Living With Type 1 Diabetes Helped Shape Who I Am
Even though most people with type 1 diabetes wouldnt chose to have the disease, managing it may lead to insights and a heightened awareness of the struggles everyone faces.
Diabetes has brought a lot of wonderful things into my life, says McKean. I am more empathetic toward anyone with a chronic condition, and I try hard to remember that you don’t usually know all that’s going on in a person’s mind, so be kind to them.
Support and relationships can grow out of a type 1 diagnosis as well. As a kid, I attended the Florida Camp for Children and Youth with Diabetes and I went back as a counselor and volunteer for six years. I met some incredible people there and really relished the chance to be surrounded by people ‘like me, says McKean. And as an adult I interned at a diabetes charity in the UK and met my husband there. So, I certainly can’t be too hard on the disease!
How The Honeymoon Phase Starts
In type 1 diabetes, your immune system — the body’s defense against germs — misfires. It destroys beta cells in your pancreas that make insulin, a hormone that helps your body store sugar for energy.
Without beta cells, your supply of insulin drops, and your levels of blood sugar go up. To get your blood sugar at the right level, you’ll need to take insulin in a shot or through a pump.
Most people with type 1 diabetes have a period of time after they’re diagnosed when their remaining beta cells can pump out enough insulin to control their blood sugar. This is the honeymoon phase. While it lasts, you may not need to take as much insulin.
Shorter Life Expectancy In Type 1 Diabetes
In the United States, diabetes of either type claims nearly 90,000 lives each year, making it the 15th leading cause of death among Americans. But many of these deaths result not from diabetes itself but from complications that might be prevented in most people by working toward a more normal A1C level.
Recent research from Manchester University in England linked higher A1C levels with decreased life expectancy in people with type 1 or , illustrating the need for people with diabetes to monitor their sugar levels closely and follow their treatment plans carefully.
Its important to note that this study did not find that type 1 diabetes, itself, shortens a persons lifespan. Rather, the study showed that poorly controlled blood glucose levels over time could lead to a poorer prognosis and shortened life expectancy in people with diabetes.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Anyone Can Get Type 1 Diabetes
It isnt completely clear what causes type 1 diabetes, but we know that diet and lifestyle habits dont. Type 1 is thought to be the result of an autoimmune response, where your body attacks the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Insulin is a hormone that acts like a key to let blood sugar into your bodys cells for use as energy. Sometimes infection with a virus seems to trigger the autoimmune response. Many people with type 1 diabetes have family members with type 1, but most dont.
The peak age for being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is around 13 or 14 years, but people can be diagnosed when theyre much younger and older .
Diabetes And Your Child
For a parent whose child is diagnosed with a life-long condition, the job of parenting becomes even tougher.
Although being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will involve coming to terms with the diagnosis, getting used to treatment and making changes to everyday life, your child can still lead a normal and healthy life.
The Diabetes UK website has information and advice about your child and diabetes.
Also Check: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes In The Workplace
There are practical and legal issues related to diabetes in the workplace. Employers and employees with diabetes should work together to find solutions and educate themselves about the rights of individuals with diabetes. Individuals with diabetes are responsible for having all necessary diabetes supplies, eating properly, and being aware of safety issues and regulations at work. The Americans with Disabilities Act states that most employers must provide reasonable accommodations to allow an individual with diabetes to safely and successfully perform a job, unless doing so would place an undue burden on the employer. We refer the reader to ADA position statement on diabetes and employment for additional information and to the relevant section of the American Diabetes Association/JDRF Type 1 Diabetes Sourcebook .
Who Gets Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can’t be prevented, and there is no real way to predict who will get it. Nothing that either a parent or the child did caused the disease.
Once a person has type 1 diabetes, it does not go away and requires lifelong treatment. Kids and teens with type 1 diabetes depend on daily insulin injections or an insulin pump to control their blood glucose levels.
Page 2
Also Check: Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat Bananas
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
Diabetes is diagnosed and managed by checking your glucose level in a blood test. There are three tests that can measure your blood glucose level: fasting glucose test, random glucose test and A1c test.
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This test is best done in the morning after an eight hour fast .
- Random plasma glucose test: This test can be done any time without the need to fast.
