Diabetes Is Diagnosed By Any One Of The Following:
Sometimes you may have symptoms of fatigue, excessive urination or thirst, or unplanned weight loss. However, often people have no symptoms of high blood glucose and find a diabetes diagnosis surprising.
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Why Is Your Diabetes Meter Inaccurate
Starting with the strip, the chemical process involved relies on an exact amount of blood entering the reservoir in a prescribed amount of time, at a pre-determined temperature and an educated guess assigned to the composition of the blood itself. Not only will one persons blood differ from anothers in chemical makeup and red blood cell count, contagions on your skin AND the presence of water or alcohol after cleaning can affect the results.
For the strip to have a chance at giving a perfect result you need to use the same amount of blood and fill the strip in the same time frame every time; your blood and the enzyme in the strip needs to be at consistent temperatures. If you think that using two drops of blood from the same lancing site should be more accurate, youd actually be wrong. The first drop of blood will have more extracellular fluid content than proceeding drops.
Known Variables to Interfere with Test results
- Meter not calibrated regularly
- Storage and handling of test strips
- Not properly cleansing the test site
- Testing site damp from alcohol prep or water
- Not enough blood applied to test strip
- Altitude, temperature, and humidity
What Should I Do If My Blood Sugar Gets Too High
High blood sugar is also called hyperglycemia . It means that your blood sugar level is higher than your target level or over 180. Having high blood sugar levels over time can lead to long-term, serious health problems.
If you feel very tired, thirsty, have blurry vision, or need to pee more often, your blood sugar may be high.
Check your blood sugar and see if it is above your target level or over 180. If it is too high, one way to lower it is to drink a large glass of water and exercise by taking a brisk walk. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is high more than 3 times in 2 weeks and you dont know why.
What Is The A1c Test
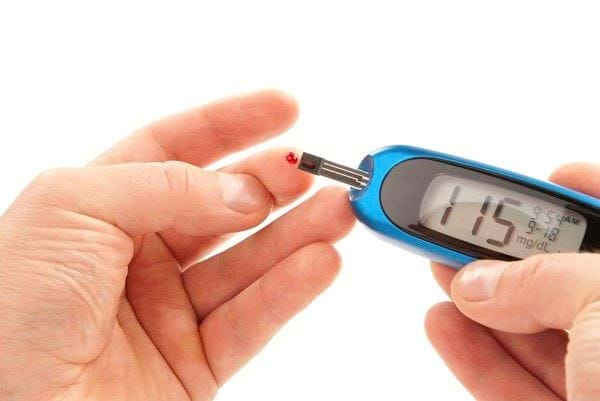
The A1C test is a blood test that provides information about your average levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, over the past 3 months. The A1C test can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.1 The A1C test is also the primary test used for diabetes management.
The A1C test is sometimes called the hemoglobin A1C, HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin, or glycohemoglobin test. Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells. Glucose attaches to or binds with hemoglobin in your blood cells, and the A1C test is based on this attachment of glucose to hemoglobin.
The higher the glucose level in your bloodstream, the more glucose will attach to the hemoglobin. The A1C test measures the amount of hemoglobin with attached glucose and reflects your average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months.
The A1C test result is reported as a percentage. The higher the percentage, the higher your blood glucose levels have been. A normal A1C level is below 5.7 percent.
Glycosylated Hemoglobin Or Hemoglobin A1c
Reflects average blood sugar levels over the preceding 90-day period. Elevated levels are associated with prediabetes and diabetes. Individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of a cardiac event. A diabetic person’s risk for heart attack is the same as a non-diabetic person, who has experienced one heart attack, having a second heart attack. Aggressive global preventive risk reduction efforts, such as lower LDL targets, diet, exercise and blood pressure control, are recommended.
Goal values :
- A range of 5.7-6.4 percent indicates an increased risk for development of diabetes , and lifestyle interventions may be beneficial.
- A value equal or greater than 6.5 percent is considered diabetic.
Preparation
This test may be measured any time of the day without fasting.
Glycosylated hemoglobin is blood glucose attached to hemoglobin . This test is often called the “diabetic report card.” It reflects the average blood sugar for the two to three month period before the test.
To calculate the average blood glucose level from the HbA1C:
HbA1C level x 33.3 86 = average blood glucose level for the past 90 days. HbA1C can be helpful to track diabetic control over time.
What Is The Difference Between Blood Sugar And Blood Glucose
Blood sugar is how we explain it to non-scientists. GLUCOSE DRIVES THE WORLD to get things done. If you are not talking about thermal vents, GLUCOSE IS THE GASOLINE OF ANIMALS and PLANTS. WE are products of the sun . When you eat Broccoli, you are consuming the sun. The Diurnal night day cycle required a way to survive the cold nights glucose stores the energy from the sun and allows you to burn it cleanly without toxic byproducts to get you through another night. Animals gave up photosynthesis and just steal it from the plants Animals further branched to become stealers of the ruminants who were very good at extracting energy from cellulose to make glucose. The entire world centers around finding enough sustenance to make it through another day. There are other ways to use energy from other sources in the body none work as cleanly as glucose breaking down to water and CO2 . Fats and proteins can be burned but leave byproducts that become toxic as they accumulate.Continue reading >>
How Often Should I Check My Blood Sugar
The number of times that you check your blood sugar will depend on the type of diabetes that you have and the type of medicine you take to treat your diabetes. For example, people who take insulin may need to check more often than people who do not take insulin. Talk with your health care team about how often to check your blood sugar.
The common times for checking your blood sugar are when you first wake up , before a meal, 2 hours after a meal, and at bedtime. Talk with your health care team about what times are best for you to check your blood sugar.
How Your Body Makes Glucose
It mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, like bread, potatoes, and fruit. As you eat, food travels down your esophagus to your stomach. There, acids and enzymes break it down into tiny pieces. During that process, glucose is released.
It goes into your intestines where it’s absorbed. From there, it passes into your bloodstream. Once in the blood, insulin helps glucose get to your cells.
Why Do I Need To Know My Blood Sugar Numbers
Your blood sugar numbers show how well your diabetes is managed. And managing your diabetes means that you have less chance of having serious health problems, such as kidney disease and vision loss.
As you check your blood sugar, you can see what makes your numbers go up and down. For example, you may see that when you are stressed or eat certain foods, your numbers go up. And, you may see that when you take your medicine and are active, your numbers go down. This information lets you know what is working for you and what needs to change.
Are Normal Range Blood Sugar Levels The Same For Everyone
Normal range blood sugar will vary throughout the day based on what you have eaten, how much physical activity you have gotten and how long it has been since you have eaten. On an empty stomach, blood sugar levels should be between 70 and 100mg/dL for a non-diabetic. However, you still not considered a diabetic until blood sugar levels following an overnight fasting are above 126mg/dL.
Let’s say that your blood sugar level on an empty stomach or after an overnight fast is around 115mg/dL. You may assume that you have diabetes – since it is above the high range or “normal” – but you do not. Rather you have what called pre-diabetes or IFG and sometimes known as IGT .
If you have been diagnosed with pre-diabetes, you are actually a step ahead of many who already live with diabetes. Pre-diabetes means that your normal range blood sugar is higher than it should be but not yet high enough to be consider as a diabetic. This being said, you still have a chance to turn your blood sugar levels around.
Knowing that you have pre-diabetes gives you the chance to attempt to lessen your risk of diabetes or completely eliminate the risk. You will first want to discuss, with your physician a plan of action. Talk about diets, exercise plans and home blood sugar testers. All of this may seem like a bit too much considering that you are only in the “pre” stage but it will pay off in the end.
What If I Have Trouble Getting To My Blood Sugar Goals
There may be times when you have trouble reaching your blood sugar goals. This does not mean that you have failed. It means that you and your health care team should see if changes are needed. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is often too high or too low. Taking action will help you be healthy today and in the future.
What Are Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
A target is something that you aim for or try to reach. Your health care team may also use the term goal. People with diabetes have blood sugar targets that they try to reach at different times of the day. These targets are:
- Right before your meal: 80 to 130
- Two hours after the start of the meal: Below 180
Talk with your health care team about what blood sugar numbers are right for you.
Can The A1c Test Result In A Different Diagnosis Than The Blood Glucose Tests
Yes. In some people, a blood glucose test may show diabetes when an A1C test does not. The reverse can also occuran A1C test may indicate diabetes even though a blood glucose test does not. Because of these differences in test results, health care professionals repeat tests before making a diagnosis.
People with differing test results may be in an early stage of the disease, when blood glucose levels have not risen high enough to show up on every test. In this case, health care professionals may choose to follow the person closely and repeat the test in several months.
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
Ideal Blood Glucose Levels
The specific level of blood glucose that’s considered ideal for you depends on your age, how long you have had diabetes, medications you take, and any other medical conditions you may have, among other factors.
What’s more, various health organizations differ in what they consider to be ideal glucose levels.
If you have diabetes and blood glucose monitoring is a part of your treatment strategy, your doctor will have the last word on what your target glucose levels at any given time during the day should be.
That said, there are some general parameters worth knowing about, according to the American Diabetes Association.
Fasting Blood Glucose Level
A glucose level below 11.1 mmol/L on a random blood sample does not rule out diabetes. A blood test taken in the morning before you eat anything is a more accurate test. Do not eat or drink anything except water for 8-10 hours before a fasting blood glucose test. A level of 7.0 mmol/L or more indicates that you have diabetes.
If you have no symptoms of diabetes but the blood test shows a glucose level of 7.0 mmol/L or more, the blood test must be repeated to confirm you have diabetes. If you do have symptoms and the blood test shows a glucose level of 7.0 mmol/L or more, the test does not need to be repeated. See the separate leaflets called Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes for more details.
Why Should A Person Get The A1c Test
Testing can help health care professionals
- find prediabetes and counsel you about lifestyle changes to help you delay or prevent type 2 diabetes
- find type 2 diabetes
- work with you to monitor the disease and help make treatment decisions to prevent complications
If you have risk factors for prediabetes or diabetes, talk with your doctor about whether you should be tested.
Small Changes In Temperature Equipment Or Sample Handling
Even when the same blood sample is repeatedly measured in the same lab, the results may vary because of small changes in temperature, equipment, or sample handling. These factors tend to affect glucose measurementsfasting and OGTTmore than the A1C test.
Health care professionals understand these variations and repeat lab tests for confirmation. Diabetes develops over time, so even with variations in test results, health care professionals can tell when overall blood glucose levels are becoming too high.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the most important thing you can do to manage type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Youll be able to see what makes your numbers go up or down, such as eating different foods, taking your medicine, or being physically active. With this information, you can work with your health care team to make decisions about your best diabetes care plan. These decisions can help delay or prevent diabetes complications such as heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation. Your doctor will tell you when and how often to check your blood sugar levels.
Most blood sugar meters allow you to save your results and you can use an app on your cell phone to track your levels. If you dont have a smart phone, keep a written daily record like the one in the photo. You should bring your meter, phone, or paper record with you each time you visit your health care provider.
Sometimes having high blood sugar can feel like a test you didnt pass. But numbers are just numbers. Think of them instead as information. Did a certain food or activity make your levels go up or down? Armed with that knowledge, you can make adjustments and get closer to your target range more often.
Is Sugar Bad For You
If you love sweets, don’t despair. You don’t have to give them up forever. Sugar will raise your blood sugar levels more quickly than other carbs, but diabetes experts now say the total amount of carbs is most important. So keep your serving sizes small and take into account the total carbs and calories.
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
Glucose Often In Prediabetic Diabetic Range
Next, the researchers wanted to see how people of different glucotypes reacted to the same meal. So, they offered all the participants three types of standard breakfasts: cornflakes with milk, bread with peanut butter, and a protein bar.
Each participant responded uniquely to these breakfasts, which suggests that different people metabolize the same food in different ways.
Additionally, the study revealed that common foods such as corn flakes caused significant blood sugar spikes in most people.
We were very surprised to see blood sugar in the prediabetic and diabetic range in these people so frequently The idea is to try to find out what makes someone a spiker and be able to give them actionable advice to shift them into the low glucotype.
Prof. Michael Snyder
Our next study will delve into the physiological causes of glucose dysregulation, continues the senior investigator. These include not only genetic variation, but also microbiome composition, and pancreas, liver, and digestive organ functions.
The researchers hope that their recent and future findings will help to prevent diabetes and its complications.
How Is The A1c Test Used After Diagnosis Of Diabetes
Your health care professional may use the A1C test to set your treatment goals, modify therapy, and monitor your diabetes management.
Experts recommend that people with diabetes have an A1C test at least twice a year.4 Health care professionals may check your A1C more often if you arent meeting your treatment goals.4
Is Blood Sugar The Same As Glucose
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
How To Stay In Target
Eating healthy, exercising and taking medication, if necessary, will help you keep your blood sugar levels within their target range. Target ranges for blood sugar can vary depending on your age, medical condition and other risk factors.
Targets are different for pregnant women, older adults and children 12 years of age and under.
What Should I Do If My Blood Sugar Gets Too Low
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia . It means your blood sugar level drops below 70. Having low blood sugar is dangerous and needs to be treated right away. Anyone with diabetes can have low blood sugar. You have a greater chance of having low blood sugar if you take insulin or certain pills for diabetes.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry, check your blood sugar. Even if you feel none of these things, but think you may have low blood sugar, check it.
If your meter shows that your blood sugar is lower than 70, do one of the following things right away:
- chew 4 glucose tablets
- drink 4 ounces of fruit juice
- drink 4 ounces of regular soda, not diet soda or
- chew 4 pieces of hard candy
After taking one of these treatments, wait for 15 minutes, then check your blood sugar again. Repeat these steps until your blood sugar is 70 or above. After your blood sugar gets back up to 70 or more, eat a snack if your next meal is 1 hour or more away.
If you often have low blood sugar, check your blood sugar before driving and treat it if it is low.
What Factors Affect Blood Sugar

You can guess that carbohydrate intake and insulin production are at least partly responsible for your blood sugar levels. But the list is much longer — almost every lifestyle choice you make can affect your blood sugar. Here’s just a partial list.
- Exercise can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to lower blood sugar for up to 48 hours.
- Alcohol intake increases insulin production, causing low blood sugar.
- Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar, because your body wants access to energy in order to escape what it perceives as a dangerous situation.
- Medications, especially statins and diuretics, can raise blood sugar. Statins are used to treat cholesterol, and diuretics for high blood pressure.
- Diet is a major player in blood sugar. Eating too many simple carbs at once can cause levels to skyrocket, while protein intake leads to a slower increase in blood sugar.
- Dehydration raises blood sugar, because with less water in your body the glucose concentration will be higher.
Other surprising factors can affect your blood sugar, like a sunburn or gum disease, so if you’re dealing with a blood sugar issue and can’t figure out what’s causing your spikes and dips, talk to a health care professional.
Blood Sugar Vs Blood Glucose: What Is The Difference
You might see some charts, or read some articles that say blood sugar chart or blood sugar levels and others that say blood glucose chart or blood glucose levels.
This tends to confuse people, especially if youre newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
The thing is, there is no difference between the terms blood sugar vs blood glucose.
Blood sugar and blood glucose both mean exactly the same thing. Therefore, the words sugar and glucose are often used interchangeably.
So if youre reading an article about blood glucose levels and another about blood sugar levels, the blood sugar and glucose values are both the same thing.
For instance, normal blood sugar levels are 140 mg/dL 2-hours after a meal vs normal glucose levels are 140 mg/dL 2-hours after a meal.
Likewise, normal fasting blood sugar is under 100 mg/dL vs normal fasting blood glucose is under 100 mg/dL .
KEY POINT: The words sugar and glucose refer to the same thing.
So from now on in whenever youre reading stuff about diabetes you can leave that confusion behind knowing they mean the same thing.

