Type 1 And Type 2 Differences
Below is a guide to some of the main differences between type 1 and type 2.
|
Your body attacks the cells in your pancreas which means it cannot make any insulin. |
Your body is unable to make enough insulin or the insulin you do make doesnt work properly. |
|
|
We dont currently know what causes type 1 diabetes. |
We know some things can put you at risk of having type 2 like weight and ethnicity. |
|
|
The symptoms for type 1 appear more quickly. |
Type 2 symptoms can be easier to miss because they appear more slowly. |
|
|
Type 1 is managed by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. |
You can manage type 2 diabetes in more ways than type 1. These include through medication, exercise and diet. People with type 2 can also be prescribed insulin. |
|
|
Currently there is no cure for type 1 but research continues. |
Type 2 cannot be cured but there is evidence to say in many cases it can be prevented and put into remission. |
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
Insulin Blood Sugar And Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a key player in developing type 2 diabetes. This vital hormoneyou cant survive without itregulates blood sugar in the body, a very complicated process. Here are the high points:
- The food you eat is broken down into blood sugar.
- Blood sugar enters your bloodstream, which signals the pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps blood sugar enter the bodys cells so it can be used for energy.
- Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar for later use.
- Blood sugar enters cells, and levels in the bloodstream decrease, signaling insulin to decrease too.
- Lower insulin levels alert the liver to release stored blood sugar so energy is always available, even if you havent eaten for a while.
Thats when everything works smoothly. But this finely tuned system can quickly get out of whack, as follows:
- A lot of blood sugar enters the bloodstream.
- The pancreas pumps out more insulin to get blood sugar into cells.
- Over time, cells stop responding to all that insulintheyve become insulin resistant.
- The pancreas keeps making more insulin to try to make cells respond.
- Eventually, the pancreas cant keep up, and blood sugar keeps rising.
Don’t Miss: Optimal A1c For Non Diabetic
How To Prevent Insulin Resistance And Safeguard Health
Youll want to step up the efforts youre making to control your weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Lifestyle change improves insulin sensitivity, says Andrew Ahmann, MD, chief of endocrinology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. Better health habits make sense for everyone but are especially important for people with type 1 diabetes who also have type 2 diabetes in their family or risk factors for insulin resistance.
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet.
- Keep weight in the normal, healthy range.
- Be physically active for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Keep tabs on blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
If youre living with type 1 diabetes, be aware that leaping into a more active lifestyle, especially if you might already be already experiencing some insulin resistance, might put you at risk for hypoglycemia . Before starting a new exercise program, talk with your doctor about how to proceed safely.
Dr. Ahmann recommends speaking candidly with your diabetes doctors and nurses about the possibility of developing insulin resistance. Together, you can set in place strategies to prevent it or treat it as early as possible to protect your health.
How Are The Signs And Symptoms Similar
There isn’t a difference between the symptoms of either disease. The “classic” symptoms are the same for both diabetes type 1 and type 2:
- Increased urine output
- Unexplained weight loss
For both type 1 and type 2, early symptoms of untreated diabetes arise due to elevated blood sugar levels and the presence of glucose in the urine. High amounts of glucose in the urine can cause increased urine output and dehydration. Dehydration, in turn, causes increased thirst.
A lack of insulin or an inability of insulin to work properly affects protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin normally encourages the storage of fat and protein, so when there is inadequate insulin or poorly functioning insulin, this eventually leads to weight loss despite an increase in appetite.
Some untreated diabetes patients also experience generalized symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. People with diabetes are also at risk for infections of the bladder, skin, and vaginal areas. Changes in blood glucose levels can lead to blurred vision. When blood sugar levels are extremely high, lethargy and coma can result.
Recommended Reading: Is It Safe For A Diabetic To Get A Tattoo
Progression Of Double Diabetes
Similar to type 2 diabetes, double diabetes, if not treated appropriately can become more severe over time.
If double diabetes is allowed to progress more insulin will need to be injected which promotes further weight gain and increases the bodys resistance to the insulin further requiring even greater insulin
Recognizing And Treating Double Diabetes
One of the early signs that you might be experiencing insulin resistance is a need for more and more insulin to meet your blood sugar control goals. However, there are treatment alternatives to continually ramping up your doses.
Its likely that patients should also be put on another medication to improve their response to insulin, but this is not yet standard of care, says Dr. Schauer. Metformin , which is often used to reduce insulin resistance in people who have type 2 diabetes, can be taken by people with type 1 diabetes as well.
