What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- In women: Dry and itchy skin, and frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
- In men: Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle strength.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly over a few weeks or months. Symptoms begin when youre young as a child, teen or young adult. Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting or stomach pains and yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes symptoms: You may not have any symptoms at all or may not notice them since they develop slowly over several years. Symptoms usually begin to develop when youre an adult, but prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes is on the rise in all age groups.
Gestational diabetes: You typically will not notice symptoms. Your obstetrician will test you for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of your pregnancy.
Countries With High Diabetes Prevalence
The International Diabetes Federation currently states that the top 5 countries with the highest amount of people with diabetes are as follows:
- China: 109 million
- 21.1%
All of the top 10 nations are small islands.
In terms of non-islands, the nation with the highest diabetes prevalence is Saudi Arabia with a 17.6% prevalence. The IDF notes that three quarters of the worlds adult population are living in low and middle-income countries.
Diabetes Facts And Figures
- More than 4.9 million people in the UK have diabetes
- 13.6 million people are now at increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the UK
- You’re more at risk of type 2 diabetes if you have a close family member who has diabetes
- 850,000 people are currently living with type 2 diabetes but are yet to be diagnosed
- Research has consistently shown that for some people, combined lifestyle interventions – including diet, physical activity and sustained weight loss – can be effective in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes by about 50%.
Recommended Reading: Are Pork Rinds Okay For Diabetics
Risk Factors For Type 1 Diabetes:
Any combination of the following factors may put people at a higher risk for type 1 diabetes:
- Self-allergy : The immune system usually protects us from disease, but in the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system turns against the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin . If you have any type of autoimmune disease, your risk of developing diabetes increases. Doctors can test for diabetes antibodies, specifically one called GAD65. Measuring this antibody early in the disease can help your medical team determine if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- Genes: People with type 1 diabetes are more likely to have inherited genes putting them at risk. Over 50% of those diagnosed with type 1 diabetes also have a close relative with the disease.
Animal Models In Dm Type 1 Research

Animal models are used in autoimmune diabetes research to understand the pathogenesis and etiology of this disease, and to find and test predictive biomarkers and therapeutic interventions. Currently available models of T1D can be divided into spontaneously autoimmune, chemically induced, virus induced and genetically induced.
Spontaneous autoimmune
- Non-obese diabetic mouse
The NOD mouse is the best known and most widely used animal model for type 1 DM research. It is an inbred, genetically well characterized mouse strain that spontaneously develops T1D. The onset of insulitis occurs at 3â4 weeks of age. The islets of Langerhans are infiltrated by CD4+, CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages and neutrophils, similar to the disease process in humans. Insulitis leads to destruction of β-cells, resulting in the apparent occurrence of T1D, which varies by sex. The incidence is about 60-80% in females and 10-30% in males. In addition to sex, breeding conditions, gut microbiome composition or diet also influence the onset of T1D. NOD Mice are used to understand the pathogenesis and etiology of the disease, to identify novel autoantigens and biomarkers or to test new intervention strategies.
- BioBreeding Diabetes-Prone rat
- LEW -1AR1 / -iddm rat
Chemically induced
Genetically induced
Virally induced
Recommended Reading: When Insulin Is Present Glucose Can Be Utilized By
Management Of Clinical Disease
Methods of managing type 1 diabetes continue to improve, and although progress is generally slow and incremental, occasionally it is punctuated by rapid change. One such moment of change happened in 1993 with the publication of the Diabetes Control and Complication Trial. This trial and the follow-up observational Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications trial convincingly showed that achieving and maintaining glucose concentrations as close to those seen in people without diabetes as possible leads to a reduction in microvascular and cardiovascular type 1 diabetes complications.
While pramlintide is the only non-insulin medication approved for improved glycaemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes, metformin, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors have also been used of-label however, fewer than 5% of patients use these medications. Metformin, an insulin sensitiser, is the most commonly prescribed drug for people with type 1 diabetes who have insulin resistance but it has not been shown to be effective in people younger than 18 years who are overweight or obese and have type 1 diabetes. Use of SGLT2 inhibitors is restricted in part because of early reports of euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis in people with type 1 diabetes treated with these compounds. A 2018 meta-analysis of these inhibitors suggests they are safe, but more data are needed.
How Do People Die From Diabetes
People rarely die from diabetes directly. Its more likely that someone with diabetes will die from complications with other organs. For example, high blood sugar can damage the kidneys over a long period of time, leading to potential kidney failure. And since diabetes is often associated with cardiovascular conditions, heart failure, and stroke are other common causes of death in diabetics. In rare cases of Type 1 diabetes, a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis can cause sudden death.
You May Like: Pasta For Diabetic
Prevalence Across Diabetes Types
Type 2 diabetes is, by far, the most prevalent form of diabetes.
In the UK, type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% of all diabetes cases and type 1 diabetes accounts for approximately 10%.
The IDF reports that the proportion of people with type 2 diabetes is on the rise in most countries.
Whilst type 1 diabetes is less common, overall, than type 2 diabetes, the vast majority of children with diabetes will have type 1.
In 2015, more than 542,000 children in the world were living with type 1 diabetes.
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
The major process that happens in type 1 diabetes is that the pancreas can no longer produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is more a result of insulin resistance , that is, it takes a large amount of insulin to move glucose out of the blood and into the cells. Over time, people with type 2 diabetes also may experience decreased insulin production in the pancreas. In type 1 diabetes, over time, the body can also develop insulin resistance — especially in people who gain a lot of weight while using insulin. This means there is some overlap in treatment and diet for people who have had diabetes of either type for a long time.
Also Check: What Does High Blood Sugar Do To Your Body
Does Eating Sugary Foods Cause Diabetes
Sugar itself doesn’t directly cause diabetes. Eating foods high in sugar content can lead to weight gain, which is a risk factor for developing diabetes. Eating more sugar than recommended American Heart Association recommends no more than six teaspoons a day for women and nine teaspoons for men leads to all kinds of health harms in addition to weight gain.
These health harms are all risk factors for the development of diabetes or can worsen complications. Weight gain can:
- Raise blood pressure, cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Increase your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Cause fat buildup in your liver.
- Cause tooth decay.
Can Diabetes Cause Hair Loss
Yes, its possible for diabetes to cause hair loss. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to persistently high blood glucose levels. This, in turn, leads to blood vessel damage and restricted flow, and oxygen and nutrients cant get to the cells that need it including hair follicles. Stress can cause hormone level changes that affect hair growth. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your immune system attacks itself and can also cause a hair loss condition called alopecia areata.
Also Check: Problems With Metformin Side Effects
How T1d Is Managed
Type 1 diabetes is a 24/7 disease that requires constant management. People with T1D continuously and carefully balance insulin intake with eating, exercise and other activities. They also measure blood-sugar levels through finger pricks, ideally at least six times a day, or by wearing a continuous glucose monitor.
Even with a strict regimen, people with T1D may still experience dangerously high or low blood-glucose levels that can, in extreme cases, be life threatening. Every person with T1D becomes actively involved in managing his or her disease.
What Are Some Juvenile Diabetes Statistics

More commonly known as Type 1 diabetes, juvenile diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and is managed by daily insulin shots. Around 1.6 million Americans have Type 1 diabetes, including 200,000 youth, and there are approximately 64,000 new cases per year. According to JDRF, between 2001 and 2009, there was a 21% increase in Type 1 diabetes prevalence in people younger than 20.
You May Like: Epinephrine And Diabetes
Does Exercise Affect Blood Sugar Levels
- Exercise is important for everyone, including people with type 1 diabetes.
- People with type 1 diabetes need to be careful to monitor their blood sugar before, during, and after exercise and have snacks with them in case blood sugar goes too low.
- When people exercise, the muscles use insulin to access blood sugar for fuel.
- This can lead to lower than expected blood sugar.
- Exercise also may trigger release of stored glucose from the liver. This can lead to higher than expected blood sugar. This is why it is important to check blood sugar, especially when beginning a new exercise program.
- People with type 1 diabetes may see their blood sugar go up or down with exercise.
Highlights From The Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects Canadians of all ages. If left uncontrolled, diabetes results in consistently high blood sugar levels , which can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, vision loss, kidney failure, nerve damage, and amputation. Fortunately, it is possible to remain healthy with diabetes through appropriate management and care.
The Public Health Agency of Canada , in collaboration with all provinces and territories, conducts national surveillance of diabetes to support the planning and evaluation of related policies and programs. This fact sheet presents an overview of diagnosed diabetes data from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System .
You May Like: Hypertriglyceridemia Low Carbohydrate Diet
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Someone With Type 1 Diabetes
Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association reported that people with type 1 diabetes live about 11 years less than average however, new research also suggests this differential can be reduced with good glycemic control. Most people with type 1 diabetes die from complications of type 1 diabetes such as heart disease or kidney disease. Thus, preventing complications and following a healthy lifestyle that prevents heart disease and controls blood sugar are the best things people with type 1 diabetes can do to live a long, healthy life.
Don’t Miss: Adverse Effects Of Metformin
Type 1 Diabetes Facts
There is nothing anyone can do to prevent T1D. Presently, there is no known cure.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when a persons pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that controls blood-sugar levels. T1D develops when the insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells are mistakenly destroyed by the bodys immune system. The cause of this attack is still being researched, however scientists believe the cause may have genetic and environmental components.
Quick Facts About Type 1 Diabetes
- Approximately 400,000 people are currently living with type 1 diabetes in the UK, including around 29,000 children.
- The number of new diagnoses of type 1 diabetes is increasing by about four per cent each year.
- In children under five, the incidence of type 1 diabetes is rising by five per cent each year.
- Among children with diabetes in England and Wales, 96 per cent have type 1 diabetes.
- Around 85 per cent of people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes have no family history of the condition.
- Although it used to be referred to as juvenile diabetes, around half of newly diagnosed cases of type 1 diabetes are in people over the age of 18.
- The UK has one of the highest rates of type 1 diabetes in the world, for reasons that are currently unknown.
- A person with type 1 diabetes will have around 65,000 injections and measure their blood glucose more than 80,000 times in their lifetime.
You May Like: What Are Normal A1c Levels For Non Diabetic
The Facts Stats And Impacts Of Diabetes
The more you know about diabetes, the more you can do about preventing it, delaying it, or lessening its harmful effects.
Chances are, you know someone with diabetes. It may be a friend, a family member, or even you. And because the best way to prevent or manage any harmful health condition is to be informed, we want to help you be in the know. Learn about the facts, stats, and impacts of diabetes.
The year 2021 marked the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin. Before insulin was discovered, people with diabetes didnt live long lives. Since then, weve come a long way in reducing the toll diabetes takes on peoples daily lives. But the fight isnt over.
Today, the number of people with diabetes is higher than it has ever been. And its not just your grandparents you have to worry about. People are developing diabetes at younger ages and at higher rates. But the more you know about diabetes, the more you can do about preventing it, delaying it, or lessening its harmful effects.
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
Don’t Miss: Do Antibiotics Affect Blood Sugar
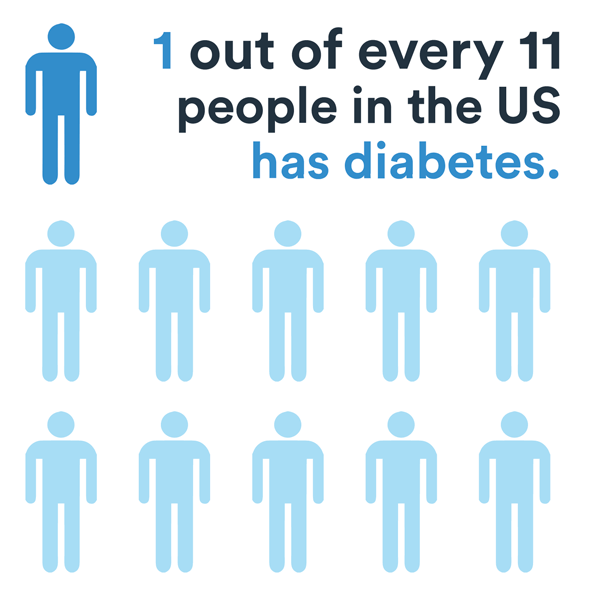
How Common Is Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the worlds fastest-growing chronic diseases. How prevalent is it? Lets take a look:
- In 1980, 108 million people worldwide had diabetes. By 2014, that number had risen to 422 million.
- An estimated 700 million adults worldwide will have diabetes by 2045.
- China has the highest number of diabetes accounts worldwide, with 116 million people with diabetes. Following China is India and then the United States .
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
You May Like: Symptom Of High Blood Sugar
Newly Diagnosed With Type 1 Diabetes
It can be difficult to know where to get started with your new type 1 diagnosis, but were here to help you find the information you need.
As well as reading through the guidance and advice on this page, why not try our Learning Zone? With videos, quizzes and interactive tools tailored just for you, its the perfect way to discover more about your diabetes.
“She made me feel normal, when my normal had completely changed.”
– Laura, on being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Read her story.