- A1c test: This test, also called HbA1C or glycated hemoglobin test, provides your average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. This test measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin, the protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen. You dont need to fast before this test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: In this test, blood glucose level is first measured after an overnight fast. Then you drink a sugary drink. Your blood glucose level is then checked at hours one, two and three.
| Type of test |
|---|
Type 1 Diabetes: Prognosis And Life Expectancy
Approximately 26 in 100,000 Americans live with some form of , and recent research suggests the life expectancy of a person with type 1 diabetes may be shorter than the average persons. However, many diabetes deaths occur due to type 1 diabetes complications, like and , which often can be prevented.
The current prognosis for looks brighter than ever, with a potential cure on the horizon. While everyone waits for that, you may be able to avoid complications and live a healthy, lengthy life by following your type 1 diabetes treatment plan closely.
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Heart Eyes Feet Nerves And Kidneys
Blood vessels are located throughout our bodys tissues and organs. They surround our bodys cells, providing a transfer of oxygen, nutrients and other substances, using blood as the exchange vehicle. In simple terms, diabetes doesnt allow glucose to get into cells and it damages blood vessels in/near these organs and those that nourish nerves. If organs, nerves and tissues cant get the essentials they need to properly function, they can begin to fail.Proper function means that your hearts blood vessels, including arteries, are not damaged . In your kidneys, this means that waste products can be filtered out of your blood. In your eyes, this means that the blood vessels in your retina remain intact. In your feet and nerves, this means that nerves are nourished and that theres blood flow to your feet. Diabetes causes damage that prevents proper function.
Why Take Care Of Your Diabetes
Taking care of yourself and your diabetes can help you feel good today and in the future. When your blood sugar is close to normal, you are likely to:
- have more energy
-
Ask your health care team what type of diabetes you have.
-
Learn where you can go for support.
-
Learn how caring for your diabetes helps you feel good today and in the future.
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
Diabetes Is A Balancing Act
It can be a bit troublesome to try to get your diet, exercise, and medications straight. All of this effort is to have your A1C stay under 7 percent, so that you are living healthy with diabetes. However, if your A1C starts creeping up, and you have tried many other diabetes medicines in order to try to get your A1C down to no avail, dont balk at starting insulin.
Lipids In Type 1 Diabetes

Patients with type 1 diabetes may show quantitative lipid disorders. There is a clear relationship between the level of glycaemic control and lipid abnormalities, with an independent correlation between HbA1c and low-density lipoprotein -cholesterol, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides. Abnormal lipid levels are associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes. The lipid profiles of patients with well-controlled type 1 diabetes are very different from those with poor glycaemic control, related possibly to the presence of adequate peripheral insulin levels in the better controlled subjects. There are direct metabolic consequences of administering insulin subcutaneously. Peripheral hyperinsulinemia is associated with increased lipoprotein lipase activity, which may account for reduced triglyceride levels. In addition, LDL-cholesterol may also be slightly reduced due to decreased very LDL production. The more sensitive the individual is to insulin, the greater is this effect.
Therefore, it can be concluded that in addition to the expected effect of dyslipidaemia , HDL-cholesterol itself exerts a significant protective effect on the development of CVD in patients with type 1 diabetes and elevated HDL-cholesterol levels appears to play a major role in longevity in these patients.
Also Check: A1c Definition Of Diabetes
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated In A Child
Children with type 1 diabetes must have daily injections of insulin to keep the blood glucose level within normal ranges. Insulin is given either by injection or insulin pump. Your childs healthcare provider will show you how to give your child insulin with either method.
Treatment will also include:
- Eating the right foods to manage blood glucose levels. This includes timing meals and counting carbohydrates.
- Exercise, to lower blood sugar
- Regular blood testing to check blood-glucose levels
- Regular urine testing to check ketone levels
Is Type 1 Diabetes Genetic
If one family member has type 1 diabetes, other relatives have an increased chance of developing the condition. One study of more than 1,400 children with type 1 diabetes showed that 12% had a first-degree relative who also had type 1in other words, a parent or sibling.
The same study also showed that children with type 1 diabetes had a slightly higher chance of having a father diagnosed with type 1 rather than a mother, brother, or sister. In some cases, family members of people with type 1 diabetes also have a history of autoimmune conditions such as celiac disease or lupus.
