How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
What Should I Expect If I Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
If you have diabetes, the most important thing you can do is keep your blood glucose level within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. In general, these targets are:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
You will need to closely follow a treatment plan, which will likely include following a customized diet plan, exercising 30 minutes five times a week, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and getting seven to nine hours of sleep a night. Always take your medications and insulin as instructed by your provider.
Growing Baby Growing Impact
Gestational diabetes affects the mother in late pregnancy, after the baby’s body has been formed, but while the baby is busy growing. Because of this, gestational diabetes does not cause the kinds of birth defects sometimes seen in babies whose mothers had diabetes before pregnancy.
However, untreated or poorly controlled gestational diabetes can hurt your baby. When you have gestational diabetes, your pancreas works overtime to produce insulin, but the insulin does not lower your blood glucose levels. Although insulin does not cross the placenta, glucose and other nutrients do. So extra blood glucose goes through the placenta, giving the baby high blood glucose levels. This causes the baby’s;pancreas;to make extra insulin to get rid of the blood glucose. Since the baby is getting more energy than it needs to grow and develop, the extra energy is stored as;fat.
This can lead to macrosomia, or a “fat” baby. Babies with;macrosomia;face health problems of their own, including damage to their shoulders during birth. Because of the extra insulin made by the baby’s pancreas, newborns may have very low blood glucose levels at birth and are also at higher risk for breathing problems. Babies born with excess insulin become children who are at risk for;obesity;and adults who are at risk for;type 2 diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Normal A1c Level
Can Gestational Diabetes Be Cured
Most women with gestational diabetes who receive treatment go on to deliver healthy babies. The risk of complications increases when blood glucose levels are not properly controlled. While some women with gestational diabetes will develop type 2 diabetes following delivery, this risk can be reduced by following a good nutritional plan, exercising, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Symptoms Associated With Gestational Diabetes
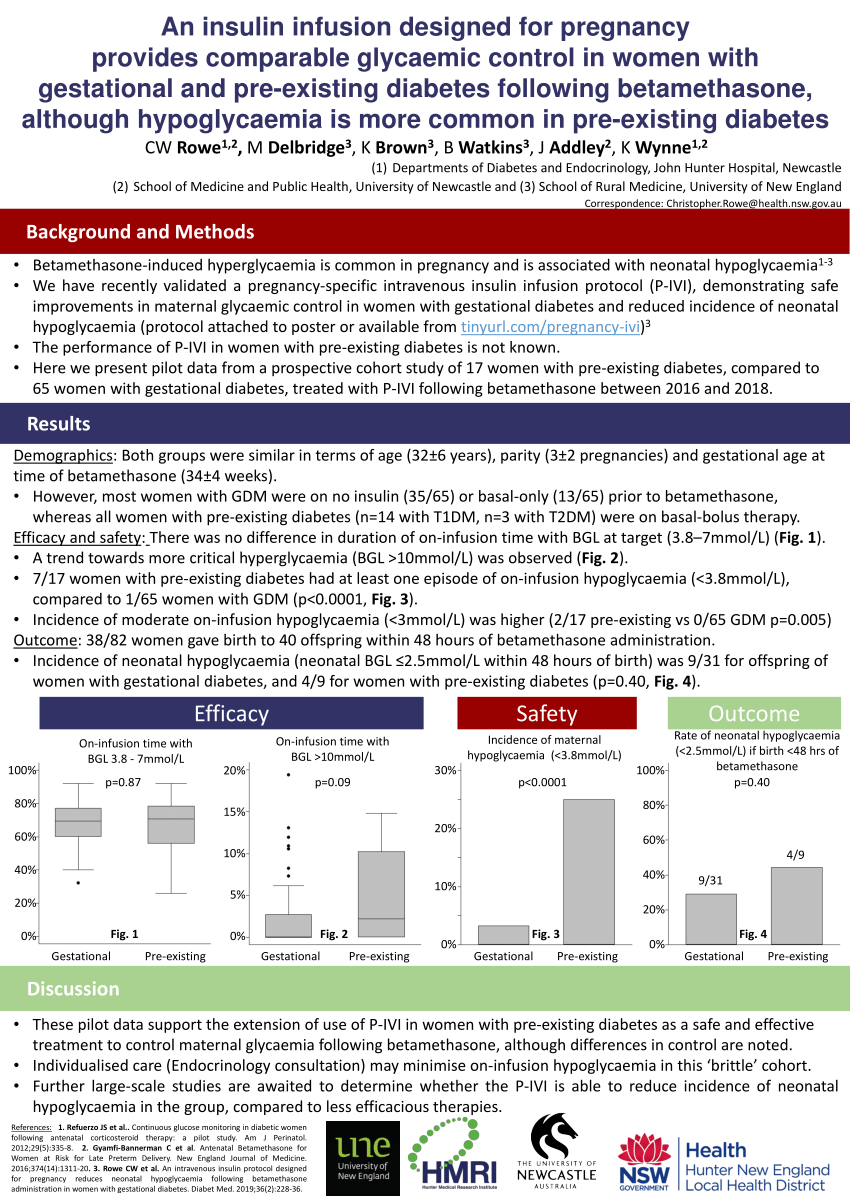
In pregnant women suffering from this disorder, the symptoms may be negligible or mild, or manifest with the appearance of the typical discomforts of the disease.;Routine tests can detect abnormally high blood sugar levels and no other evidence of the disease can be found.
