Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Appropriately managing patients with diabetes mellitus is of absolute importance to the entire healthcare team. DM is on the rise in the U.S epidemiology statistics, so ensuring the appropriate use of insulin to control this disease is essential. The interprofessional team must recognize the importance of insulin in the treatment of DM, considering it will significantly benefit the patient in his morbidity and mortality. Clinicians, nurses, and pharmacists should know of insulin’s labeled and off-label indications as well as adverse effects.
Physicians will be prescribing the medication, while the nurse will administer the drug if inpatient and will follow-up on side effects if outpatient, while the pharmacist will work in collaboration with the physician to ensure the proper dosage, indication, and duration of the medication. Finally, the nurse is the first contact with the patient and should coach the patient on administering the medication and being aware of its adverse effects. This interprofessional collaboration will optimize patient outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
Factors That Speed Insulin Absorption
Variation in insulin absorption can cause changes in blood glucose levels. Insulin absorption is increased by:
- injecting into an exercised area such as the thighs or arms
- high temperatures due to a hot shower, bath, hot water bottle, spa or sauna
- massaging the area around the injection site
- injecting into muscle this causes the insulin to be absorbed more quickly and could cause blood glucose levels to drop too low.
Basal And Bolus Insulin
Regardless of type of diabetes, those needing multiple daily injections will need background insulin as well as insulin to cover meals and corrections .
Depending on which delivery mechanism is used, the basal can be a long-acting insulin or a rapid-acting insulin while boluses will always be rapid-acting or short-acting insulin .
Also Check: Can Diabetes Make You Dizzy
Main Differences Between Nph And Regular Insulin
Insulin Analogs Are Now Replacing Human Insulin In The Us
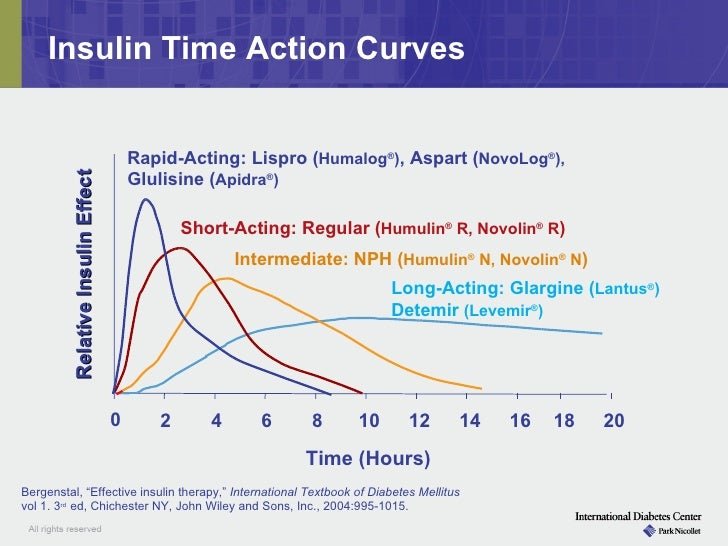
Insulins are categorized by differences in onset, peak, duration, concentration, and route of delivery.
Human Insulin and Insulin Analogs are available for insulin replacement therapy. Insulins also are classified by the timing of their action in your body specifically, how quickly they start to act, when they have a maximal effect and how long they act.Insulin analogs have been developed because human insulins have limitations when injected under the skin. In high concentrations, such as in a vial or cartridge, human clumps together. This clumping causes slow and unpredictable absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and a dose-dependent duration of action . In contrast, insulin analogs have a more predictable duration of action. The rapid acting insulin analogs work more quickly, and the long acting insulin analogs last longer and have a more even, peakless effect.
Recommended Reading: Is Metformin Bad For Your Heart
How Do Different Types Of Insulin Work
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use sugar from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Diabetes is a health condition in which the body is unable to regulate blood sugar on its own through insulin. There are two distinct types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes :T1D, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to T1D.
Type 2 Diabetes :T2D is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar. In T2D, the body either resists the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Genetics and environmental factors, such as being overweight and inactive, have been established as contributing factors.
All patients with T1D and patients with more serious forms of T2D need to take insulin medications to help their body regulate blood sugar.