Type 2 diabetes is caused by lifestyle and other factors, while type 1 is either genetic or acquired after the onset of an illness.
Also Check: Is Greek Yogurt Good For Diabetes
What Is The Treatment For Type 1 Diabetes Can It Be Cured
Currently, type 1 diabetes cannot be cured. People with type 1 diabetes require injectable insulin because their pancreas does not produce enough on its own. There are different types of insulin and different routes of administration. Most people with type 1 diabetes use both a long-acting insulin , and inject additional insulin before or after meals to match the carbohydrate content of the meal. An insulin pump may also be used to optimize insulin delivery to the body’s needs.
- Unfortunately, one of the major side effects of insulin is weight gain. People with type 1 diabetes can reduce weight gain by:
- Eating a healthy low-carbohydrate diet,
- Getting plenty of exercise, and
- Learning to use insulin correctly in order to use just the right amount
- Diet and level of activity.
The Role Of Glycaemic Control
All-cause mortality and the association of glycaemic control .
The evidence therefore suggests that while early good glycaemic control is important in the prevention of CVD and survival, the importance of glycaemic control may diminish as patients survive longer. While glycaemic control is clearly a risk factor for CAD and mortality in type 1 diabetes, this is not the major determinant of survival. Good glycaemic control alone cannot explain why some type 1 patients survive into old age.
Recommended Reading: How Many Hours After A Meal Should A Diabetic Train
It Cant Be Cured With Lifestyle Changes
As with other autoimmune disorders, the exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not known. There is no cure or way for a person with type 1 to eliminate their need for insulin therapy, which is an important distinction between type 1 and type 2.
Morgan McKean, 29, who currently works abroad in health promotion for a charity foundation, sees a lack of knowledge about both types of diabetes. People think only overweight people get diabetes or that you can always get rid of it through a better diet and exercise. Thats not the case in type 1, and it isnt always true in type 2 diabetes either, she says.
How A Diabetes Diagnosis May Actually Improve Life Quality
Many people live with diabetes for years before being diagnosed, but once they are, they can approach the condition head on. As a result of their efforts, many people may actually find their quality of life is better than it was before diagnosis.
Once they have the diagnosis and take action whether that action is just behavioral change because they didn’t have diabetes for long, or behavioral changes combined with a medication regimen they feel that they have a much higher quality of life after they were diagnosed, says Rinker.
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Type 1 Diabetes Disclaimer
This article is not for people with Type 1 diabetes because it is imperative that people with Type 1 diabetes require insulin every day without question. A person with Type 1 diabetes produces very little, or no insulin. Without insulin, you cannot convert food into usable energy. Simply put, without insulin, a person with Type 1 diabetes cannot survive. 2
When Robert contacted TheDiabetesCouncil, he was concerned that one day he would have to take insulin shots for his Type 2 diabetes. He had heard a few of his friends with diabetes at church talking about how they had to take insulin injections. Robert was afraid of needles, and the thought of giving himself a shot scared him.
Is Robert going to need to start taking insulin, or is there any way he can avoid it at this point? If he avoids it, what effects would this have on his health? Will he develop long term complications of diabetes if he doesnt start giving himself shots of insulin?
I suggest also reading these:
At TheDiabetesCouncil, we decided to take a look at this particular question in depth, for Robert and for others with diabetes who might benefit from reading this information.
