We Dont Even Need To Follow The A1c For Some Patients
Elderly patients, and those with serious medical conditions, will benefit from simply controlling the symptoms they have from high blood sugars, like frequent urination and incontinence, rather than aiming for any particular A1c level. Who would be included in this group? People with a life expectancy of less than 10 years, or those who have advanced forms of dementia, emphysema, or cancer or end-stage kidney, liver, or heart failure. There is little to no evidence for any meaningful benefit of intervening to achieve a target A1c in these populations there is plenty of evidence for harm. In particular, diabetes medications can cause low blood sugars, leading to weakness, dizziness, and falls. There is the added consideration that elderly and sick patients often end up on a long list of medications that can interact, causing even more side effects.
Can You Have A High A1c And Not Have Diabetes
Yes, you can have a high A1C level and not have diabetes. This is because an A1C test measures the amount of glucose thats attached to hemoglobin. So anything that affects hemoglobin can alter the results. Certain medications, such as steroids, can also raise blood glucose levels in people who dont have diabetes.
Stick To A Regular Schedule So You Can More Easily Follow Your Healthy Diet And Lifestyle
Skipping meals, letting too much time pass between meals, or eating too much or too often can cause your blood sugar levels to fall and rise too much, the ADA points out. This is especially true if you are taking insulin or certain diabetes drugs. Your doctor can help you determine the best meal schedule for your lifestyle.
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes Require Insulin
Recommended Reading: Prognosis Of Diabetes
Normal Levels For Hemoglobin A1c
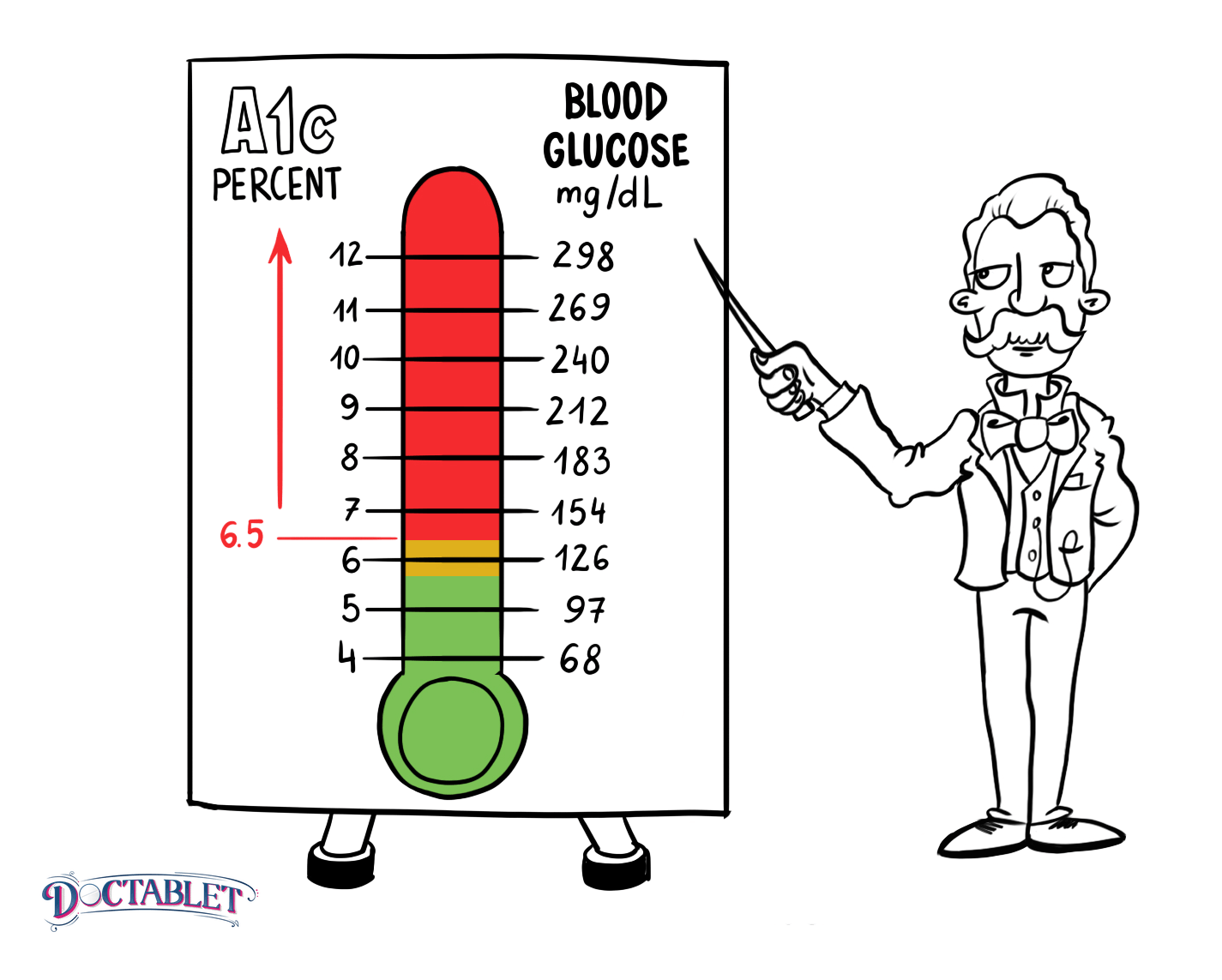
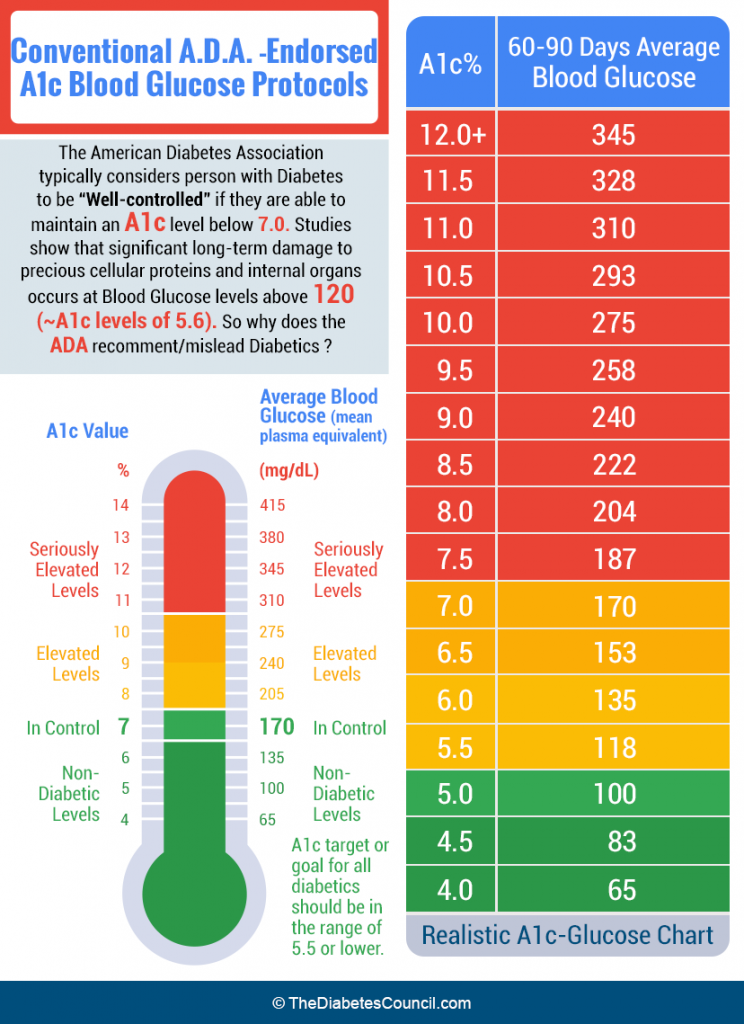
People who dont have diabetes will have a hemoglobin A1c level of between 4 and 5.6 percent. If the hemoglobin A1c level is between 5.7-6.4 percent, this indicates prediabetes and indicates that a person is at risk for diabetes. Any hemoglobin A1c level of greater than 6.5 percent is a presumptive diagnosis of diabetes. The goal for diabetics is to have the hemoglobin A1c level less than 7 percent. At this level, there is less risk for having complications of diabetes mellitus.