You May Like: Is Diabetes Mellitus–an Autoimmune Disease
Comparing And Contrasting Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is generally characterized as a lifetime disease, in that is often diagnosed in early to late childhood. Unlike type 2 diabetes, type 1 is not necessarily associated with excess body weight as an indicator or risk factor, and insulin injections or a pump are absolutely required throughout the lifetime.
In contrast, type 2 diabetes tends to develop later in life, usually in people who are in their 30s. For this reason, type 2 is frequently referred to as adult onset diabetes. Although some individuals with adult onset diabetes are with a perfectly healthy body weight, obesity is a definite risk factor for this type of the disease.
High blood pressure and cholesterol are also associated with adult onset diabetes, although it is not clear whether this is a causative factor or simply a concurrent one that has resulted from the excess weight. Although some individuals with type 2 diabetes may still require insulin shots regularly, many individuals are able to manage the disease with lifestyle changes and even intermittent oral medications.
The reason that type 1 diabetics are also considered insulin reliant is due to the fact that the body is no longer capable of producing practically any insulin, as the destruction of beta cells is ongoing throughout life. Although beta cells do regenerate, the auto-immune condition eliminates them as quickly as they are formed.
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
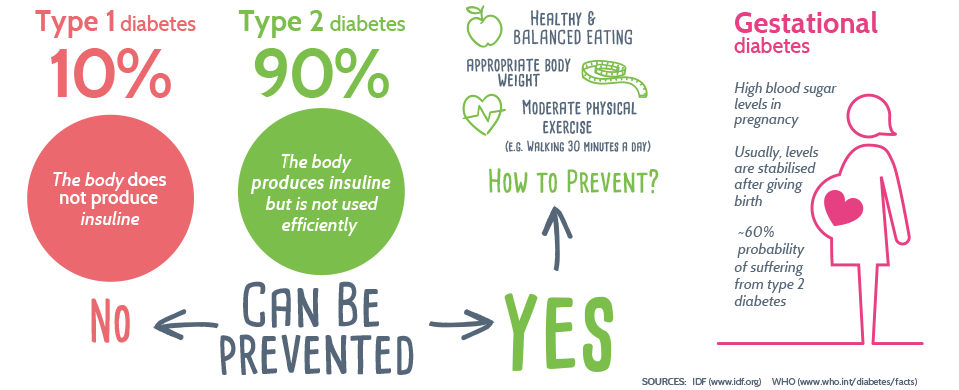
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
Don’t Miss: Metformin And A1c Levels
Type 1 Diabetics Can Get ‘double Diabetes’ From Insulin Resistance Says University Of Pittsburgh
- Date:
- University Of Pittsburgh Medical Center
- Summary:
- Insulin resistance, a condition commonly associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, is likely a major cause of heart disease in people with type 1 diabetes, according to study results published by University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health researchers in the May 2003 issue of Diabetes Care, a journal of the American Diabetes Association.
PITTSBURGH, April 21 Insulin resistance, a condition commonly associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, is likely a major cause of heart disease in people with type 1 diabetes, according to study results published by University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health researchers in the May 2003 issue of Diabetes Care, a journal of the American Diabetes Association.
“Heart disease is a major complication for people with diabetes, including those with type 1 diabetes, and until now there has been no clear explanation for its cause,” said principal investigator Trevor Orchard, M.D., professor and acting chair, department of epidemiology, GSPH. “We now suspect that insulin resistance occurs in those with type 1 diabetes in the same way as it does in those with type 2, essentially giving these individuals double diabetes and greatly increasing their risk of heart disease.”
Insulin resistance was a risk factor that predicted all adverse events, and it was the most severe among those participants who experienced the most serious events.
Story Source:
Can You Lower The Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes
There are many ways that women and those AFAB with PCOS can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but as Dr Bajekal says âitâs important to treat the root cause of the issue the insulin resistance.â
She notes: âIt is possible to reverse insulin resistance, particularly in the early stages. The aim is to make the bodys cells sensitive to the action of insulin again so that the glucose gets cleared from your bloodstream and picked up by your cells more efficiently, meaning your pancreas can stop producing so much.â
So, how exactly can you do that? âBy making changes to your lifestyle you can sensitise your tissues to insulin and help avoid the longer-term effects of untreated insulin resistance which can cause type 2 diabetes,â says nutritionist Rohini Bajekal.
Rohini continues: âLosing even small amounts of excess body weight reduces the amount of intracellular fat within the cells, making them more sensitive to insulin. This in turn lowers insulin levels and improves insulin resistance, with many noticing an improvement in their PCOS symptoms.â
Also Check: What Is The Maximum Dose Of Metformin You Can Take
Differences Between Type 1 And Type 2
Just because these types share the same symptoms doesnt mean they are co-related. Both type 1 and type 2 have distinct mechanisms making them separate diseases.
Besides the abnormality in blood sugar, type 1 diabetes is also recognized as an autoimmune illness. It means that the bodys immune system erroneously attacks its organ-producing insulin. In terms of age group, younger individuals are more prone to having this condition. People with type 1 diabetes are prescribed insulin medications, which greatly help to control blood sugar levels.
Meanwhile, type 2 diabetes usually happens in adults. Besides insulin medications, there are oral medicines that people with this condition take. This condition is more common than type 1 however, it is not an autoimmune disease. It develops because the body is not capable of using insulin properly or there isnt an adequate supply of insulin to balance the levels of blood glucose.
It is also necessary to note that age is not only the factor why both of these conditions develop. Today, there are already cases of type 1 diabetes, that involves older people. Some of the risk factors associated with both types may include weight, lifestyle, and genetic circumstances.
Signs Of Type 2 Diabetes
Are you rapidly gaining weight? Do you fail to have the motivation to do activities or be active? Are you thirsty a lot? These and several other signs can represent type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetes conditions. Many symptoms are similar or the same as Type 2 symptoms, but there are a few differences.
Type 2 diabetes signs may include but are not limited to the following:
- Frequent urination
- Frequent yeast infections
- Vaginal thrush
If you have just a couple of the listed issues or some are not that frequent, it may just be other health issues. If you notice that most problems on the list fit you to the tee, then you may have type 2 diabetes or will have it soon.
Don’t Miss: Glucose Metabolism Begins With
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if youre not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
Monitoring Your Dogs Blood Sugar
Your veterinarian will monitor your dog’s blood glucose, performing a blood-glucose curve where they take measurements every one to two hours over the course of 12-24 hours.
Your veterinarian is looking to see how high your dog’s blood sugar gets, and then how low it drops. This indicates how well the body is responding to insulin and will be periodically reevaluated throughout your dog’s life.
Read Also: Cure Hypoglycemia Permanently
There Are A Few Ways To Treat Type 1 Diabetes:
- Monitor your blood sugar. Living with diabetes means getting familiar with healthy blood sugar levels and checking yours regularly. Depending on your health care providers specific recommendation, you might need to check it four to ten times daily. Youll use a small blood sugar meter called a glucometer to measure glucose levels in a pin-prick of blood on a disposable test strip. Another option is to have a continuous glucose monitor, which automatically measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted underneath the skin.
- Take insulin. Because your body doesnt produce it on its own, youll have to get it another way. There are a few methods for taking insulin, including regular injections or a wearable insulin pump, which delivers small, steady doses of fast-acting insulin throughout the day through a thin tube. Though its certainly not the most convenient lifestyle, it often becomes second nature for people living with type 1 diabetes.
- Maintain a balanced diet. You dont have to be extremely restrictive, but carbohydrates are the foods youll want to watch, making sure to eat them consistently but not go overboard. If youre taking a fixed amount of insulin, keeping your carbohydrate intake consistent to match is important.
- Exercise. Staying active is always an important component of health, but for people with type 1 diabetes, it can help keep blood sugar levels in check and cause your body to use the insulin more efficiently.
Who Gets Type 2 Diabetes
No one knows for sure what causes type 2 diabetes. But many kids who develop it have at least one parent with diabetes and a family history of the disease, so there seems to be a genetic risk.
Most people with type 2 diabetes are overweight. Excess fat makes it harder for the cells to respond to insulin, and not being physically active makes this even worse. Type 2 diabetes used to mostly affect adults, but now more and more U.S. kids and teens, especially those who are overweight, are developing the disease.
Also, kids in puberty are more likely to have it than younger kids, probably because of normal rises in hormone levels that can cause insulin resistance during this stage of fast growth and physical development.
p
Read Also: What Is Your Sugar Supposed To Be
How Long Can You Live With Diabetes
It is not very uncommon to hear that diabetes will shorten the expected life of the concerned patient. But the question is: How much?
There are different opinions about the subject. As per a few types of research conducted, diabetes can shorten life by 8.5 years in a 50-year old individual. On the other hand, Diabetes UK estimates that the expected life span of type 1 diabetic patient is reduced by more than 20 years while a type 2 diabetes patient lives 10 years shorter as compared to the healthier counterparts.
Besides, the University of Pittsburg has estimated through various studies that people who are born after 1965 and are suffering from type 1 diabetes have a life expectancy of somewhere around 69 years.
Having said the above, we should not forget that with proper diabetes care and management, it is very much possible to extend the total life of a diabetes patient. In the following paragraphs, we shall dive into and analyze the causes and conditions which lead to deaths in the patients who suffer from the condition.

