience stores, or fill large containers with tap water in case of an emergency. Others can control their DI symptoms through hormone replacements or other medications. A lucky few will have their symptoms resolve.
Use the information here to ask questions about diabetes insipidus if you see the signs and symptoms of it at your next medical appointment. Do not self-diagnose. This will just create more stress and anxiety, which can enhance the symptoms. Keep fluid intakes at healthy levels and follow any treatment plan as instructed and diabetes insipidus can become one more challenge that has been defeated.
More Severe Symptoms Of Untreated Type 1 Diabetes
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
When type 1 diabetes goes untreated, it can lead to organ failure, coma, and even death. This happens because the body can no longer turn glucose into fuel, and it starts burning fat, which then produces ketones in the blood and urine.
A small amount of ketones aren’t dangerous and can usually be detected if a person has been fasting or is on a low-carbohydrate diet. But too many ketones can actually change the bloods acidity and result in a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis.
If you have one or more of these symptoms contact your doctor.
Symptoms of type1 diabetes tend to look different in children than adults, according to Dr. Christofides.
Also Check: Does Red Wine Lower Blood Sugar
The Risk Of Type 1 Diabetes In Patients Near Relatives
Siblings of a child with type 1 diabetes have an approximately 5% risk of developing the disease in children of a parent with type 1 diabetes, the risk lies between 5% and 7%.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young , a further variety of diabetes with a molecular genetic but not immunological basis, is about as common among children and adolescents as type 2 diabetes. Of the 14 known types of MODY, types 2 and 3 are the most common its overall prevalence has been estimated at 2.4 per 100 000 individuals . In patients with a negative autoantibody status and an uneventful long-term course of illness, such special types of diabetes should be considered in the differential diagnosis and looked for with molecular genetic studies, as their treatment differs markedly from that of type 1 diabetes. Other varieties of diabetes mellitus in childhood include neonatal diabetes and diabetes in the setting of cystic fibrosis and other rare syndromes . No precise figures on the incidence and prevalence of these rare varieties of diabetes have been published to date. The only available data are derived from individual regions, or from registries .
Are The Same Tests Used To Diagnose Both Types
A fasting blood sugar measurement can be used to diagnose any type of diabetes. This test measures the level of sugar in the bloodstream in the morning before eating breakfast. Normal fasting plasma glucose levels are less than 100 milligrams per deciliter . Fasting plasma glucose levels of more than 126 mg/dl on two or more tests on different days indicate diabetes. A random blood glucose test can also be used to diagnose diabetes. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
Another test that is often used is a blood test to measure levels of glycated hemoglobin . This test provides a measure of the average levels of blood glucose over the past 3 months. Other names for the A1C test are HbA1C and glycosylated hemoglobin test.
Tests to identify the abnormal antibodies produced by the immune system are used to diagnose type 1 diabetes. Some of the antibodies seen in type 1 diabetes include anti-islet cell antibodies, anti-insulin antibodies and anti-glutamic decarboxylase antibodies.
Type 1 treatment: Insulin is the treatment of choice for type 1 diabetes, because the body responds appropriately to insulin and the problem is a lack of insulin production by the pancreas.
Read Also: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
Like type 1 diabetes, LADA is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. In contrast to type 1 diabetes, however, LADA progresses slowly and usually occurs in adults over the age of 30 . Because people with LADA often still produce some insulin for months or years after they are diagnosed, it is frequently misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes . Low C-peptide levels and high levels of antibodies against pancreatic islets can help distinguish LADA from type 2 diabetes . LADA is sometimes called type 1.5 diabetes because it shares characteristics with both types 1 and 2. Some researchers believe LADA is varied and can exist on a diabetes continuum of sorts between types 1 and 2 . At first, LADA can often be managed with diet, exercise, and potentially medication, but it eventually requires insulin therapy . It is estimated that LADA may account for 2 12% of all cases of diabetes in adults .
What Are The Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes must be treated with insulin. To do this, a person with type 1 diabetes must inject insulin under their skin where it can be absorbed into their bloodstream to help glucose access the cells that require it. Insulin cant be taken in pill form because the digestive juices in the stomach would destroy the insulin before it could work.
Treating T1D is all about the amount and timing of insulin, as well as the best way to get the right dose of this essential hormone to assure that the glucose circulating in your blood is able to be properly absorbed by your body. Having too much glucose in your body can cause serious complications as can having too little glucose in your blood .
Insulin can be delivered by:
Lexie, known as the divabetic, is a Black diabetes advocate who posts everything from giveaways to advice on dating with type 1 diabetes. She frequently shares posts about diabetes-friendly food and humor.
You May Like: Bananas And Diabetes Type 2
Can Diabetes Cause Headaches Or Dizziness
Yes, its possible to develop headaches or dizziness if your blood glucose level is too low usually below 70 mg/dL. This condition is called hypoglycemia. You can read about the other symptoms hypoglycemia causes in this article.Hypoglycemia is common in people with Type 1 diabetes and can happen in some people with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin or medications such as sulfonylureas.