If the hemoglobin A1c level is chronically elevated above 7.0 percent, it means the individual is at a high risk for developing complications of diabetes, such as diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy, and heart disease complications.
Why Is My A1c High
As blood sugar level rises, so do A1C levels. A high A1C indicates that blood sugar control is not optimal. This in itself is not an emergency, but it gives your healthcare provider a picture of how blood glucose has, or has not, been controlled, says Dr. Williams.
Poor diabetes control or a need for medication adjustments might cause higher A1C. Diet changes, daily exercise, or medication adjustments might quickly lower A1C. Because Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease, adjustments to ones treatment might be a part of the process of controlling diabetes. Poor diabetes control does not always mean a patient is doing something wrong. But there are other reasons why levels might be high.
As previously mentioned, other health conditions can cause skewed results. These include kidney disease, anemia, liver disease, asplenia, blood loss, hypothyroidism, uremia, and sickle cell anemia. Other factors that might lead to a high A1C level include increased age, pregnancy, and gestational diabetes.
Also Check: Diabetes And Dizziness
Facts And Definition Of Hemoglobin A1c
- Hemoglobin A1c, often abbreviated HbA1c, is a form of hemoglobin that is bound to glucose.
- The blood test for HbA1c level is routinely performed in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Blood HbA1c levels are reflective of how well diabetes is controlled.
- The normal range for level for hemoglobin A1c is less than 6%.
- HbA1c also is known as glycosylated, or glycated hemoglobin.
- HbA1c levels are reflective of blood glucose levels over the past six to eight weeks and do not reflect daily ups and downs of blood glucose.
- High HbA1c levels indicate poorer control of diabetes than levels in the normal range.
- HbA1c is typically measured to determine how well a type 1 or type 2 diabetes treatment plan is working.
What Happens During An A1c Test
Some healthcare provider offices have an A1c machine that requires only a small drop of blood from the fingertip and provides a result in just a few minutes.
Other healthcare providers may order the A1c as a lab test to be drawn in the medical office, a hospital or a lab. The test usually takes less than five minutes, and it often takes a day or two to get the result.
The person drawing your blood will:
- Ask you to expose your upper arm .
- Put a tight band called a tourniquet around your upper arm.
- Clean the area on the inner arm, where it bends.
- Insert a thin needle into a vein.
- Collect blood into a tube attached to the needle.
- Remove the needle, then put a bandage on the tiny hole.
You May Like: List Of Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Type 2
How Is The A1c Test Used After Diagnosis Of Diabetes
Your health care professional may use the A1C test to set your treatment goals, modify therapy, and monitor your diabetes management.
Experts recommend that people with diabetes have an A1C test at least twice a year.4 Health care professionals may check your A1C more often if you arent meeting your treatment goals.4
Your Diabetes Care Team Is Here To Help
Never avoid going to see your health care team because you feel like a failure or are afraid of disappointing them. The members of your diabetes care team are your coaches. They understand there are multiple life challenges that influence diabetes each day and night. Life is always changing, and you/your child will need support along the way. This is all part of the process of living with diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetics Have Mac And Cheese
What Is A1c And Why Is It Used
A1c estimates a persons average blood sugar levels over a 2 to 3-month span. It is the best measure we have of how well blood glucose is controlled and an indicator of diabetes management.
Though A1c doesnt provide day-to-day information, keeping A1c low has been proven to lower the risk of microvascular complications like kidney disease , vision loss , and nerve damage . The relationship between A1c and macrovascular complications like heart disease is harder to show in clinical trials, but having high blood sugar is a major risk factor for heart disease.
A1c is usually measured in a lab with routine blood work, or with a countertop machine in a doctors office using a fingerstick.
A1c measures the quantity of glycated hemoglobin, which refers to sugar attached to a red blood cell protein called hemoglobin. The number is reported as a percentage of the total hemoglobin in the blood. If a person consistently has higher blood glucose levels over time, A1c levels go up because more red blood cells are coated with sugar. The test is representative of a 2 to 3-month average because once a red blood cell becomes coated with sugar, the link is irreversible. It is only when the red blood cell is “recycled” that the sugar coating disappears.
What Is An A1c Blood Test
The A1C test is a common blood test that measures the amount of glucose in the blood. The A1C blood test goes by many other names, including A1C, HbA1C, glycated hemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A1C. Hemoglobin is a protein found in the red blood cells that carries oxygen to the cells. Glucose attaches to hemoglobin in your blood cells, and the A1C test measures the amount of hemoglobin with attached glucose.
The test results reflect your average blood sugar over the past 2-3 months. As your red blood cells have a lifespan of around 3 months, this is why the test gives us an average of what has been going on in your blood for the past few months.
The higher your A1C level, the greater your risk of developing diabetes, and the poorer your blood sugar control if you already have diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Gluconeogenesis
Diabetes Tracking And Treatment
- Follow your diabetes treatment plan: Understand the treatment plan before leaving the healthcare providers office and discuss barriers that could prevent you from following the program. Attend all follow-up visits.
- Consistently take prescribed medications: If a healthcare provider has prescribed medications to reduce blood sugar levels, take them regularly. Some people only take medication when they arent feeling well, but these medications dont work unless taken consistently.
- Monitor and track blood sugar: Regular blood sugar monitoring is the most important step in diabetes management, according to the CDC. Healthcare providers can inform patients of different types of meters and help patients find the best one for them. Providers can also tell patients how often to check their blood sugar and what their target blood sugar range is.Keep a log of your blood sugar levels to look for patterns and triggers for blood sugar spikes and lows. If you wear a continuous glucose monitor, you can use the data. Learning what causes blood sugar to rise or decrease can help you create a plan to keep it consistent.
A1c/average Blood Sugar Chart

A1c test results come out as percentages. According to the NIH, normal A1c levels are at or below 5.7%. An A1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% may indicate prediabetes, and an A1c level of 6.5% or higher may indicate diabetes. For example, if hemoglobin A1c 5.9% is your percentage, your doctor may diagnose you with prediabetes.
The NIH adds that your A1c level should be kept below 7% if you have diabetes. Your doctor will work closely with you to reduce your A1c to normal levels if they are too high and may recommend eating healthier foods and exercising regularly to help regulate your blood sugar.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Side Effects Of High Blood Sugar
What Does The A1c Test Measure
When sugar enters your bloodstream, it attaches to hemoglobin, a protein in your red blood cells. Everybody has some sugar attached to their hemoglobin, but people with higher blood sugar levels have more. The A1C test measures the percentage of your red blood cells that have sugar-coated hemoglobin.
Is There An Alternative To The A1c Test
There are other tests that are helpful when screening for diabetes. They include:
-
Fasting blood glucose
-
Oral glucose tolerance testing
-
Fructosamine testing
You do fasting and oral tolerance testing first thing in the morning, before you eat or drink anything. With a mixed-meal tolerance test, youll have a sugary drink shortly before the blood glucose test.
Your provider may order a fructosamine blood test if A1C testing isnt accurate for you. It checks for the concentration of fructosamine, a protein in your blood, to get an estimate of blood glucose levels over time.
You May Like: Bad Carbs For Diabetics
What Is The A1c Metric
An A1C has many names. It can be called a hemoglobin A1C, glycated hemoglobin or HbA1c. Overall, its the lab that your provider collects when they want to see what your average blood sugar is over the course of three months. It is used to diagnose prediabetes or diabetes, or if you already have diabetes, monitor how youve been managing your blood sugars over a long period of time. A higher A1C means your blood sugars have been running higher lower A1C means your blood sugars have been running lower.
Think about it this way when you spill honey on your countertop, it gets sticky. When your blood sugar is high, your blood gets sticky, too, and the little sugar molecules will stick onto the protein on your red blood cells at a higher rate. The test is telling you what percentage of your red blood cells have a sugar-coated hemoglobin.
