During And After Delivery
Monitoring blood sugar and insulin. Your blood sugar levels may rise during labor, but they may drop just before you give birth or immediately afterregardless of whether you have a vaginal delivery or a Cesarean . Your doctor can help you plan for the insulin dose changes and monitoring throughout your delivery and after. You may wear your insulin pump or CGM during delivery.
Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding offers many health benefits to both the mother and baby. For the mother, it can help you lose extra weight you may have gained during pregnancy, and it can reduce the risk of high blood pressure, ovarian cancer, and breast cancer. Breastfeeding gives the baby the best nutrition to stay healthy, while reducing the risk of asthma, obesity, and severe lung disease. Women with type 1 diabetes can breastfeed their babies. Having diabetes may delay your ability to produce breast milk at first, but it should improve over time. Breastfeeding is an energy-consuming activity, just like physical activity. This can cause low blood sugar, so you should let those who will be around you know the signs of low blood sugar and how to treat it.
Careful planning and attention to your medical needs give you the best chance to stay healthy during pregnancy and have a healthy baby. You can do it!
Will My Diabetes Management Change After I Have The Baby
After your baby is born your diabetes management will need to be reviewed.
If you have type 1 diabetes, you are likely to need less insulin for the first few days after delivery and insulin doses are usually reduced by 1020% if you are breastfeeding. Your target blood glucose levels will be higher after the birth to reduce the risk of hypos.
If you have type 2 diabetes and you were taking metformin during pregnancy, this may be continued after your baby is born . If you were changed from tablets to insulin before or during pregnancy, your doctor will advise you on whether you still need insulin or whether you may return to treatment with tablets. If you continue using insulin the doses will be much lower and will need to be reviewed more often, especially in the first week after delivery. Your target blood glucose levels will be higher and you will still need to do frequent blood glucose monitoring after your baby is born.
At this stage when you have a new baby to care for, it is very important to try to avoid hypos. Your diabetes in pregnancy team will discuss changes to your diabetes management plan with you.
How Do I Know If I Have Gestational Diabetes
Most women experience no noticeable symptoms of gestational diabetes. However, some possible signs can include:
Snoring
Excessive weight gain
The only way to know for sure about gestational diabetes is to get a glucose screening or glucose tolerance test during pregnancy. This screening is routine during the second trimester of pregnancy. Women who are at higher risk for gestational diabetes may want to discuss being screened earlier with a healthcare provider.
Read Also: Metformin For Insulin Resistance
What If I Find Out Im Pregnant And It Isnt Planned
Finding out about an unplanned pregnancy may come as a shock. There are many thoughts that will go through your mind and you may be overwhelmed with emotions. But there is no right or wrong way to feel at this time.
Make an appointment with your doctor and diabetes health professionals straight away to discuss your options and any concerns you may have.
Read more about unplanned pregnancy.
Oligomenorrhea And Secondary Amenorrhea

Oligomenorrhea is the term for irregular periods that arrive at intervals of 35 days or more between each period.
Secondary amenorrhea is said to occur if you have previously had a normal menstrual cycle but have stopped getting a periods for 6 months or longer.
Both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are associated with increased risks of late and absent periods .
PCOS and obesity can contribute to these conditions and so can being underweight, with women going through diabulimia at particular risk.
Read Also: Non Diabetic A1c Range
Diabetic Eye Screening In Pregnancy
You will be offered regular diabetic eye screening during your pregnancy. This is to check for signs of diabetic eye disease .
Screening is very important when you are pregnant because the risk of serious eye problems is greater in pregnancy.
Diabetic retinopathy is treatable, especially if it is caught early.
If you decide not to have regular screening tests, you should tell the clinician looking after your diabetes care during pregnancy.
Read Diabetic eye screening.
How To Reduce The Risks
Strict blood sugar control from preconception to delivery and close monitoring by a multidisciplinary team in a specialized centre can greatly reduce most of these risks.
It is advisable for diabetic women who want a child to keep their glycated hemoglobin , below 7.0 % to reduce the risk of complications and deformities. This may seem a tall order, but it is achievable. If you cant reach that number, remember that any decrease in A1C whatsoever improves your chances of having a healthy baby.
Note: women with A1C above 10.0% should seriously consider delaying pregnancy until they reach their blood glucose targets.
To help you succeed, your doctor may suggest increasing or modifying your current treatment. For some women with type 2 diabetes, it is sometimes advisable to start insulin treatment prior to pregnancy to ensure better blood glucose control.
Be aware that stricter control of blood glucose using antidiabetic medication or insulin may increase the risk of hypoglycemia. In short, women with diabetes who are planning a pregnancy and who need antidiabetic medication or insulin should monitor their blood glucose levels more frequently to avoid hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Women with type 1 diabetes are also advised to test for ketones in their urine or blood when their blood glucose level stays high for several hours. Ask your healthcare provider to show you how to do this test.
Also Check: Do Type 1 Diabetics Have High Or Low Blood Sugar
Can A Child Be Born Diabetic
Very infrequently, diabetes is present at birth. This is known as neonatal diabetes and is caused by a genetic defect. Neonatal diabetes may resolve by the time a baby is 12 months old, but it often returns later in life. About 26 per 100,000 children under the age of 5 in Australia have type 1 diabetes.
How Is Diabetes During Pregnancy Diagnosed
Nearly all nondiabetic pregnant women are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. A glucose screening test is given during this time. For the test, you drink a glucose drink and have your blood glucose levels tested after 2 hours.
If this test shows a high blood glucose level, a 3-hour glucose tolerance test will be done. If results of the second test are not normal, gestational diabetes is diagnosed.
Also Check: Is Metformin Bad For Your Kidneys
Insulin Pumps And Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Many women with diabetes before pregnancy will be treated with insulin during pregnancy. There have been technological advances in the treatment of diabetes and these advances are now being used for some women when they are pregnant.
Most women give themselves injections of insulin after each meal and in the evening. Insulin pumps can be programmed to give insulin more regularly throughout the day which is closer to the way that insulin is normally produced.
Continuous glucose monitors are machines which are stuck to your skin and which monitor the glucose levels every minute. They have been shown to improve blood glucose control compared to finger-prick testing.
See Your Gp Or Diabetes Specialist Nurse
As soon as you start thinking about having a baby, its very important to make an appointment with your GP or nurse. They can give you advice and will refer you to a pre-conception clinic.
The clinic is usually run by a diabetes midwife and a Diabetes Specialist Nurse. Here youll get information about managing blood sugar levels, which medication you need to change or stop, taking folic acid, and how to plan for any problems that might happen.
Women with diabetes are 5x more likely to have a pre-term baby.
Knowing what to expect when you’re pregnant, and after the birth will help you plan a healthy pregnancy. Its not just about understanding how diabetes affects pregnancy, but also how pregnancy affects diabetes.
Youre more likely to have a healthy baby if you manage your blood sugar levels before you get pregnant, as well as during pregnancy.
Don’t Miss: What A1c Requires Insulin
Fact: Just Because Im At High Risk For Diabetes Doesnt Mean I Will Get It
Absolutely true! However, knowing relevant and appropriate information is necessary to lower glucose levels. This can improve fertility and reduce risks to the mother and her unborn child.
Controlling glucose levels and getting them closer to a normal level is possible, especially with the help of trained professionals. Doing so will accomplish several goals – it will reduce risks and create a safer pregnancy, in turn increasing the odds of a healthy pregnancy and child.
We can all reduce our risks for diabetes by seeking medical guidance, when necessary, and by making important lifestyle modifications.
Some common recommendations for those at risk for diabetes:
- Lose 5-10% of body weight
- Participate in 30-60 minutes of physical activity each day
- Eliminate smoking and recreational drugs
- Eat regular meals
- Find tools or methods to manage your stress
- Engage in good sleep hygiene to improve your quality of sleep
Healthy dietary guidelines:
- Choose foods low in saturated fats
- Pick clean meats or fish and low-fat dairy
- Include high fiber foods by eating fresh vegetables and fresh fruits
- Choose heart-healthy fats, while limiting high-fat foods
- Avoid processed carbohydrates, low added sugars, limit sweets
- Choose complex carbohydrates/whole grains
Pregnancy And High Blood Sugar

When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates from foods into a sugar called glucose. The sugar goes into your bloodstream. From there, it travels to your cells to give your body energy. An organ called the pancreas makes a hormone called insulin, which helps move sugar into your cells and lower the amount in your blood.
During pregnancy, the placenta — the organ that feeds and delivers oxygen to your baby — releases hormones that help your baby grow. Some of these make it harder for your body to make or use insulin. This is called insulin resistance.
To keep your blood sugar levels steady, your pancreas has to make more insulin — as much as three times more than usual. If it can’t make enough extra insulin, your blood sugar will rise and you’ll get gestational diabetes.
Also Check: What Color Is The Diabetes Ribbon
Does Having Diabetes Increase The Chance Of My Baby Developing Diabetes
For mothers with type 1 diabetes, the chance of your child developing type 1 diabetes before the age of 20 is around 23%. If you have type 2 diabetes, your child will have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. A healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, making healthy food choices and maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of future type 2 diabetes.
Pay Close Attention To Your Blood Sugar
Blood sugar changes are very rapid in diabetes, even more if you are on insulin. Pregnancy causes rapid changes in the body and it is very important to know how to handle the changes with insulin, food and exercise. Ensure that you carry glucose or candy in case of emergencies. Also let people around you know about your condition and what to do in case you have a low blood sugar level reaction.
Don’t Miss: Type 1 Diabetes Too Much Insulin
How Is Having Type 2 Diabetes In Pregnancy Different From Gestational Diabetes
Some women will develop type 2 diabetes after having gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy.
Unlike gestational diabetes , having type 2 diabetes can have an effect on the baby in the early stages of pregnancy. If you now have type 2 diabetes and are planning another pregnancy you will need to plan and prepare before you fall pregnant.
Planning and preparing for a pregnancy with type 2 diabetes involves reviewing your diabetes management to ensure blood glucose levels are within the target range, being checked for diabetes-related complications, starting high dose folic acid supplements, having a review of your current medications and routine blood tests. Read more about before you fall pregnant.
Management Of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
GDM is characterized by increased risk of macrosomia and birth complications and an increased risk of maternal type 2 diabetes after pregnancy. The association of macrosomia and birth complications with oral glucose tolerance test results is continuous, with no clear inflection points . In other words, risks increase with progressive hyperglycemia. Therefore, all women should be tested as outlined in Section 2 Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Although there is some heterogeneity, many randomized controlled trials suggest that the risk of GDM may be reduced by diet, exercise, and lifestyle counseling .
Don’t Miss: Is Diabetes Type 2 Hereditary
Transmission Of Diabetes To Thebaby
The risk of passing on Type 1 diabetes is low, at around 3 to 4%. The transmission of T1D involves several genes. But this figure needs to be put into perspective because, despite this genetic predisposition, more than 90% of people who develop Type 1 diabetes have no history of the condition in their family.
A few recommendations
- Closely monitor blood sugar from before conception until delivery, with the support of a specialized team.
- Keep glycated hemoglobin levels under the 7.0% mark to reduce the risks of complications and malformations. Warning: women with HbA1C levels of above 10.0% should seriously consider delaying pregnancy until they have reached their blood glucose targets.
- Perform blood or urine ketone tests when blood glucose levels are high for a few hours.
- Perform an eye examination and kidney function investigation before conception and continue monitoring the eyes during pregnancy.
- Control high blood pressure.
- Favor folic acid-rich foods: this vitamin is very important to help prevent defects in the babys brain and spine . Folic acid supplementation is now routine before conception and during early pregnancy.
While there are no particular contraindications for women with Type 1 diabetes having a baby, a pregnancy requires precautions before and during pregnancy and right up to delivery. The risks are substantially limited if the diabetes is well controlled, so it is very important for women to talk to their doctor when planning a pregnancy.
How Is Diabetes During Pregnancy Treated
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, your age, and your general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Treatment focuses on keeping blood glucose levels in the normal range, and may include:
-
A careful diet with low amounts of carbohydrate foods and drinks
-
Exercise
-
Oral medicines for hypoglycemia
You May Like: Sugar Level 400
How Can I Manage My Diabetes During Pregnancy
The Pregnancy in Diabetes Program manages patients with gestational diabetes and pre-gestational type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The goal of the Program is to provide comprehensive care to meet the full range of women’s needs before, during, and after pregnancy. In addition to care during pregnancy, preconception consultation is available with specialists in maternal-fetal medicine and endocrinology to better ensure that women enter pregnancy with type 1 or type 2 diabetes well-informed and as healthy as possible.
What is diabetes? What is insulin? How does diabetes affect the body? Marie McDonnell, M.D., Chief of the Diabetes Section of the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Hypertension at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, answers patients’ most commonly searched questions about diabetes.
I Have Diabetes And Want To Become Pregnant: What Should I Do
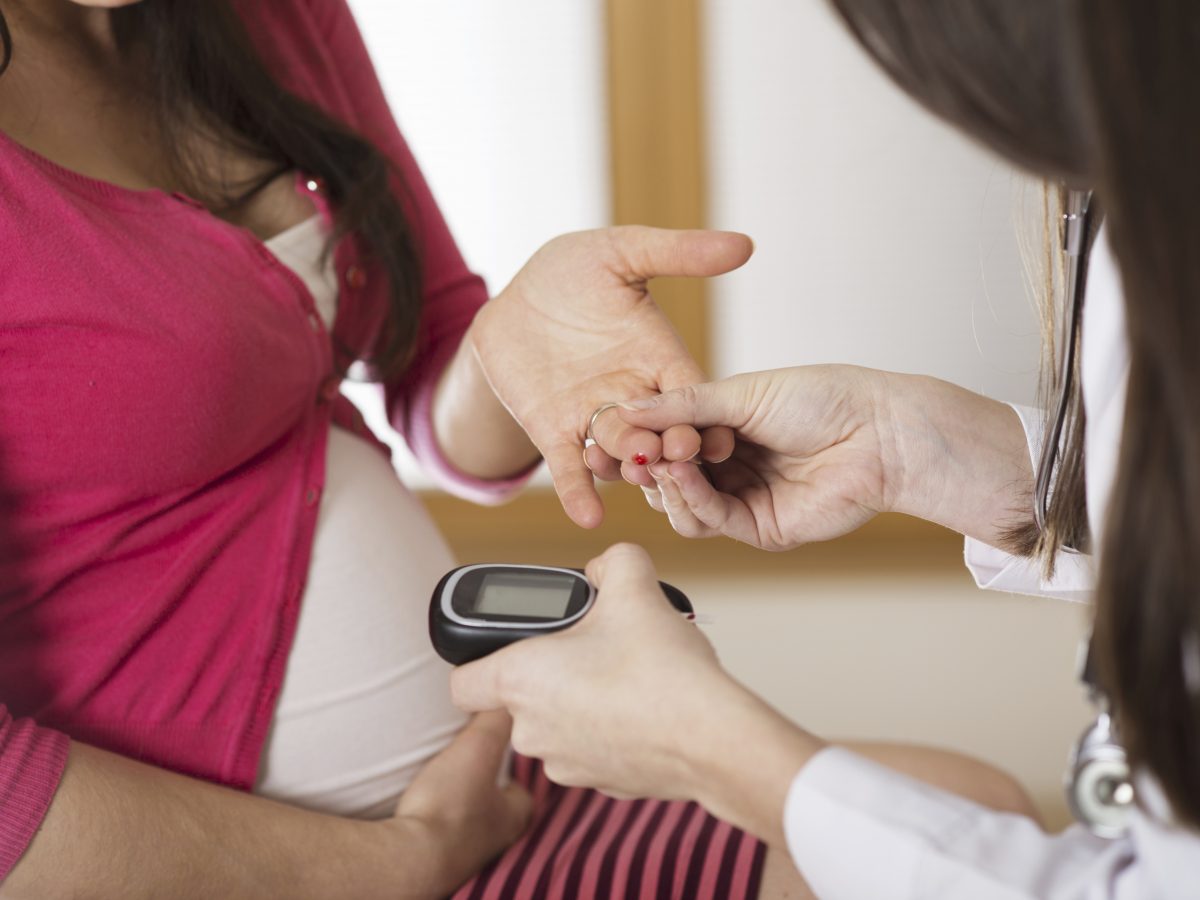
Seeing your doctor for pre-pregnancy planning is an important step in ensuring the best outcome for you and your baby. You have a pre-existing condition, so you can plan ahead and discuss with your doctor what you need to do before you become pregnant, and what you can do to manage your diabetes during pregnancy.
For example, if you have diabetes, you have a slightly higher risk than other women of your baby:
- having a birth defect
- weighing too much or too little
- having jaundice or
- having dangerously low blood sugar levels after birth.
You yourself have an increased risk of having a miscarriage or of developing high blood pressure during the pregnancy. However, you can minimise these risks by planning ahead and gaining the best possible control of your blood sugar at the time of conception and throughout the first 2 months of pregnancy.
If you have type 2 diabetes and are taking tablets to help control your blood sugar , you can plan ahead and, if appropriate, switch to taking insulin instead, before you become pregnant.
If you have high blood pressure now is the time to get your blood pressure under control using medications that are safe to continue once you are pregnant.
You may need to stop taking some medications, such as certain cholesterol-lowering medicines, while you are pregnant check with your doctor.
Don’t Miss: What Can A Type 1 Diabetic Eat
Targets Of Glycemic Control
Elevated BG levels have adverse effects on the fetus throughout pregnancy. At conception and during the first trimester, hyperglycemia increases the risk of fetal malformations and intrauterine fetal demise . Later in pregnancy, it increases the risk of macrosomia, fetal and infant death as well as metabolic and obstetrical complications at birth . As a result, meticulous glycemic control throughout pregnancy is required for optimal maternal and fetal outcomes.
An important first step in achieving optimal glycemic control is to set target BG levels . However, optimal targets for fasting, preprandial and postprandial BG levels in women with pre-existing diabetes have not been examined in randomized controlled trials and a variety of BG targets are used in clinical practice. Older studies confirm that the lower the mean BG, the better the outcome, with some suggesting a target mean BG < 6.7 mmol/L and, others, a mean < 6.9 mmol/L. A fasting BG target < 5.9 mmol/L is still associated with a 29% macrosomia rate . Recent retrospective data demonstrated that a mean A1C 6.0% in pregnant women with type 2 diabetes was associated with increased risk of neonatal complications compared to women with an A1C < 6.0% . In women with type 1 diabetes and good glycemic control during pregnancy with an A1C of 4.5% to 7.0%, there is still a linear relationship between third trimester A1C and risk of macrosomia .

