Don’t Shortchange Your Sleep
Getting enough sleep at night is crucial for overall health and wellbeing, but especially for blood sugar control. Sure, one night of shortened or interrupted sleep may not have a detrimental effect, but don’t kid yourself that you can get away with too little shut-eye regularly without it causing an imbalance in blood sugar levels.
“It’s recommended that we snooze for seven to nine hours per night, and missing out on quality sleep can trigger stress hormones that increase blood sugar levels,” Harris-Pincus explains.
Plus, stress is unhealthy in general, and it can lead to an increase in cravings, moodiness, physical discomfort, GI distress, and higher risk of disease, among other various concerns.
Why They Happen And How To Try And Reduce Them If You Live With Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes requires you to regularly check your blood sugar levels before you eat. However, we may not always consider what happens to our sugar levels immediately after we eat where it is very normal for people who dont have diabetes, let alone those who do, to temporarily have high sugar levels. Given that having high sugar levels can give you symptoms like thirst, tiredness and needing to go to the toilet a lot, learning about ways to try and reduce spikes in your sugar levels after meals may make a difference to your overall health and wellbeing.
Strike The Spike Ii: How To Manage High Blood Glucose After Meals
Dealing With High Blood Sugar After Meals
Several years ago, I wrote an article for Diabetes Self-Management about the management of high blood glucose after meals. It was called Strike the Spike and no article Ive ever written has led to greater reader response. To this day, I still receive calls and e-mails thanking me for offering practical answers to this perplexing challenge. Ive even been asked to speak on the topic at some major conferences. So when presented with the opportunity to readdress the issue, I jumped at the chance.
A lot has changed in recent years: we know more than ever about the harmful effects of after-meal blood sugar spikes, but we also have a number of potent new tools and techniques for preventing them. And now that I know how meaningful this topic is to so many people, Ill do my absolute best to provide some answers.
Also Check: Diabetic Reaction To Too Much Sugar
How To Tell If Its Safe To Exercise
Before you begin your workout, start by measuring your blood sugar, Dr. Hatipoglu says.
When you initiate exercise, your body releases stress hormones, which can briefly raise your blood sugar.
If you have diabetes and your body doesnt manage blood sugar well, it can increase too much during the first half hour of exercise before it begins to lower.
If you start exercising with very high blood sugar, it might be dangerous, she says. You might need to wait for it to go down a bit before starting your workout.
She offers four tips for ensuring that your glucose levels are safe for exercise:
The American Diabetes Association recommends about 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of rigorous exercise weekly.
How To Control Blood Sugar Level:
Maintaining blood sugar is very important in order to live a healthy and disease-free life. For diabetes patients, the doctrine of the three Ds is the best possible method to keep blood glucose under check. These three Ds are Dose, Diet and Discipline.
Improve your metabolism and regulate healthy sugar levels. All Natural. No Side Effects. 25M+ Sugar Balance satisfied users. Get Sugar Balance for as Low as $33/Bottle. 180 Days 100% Money back Guarantee. Get Lowest Price Here!
Read Also: Pasta For Diabetic
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- s: Stop smoking or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
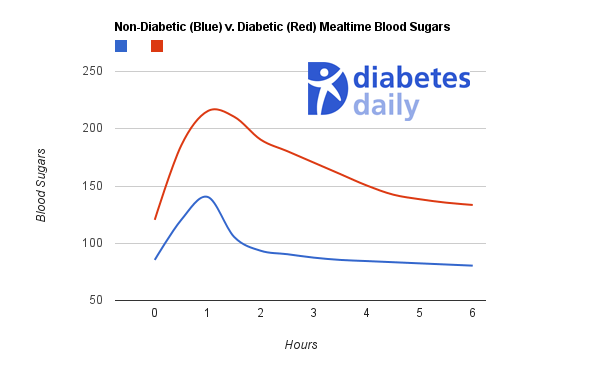
How Long After Eating Will Blood Sugar Peak
How long it takes for blood sugar levels to peak after eating greatly depends on what you eat. However, typically blood glucose levels will begin rising after about 15 minutes of eating. Your blood sugar will typically peak at about one-hour post-meal.
A person without diabetes may experience a slight spike in blood sugar levels after eating. Normal blood sugar after a meal should not exceed around 150 mg/dL.
A person with diabetes should shoot to keep their blood sugar from spiking as much as possible. A good general goal for those with diabetes should be a blood glucose level of around 180 mg/dL after a meal.
Don’t Miss: Life Expectancy On Dialysis With Diabetes
Learn More About Blood Glucose Management> >
The reason blood glucose tends to spike after eating in many people with diabetes is a simple matter of timing. In a person who doesnt have diabetes, eating foods containing carbohydrate causes two important reactions in the pancreas: the immediate release of insulin into the bloodstream, and the release of a hormone called amylin. The insulin starts working almost immediately and finishes its job in a matter of minutes. The amylin keeps food from reaching the small intestine too quickly . As a result, the moment blood glucose starts to rise, insulin is there to sweep the incoming glucose into the bodys cells. In most cases, the after-meal blood glucose rise is barely noticeable.