Newly Diagnosed With Type 1 Diabetes
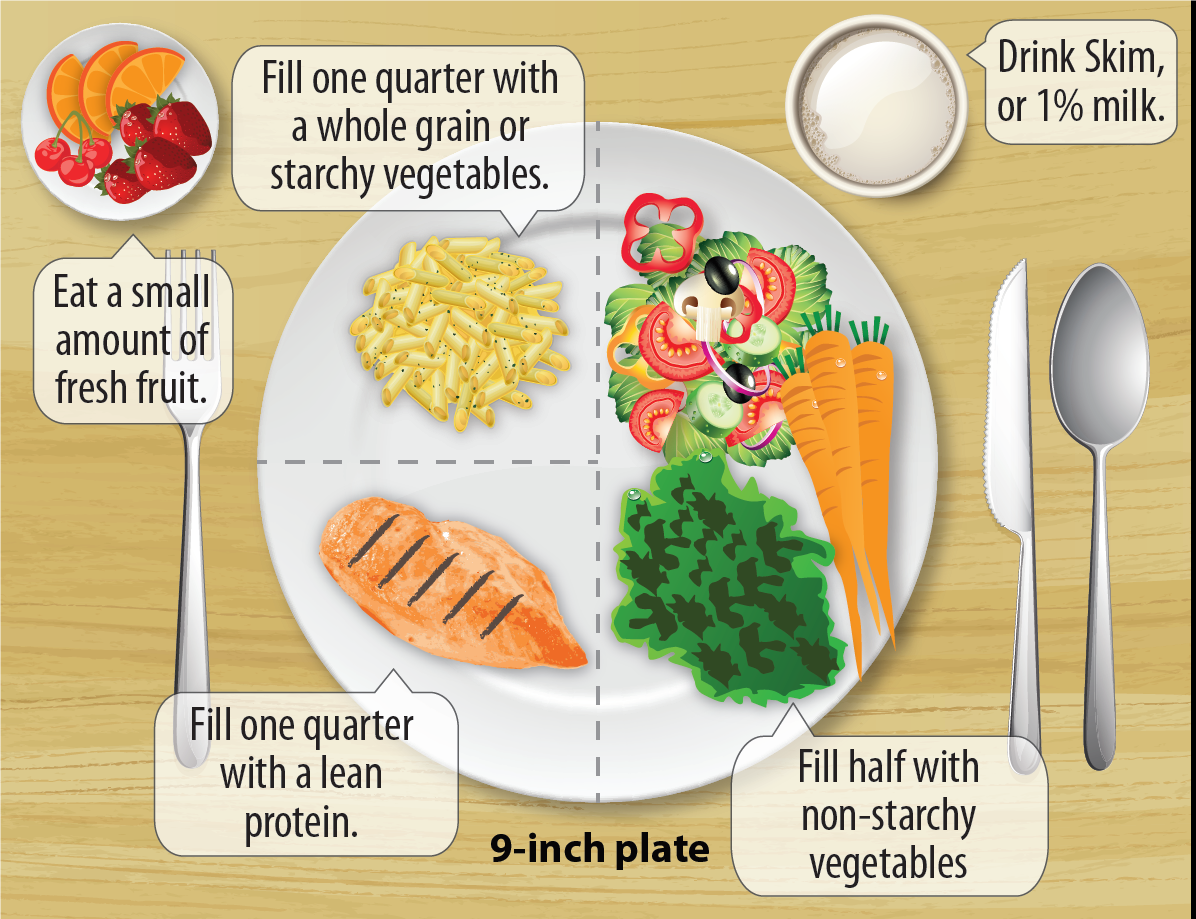
It can be difficult to know where to get started with your new type 1 diagnosis, but were here to help you find the information you need.
As well as reading through the guidance and advice on this page, why not try our Learning Zone? With videos, quizzes and interactive tools tailored just for you, its the perfect way to discover more about your diabetes.
“She made me feel normal, when my normal had completely changed.”
– Laura, on being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Read her story.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Type 2 Diabetics Can Live Longer Than People Without The Disease
- Date:
- Cardiff University
- Summary:
- A commonly prescribed diabetes drug could offer surprising health benefits to non-diabetics. metformin, used to control glucose levels in the body and already known to exhibit anticancer properties, could offer prognostic and prophylactic benefits to people without diabetes, researchers report in a new article.
Patients treated with a drug widely prescribed for type 2 diabetes can live longer than people without the condition, a large-scale study involving over 180,000 people has shown.
The findings indicate that a drug known as metformin, used to control glucose levels in the body and already known to exhibit anticancer properties, could offer prognostic and prophylactic benefits to people without diabetes.
Published in a leading diabetes journal, Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism by scientists from Cardiff University, the study set out to compare the survival of diabetes patients prescribed with metformin with patients prescribed with another common diabetes drug called sulphonylurea.
Importantly, the life expectancy of these cohorts was also compared against non-diabetics who were matched based on criteria that included age, gender, same general practice, smoking status and clinical status.
“What we found was illuminating,” said lead author Professor Craig Currie from Cardiff University’s School of Medicine.
Type 2 diabetes affects 8% of the US population and 6% of the UK population.
Story Source:

