What Increases Your Risk
Your risk for diabetic retinopathy depends largely on two things: how long you have had diabetes and whether or not you have kept good control of your blood sugar.
You can control some risk factors, which are things that may increase your risk for diabetic retinopathy and its complications. Risk factors that you can control include:
If you have type 2 diabetes and use the medicine rosiglitazone to treat your diabetes, you may have a higher risk for problems with the center of the retina . The U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the makers of the drug have warned that taking this medicine could cause swelling in the macula, which is called macular edema.
What Are The Treatments For Diabetic Eye Problems
Treatment for diabetic eye problems depends on the problem and how serious it is. Some of the treatments include:
- Lasers to stop blood vessels from leaking
- Injections in the eye to stop new, leaky blood vessels from growing
- Surgery to remove blood and scar tissue or replace a cloudy lens
- Eye drops to lower fluid pressure in the eye
But these treatments aren’t cures. Eye problems can come back. That’s why your best defense against serious vision loss is to take control of your diabetes and get regular eye exams. It’s also important to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol in a healthy range.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
What Can You Do To Improve Your Diabetes
You can reduce your risk of developing serious diabetic retinopathy if you:
- Continue to attend your regular diabetic eye appointments with OCT Scans and Ultra Widefield imaging of your retina. Here at The Retina Clinic London, we specialise in Diabetic screening and we would be happy to book an appointment for you to be checked.
- Maintain blood sugar , blood pressure and cholesterol at the levels agreed with your diabetic specialist and GP.
- Exercise regularly, stay active and have a healthy diet involving portion control
- If you are a smoker, try to cut down or perhaps quit.
- Reduce alcohol consumption.
- We recommend visiting websites such as Diabetes UK for the most up to date information about the condition, diet, local social groups, and research, to help you better manage your diabetes.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Side Effects Of Metformin
Four Stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy
When it comes to the leading cause of blindness in American adults, diabetic retinopathy is to blame. This diabetes-related eye disease causes semi or complete loss of vision by changing the blood vessels in the retina. Diabetic retinopathy has four different stages. There are different symptoms depending on which stage it is in.
The four stages of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy
- This beginning stage is often where swelling begins in the retinas blood vessels. Because they are so tiny, leaking may begin to occur.
