Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
Can You Be Born With Diabetes Is It Genetic
You arent born with diabetes, but Type 1 diabetes usually appears in childhood. Prediabetes and diabetes develop slowly over time years. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy.Scientists do believe that genetics may play a role or contribute to the development of Type 1 diabetes. Something in the environment or a virus may trigger its development. If you have a family history of Type 1 diabetes, you are at higher risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. If you have a family history of prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes, youre at increased risk of developing prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Why Is My Blood Glucose Level High How Does This Happen
The process of digestion includes breaking down the food you eat into various different nutrient sources. When you eat carbohydrates , your body breaks this down into sugar . When glucose is in your bloodstream, it needs help a “key” to get into its final destination where it’s used, which is inside your body’s cells . This help or “key” is insulin.
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas, an organ located behind your stomach. Your pancreas releases insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin acts as the key that unlocks the cell wall door, which allows glucose to enter your bodys cells. Glucose provides the fuel or energy tissues and organs need to properly function.
If you have diabetes:
- Your pancreas doesnt make any insulin or enough insulin.
- Your pancreas makes insulin but your bodys cells dont respond to it and cant use it as it normally should.
If glucose cant get into your bodys cells, it stays in your bloodstream and your blood glucose level rises.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
Ethical approval was obtained from Institutional Review Board of Bahir Dar University prior to enrolment. Written consent was sought from each participant. Every identified diabetic and pre-diabetic and/or hypertensive and pre-hypertensive individuals were advised to visit health institution as soon as possible and we arranged conditions to visit health institution when necessary. Data are kept confidential and communicated without disclosing individual identity.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Basic Characteristics Of The Study Groups
We used data from August 1, 2018, to March 1, 2019. Of the 18,759 pregnant women, information on baseline characteristics was missing for 20, 1,563 did not receive an OGTT at 2428 gestational weeks, and 31 had a history of diabetes. After excluding these 1,614 women , a total of 17,145 participants were included in the analysis for this study. Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants and this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital Ethics.
Characteristics of women with and without GDM are shown in Table 1. Overall, the incidence and age-adjusted incidence of GDM were 17.42 and 17.45%. The mean age was 30.20 years old, and the mean pre-pregnancy BMI was 22.43 kg/m2 2,980 women were overweight, and 611 were obese. In comparison with women without GDM, those with GDM were older , and more likely to be obese , have an active occupational physical activity , have a parity of more than one , have had assisted reproduction , and have a greater gestational BMI gain from pre-pregnancy to 1520 weeks’ gestation . Pregnant women with GDM were more likely to have a history of GDM . Women without GDM were also more likely to have a higher level of education , eat less meat and have anemia .
Table 1. Characteristics of the study population according to gestational diabetes mellitus.
Why Does The Incidence Of Diabetes Mellitus Increase With Age
4.5/5IncreasesWhy does the incidence of diabetes mellitus increase with ageAge
The risk for diabetes increases with age, making diabetes common in older adults. Diabetes means that your blood glucose level is too high. Your body’s cells need glucose for energy. When you eat, your pancreas releases the hormone insulin, which helps the glucose from food get into your cells.
Additionally, does diabetes get worse as you age? About 1 in 4 adults over age 60 have diabetes. Having the disease makes you more likely to get some serious complications. And so does getting older. The combination of the two can even make some health problems worse.
Considering this, do blood glucose levels increase with age?
Population studies confirm the finding that average blood glucose levels in the fasting state increase with age. The small change in blood glucose levels with ad- vancing years is magnified to a considerable extent in conditions other than fasting. Postprandial values change at the rate of 4 mg. per 100 ml.
What age group is most likely to get Type 2 diabetes?
You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, type 2 diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight or obese.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Can Diabetes Be Cured Or Reversed
Although these seem like simple questions, the answers are not so simple. Depending on the type of your diabetes and its specific cause, it may or may not be possible to reverse your diabetes. Successfully reversing diabetes is more commonly called achieving remission.
Type 1 diabetes is an immune system disease with some genetic component. This type of diabetes cant be reversed with traditional treatments. You need lifelong insulin to survive. Providing insulin through an artificial pancreas is the most advanced way of keeping glucose within a tight range at all times most closely mimicking the body. The closest thing toward a cure for Type 1 is a pancreas transplant or a pancreas islet transplant. Transplant candidates must meet strict criteria to be eligible. Its not an option for everyone and it requires taking immunosuppressant medications for life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs.
