How To Prevent Gestational Diabetes
While theres no way to avoid gestational diabetes completely, a few things can minimize the chances of developing the condition.
Start before youre expecting. Make a point of eating nutritiously and reaching a healthy weight before you even start trying to conceive. Preparing three to six months before getting pregnant is the first step in lowering your risk for gestational diabetes, Ross advises. Being overweight can affect your ability to get pregnant and to have a healthy pregnancy.
Go Mediterranean. The Mediterranean diet has been embraced by the medical community as the model of healthy living, Ross says. Plant foods, fresh fruit, whole grains, fish, lean meats, unprocessed foods and healthy fats are the highlights of this diet.
Get moving. As little as 30 minutes of moderately intense exercise a day can improve your health and well-being, Ross says. Exercise can reduce blood pressure, reduce blood sugar levels, lower cholesterol levels, control body weight and body fat and lower your risk of gestational diabetes and other pregnancy complications. Aim to work out three to five times per week.
Expert bios:
Sherry A. Ross, MD, is an ob-gyn and womens health expert at Providence Saint Johns Health Center in Santa Monica, California, and author of She-ology and She-ology, the She-quel: lets Continue the Conversation.
Delivery When You Have Gestational Diabetes
When planning for the baby’s arrival, the doctor will access the size of the baby to determine if you can deliver vaginally. If you have been able to keep your blood glucose well- controlled, your baby’s weight is within an appropriate range, you don’t have any other pregnancy concerns such as high blood pressure, and you are not on medication, than your labor should proceed just as it would if you didn’t have gestational diabetes. Of course, your delivery team will monitor your blood sugar throughout.
If your baby is considered too large for you to deliver vaginally than you will likely be induced at weeks 38 or 39. You and your doctor may also decide that a cesarean section may be a better route for delivering the baby. Should blood sugar levels get too high during labor, the baby may release more insulin in response. That increases the risk of the baby developing low blood glucose after birth so a C-section may be considered.
What Types Of Diabetes Are There
There are two main types of diabetes that could affect your child: type 1 diabetes and type 2. A third type â gestational diabetes â only affects mums-to-be during pregnancy, but this could also affect your newborn babyâs health and wellbeing if it goes untreated.
So what is the difference between the different types of diabetes?
Dont Miss: Normal A1c Readings For Non Diabetics
Recommended Reading: Can You Eat Pasta With Diabetes
What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Diabetes Seen In Pregnancy
Diabetes during pregnancy can be a risk to the mother as well as the fetus, if uncontrolled. Hence, it is necessary to control and monitor the blood sugar level during pregnancy.
The common symptoms seen in gestational diabetes are:
- Increased thirst
The complications of gestational diabetes are:
- Premature delivery
Related Conditions And Causes Of Gestational Diabetes

Many people may not realize that type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes are different kinds of diabetes.
As previously mentioned, gestational diabetes is caused by the effects of placental hormones and develops only in pregnant women who didn’t have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Type 1 Diabetes is when the pancreas doesnt produce insulin or makes very little insulin. It is believed to be caused by an immune reaction and cant yet be prevented. Type 1 diabetes occurs most often in children, teens, and young adults and often starts quickly and has severe symptoms. People with type 1 diabetes need to use insulin daily.
Type 2 Diabetes comes on gradually, developing over many years. It can be prevented or delayed with lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, and eating a healthy diet. Type 2 diabetes mainly occurs in older adults, although kids, teenagers, and younger adults can develop it, as well.
Prediabetes
Conditions that may increase the risk of gestational diabetes include obesity and PCOS.
ObesityPolycystic ovary syndrome Postpartum Depression Depression and Anxiety
You May Like: Side Effects Of Diabetes Type 1
Diagnosing And Treating Gestational Diabetes
Your doctor will ask you to schedule a glucose challenge test around 24 or 28 weeks of pregnancy. During your appointment, youll drink a glucose solution and be asked to wait one hour in the office. After one hour, you will have a blood sugar test. Your doctor will let you know if results are abnormal and if another test is needed.
The follow-up test, a glucose tolerance test, is also given in your doctors office. Youll need to fast overnight. Then, arriving in your doctors office you will have your blood drawn. After the first blood test, you will drink a glucose solution. Your blood will then be checked once an hour over three hours. A gestational diabetes diagnosis is given if two of the three blood draws have higher than normal blood sugar levels.
Your health care provider will discuss a treatment plan thats right for you if you do have gestational diabetes. That may include:
- More frequent doctor appointments to check your blood sugar levels
- Healthy eating
- Limiting refined sugar and carbohydrates
- Monitoring blood sugar at home
If you are having a hard time managing your gestational diabetes, you may need insulin. Your doctor will help decide whats right for you.
If you have questions about gestational diabetes or are concerned about your risk, talk to your provider today. Find a doctor near you.
What Is The Treatment For Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Specific treatment for gestational diabetes will be determined by your doctor based on:
-
Your age, overall health, and medical history
-
Extent of the disease
-
Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
-
Expectations for the course of the disease
-
Your opinion or preference
Treatment for gestational diabetes focuses on keeping blood glucose levels in the normal range. Treatment may include:
-
Special diet
-
Insulin injections
Read Also: Prognosis Type 1 Diabetes
Complications From Gestational Diabetes
The effects that diabetes has on the fetus can be long-term. In fact, they may have complications that follow them throughout life. Its not uncommon for the child to develop lifelong illnesses due to the high levels of sugar they were exposed to in the womb.
Treatment is the best option to keep the fetuss risks lowered, as it can affect the overall health and wellbeing of the child. Here are the most observed complications of pregnancy-related diabetes:
- Baby can have low blood sugar at birth
- Jaundice
- Baby growth is abnormal in the womb
- Pale skin
- Increased risk of the child developing diabetes in life
- Mother may have increased sugar levels after delivery
- Baby can have respiratory issues
- Mother can develop blood cancer called polycythemia
- Intrauterine growth restrictions
- Placental insufficiency
How Do I Get Tested
Diabetes screening is part of your prenatal care, and Dr. Ahmed usually starts testing during your second trimester, between your 24th and 28th week of pregnancy.
The test is done at this time because the placenta produces large amounts of hormones that may cause you to become insulin resistant. If your results indicate elevated glucose levels, he does further testing to confirm a gestational diabetes diagnosis.
If you’re at high risk overweight or obese before pregnancy or have a family member with diabetes he may test you early on, likely at your first prenatal visit. Interventions, as with Type 2 diabetes, include lifestyle changes and, possibly, medication.
Are you pregnant and experiencing signs of gestational diabetes, or are you concerned you might develop it due to family and other risk factors? Dr. Ahmed can help. Call the office or make your appointment online. Its never too soon to ensure you and your baby remain safe.
You Might Also Enjoy…
Don’t Miss: High Glucose Symptoms
Extremely Dry Mouth And Constant Thirst
Having an alarmingly dry mouth during the day is a glaring symptom of gestational diabetes.
As a result you may be inclined to drink exorbitant amounts of water each day, upwards of 5 litres or more. This habit feeds back into the excessive urination cycle The more you drink, the more you pee.
Why does this happen? This is the bodys natural response to increased fluid loss. Excessive urination leaves us extremely dry and thirsty.
Gestational Diabetes: Symptoms & Signs
- Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD
Medically Reviewed on 9/10/2019
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes may go away after the baby is born, but women who have gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at greater risk of developing diabetes later in life.
Most women with gestational diabetes do not have symptoms. However, the condition can lead to complications, including excessive birth weight in the newborn, increased risk of preterm birth, low blood sugar in the baby after birth, and an increase in risk of respiratory distress in the newborn.
Causes of gestational diabetes
Doctors do not understand the exact cause of gestational diabetes. Certain women are known to be at greater risk, including those over 25 years of age, those who are a nonwhite race, are overweight, or have a personal or family history of diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Other gestational diabetes symptoms and signs
Don’t Miss: Glucokinase Insulin
What Is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes in which the body does not produce adequate amounts of insulin to regulate sugar during pregnancy. It may also be called glucose intolerance or carbohydrate intolerance.In women with gestational diabetes, blood sugar usually returns to normal soon after delivery. But if youve had gestational diabetes, you have a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Youll need to be tested for changes in blood sugar more often.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Managed After Pregnancy
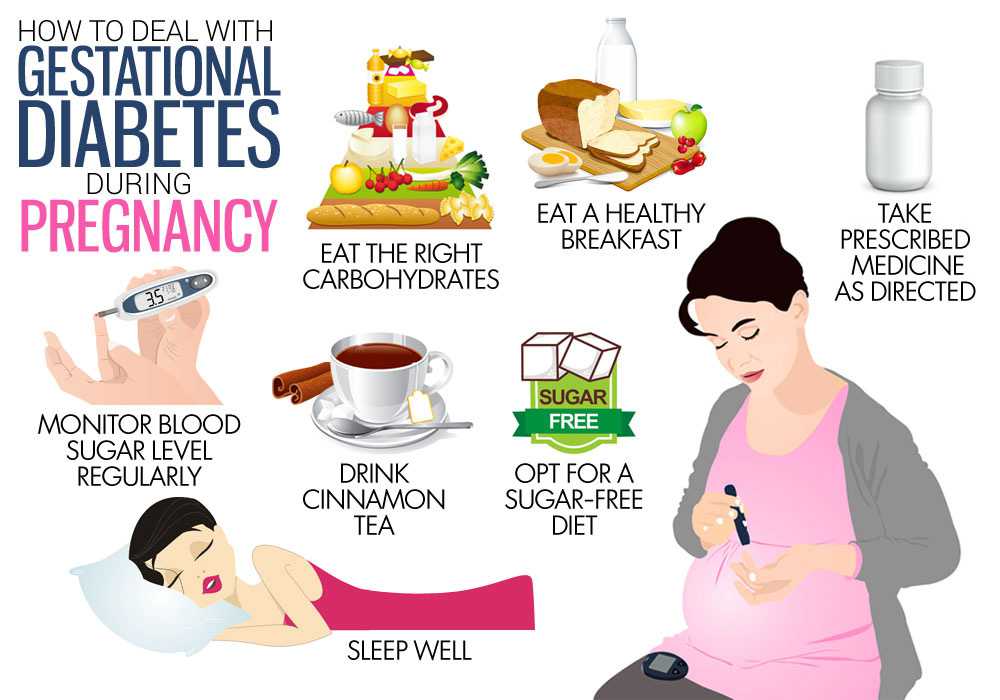
Research has shown that women with gestational diabetes have a 3 to 7 percent chance of developing type 2 diabetes within five to 10 years which is why its so important to make those healthy habits routine during pregnancy and keep a check on your health even after your pregnancy is over.
Here are a few ways to stay healthy after baby is born:
You May Like: Antagonist Of Insulin
Gestational Diabetes: Symptoms Causes Treatment
Gestational diabetes mellitus, often called gestational diabetes, is a common condition in which a persons blood sugar levels increase during pregnancy.
While there are some risk factors that make gestational diabetes more likely, it can also occur in pregnant people with no risk factors.
The American Diabetes Association estimates that gestational diabetes occurs in 10% of pregnancies in the United States.
As long as the condition is detected early and treated, people with this form of diabetes can have healthy pregnancies and deliver healthy babies.
Heres what you need to know about gestational diabetes.
Whos At Risk Of Gestational Diabetes
Any woman can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, but youre at an increased risk if:
- your body mass index is above 30 use the healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI
- you previously had a baby who weighed 4.5kg or more at birth
- you had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- 1 of your parents or siblings has diabetes
- you are of south Asian, Black, African-Caribbean or Middle Eastern origin
If any of these apply to you, you should be offered screening for gestational diabetes during your pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: Took Too Much Metformin
Is There A Special Diet Plan For Women With Diabetes During Pregnancy
While there is no one specific diet that is recommended for all women with gestational diabetes, following a meal plan can help keep your blood sugar levels under control and avoid complications.
- A nutritionist may be helpful in designing a meal plan that takes into account individual schedules and preferences.
- Eating a variety of foods is recommended, and it is better to eat smaller portions throughout the day rather than just a few large meals.
- Many women with gestational diabetes will be advised to eat fewer carbohydrates than in their normal diet and to eat complex carbohydrates that contain fiber. Its important to limit consumption of foods containing large amounts of simple sugars.
- High-fiber foods like fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as whole-grain products, are not only nutritious but also effective in keeping blood sugar levels stable.
- Skipping meals is not recommended because this leads to undesirable fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Who Gets Gestational Diabetes And Why Do I Have To Be Tested
Approximately 2-5% of pregnant women develop gestational diabetes this number may increase to 7-9% of mothers who are more likely to have risk factors. The screening for this disease usually takes place between your 24th and 28th week of pregnancy.