Other patients, on the other hand, may notice some of the following;symptoms associated with gestational diabetes :
- Blurred vision;.
- Thirst and polydipsia .
- Polyuria: increased urination.
- Urinary infections;,;vaginal;yeast;infection;.
Don’t Miss: Should I Take Metformin If My Blood Sugar Is Low
What Is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a kind of diabetes that some women get during pregnancy. Its a condition in which your body has too much sugar in the blood.;
When you eat, your body breaks down sugar and starches from food into glucose to use for energy. Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin that helps your body keep the right amount of glucose in your blood. When you have diabetes, your body doesnt make enough insulin or cant use insulin well, so you end up with too much sugar in your blood. This can cause serious health problems, like heart disease, kidney failure and blindness.;
Most pregnant women get tested for GDM at 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. Most of the time it can be controlled and treated during pregnancy. If its not treated, GDM can cause problems for you and your baby. It usually goes away after you have your baby. But if you have GDM, youre at increased risk of developing diabetes later in life.
In the United States, 7 out of every 100 pregnant women develop gestational diabetes. Youre more likely than other women to have GDM if youre African-American, Native American, Asian, Hispanic or Pacific Islander. ;
Great Exercises For People With Diabetes
Use medication. Sometimes, lifestyle changes may not be enough to manage gestational diabetes sufficiently. If blood sugars remain elevated despite modifications in diet, the treatment for gestational diabetes is use of insulin, Borst says. This is safe and effective in pregnancy.
Your healthcare provider will teach you how to use a small needle to give yourself insulin shots. Some doctors may prescribe a different medication to take orally.
You May Like: Is Unsweetened Applesauce Good For Diabetics
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
Testing For Gestational Diabetes
Its important to be;tested for gestational diabetes so you can begin treatment to protect your health and your babys health.
Gestational diabetes usually develops around the 24th week of pregnancy, so youll probably be tested;between 24 and 28 weeks.
If youre at higher risk for gestational diabetes, your doctor may test you earlier. Blood sugar thats higher than normal early in your pregnancy may indicate you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than gestational diabetes.
You May Like: What Can You Eat To Lower Your Blood Sugar
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Screening tests for gestational diabetes include:
Glucose ChallengeTest This test involves drinking a syrupy glucose solution, and then undergoing blood test to measure your blood sugar level one hour later. Generally, a blood sugar level is considered normal if it is below 140 milligrams per deciliter or 7.8 millimoles per liter , according to the Mayo Clinic. A blood sugar level of 190 mg/dL or 10.6 mg/dL indicates gestational diabetes.
Follow-Up Glucose Testing If your blood sugar level was higher than normal during the initial glucose challenge test, youll need to complete another one to determine if you have gestational diabetes. This test will be similar to the first screening except the glucose solution will be sweeter and your blood will be checked hourly for three hours. If two of these blood tests come back high, you will receive a gestational diabetes diagnosis.
Risks Of Diabetes In Pregnancy
Maternal diabetes during pregnancy increases the risk for preterm labor . Some of this risk may be due to increased uterine volume caused by macrosomia and/or polyhydramnios, which are associated with GDM. Maternal hypertension and urinary tract infections are also associated with GDM and increase the risk for preterm labor. Women with pre-existing diabetes who have vascular symptoms also have a higher risk for preterm labor.
9 . Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding polyhydramnios?
| A) | It occurs in about 1% of women with GDM. | |
| B) | Fetal hyperglycemia is the most likely cause of polyhydramnios in GDM. | |
| C) | Polyhydramnios is diagnosed when the amniotic fluid volume is greater than 500 mL. | |
| D) | ; | There are no safe treatments to relieve the pressure of polyhydramnios and prevent premature rupture of the membranes. |
Recommended Reading: How To Dispose Of Insulin Pens
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day; women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
Read Also: Can Type 2 Diabetics Donate Blood
After Your Baby Is Born
Gestational diabetes can cause problems for you and your baby after labour;and in the long term.;If youve had gestational diabetes, you are also at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes during your life.;Babies of mothers with gestational diabetes may also be at greater risk of developing obesity or diabetes in later life.
You can reduce your risk of health issues in the future by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet and taking regular exercise.
Find out more about the long-term implications of gestational diabetes.