How Does Diabetic Retinopathy Occur
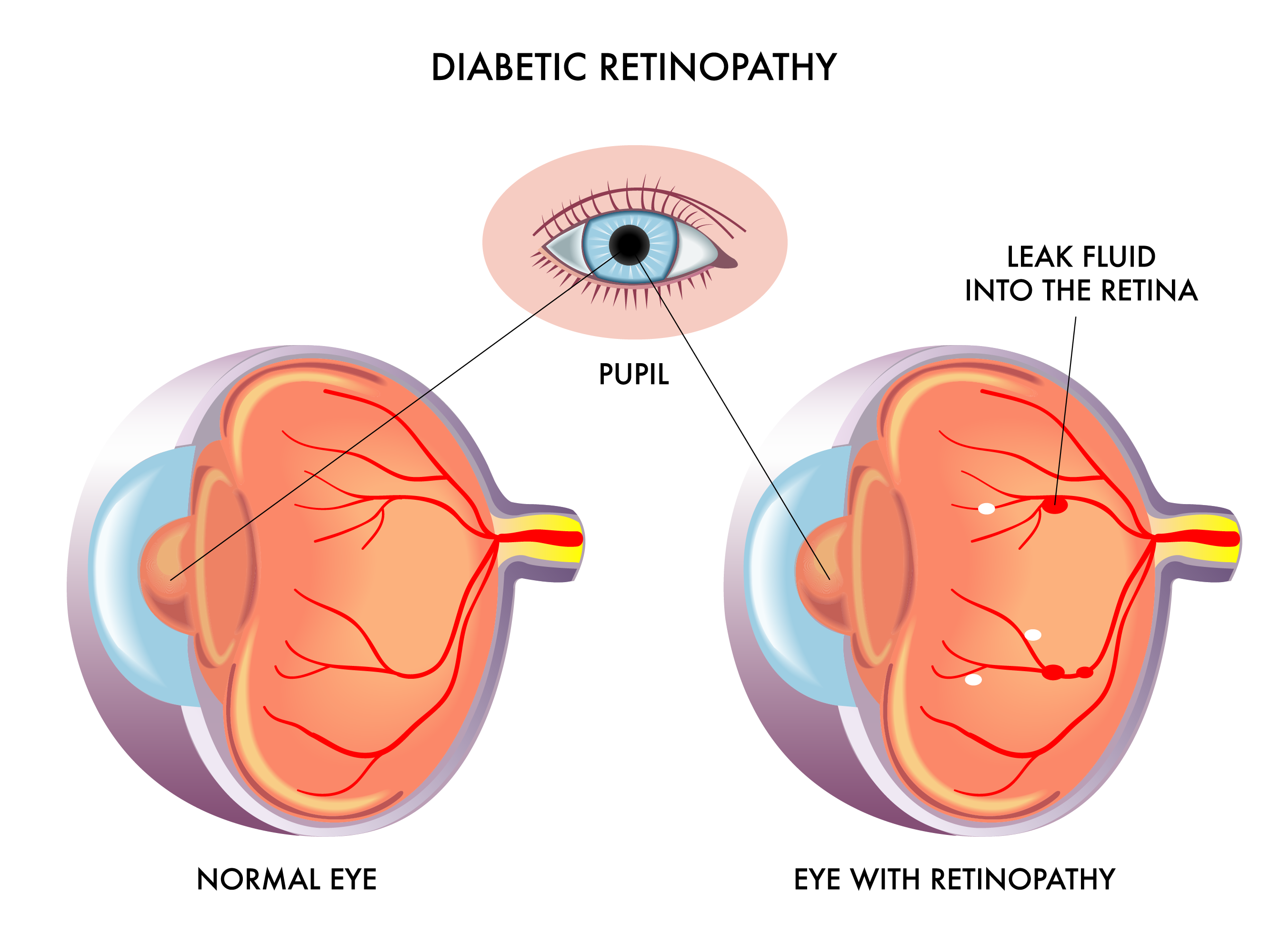
Over several years, a high blood sugar level can weaken and damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina. This can result in various problems which include:
- Small blow-out swellings of blood vessels .
- Small leaks of fluid from damaged blood vessels .
- Small bleeds from damaged blood vessels .
- Blood vessels may just become blocked. This can cut off the blood and oxygen supply to small sections of the retina.
- New abnormal blood vessels may grow from damaged blood vessels. This is called proliferative retinopathy. These new vessels are delicate and can bleed easily.
The leaks of fluid, bleeds and blocked blood vessels may damage the cells of the retina. In some severe cases, damaged blood vessels bleed into the jelly-like centre of the eye . This can also affect vision by blocking light rays going to the retina.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When You Stop Taking Insulin
What Can I Do To Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
Managing your diabetes is the best way to lower your risk of diabetic retinopathy. That means keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. You can do this by getting regular physical activity, eating healthy, and carefully following your doctors instructions for your insulin or other diabetes medicines.
To make sure your diabetes treatment plan is working, youll need a special lab test called an A1C test. This test shows your average blood sugar level over the past 3 months. You can work with your doctor to set a personal A1C goal. Meeting your A1C goal can help prevent or manage diabetic retinopathy.
Having high blood pressure or high cholesterol along with diabetes increases your risk for diabetic retinopathy. So controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol can also help lower your risk for vision loss.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy And Maculopathy
When diabetes affects the small blood vessels in the part of your eye called the retina, this is known as diabetic retinopathy. The retina lines the inside of the eye and acts rather like the film in a camera.
The macula is the small central part of the retina that you use to read and see things clearly. You use the rest of your retina to see things around you and to see in the dark.
Blood vessels bring oxygen and nourishment to your retina. These blood vessels may be damaged in a number of ways if you have diabetes. Severe changes to the retinal blood vessels will affect the health of your retina and this can damage your sight.
Also Check: Average A1c Levels For Non Diabetics
Symptoms Of Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic retinopathy causes blood vessel damage in the retina. Left untreated, it can cause vision loss and can develop into DME.