Doctors test for gestational diabetes during this time because the placenta is producing large amounts of hormones that may cause insulin resistance. If the results indicate elevated levels, further testing would be done to confirm a gestational diabetes diagnosis.
You May Like: What’s Worse Type1 Or Type 2 Diabetes
Test For Gestational Diabetes
Though Gestational Diabetes shows some warning signs of insulin resistance, the confirmation of gestational diabetes is only followed by an appropriate test for gestational diabetes. Usually, between week 8 to week 12, the gynecologist would ask the pregnant mother certain questions in order to ascertain whether the women are at risk of having gestational diabetes. Though anyone can develop gestational diabetes, some of the women who are at risk of getting the disease include
- Body Mass Index is more than 30
- Prior delivery of a baby weighing 4.5 kilograms or more
- Prior history of gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- Either one of the parent or sibling of the woman has a history of gestational diabetes
- The woman belongs to a family originating from Chinese, South Asian, African-Caribbean or Middle Eastern region
In case, the woman is found to be in the risk category, the gynecologist usually suggests an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test . This test usually takes two-three hours. This test for determining gestational diabetes include having a blood test while the pregnant woman is fasting .
After the blood test, a glucose drink is provided to the woman. Once the drink is consumed, another blood sample is collected after two hours in order to understand how the body deals with such intake of glucose. Considering the risk of gestational diabetes, OGTT can be repeated again between 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.
How Does It Impact The Health Of The Mom And Baby
Gestational diabetes affects both mom and baby. The mom may experience weight gain and increased sugar levels. There may be hormonal fluctuations, too, which can cause mood swings. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes also have a higher rate of Cesarean sections. If the baby is larger, theres also a higher rate of shoulder dysplasia, which could be traumatic to the baby. In the long-term, the baby potentially has a higher risk of experiencing metabolic issues, earlier onset of diabetes, along with high blood pressure, thyroid abnormalities, and polycystic ovary syndrome. One thing leads to another, Dr. Yu explains.
You May Like: Regular Insulin Adverse Effects
Previous Pregnancies With Diabetes
If youve had any previous pregnancies with signs of diabetes, then you may be at high risk of getting it again.
A study in Diabetes Care shows that up to 69% of women with a history of gestational diabetes may suffer a recurrencein subsequent pregnancies.
The same research also reveals that if you needed insulin to regulate your blood sugar in a previous pregnancy, the same could happen again.
So what does this mean for you?
Be mindful of your medical history and take care during your next pregnancies. Make sure to check your blood sugar levels now and then. Stay alert and notice any subtle early signs of gestational diabetes in your body.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Treated

Fortunately, you can eliminate virtually all of the potential risks associated with diabetes in pregnancy by carefully controlling your blood sugar levels.
If youre diagnosed with GDM, doctors and researchers recommend the following:
- Monitor your blood sugar level several times a day. Check first thing in the morning to get your fasting rate and then an hour after you eat each meal to make sure your blood sugar stays in a healthy range . Most doctors suggest that you buy a diabetes kit, which includes needles to prick your finger and a little machine that reads your blood sugar. Dont worry, the finger prick doesnt hurt, and its the most accurate way to tell how your body is processing various foods. Its empowering when you make healthy food choices and your blood sugar reading is good youre taking an active role in your own health .
- Meet with a registered dietitian. She can help you review healthy food options and make a meal plan. Many women stick to their gestational diabetes diet of well-balanced meals long after birth.
- Keep a food log. After each meal, write down everything you ate along with your blood glucose number. This helps you to better understand what foods are spiking your glucose levels so you can avoid them.
- Get moving. Go for a walk or take the stairs after a meal to lower your glucose levels.
Supplementary insulin can be given in shots, though the oral drug glyburide is being prescribed more and more often for GDM.
You May Like: Can You Be Born With Insulin Resistance
What Triggers This Form Of Diabetes
Sugar is a form of energy used by the body. The pancreas works hard to create insulin that helps turn this sugar into fuel, and it also establishes the metabolism. The placenta is rich in hormones, and these hormones can block insulin production, which prevents the body from regulating glucose levels.
When insulin production is blocked, the glucose levels in the blood rise to dangerous levels. These high sugar levels will damage the organs, blood vessels, and nerves inside the body. Sadly, the high sugar levels might resolve after pregnancy, but the organ and other damage are permanent.