What Is Diabetes And What Are The Different Types
Anyone that has diabetes understands what it is because it is often a life or death situation if you dont. Diabetes is a serious, yet manageable disease, but you need to stay educated if you want to stay healthy and keep a safe blood glucose level. Besides a few exceptions, most people without diabetes dont understand it fully. This makes a new diagnosis in yourself or a family member scary. The more you understand about something, the easier it is to cope with.
Whether youve just received a new diagnosis or you want to brush up on the science behind diabetes, youve come to the right place. As with everything, starting at the basics is essential. So what exactly is diabetes and what are the different types?
Read Also: Alpha Beta Cells Pancreas
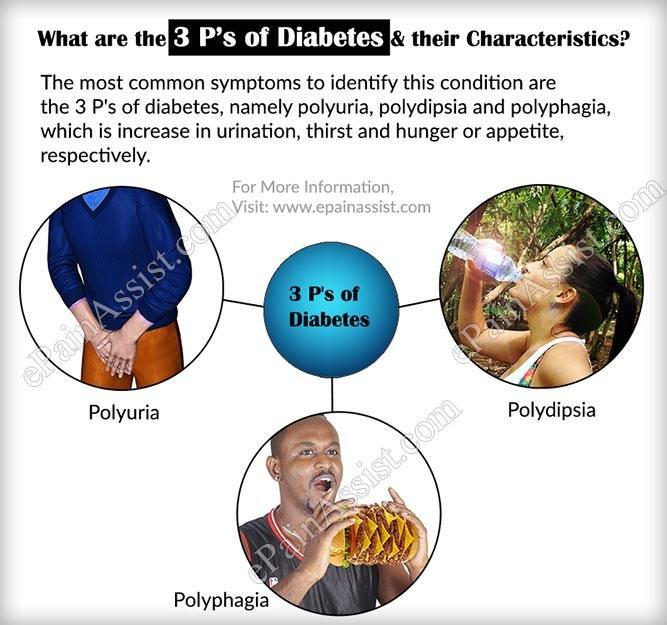
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
- Let us analyze the symptoms of these conditions in a detailed manner. In both these cases, the symptoms are usually the same as both of them lead to high blood sugar levels in the body. In this way, the lack of insulin in the body makes it difficult for the body to use excess sugar, and this leads to various health complications in the long run.
- Some of the general symptoms that can be seen in diabetes patients are frequent urination, and they will face this problem regularly without any seasonal changes.
- Apart from that, the thirst levels increase without any reason, and this can also become a problem as the body is dehydrated frequently, which can cause several health problems.
- Due to the excess load on the body with regards to handling additional blood sugar, the patients feel tired often, and this can hamper their overall productivity in every area. When the symptoms continue for many years, the body becomes entirely dependent on insulin from external sources, and the pancreas produces less insulin even in Type 2 diabetes. In this manner, it can lead to a host of other health problems that include blurry vision and organ failure.
- It is often noticed that people who have diabetes will not get quick relief from wounds, and this can also lead to infections in many cases when timely medication is not provided to the patients.
The Diagnosis And Initial Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes
The diagnosis is made on the basis of typical symptoms and blood sugar measurement. The clinical history and a single capillary blood sugar measurement almost always suffice to establish the diagnosis. Further clinical signs can also include an impaired general state of health, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, or vomiting. In earlier times, diabetes was occasionally misdiagnosed as asthma or possible appendicitis such errors should not be made in todays world of rapid laboratory testing. Further laboratory tests that can be performed in case of doubt are not needed for the initial diagnosis and should be left to specialized diabetes treatment centers for differential diagnostic investigation, as indicated.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
The types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. Its usually diagnosed in children and young adults . It was once better known as juvenile diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or your bodys cells dont respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it having a touch of sugar.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you’re at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Less common types of diabetes include:
Diabetes insipidus is a distinct rare condition that causes your kidneys to produce a large amount of urine.
How Are The Signs And Symptoms Similar
There isn’t a difference between the symptoms of either disease. The “classic” symptoms are the same for both diabetes type 1 and type 2:
- Increased urine output
- Unexplained weight loss
For both type 1 and type 2, early symptoms of untreated diabetes arise due to elevated blood sugar levels and the presence of glucose in the urine. High amounts of glucose in the urine can cause increased urine output and dehydration. Dehydration, in turn, causes increased thirst.
A lack of insulin or an inability of insulin to work properly affects protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin normally encourages the storage of fat and protein, so when there is inadequate insulin or poorly functioning insulin, this eventually leads to weight loss despite an increase in appetite.
Some untreated diabetes patients also experience generalized symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. People with diabetes are also at risk for infections of the bladder, skin, and vaginal areas. Changes in blood glucose levels can lead to blurred vision. When blood sugar levels are extremely high, lethargy and coma can result.
Recommended Reading: How To Keep Blood Sugar From Dropping