Approximately 40% to 45% of patients with diabetes have symptoms of diabetic retinopathy, though many don’t notice it. Symptoms can include:
- Blurry vision
- Floaters
- Faded, washed out appearance of colors
- Blank or dark areas in your field of vision
Diabetic macular edema is a build-up of fluid in the center of the retina, or the macula. This part of the eye is responsible for sharp vision and most of our color vision. Symptoms can include:
- Blurry or wavy vision in the center of your field of vision
- Floaters
- Noticing colors appear faded or washed out
Both forms of diabetic eye disease are treatable. Types of treatment and effectiveness depend on the severity of the condition.
At UT Southwestern, we take a multidisciplinary approach to diagnose and treat diabetic eye disease. If we detect diabetes-related eye symptoms and you have been diagnosed with diabetes, we can recommend that you follow up with your endocrinologist or primary care doctor.
If we see signs of eye damage but you have not been diagnosed with diabetes, we can refer you to a diabetes expert at UT Southwestern. The ophthalmology team works closely with our endocrinology doctors and nurses to make sure you have the treatment and information you need to reduce your risks.
What Are The Risks Of Laser Treatment For Maculopathy
Some people can see the laser pattern after treatment. Usually, this continues for up to two months and very occasionally, for up to six months after treatment.
Usually, this continues for up to two months and very occasionally, for up to six months after treatment.
Around one in 10 people report seeing a small but permanent blind spot close to the centre of their sight.
The chance of you completely losing your central vision after laser treatment for maculopathy is around one in 300 .
You May Like: Metformin And Dehydration
What Does Microaneurysm Mean
3.9/5
Then, what causes Microaneurysm?
Any form of vascular disease or high blood pressure may contribute to a retinal microaneurysm, however the most common cause is diabetes mellitus.
Secondly, what is the first sign of diabetic retinopathy? Signs and symptoms of diabetic retinopathy may include: blurred vision. the impairment of color vision. floaters, or transparent and colorless spots and dark strings that float in the patient’s field of vision.
Also to know, what do retinal Microaneurysms look like?
Microaneurysms. The retinal capillary microaneurysm is usually the first visible sign of diabetic retinopathy. Microaneurysms, identified clinically by ophthalmoscopy as deep-red dots varying from 15 m to 60 m in diameter, are most common in the posterior pole.
Can you get retinopathy without diabetes?
Retinopathy in persons without diabetes or retinal vein occlusion is common, occurring in 1% to 15% of the nondiabetic general population. It is usually manifest by one or two retinal microaneurysms or blot hemorrhages. These associations suggest that isolated retinopathy signs are markers of systemic vascular disease.
Types Of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Non-proliferative retinopathy is an early form of the disease, where the retinal blood vessels leak fluid or bleed.
- Macular oedema is a swelling of the macula, caused by the leakage of fluid from retinal blood vessels. It can damage central vision.
- Proliferative retinopathy is an advanced form of the disease and occurs when blood vessels in the retina disappear and are replaced by new fragile vessels that bleed easily, and that can result in a sudden loss of vision.
Recommended Reading: What Are Side Effects Of Metformin 500 Mg
Look Out For Any Changes To Your Eyesight
You might not have any symptoms of retinopathy before it starts to affect your sight. So it’s important to go to your eye screening appointments.
But some people do notice changes to their vision. These wont be the same for everyone, but here are some of the early signs:
- seeing floaters these look like whispy clouds, floating in and out of your vision
- dimmer vision like youre wearing sunglasses all the time
- struggling to see when its dark.
If you notice any changes, or youre struggling to see as clearly as normal, make an appointment with your doctor straight away. Dont wait until your next screening.
Your eyesight can also go a bit blurry if your blood sugar goes higher than usual, even for a short time. This is normal and is a symptom of high blood sugars. Get your sugar levels back to your target level and when theyve settled, your vision should go back to normal.
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetic Retinopathy
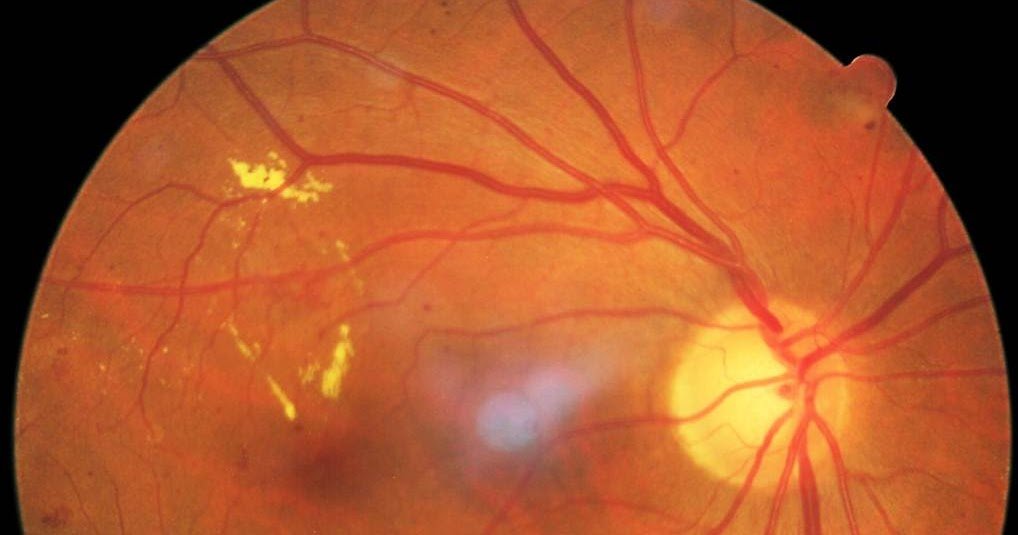
The early stages of diabetic retinopathy usually dont have any symptoms. Some people notice changes in their vision, like trouble reading or seeing faraway objects. These changes may come and go.
In later stages of the disease, blood vessels in the retina start to bleed into the vitreous . If this happens, you may see dark, floating spots or streaks that look like cobwebs. Sometimes, the spots clear up on their own but its important to get treatment right away. Without treatment, the bleeding can happen again, get worse, or cause scarring.
You May Like: Which Factors Will Cause Hypoglycemia In A Client With Diabetes Select All That Apply.
How Will My Eye Doctor Check For Diabetic Retinopathy
Eye doctors can check for diabetic retinopathy as part of a dilated eye exam. The exam is simple and painless your doctor will give you some eye drops to dilate your pupil and then check your eyes for diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems.
If you have diabetes, its very important to get regular eye exams. If you do develop diabetic retinopathy, early treatment can stop the damage and prevent blindness.
If your eye doctor thinks you may have severe diabetic retinopathy or DME, they may do a test called a fluorescein angiogram. This test lets the doctor see pictures of the blood vessels in your retina.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by high blood sugar due to diabetes. Over time, having too much sugar in your blood can damage your retina the part of your eye that detects light and sends signals to your brain through a nerve in the back of your eye .
Diabetes damages blood vessels all over the body. The damage to your eyes starts when sugar blocks the tiny blood vessels that go to your retina, causing them to leak fluid or bleed. To make up for these blocked blood vessels, your eyes then grow new blood vessels that dont work well. These new blood vessels can leak or bleed easily.
Also Check: Diabetes And Hypertension Relationship
Who Is More Likely To Develop Diabetic Eye Disease
Anyone with diabetes can develop diabetic eye disease. Your risk is greater with
- high blood glucose that is not treated
- high blood pressure that is not treated
High blood cholesterol and smoking may also raise your risk for diabetic eye disease.
Some groups are affected more than others. African Americans, American Indians and Alaska Natives, Hispanics/Latinos, Pacific Islanders, and older adults are at greater risk of losing vision or going blind from diabetes.
If you have diabetes and become pregnant, you can develop eye problems very quickly during your pregnancy. If you already have some diabetic retinopathy, it can get worse during pregnancy. Changes that help your body support a growing baby may put stress on the blood vessels in your eyes. Your health care team will suggest regular eye exams during pregnancy to catch and treat problems early and protect your vision.
Diabetes that occurs only during pregnancy, called gestational diabetes, does not usually cause eye problems. Researchers aren’t sure why this is the case.
Your chances of developing diabetic eye disease increase the longer you have diabetes.
Treatment For Diabetic Retinopathy And Maculopathy
If you develop Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy or Maculopathy, you will be advised to undergo tests and treatment.
The aim of treatment in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy is to stop the retina from forming new abnormal blood vessels.
If the treatment is successful, the new vessels will shrink and some of them even disappear over a few months.
The aim of treatment in Diabetic Maculopathy is to reduce the swelling or Oedema.
Treatment is tailored to the stage of disease and patient and can include one or more of the following: anti-VEGF or steroid injections, Pascal® laser or vitrectomy surgery.
Laser treatment can be applied either to a localised area or the entire retina with the exception of the macula, or both.
If you develop high eye pressure or glaucoma, then drops may be given to help control the pressure and decrease the change for any long-term damage.
If you have developed a cataract, then surgery is needed to remove the lens in your eye which is replaced with a clear artificial lens implant .
If you have developed a vitreous haemorrhage or scar tissue causing a retinal detachment, it may be necessary for you to undergo vitrectomy surgery.
Also Check: Is Greek Yogurt Good For Diabetes
What Should I Expect After Intravitreal Injection Treatment
Most people will experience floating spots, blobs or webs that last 2 to 3 days immediately after the injection and should not increase after 24 hours. These are bubbles in the injected drug.
It is NOT uncommon to have a bloodshot eye or bruising of the white part of the eye. This may increase over the first few days and can look very serious. If your eye is NOT painful and your vision is NOT worse this does not require you to be seen by the doctor. It usually resolves within 2 weeks. It is common to have some minor irritation or feeling of grit or sand in the eye, but this should not increase or be severe.
Please contact us if you notice any of the following symptoms in the eye that received the injection:
- If you notice that your vision is deteriorating.
- If you find that you have increasing pain within that eye.
- If you notice increasing amounts of floating spots, blobs or webs.
- If you notice increasing swelling around the eye.
- If you notice increasing discharge from the eye. A minor amount of tearing or watering of the eye is to be expected.
What Is The Treatment For Proliferative Retinopathy
The eye doctor will apply a large number of laser burns to your peripheral retina. The peripheral retina is the part of the retina that allows you to see to the side and in the dark.
This treatment is called pan-retinal photocoagulation and you will usually have more than one session, two to three sessions are usually required at the start. The ophthalmologist may give you an injection of an anaesthetic under the white of the eye to make you more comfortable during the treatment.
Also Check: Long Term Effects Of Insulin
Keep On Top Of Your Cholesterol And Blood Pressure
High blood pressure and a lot of fat in your blood will increase your chances of getting eye problems. This is because your blood vessels can get damaged or blocked, so the blood cant move around your eye properly.
We have advice and information to help you manage your blood pressure and cholesterol. Your healthcare team will also be able to support you with this.
What Does A Diabetic Eye Exam Include
Diabetic eye exams can vary in length and scope, depending on what your eye doctor feels is necessary to successfully manage your condition.
For example, if you have just been diagnosed with diabetes and youve recently had a comprehensive eye exam that showed no signs of diabetic retinopathy, your follow-up diabetic eye exam may require your doctor to simply recheck the condition of your retina.
But if youve had diabetes for a number of years and your doctor has already detected signs of retinopathy or other eye problems related to your disease, your diabetic eye exam may be more extensive and may even include some form of in-office treatment.
The following tests and procedures are commonly performed in most diabetic eye exams:
Recommended Reading: Metformin Dosage For Ketosis
Stage : Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is an advanced stage of the disease, in which new blood vessels form in the retina. Since these blood vessels are often fragile, theres a higher risk of fluid leakage. This triggers different vision problems such as blurriness, reduced field of vision, and even blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy doesnt usually cause symptoms during the nonproliferative stages, so its possible to have it and not know it. This is because blood vessels dont always leak in these stages.
Many people dont have symptoms until the disease progresses to proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
However, an eye examination by an eye care specialist or ophthalmologist can detect diabetic retinopathy in its earlier stages, before symptoms become apparent.
Symptoms of proliferative diabetic retinopathy include:
- depth perception
- curvature of the cornea
Your doctor will likely also dilate your eyeto examine your optic nerve and retina using special eye drops.
Doctors can also diagnose diabetic retinopathy with fluorescein angiography, which checks for abnormal blood vessel growth or leakage.
Theyll inject a yellow dye into a vein in your arm, allowing the dye to travel through your blood vessels. A special camera takes images of the dye as it travels through the blood vessels in your retina.
Keeping blood sugar within a healthy range can slow the progression of vision loss.
If youre in a nonproliferative stage but experience some eye damage, treatment options might include:

