What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
What Does Insulin Do
Insulin is a hormone from the pancreas that allows sugar to enter the cells. Insulin also lowers the amount of sugar in the bloodstream. Without insulin, sugar is unable to enter the cells. This means that cells that make up muscles and other tissues will not be able to receive their main source of energy. People with type 1 diabetes may have a buildup of sugar in the bloodstream, causing life-threatening conditions.
Insulin Side Effects
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Can Diabetes Cause Hair Loss
Yes, its possible for diabetes to cause hair loss. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to persistently high blood glucose levels. This, in turn, leads to blood vessel damage and restricted flow, and oxygen and nutrients cant get to the cells that need it including hair follicles. Stress can cause hormone level changes that affect hair growth. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your immune system attacks itself and can also cause a hair loss condition called alopecia areata.
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- In women: Dry and itchy skin, and frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
- In men: Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle strength.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly over a few weeks or months. Symptoms begin when youre young as a child, teen or young adult. Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting or stomach pains and yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes symptoms: You may not have any symptoms at all or may not notice them since they develop slowly over several years. Symptoms usually begin to develop when youre an adult, but prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes is on the rise in all age groups.
Gestational diabetes: You typically will not notice symptoms. Your obstetrician will test you for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of your pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: Alpha Cells Glucagon
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
Testing For Type 1 Diabetes
A simple blood test will let you know if you have diabetes. If youve gotten your blood sugar tested at a health fair or pharmacy, follow up at a clinic or doctors office to make sure the results are accurate.
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also be tested for autoantibodies that are often present with type 1 diabetes but not with type 2. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
Are There Other Treatment Options For Diabetes
Yes. There are two types of transplantations that might be an option for a select number of patients who have Type 1 diabetes. A pancreas transplant is possible. However, getting an organ transplant requires taking immune-suppressing drugs for the rest of your life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs. However, if the transplant is successful, youll likely be able to stop taking insulin.
Another type of transplant is a pancreatic islet transplant. In this transplant, clusters of islet cells are transplanted from an organ donor into your pancreas to replace those that have been destroyed.
Another treatment under research for Type 1 diabetes is immunotherapy. Since Type 1 is an immune system disease, immunotherapy holds promise as a way to use medication to turn off the parts of the immune system that cause Type 1 disease.
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option thats an indirect treatment for diabetes. Bariatric surgery is an option if you have Type 2 diabetes, are obese and considered a good candidate for this type of surgery. Much improved blood glucose levels are seen in people who have lost a significant amount of weight.
Of course other medications are prescribed to treat any existing health problems that contribute to increasing your risk of developing diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high cholesterol and other heart-related diseases.
Who Is At Risk For Type 2 Diabetes
Many Americans are at risk for type 2 diabetes. Your chances of getting it depend on a combination of risk factors such as your genes and lifestyle. The risk factors include
- Having prediabetes, which means you have blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes
- Being overweight or having obesity
- Being age 45 or older
- A family history of diabetes
- Being African American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asian American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander
- Having acanthosis nigricans, a skin condition in which your skin becomes dark and thick, especially around your neck or armpits
- Smoking
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
The types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. Its usually diagnosed in children and young adults . It was once better known as juvenile diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or your bodys cells dont respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it having a touch of sugar.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you’re at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Less common types of diabetes include:
Diabetes insipidus is a distinct rare condition that causes your kidneys to produce a large amount of urine.
Also Check: What Hormone Is The Primary Antagonist Of Glucagon
How Immunotherapy Could Stop And Prevent Type 1 Diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes need lifelong treatments of daily insulin injections to manage their condition that still leave them at risk of long-term complications. Immunotherapy could one day become an insulin-free alternative to stop, prevent, and potentially cure this chronic disease.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are wrongly detected as foreign and destroyed by the immune system.
There is no cure once initiated, the disease will progress to complete destruction of the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, Pierre Vandepapelière, previous CEO of Imcyse, told me. This Belgian company is developing an innovative form of treatment that could change the way type 1 diabetes is treated.
Currently, the standard treatment for the disease consists of monitoring glucose levels and frequent insulin injections to keep healthy blood sugar levels. However, even with the best control measures, patients are still at risk of complications affecting the eyes, kidneys and nerves in the long term. Insulin treatment also carries the risk of inducing episodes of extremely low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, which can be life-threatening.
What Are Some Easy Ways You Can Prevent Heart Disease And Diabetes

Diet plays a large role in chronic disease prevention. For example, while eating a pint of ice cream every once in a while won’t necessarily increase your risk, routinely eating these types of unhealthy foods most likely will.
“Studies show that people who regularly eat more whole grains, vegetables, fruit, beans, and nutsand less red meat, processed meat, saturated fats, highly processed foods, and sugartend to have lower rates of both diabetes and heart disease,” she says.
Eating a predominantly plant-based diet is one key way to reduce your risk of chronic disease, as the foods tend to be higher in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Not to mention, plant-based foods also tend to be much lower in saturated fat.
“Red and processed meats, on the other hand, are high in saturated fat,” Ramsing says. “And eating too much can raise your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and even some cancers.”
On the contrary, substituting beans and lentils for red meat can help improve blood sugar levels, which is critical for diabetes prevention, as well as cholesterol and blood pressure levelstwo major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Ramsing suggests incorporating Meatless Monday into your weekly routine to help you reduce your consumption of meat while increasing your intake of plant-based foods.
Recommended Reading: How To Keep Blood Sugar From Dropping
Proposal For The Road Ahead
Are we truly impaled upon the horns of a dilemma? Is there no middle road between the alternatives of intervening too early or too late? One practical option has been to sidestep this whole issue and focus intervention on the newly diagnosed patient. The rationale here is relatively simple: all newly diagnosed subjects have the disease, so there are no false positives. They are all on a path leading to near-total -cell failure, so any preservation of -cell function, even transient, could be beneficial. The knowledge that study entrants are already condemned to lose most of their residual -cells adds a useful comfort factor to the equation when the theoretical possibility that some interventions might inadvertently accelerate -cell destruction is under consideration. This approach, using endogenous insulin secretion as its end point, allows a number of interventions to be screened in parallel and within a relatively short time frame. The disease process may be too advanced for there to be much prospect of lasting clinical benefit, let alone a cure, but any hint of efficacy could provide a basis for future endeavors. What form should these take?
What Types Of Diabetes Require Insulin
People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin to live. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your body has attacked your pancreas, destroying the cells that make insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, your pancreas makes insulin, but it doesnt work as it should. In some people with Type 2 diabetes, insulin may be needed to help glucose move from your bloodstream to your bodys cells where its needed for energy. You may or may not need insulin if you have gestational diabetes. If you are pregnant or have Type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider will check your blood glucose level, assess other risk factors and determine a treatment approach which may include a combination of lifestyle changes, oral medications and insulin. Each person is unique and so is your treatment plan.
You May Like: Greek Yogurt Diabetes
Is Type 1 Diabetes A Genetic Disease
There is a strong genetic link with type 1 diabetes. This can be tested for by looking at the human leukocyte antigen genotype. First-degree relatives are at higher risk. However, with any genetic condition, it is important to remember that gene expression changes in response to the epigenetic environment, and risk factors can be addressed with a health care professional or nutrition/functional/naturopathic practitioner knowledgeable about epigenetics.
Recommended Reading: What Are The First Signs Of Diabetes
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
Read Also: What Does Diabetes Do
How Can I Prevent Or Delay Getting Type 2 Diabetes
If you are at risk for diabetes, you may be able to prevent or delay getting it. Most of the things that you need to do involve having a healthier lifestyle. So if you make these changes, you will get other health benefits as well. You may lower your risk of other diseases, and you will probably feel better and have more energy. The changes are
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
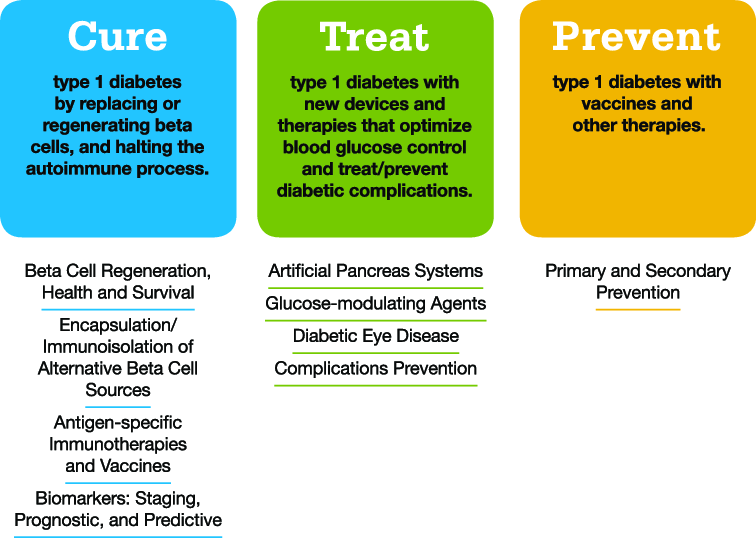
Towards The Future: Prevention And Cure
Although the first goal of immunotherapy treatments for type 1 diabetes is to stop the progression of the disease in people who still have some insulin-producing cells, this technology has potential to go beyond that.
Immunotherapy could also prevent the development of type 1 diabetes in people known to be at risk. The risk of developing type 1 diabetes can be predicted 3 to 5 years before its onset, said Vandepapelière. It could therefore be possible to prevent the disease by halting this autoimmune process early. If conducted on a nationwide scale, this could possibly eradicate the disease.
Imcyse is contemplating testing the ability of its immunotherapy to prevent type 1 diabetes. To do so, it would have to implement a wide screening, particularly in children, to identify the subjects most at risk of developing the disease. This, however, would take considerable time. A longer study is needed to demonstrate the preventive efficacy, as with most vaccine developments, said Vandepapelière.
Further down the line, but already a tangible possibility, immunotherapy could be the key to the much-wanted cure for type 1 diabetes. In patients with established type 1 diabetes, an extinction of the autoimmune and inflammatory process could regenerate the beta cells, either spontaneously or after grafting beta cells, said Vandepapelière.
This article was originally published in January 2019 and has since been updated to reflect the latest developments.
Explore Related Topics:
You May Like: Is Ginger Ale Good For Diabetics
Staging Of Type 1 Diabetes
These birth cohort studies, in addition to non-birth cohorts such as the large Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 and the Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Pathway to Prevention studies have allowed us to further characterize the time period before diagnosis. Although the actual diagnosis of diabetes has traditionally been based on American Diabetes Association criteria , it is clear that the onset of the disease per se, often occurs years before the onset of symptoms. Thus, pre-type 1 diabetes is a unique physiologic state where autoimmunity is present and progression to metabolic derangement and clinical onset can be predicted especially in younger children and adolescents. As such, the ADA, JDRF, and Endocrine Society released a joint position statement for the staging of pre-type 1 diabetes 2) . Stage 1 is defined by the presence of 2 or more islet autoantibodies with normoglycemia . Stage 2 shows progression to dysglycemia in the setting of 2 or more islet autoantibodies, and stage 3 occurs when a patient meets ADA criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes.
Early stages of type 1 diabetes. Reproduced with permission from Insel et al. .