Its possible to reverse prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes with a lot of effort and motivation. Youd have to reverse all your risk factors for disease. To do this means a combination of losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy . These efforts should also lower your cholesterol numbers and blood pressure to within their normal range. Bariatric surgery has been shown to achieve remission in some people with Type 2 diabetes. This is a significant surgery that has its own risks and complications.
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetic ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed.If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
Don’t Miss: Somatostatin Cells
Ethics And Consent Statement
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Institute of Public Health College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants and confidentiality was kept. All the study participants answered the administered pre-tested questionnaires voluntarily and confidently.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening condition. It happens when your liver breaks down fat to use as energy because theres not enough insulin and therefore glucose isnt being used as an energy source. Fat is broken down by the liver into a fuel called ketones. The formation and use of ketones is a normal process if it has been a long time since your last meal and your body needs fuel. Ketones are a problem when your fat is broken down too fast for your body to process and they build up in your blood. This makes your blood acidic, which is a condition called ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis can be the result of uncontrolled Type 1 diabetes and less commonly, Type 2 diabetes.Diabetic ketoacidosis is diagnosed by the presence of ketones in your urine or blood and a basic metabolic panel. The condition develops over several hours and can cause coma and possibly even death.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Sickness Symptoms
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Level Why Is This Important
Checking your blood glucose level is important because the results help guide decisions about what to eat, your physical activity and any needed medication and insulin adjustments or additions.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level is with a blood glucose meter. With this test, you prick the side of your finger, apply the drop of blood to a test strip, insert the strip into the meter and the meter will show your glucose level at that moment in time. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often youll need to check your glucose level.
Risk Factors For Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
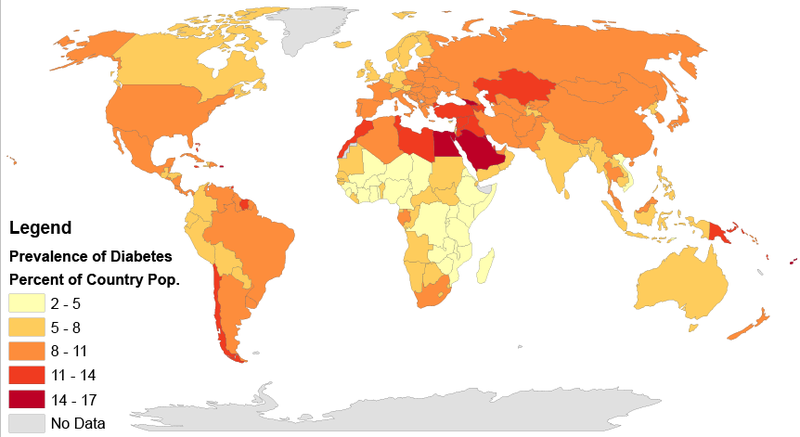
Table 2 shows the results of multiple logistic regression analysis on associations between potential risk factors and GDM. After adjustment for potential risk factors, age 30 years, BMI gain from pre-pregnancy to 1520 weeks of gestation, history of GDM and thyroid diseases were significantly associated with the risk of GDM .
Table 2. Factors associated with the incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus by multivariate logistic regression models.
You May Like: Can Type 2 Diabetics Donate Blood
Trends In Incidence Among Adults
- Among adults aged 18 years or older, the age-adjusted incidence of diagnosed diabetes was similar in 2000 and 2018 . A significant decreasing trend in incidence was detected from 2008 through 2018. .
Figure 4. Trends in age-adjusted incidence of diagnosed diabetes among adults aged 18 years or older, United States, 20002018
Notes: Data shown are estimated incidence rates and 95% confidence intervals . Joinpoint identified in 2008 .
Data source: 20002018 National Health Interview Survey.
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
You May Like: How To Keep Blood Sugar From Dropping
Age And Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular disease remains to be the most important cause of death in all countries over the world. Although certain reports from some developed countries indicate the incidence tends to decrease, from many countries there are reports mentioning that its incidence tends to increase. Cardiovascular disease is a complex disease too many risk factors are involved in its pathogenesis. In general, risk factors for CVD can be divided into two main groups, namely traditional and non-traditional risk factors. Traditional risk factors include age , male sex, family history of coronary heart disease, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, central obesity, unhealthy cholesterol levels , and low physical activity . In addition, some non-traditional risk factors for CVD are reported elsewhere .
Peripheral artery disease , a marker of systemic atherosclerosis, is frequently related with age. It mostly starts at 40 and increases after the age 70 years. PAD is the independent risk factor for mortality caused by CVD . A study by Kuswardhani and Suastika on elderly patients who visited the Geriatric Outpatient Clinic, Sanglah Hospital showed that diabetic patients with PAD had higher age and higher homocystein levels , compared with those without PAD. High age had 7.4 times risk than those with lower age and high homocystein levels had 2.5 times risk than those with lower homocystein levels, to develop PAD. By multivariate analysis , it was found that only age played a role in PAD event.
Age Insulin Resistance And Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a group of metabolic abnormalities of which central obesity and insulin resistance are believed to be the primary backgrounds. The diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome have been proposed by several organizations and associations, all of which are based on five parameters i.e. central obesity, high blood pressure, high fasting blood glucose levels, high TG levels and low levels of HDL-C. The pathogenesis of how central obesity causes insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome has been explained in many publications. Decreased insulin sensitivity, reduced muscle mass, and increased body fat mass, especially visceral fat that accompanies aging contribute to insulin resistance in the elderly. Aging process is also associated with reduced compensatory beta cell mass function of the pancreas and to insulin resistance as well as with decreased mitochondrial function that contributes to insulin resistance . A study by Gupta et al. showed that hepatic insulin resistant was related to body fat and its distribution, and hepatic insulin action could be preserved by caloric restriction in aging caloric restriction rat.
Also Check: Hyperglycemia Symptoms Chart
How Many Canadians Live With Diabetes
According to the most recent data , about 3.0 million Canadians were living with diagnosed diabetes in 20132014, representing 1 in 300 children and youth , and 1 in 10 adults . The prevalence of diagnosed diabetes generally increases with age and is higher among males than among females , both overall and in most age groups .
Figure 1: Prevalence of diagnosed diabetes , by age group and sex, Canada, 20132014
| 8.7 | 7.6 |
Note: The 95% confidence interval shows an estimated range of values which is likely to include the true value 19 times out of 20.Data source: Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2017.
How Can Diabetes Be Prevented And Managed
It is possible to control certain risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including making healthy lifestyle choices like eating well, exercising, and reaching/maintaining a healthy weight. For individuals with pre-diabetes, medication can also help prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.Footnote 4 Since the causes of type 1 diabetes are not all well understood, no measures are currently recommended to prevent this disease.
It is also possible to remain healthy with diabetes through appropriate management and care. Treatment plans and targets are based on each individual’s profile, but they all aim to avoid short-term risks of high or low blood sugar levels and to prevent or delay long-term complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and a healthy weight, together with medication to control blood sugar levels and vascular risk factors, are common cornerstones of diabetes management.Footnote 1
Don’t Miss: Does Metformin Cause High Cholesterol
Diabetes In The World
The seriousness of diabetes has been acknowledged at the global level. In one of its resolutions, the United Nations General Assembly recognized that: “iabetes is a chronic, debilitating and costly disease associated with severe complications, which poses severe risks for families, Member States and the entire world “.Footnote 5 However, providing accurate estimates of the global burden of diabetes, in terms of morbidity and mortality, poses several challenges including the lack of valid and timely data in some countries, as well as the variability of diagnostic criteria used across the globe.
Keeping in mind these limitations, the International Diabetes Federation estimated that the global age-standardized prevalence of diabetes among adults aged 20 to 79 years was 6.4% in 2010, representing 285 million people worldwide.Footnote 6 ,Footnote 7 Compared with the prevalence of diabetes in European, American and Oceania countries included in this study , the rate for Canada was the third highest. Compared to the rate of 9.2% in Canada, rates were much lower in all African countries, as well as in most Asian and Latin American/Caribbean countries. On average, countries in the Middle-East Crescent had higher rates than those seen in Europe, North America, and Oceania countries.
Figure 1-8. Prevalence of diabetes among individuals aged 20 to 79 years, Europe, North America and Oceania, 2010
Standardized to the global population.