However, in people with diabetes, the situation is like that of a batter with very slow reflexes facing a pitcher who throws 98-mph fastballs: The timing is all fouled up. Rapid-acting insulin that is injected at mealtimes takes approximately 15 minutes to start working, 6090 minutes to peak, or reach maximum effectiveness, and four hours or more to finish working. Meanwhile, amylin is either produced in insufficient amounts or not at all, so the movement of food from the stomach to the intestines is not slowed the way it should be. As a result, food digests even faster than usual. This combination of slower insulin and faster food can cause the blood glucose level to rise quite high soon after eating. Once the mealtime insulin finally kicks in, the high is followed by a sharp drop.
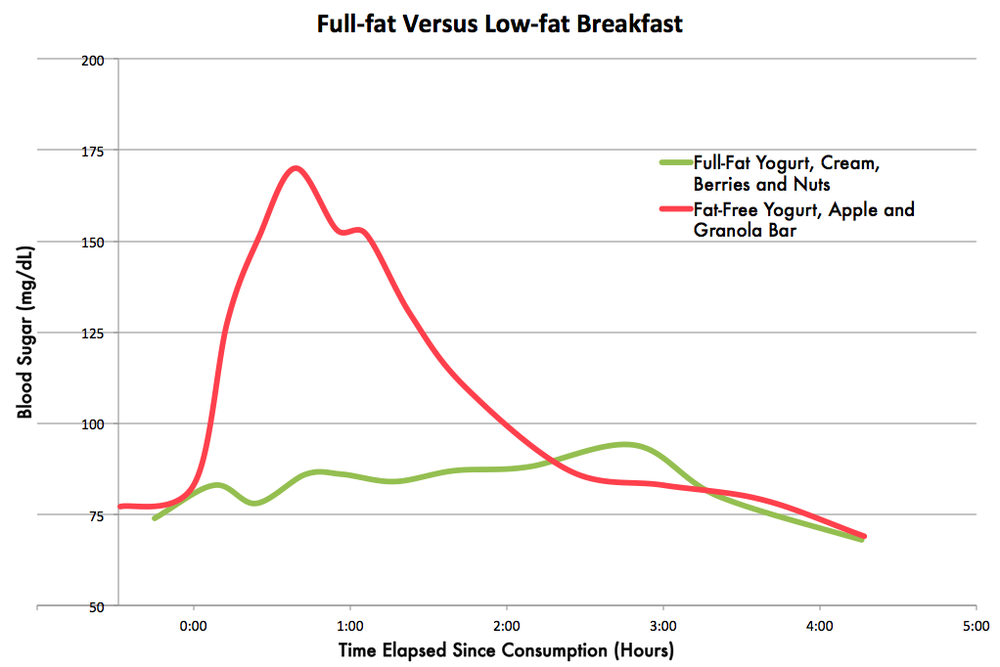
Make Sure To Eat Fiber At Meals And Snacks
When you eat refined white flour, such as pizza crusts, pasta, or crackers, your body is taking in carbs and sugars only and will experience more significant spikes in blood sugar, as there’s no fiber to keep levels stable or to slow digestion.
“Focus on fiber-rich foods to not only manage a post-meal rise in blood sugar but also to assist with gut health as well,” Harris-Pincus says.
Indeed, eating fiber-rich and blood sugar-friendly foods will promote your body’s gut-healthy bacteria, which can further help to balance blood sugar, while keeping your digestive system regular. High-fiber foods include fruits with skin, vegetables, beans and legumes, nuts and seeds, and whole grains, as well as other fortified cereals.
Related:
Also Check: Glucagon Deficiency Symptoms
Time To Strike High Blood Glucose
Given the many short- and long-term benefits of post-meal blood glucose control, it is certainly worth the effort to start measuring and evaluating your after-meal control. If your blood glucose levels are higher than they should be, talk with your healthcare team about new or different medical treatments that might help. And take a look at your personal choices in terms of food and activity. Even without a perfectly functioning pancreas, there is still a multitude of options for tackling those high blood glucose spikes!
Disclaimer Statements: Statements and opinions expressed on this Web site are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the publishers or advertisers. The information provided on this Web site should not be construed as medical instruction. Consult appropriate health-care professionals before taking action based on this information.
Walking After A Meal: The Simplest Habit For Stable Blood Sugar
Taking a post-meal walk can help stabilize blood sugar and give you more energy. New research explores when and how to walk for best results.
Exercise at any time is good for your overall health and well-being. But a growing body of research shows that walking after a meal is especially beneficial for your metabolic healthparticularly if your post-meal walk falls within a specific sweet spot window.
Metabolic health describes how well your body generates and uses energy at the cellular level. Those who are metabolically healthy tend to feel more energetic, have better memory function, and are more able to burn fat and maintain a healthy weight, among many other benefits.
One key indicator of your bodys metabolic health is its ability to efficiently process glucose, the sugar in your blood that comes from the foods you eat. Eating foods with carbohydrates raises our blood sugar. Still, in general, we want to maintain stable glucose for short-term benefits and long-term benefits .
Choosing whole foods low in refined carbohydrates and sugar can help with that steady blood sugar, but so can exercise since muscles can use glucose from the bloodstream for energy. Recent research suggests a simple walk after a meal can help blunt the immediate glucose spike after that meal and significantly lower overall levels of insulin, a hormone that helps our cells take up glucose but can be damaging if our bodies produce too much. Thats a good thing for long-term metabolic health.
Read Also: Diabetes Cardiac Complications
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
The Effect Of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the main constituent of food that can raise your blood sugar levels. The amount and the type of carbohydrates you eat influence how quickly your blood sugar levels change after eating. Carbohydrates from liquids, such as juices and soft drinks, are usually digested more rapidly, while carbohydrates from solid foods, such as pasta and fruits, take a bit more time to break down. Foods that don’t contain carbohydrates or only very little, such as non-starchy vegetables, butter, eggs, meat, poultry, fish, cheese and nuts, do not have the ability to significantly influence your blood sugar levels.
You May Like: How Does It Feel When Your Blood Sugar Is High
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
Exercise And Blood Sugar
Exercise can have a big effect on your blood sugar levels because blood sugar is used for energy. When you use your muscles, your cells absorb sugar from the blood for energy.
Depending on the intensity or duration of exercise, physical activity can help lower your blood sugar for many hours after you stop moving.
If you exercise regularly, the cells in your body may be more sensitive to insulin. This will help keep blood sugar levels within normal ranges.
Read Also: What Colors Represent Diabetes
What Is Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Non
It would be remiss of me, if I left you hanging without letting you in on what normal blood sugars should be after eating if you are non-diabetic.
Whats the point of telling about blood sugar spikes in non-diabetics if I dont reveal what normal blood sugars should be after eating.
The essential point here though is the importance of non-diabetics having a control on their diet. What you eat has either a positive effect on your health or a negative one.
Let me repeat that.
Non-diabetics are obliged to take control of their food choices, if they are to avoid the health implications of blood sugar highs. This is the whole point of this exercise.
You may want to use the figures below as your non-diabetic blood sugar chart if you like. It works just the same way.
So, below is your non-diabetic blood sugar or glucose chart and this is what is recommended by the American College of Clinical Endocrinologists.
Of particular interes,t are the values there that represent what you, as a non-diabetic should be aiming for at 1 hour after eating and 2 hours post meal. They represent what should be normal blood sugar levels after eating your meal.
As you can see it is anticipated that your blood sugar should peak 1 hour after you have eaten but some foods may swing either way.
For instance, an oatmeal may peak just beyond the 1-hour mark compared to a bagel, doughnut or potato fries which might peak much earlier.
Expected Blood Glucose After A High
Related Articles
Blood glucose levels normally rise after a high-carbohydrate meal and drop back to normal levels within a few hours. But if your glucose levels rise higher than normal and recover more slowly, you might have diabetes. Your doctor can administer tests that measure your blood glucose levels immediately before you consume a high-carbohydrate meal and for several hours afterward. If you already have diabetes, your doctor might want you to check your blood glucose levels after meals, to make sure you’re keeping your glucose within the expected range.
You May Like: Pasta Good For Diabetics
How To Deal With High Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels
Obviously, check your levels first meaning at least 90 minutes after a meal. Why? By that time rapid-acting analog insulin has reached its maximum effect By the way, the blood sugar reminder in the mySugr app is a great way to check your glucose after a meal. After all, no one can be expected to remember everything! Just set the reminder for a specific time and youll automatically be reminded. If you have type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar should be between 5 and 9 mmol/liter at least 90 minutes after eating . Of course, your doctor may recommend another postprandial level according to your personal needs and state of health.
The Relationship Between Exercise And Glucose
Scientists are still studying all the factors that regulate glucose delivery from the bloodstream to muscle cells, but one thing is certain: Our muscles are glucose processing workhorses.
In fact, exercise can boost glucose uptake by up to 50 times compared to when we are sedentary. Three primary mechanisms cause your body to use more glucose during exercise:
Put simply, when you exercise, muscle membranes become more efficient at absorbing glucose, the heart pumps more glucose-containing blood to your muscles, and changes in chemical enzymes further aid glucose transport. With all of these mechanisms occurring simultaneously, our muscle cells enjoy the glucose they need to power a workout, and our blood glucose levels drop.
Also Check: Long-term Side Effects Of Insulin Use
How To Measure Your Spikes
The American Diabetes Association recommends you check your blood sugar levels right before mealtime with a blood sample from a finger stick. Then do it again 1 to 2 hours after that first bite of food.
Keep this up for a week or so. Write down the time and the blood sugar number. Make a note about anything you think might affect your levels, like medicine or exercise. And don’t forget to log exactly what you ate, along with portion sizes and the amount of carbs.What levels are too high after a meal? Experts vary on what the number should be, but the ADA says a general goal is a blood sugar level under 180 mg/dL, 1 to 2 hours after a meal. Talk to your doctor about what you should aim for, and don’t adjust your medicine without speaking to them first.