When To See Your Doctor
Working closely with your healthcare provider is the best way to manage your diabetes and maintain normal A1C goals. Even if you haven’t been diagnosed with diabetes, it’s important to have your A1C levels checked if you have certain risk factors. Be sure to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider if you:
-
Have symptoms of high or low blood sugar
-
Are having a difficult time managing your diabetes or maintaining normal A1C levels
-
Are experiencing complications from diabetes
-
Have questions about your condition or treatment plan
Signs of diabetes include:
-
Hunger
Read Also: Can A Diabetic Person Get A Tattoo
What Other Factors Can Influence Your A1c Test
If your A1C test results are outside of the normal range, talk to your provider. A lab result may seem to give a clear answer, but that isnt always the case. Your provider will account for your health history before diagnosing prediabetes or diabetes. As mentioned above, there are many reasons your A1C may be higher or lower than expected.
Any situation that affects your red blood cells can alter A1C results. This includes people who have a hemoglobinopathy a different type of hemoglobin. This is more common in some families than others. Let your provider know if you or your family are from Africa, South or Southeast Asia, or the Mediterranean.
What Are The Limitations To Measuring Hemoglobin A1c
Since HbA1c is not influenced by daily fluctuations in blood glucose concentration, it cannot be used to monitor day-to-day blood glucose concentrations and is inappropriate to be used for adjusting insulin doses nor can it detect the day-to-day presence or absence of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. HbA1c may be increased falsely in certain medical conditions. These conditions include
You May Like: Is Type 2 Diabetes Reversible With Diet And Exercise
You May Like: Does Metformin Lower Cholesterol
How High Blood Sugar Creates Hba1c
Red blood cells are exposed to glucose in the blood. The higher the blood glucose level gets the more HbA1c forms throughout the lifespan of a red blood cell .
The lifespan of a red blood cell varies from person to person but averages out to approximately 117 days in men and 106 days in women. Therefore, the HbA1c is an index of average blood sugar levels over the preceding 2 to 3 months. Of this 2 3 month period, the immediately preceding 30 days contribute 50% to HbA1c .
Normal adult hemoglobin consists predominantly of HbA1, of which HbA1c comprises approximately 5% .
However, HbA1c does not always correlate with blood glucose levels. It is possible to have high blood glucose but low HbA1c due to the presence of hemoglobin variants, inflammation, or other factors that increase red blood cell turn over.
If your red blood cells live longer than 90 days or they are smaller , then your HbA1C will be artificially higher.
Maintain A Healthy Weight
Eating a balanced diet and exercising can help you lose or maintain weight. Ask your doctor what a healthy weight is for you.
Work with them to determine how many calories you should be eating. If you need to lose weight, ask them how much weight you should be losing per week to stay healthy.
Crash diets and extreme workout plans may make for entertaining television, but they arent realistic for long-term maintenance. Theyre often unhealthy as well.
Also Check: Metformin How Long To Work
Perspective On Treatment Targets
Medical treatment guidelines reflect an extensive body of research and the time-tested input from leading experts within a given field. The expectation we all have is that this process provides recommendations that are reflective of best practice for the general patient population they address. Ideally, these guidelines provide a framework for treatment, and then they are individualized to best meet the needs of the patient and their unique physiology and lifestyle. The approach to handling T2D is no different. In addition to medical intervention, how we eat, move, sleep and think all have the power to dramatically influence our health. What we know and how we approach the treatment of T2D is a dynamic and evolving process, but a thorough understanding of the treatment targets for the disease and how they influence the possible outcomes for patients must be our ultimate guide on the journey to wellness.
Also Check: Are Protein Shakes Good For Diabetics
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
Also Check: Meal Replacement Shakes For Diabetics Uk
Don’t Miss: Which Statement Is Correct Regarding Glargine Insulin
Some Medications Such As Opioids Can Cause High A1c Levels
Several different medications can interfere with A1C test results. Some can even cause errors in readings or bring up inaccurate results. Some opiates and even over-the-counter drugs can increase your A1C levels. According to a study by the NIH, common drugs like aspirin also cause high or low A1C levels.
Of course, taking the occasional aspirin wonât affect your levels too much. It usually only starts to skew the results of an A1C test if you are taking these medications at regular, larger doses over a long period. This isnât a one size fits all rule, though. For example, among those with type 2 diabetes, aspirin didnât show any elevated levels at all.