Diagnosis Of Gestational Diabetes
One of the routine tests that pregnant women are currently subjected to is a screening test called the;O test. Sullivan;.;This test consists of determining the blood glucose level after ingesting 50g of glucose, regardless of the time of day and previous food intake.;A result equal to or greater than 140mg / dl will mean a positive result for the;diagnosis of gestational diabetes;.
This test is performed on all pregnant women who are;between the 24th and 28th week of gestation;;;In cases where;high risk factors;are detected;, the test will be performed in the first trimester of pregnancy.
If the OSullivan test is positive, a confirmatory diagnostic test will be performed using;oral glucose overload ;.;To carry out this test, the patient must be fasting and have followed a diet without carbohydrate restriction in the three days prior to it.;Before administering glucose, a first blood draw will be carried out;;then the woman must ingest 100 grams of glucose dissolved in water or some other liquid.;Subsequently, extractions will be carried out at the next hour, two hours, and three hours, to measure blood sugar levels.;To avoid altered results, it is recommended that the woman remain at rest during the development of the test.
Read Also: Are Pumpkin Seeds Good For Diabetics
Which Of The Following Is Not Associated With Gestational Diabetes Best 3 Diabetes Programs For 2021
Diabetes is a really usual health problem worldwide. In the United States, 1 in 10 adults have diabetic issues, while an approximated 1 in 3 have prediabetes. Directly I do have family participants with diabetes mellitus. which of the following is not associated with gestational diabetes
While one may often be caught up in the various sorts of diabetes, something is clear: Type 2 diabetes mellitus account for greater than 90% of the diabetes mellitus situations in the world. The bright side is that Type 2 diabetes mellitus is due to our lifestyle as well as is well within our control.
When a person is prediabetic, it is important to manage it. Thats since it can quickly intensify to a full-on diabetes mellitus which may create several dangerous problems. Some issues are kidney failure, damages to the retina in the eye, as well as various other nerves too. which of the following is not associated with gestational diabetes
Standard western medicine starts from insulin medications after that to insulin injections. Nonetheless, this has a tendency to lead us down a domino effect to being eventually depending on it permanently. Because of this, increasingly individuals are searching for effective all-natural remedies for diabetes mellitus.
Key Points About Diabetes During Pregnancy
-
Diabetes is a condition in which the body can’t produce enough insulin, or it can’t use it normally.
-
There are;3 types of diabetes: Type 1, tType 2, and gestational diabetes.
-
Nearly all pregnant women without diabetes are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
-
Treatment for diabetes focuses on keeping blood sugar;levels in the normal range.
-
Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes in later life. Follow-up testing is important.
Read Also: Qu? Fruta No Puede Comer Un Diabetico
Are You At Risk For Gestational Diabetes
You may be more likely than other women to develop gestational diabetes if:
- Youre older than 25.
- Youre overweight or obese and not physically active.
- You had gestational diabetes or a baby with macrosomia in a past pregnancy.
- You have high blood pressure or youve had heart disease.
- You have polycystic ovarian syndrome . This is a hormone imbalance that can affect a womens reproductive and overall health.
- You have prediabetes. This means your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diabetes.
- You have a parent, brother or sister who has diabetes.
Even women without any of these risk factors can develop gestational diabetes. This is why your health care provider tests you for GDM during pregnancy.;
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetic ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed.If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Unit Of Insulin
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
Treatments For Gestational Diabetes

If you have gestational diabetes, the chances of having problems with your pregnancy can be reduced by controlling your blood sugar levels.
You’ll be given a blood sugar testing kit so you can monitor the effects of treatment.
Blood sugar levels may be reduced by changing your diet and exercise routine.;However, if these changes don’t lower your blood sugar levels enough, you will need to take medicine as well. This may be tablets or insulin injections.
You’ll also be more closely monitored during your pregnancy and birth to check for any potential problems.
If you have gestational diabetes, it’s best to give birth before 41 weeks. Induction of labour or a caesarean section may be recommended if labour does not start naturally by this time.
Earlier delivery may be recommended if there are concerns about your or your baby’s health or if your blood sugar levels have not been well controlled.
Find out more about;how gestational diabetes is treated.
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Diabetes 1 And 2
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
WEEK 8 final exam nutrition and health.docx
DeVry University, Henderson
WEEK 8 SCI 288 FINAL EXAM.docx
DeVry University, Decatur
University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign
FSHN 120
DeVry University, New York SCI 228
SCI 228 Final Exam.docx
DeVry University, Henderson SCI 228
WEEK 8 final exam nutrition and health.docx
test_prep
DeVry University, Decatur SCI 288
WEEK 8 SCI 288 FINAL EXAM.docx
University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign FSHN 120
fshn120 exam 3
DeVry University, Chicago SCI 228
DW Week 5 NutritionEssayFinalQuestions
DeVry University, Chicago SCI-228-10 SCI-228-10
14 questions