There are many types of insulin medications available. Each kind has its own unique action and they are not interchangeable. The chart below will help you understand how the various insulin medications work and why your healthcare provider has prescribed them for you.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use insulin regular if you are allergic to insulin, or if you are having an episode of hypoglycemia .
Regular insulin is not approved for use by anyone younger than 2 years old. This medicine should not be used to treat type 2 diabetes in a child of any age.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
-
liver or kidney disease or
Taking certain oral diabetes medicines while using insulin may increase your risk of serious heart problems. Tell your doctor if you also take medicine that contains pioglitazone or rosiglitazone.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Follow your doctor’s instructions about using regular insulin if you are pregnant or you become pregnant. Controlling diabetes is very important during pregnancy, and having high blood sugar may cause complications in both the mother and the baby.
Also Check: Can Metformin Cause Hypoglycemia
Exceptions To Insulin Dosing And Timing
Long-acting insulins arenât tied to mealtimes. Youâll take detemir once or twice a day no matter when you eat. And youâll take glargine once a day, always at the same time. Deglutec is taken once a day, and the time of day can be flexible. But some people do have to pair a long-acting insulin with a shorter-acting type or another medication that does have to be taken at meal time.
Rapid-acting products can also be taken right after you eat, rather than 15 minutes before mealtime. You can take some of them at bedtime.
For more information about when to take insulin, read the “dosing and administration” section of the insulin product package insert that came with your insulin product, or talk with your doctor.
How Do You Inject Insulin
When injecting insulin, always make sure youre giving yourself the correct insulin type and dosage according to your prescription. Injecting too much insulin can lead to low blood sugar and can turn into a medical emergency quickly . Also, never mix or dilute insulin unless your doctor tells you to, and never use expired insulin.
Your doctor or pharmacist can explain how to properly inject insulin. But here is an overview of the steps you should follow if you are using a vial and a syringerather than an insulin pento inject your insulin:
First, gather these supplies:
Soap and water or hand sanitizer
Alcohol wipes
Sharps container
Wash your hands with soap and water or clean them with hand sanitizer.
Gently roll the insulin vial between your hands to mix. Never shake a vial of insulin.
Wipe the top of the insulin vial with an alcohol wipe.
Remove the cap of your insulin needle and pull back the plunger of the syringe to match the marking of your insulin dose.
Push the needle into the top of the insulin vial and then push the plunger down.
Turn the vial upside down with the needle still inside.
Now, slowly pull the plunger down to the desired dosage again.
Check the syringe for bubbles. If you see bubbles, tap the side of the syringe to float the bubbles to the tip. Next, gently push the plunger to get the bubbles out of the syringe. Do this step while the vial is still upside down with the syringe inside. Repeat until all bubbles are removed.
You May Like: Gluconeogenesis And Diabetes
What Should I Avoid While Using Regular Insulin
Do not change the brand of insulin or syringe you are using without first talking to your doctor or pharmacist. Some brands are interchangeable, while others are not. Your doctor and/or pharmacist know which brands can be substituted for one another.
Insulin can cause low blood sugar. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how this medicine will affect you.
Avoid medication errors by always checking the medicine label before injecting your dose.
Avoid drinking alcohol. It can interfere with your diabetes treatment.
Nph Vs Regular Insulin
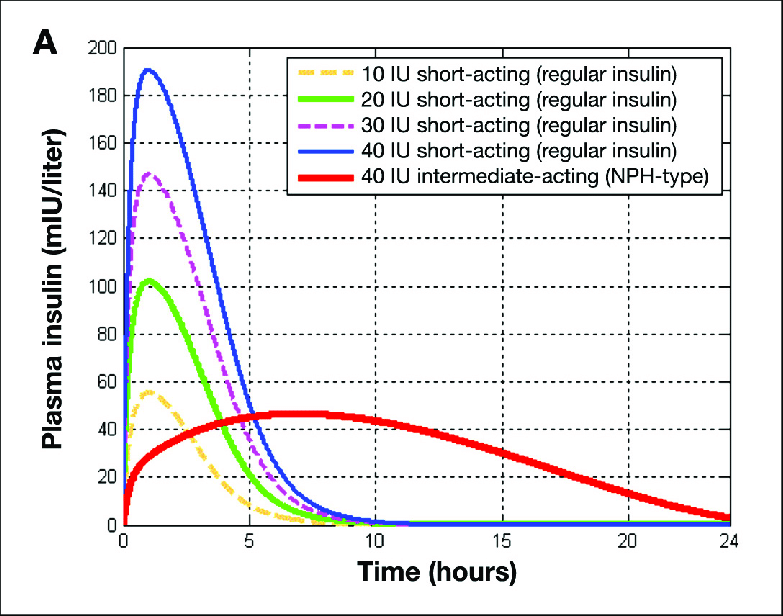
The main difference between NPH And Regular Insulin is that NPH does not result in a rapid drop in blood glucose levels, whereas Regular human insulin, that lowers blood glucose levels rapidly. NPH insulin is slower in time of onset and lasts longer, whereas Regular insulin is faster in terms of onset and shorter in terms of duration.
NPH insulin is found to be the combination of two insulins that can lower the blood glucose levels at a normal rate even when they are too high, moreover, NPH insulin is slower in time of onset, however, NPH lasts longer than any other insulins.
Regular insulin is found to lower the blood glucose levels rapidly when they are too high, and isophane insulin, which works when things are fine with the amount of sugar in the bloodstream, moreover Regular insulin is faster in terms of onset and shorter in terms of duration.
Read Also: Blood Sugar Not Responding To Metformin
Injections Via Pen Or Syringe
This method has been around the longest, since the discovery of insulin in 1921 by Frederick Banting and Charles Best.
Insulin is injected subcutaneously in one of many injection sites on the body: abdomen, thighs, upper arms, or butt. This can be done with a pre-filled insulin pen or by using a syringe to draw up the desired amount of insulin from a traditional vial. Typically, users will need a long-acting basal insulin paired with a rapid-acting insulin for mealtimes.
While insulin pens and syringes cannot offer the extremely precise measured doses a pump or pod can administer, they are certainly the most affordable method of insulin delivery. For those who dont like the bulk of wearing a pump or pod, using a pen or syringe can be just as an effective way of managing blood sugars.
What Happens If I Overdose
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. Insulin overdose can cause life-threatening hypoglycemia. Symptoms include drowsiness, confusion, blurred vision, numbness or tingling in your mouth, trouble speaking, muscle weakness, clumsy or jerky movements, seizure , or loss of consciousness.
Read Also: Blood Sugar Too High Symptoms
Indications Dosing And Administration
Insulin lispro is available only by prescription and is indicated for the management of hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus. Guidelines for glycemic control are listed in Table 4.20,21 Because of its more rapid onset and shorter duration of action, insulin lispro should always be part of a regimen that includes a longer-acting human insulin,5 except when continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy is used.22
|
Greater than 8 percent |
*These values given in this table are for patients who are not pregnant.
The action suggested depends on the individual patient. The action may include increased patient education, more frequent self-monitoring of blood glucose levels or referral to an endocrinologist.
Hemoglobin A1Cis referenced to a nondiabetic range of 4.0 to 6.0 percent .
Adapted with permission from the American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus . Diabetes Care 1996 19:S8S15, and American Diabetes Association. Clinical practice recommendations 1997 . Diabetes Care 1997 20:S1S70.
TTD = total daily insulin dose.
*Insulin lispro intermediate-acting human insulin long-acting human insulin .
The treatment recommendations in this table represent only some of the many possible approaches to initiating insulin lispro therapy. The selection of a specific regimen depends on the physician’s judgment, based on his or her knowledge of the specific patient.
How Do I Take It
Many people get insulin into their blood using a needle and syringe, a cartridge system, or pre-filled pen systems.
The place on the body where you give yourself the shot may matter. You’ll absorb insulin the most evenly when you inject it into your belly. The next best places to inject it are your arms, thighs, and buttocks. Make it a habit to inject insulin at the same general area of your body, but change up the exact injection spot. This helps lessen scarring under the skin.
Inhaled insulin, insulin pumps, and a quick-acting insulin device are also available.
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Low Blood Pressure
Synthetic Human Insulin Is Identical To Your Own
However, relative to the rapid-acting insulin analogs, regular human insulin has several undesirable features.
Synthetic human insulin is identical in structure to your own natural insulin. But when it is injected under the skin it doesnt work as well as natural insulin. This is because injected human insulin clumps together and takes a long time to get absorbed. The activity of this synthetic human insulin is not well synchronized with your bodys needs.
What Is The Difference Between Regular Insulin And Humalog
Health2Wellness 6 months ago 0
Did you know that, if not managed properly, diabetes mellitus might cause vision problems, slow injury healing, or even amputation? However, you might still continue to lead a normal life when living with the disease in case of timely and regular treatment. Fortunately, there is a great number of medications that are used to treat diabetes mellitus these days. Therefore, you will definitely find the one that will fit your needs best.
In this article, we will compare and contrast different insulin types and figure out how Humalog differs from regular insulin. So, lets delve right in!
If you want to buy Humalog online, check out Insulin.Store, which is a trusted insulin supplier from Canada.
Also Check: What Happens If You Don’t Treat Diabetes
Table Of Insulin Actions
The table gives a guide as to quickly the insulins start to act, between which times they peak and how long their activity lasts for.
The speed at which insulin acts may vary in different people and where you inject can have a significant effect too, so the table should only be used as a rough guide to understand how insulin action times can vary.
| Insulin |
|---|
What Are The 6 Different Types Of Insulin
If you need insulin, your doctor will recommend a specific type depending on your lifestyle, the type of diabetes you have, and your blood sugar levels at different times of the day. You may need more insulin coverage at mealtimes, overnight, or throughout the entire day. Currently, there are 5 types of injectable insulins and 1 inhaled insulin.
Types of insulin and how they work in your body
| How long it takes to start working | How long it lasts |
|---|---|
| Inhaled insulin |
Read Also: Side Effects Of Regular Insulin
Rapidly Acting Insulin Analogues
Regular insulin monomers form hexamers in currently available insulin preparations. The hexameric form delays absorption and onset of action. Insulin analogs have been developed that maintain a monomeric or dimeric configuration, increasing their speed of absorption and reducing time to onset to 5 to 15 minutes. They are identical to human insulin except for substitutions of amino acids at one or two positions. Such rapidly acting insulin preparations include insulin lispro, insulin aspart, and insulin glulisine. The use of insulin lispro rather than regular insulin can decrease the incidence of hypoglycemia and improve glycemic control. In clinical trials, insulin aspart has effects similar to insulin lispro on hypoglycemia frequency and glycemic control and causes less nocturnal hypoglycemia than regular insulin.3 Insulin glulisine has similar properties.
Martin L. De Ruyter, Barry A. Harrison, in, 2007
What Is The Difference Between Regular Insulin And Lantus
of insulinLantusof insulin glargineinsulininsulin glargineinsulin
. Considering this, what insulin is comparable to Lantus?
Basaglar is biologically similar to Sanofi’s basal insulin Lantus , including the same protein sequence and a similar glucose-lowering effect. While the FDA does not call it a biosimilar drug for regulatory reasons, it can essentially be thought of as an alternative form of Lantus.
Similarly, how is Lantus insulin different from others? Glargine is an insulin analog recently available in the U.S. It is a long-acting insulin but differs from other long-acting insulins because it is clear as opposed to cloudy. It also has an acidic pH and should not be mixed with other insulins.
Also question is, is Humulin and Lantus the same?
Lantus and Humalog are both forms of insulin used to treat type 1 or type 2 diabetes. A difference is that Humalog is usually given together with another long-acting insulin.
What are the differences between insulins?
Insulins are categorized by differences in onset, peak, duration, concentration, and route of delivery. In contrast, insulin analogs have a more predictable duration of action. The rapid acting insulin analogs work more quickly, and the long acting insulin analogs last longer and have a more even, peakless effect.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have High Blood Sugar
What Is Difference Between Nph And Regular Insulin
January 1, 2022 Posted by Dr.Samanthi
The key differencebetween NPH and regular insulin is that NPH does not lower blood glucose levels rapidly while regular insulin lowers blood glucose levels rapidly.
Insulin is a hormone produced in the Beta cells of islets of Langerhans . Insulin acts on blood glucose to lower blood glucose levels when normal values are exceeded. It allows the cells to take up blood glucose from the bloodstream and lower blood glucose levels.

