Blood Sugar Level During Pregnancy
Picture 2: Diabetes induced pregnancy is called gestational diabetes.Photo Source: cdn2.momjunction.com
Some women develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy. A high blood sugar level during pregnancy may have a detrimental effect on the baby if left unmanaged.
Symptoms of gestational diabetes are quite difficult to identify as symptoms are similar to that of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The best way to determine if the pregnant woman has gestational diabetes is by measuring the blood glucose level sometime between the 24th and 28th weeks.
Pregnant women at risk for gestational diabetes include:
- 25 years old and above
- Overweight
- African-American, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American women
- Family history of diabetes mellitus
- Women diagnosed with pre-diabetes
An oral glucose tolerance test is performed to check for gestational diabetes. A pregnant woman is positive for gestational diabetes if the result of oral glucose tolerance test is elevated more than ones. Above-normal blood glucose level has the following figures:
- Fasting blood sugar level – 92 mg/dL and above
- One hour – 180 mg/dL and above
- Two hours – 153 mg/dL and above
How To Reduce Blood Sugar
You can take steps to reach your blood sugar goals as soon as you find out that it is high. This is how to reduce blood sugar if you have a single high reading that may be dangerous:
- Ask your doctor what to do if you missed a dose of insulin or another diabetes medication
- Ask your doctor if your medication types and doses are still appropriate for you
- Drink water to dilute the sugar
- Exercise for 15 minutes
- Eat a small protein snack, such as a hard-boiled egg, ½ ounce of peanuts or pistachios or other nuts, ½ cup of beans, or ½ cup of plain yogurt or cottage cheese
If you have chronically high blood sugar in prediabetes or diabetes, you can follow this treatment plan:
- Exercise regularly, assuming your doctor approves it
- Lose weight if you are overweight or obese
- Eat a higher proportion of vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fruit
- Limit sugary foods and beverages, fried foods, refined starches, and processed and fatty red meats
- Beware of starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes, which can spike your blood sugar. Check out our guide of which veggies to avoid!
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federation’s target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Levels In The Morning
The best time to check blood sugar levels in the morning is right when you wake up and before you eat anything. This gives you a glimpse of what may be happening overnight, and it gives you a baseline for the day.
These are goal levels, according to The Joslin Diabetes Center:
- Under 70 mg/dl if you do not have diabetes.
- 70 to 130 mg/dl if you have diabetes.
The dawn effect can often lead to a high morning measurement in diabetes. This is your body’s tendency to get ready for the day by raising blood sugar by increasing levels of counter-regulatory hormones – the ones that counteract insulin as in normal blood sugar. For people with diabetes, you do not have the capacity to counterbalance this rise in blood sugar, so levels can be dangerously high
Ways to lower your morning blood sugar value include:
- Eating dinner earlier
- Checking your medications – making sure you are taking them properly and asking your doctor if they are correct
- Going for a walk after dinner
- Including protein with your dinner
Where Do Babies Get Their Glucose From
In the uterus , babies get glucose from their mother through the placenta and umbilical cord. Some glucose is used immediately as energy and some is stored in preparation for birth. Newborn babies are able to make glucose from these stores. In this way, healthy, well-grown babies keep their blood glucose levels normal for the first few days of life and until they are feeding well.
Once a supply of breastmilk is established , milk becomes the main source of sugar for the baby. The lactose sugar in milk is converted to glucose in the body. In addition to using sugar from milk for activity and growth, your baby will again store sugar to avoid low blood glucose between feeds.
Low Blood Sugar In Babies Causes
Babies need blood sugar for energy. Most of that glucose is used by the brain.
The baby gets glucose from the mother through the placenta before birth. After birth, the baby gets glucose from the mother through her milk or from formula, and the baby also produces it in the liver.
Glucose level can drop if:
- There is too much insulin in the blood. Insulin is a hormone that pulls glucose from the blood.
- The baby is not producing enough glucose.
- The baby’s body is using more glucose than is being produced.
- The baby is not able to feed enough to keep the glucose level up.
Low blood sugar level is more likely in infants with one or more of these risk factors:
- Born early, has a serious infection, or needed oxygen right after delivery
- Mother has diabetes
- Have slower than usual growth in the womb during pregnancy
- Are smaller or larger in size than normal for their gestational age.
How Long Will Blood Glucose Checks Or Additional Treatments Be Needed
Blood glucose levels usually get back to normal within 12 hours to 72 hours of birth, especially once your baby is feeding regularly.
It’s rare for full-term babies to continue having trouble with their blood glucose levels. If this happens beyond 24 hours, your baby’s doctor may want to do more tests.
Does My Baby Have Diabetes
In adults, blood sugar problems are often caused by diabetes. If a mother has diabetes, her baby is more likely to have short-term low blood sugar at birth. The problem continues until the baby’s pancreas adjusts to his or her normal blood sugar level. But the blood sugar problem your baby has does not mean your baby has diabetes. If your baby has low or high blood sugar as a newborn, it doesn’t mean your baby is likely to grow up to have diabetes, either.
What Are The Risk Factors That Lead To Low Blood Sugar Levels In Infants
A baby may acquire a low blood sugar level if he/she has signs of one or more below-mentioned factors;
- Is born early and has a grave infection
- The need for oxygen as soon as delivery
- The mother is a diabetic and in such conditions, infants are larger
- A slow growth rate than normalcy when in the womb
- Are larger or smaller in size than usual for their gestational age
Erythroblastosis Fetalis And Beta
Although maternal diabetes is themost common cause ofhyperinsulinism in the newborn, postnatal insulinsecretion may be abnormal due toseveral other disorders. Infants whohave erythroblastosis fetalis haveincreased levels of insulin and anincrease in the number of pancreaticbeta cells. The mechanism for thisdevelopment is unclear, but onepossibility is that glutathione releasedfrom hemolyzed red cells inactivatesinsulin in the circulation, whichtriggers more insulin secretion andupregulates the beta cells. Exchangetransfusions may exacerbate theproblem because transfused bloodusually is preserved with acombination of dextrose and other agents.During the exchange, the infantreceives a significant glucose load,with subsequent exaggerated insulinresponse from the hyperplasticpancreas. At the end of the exchange,the rate of dextrose administrationreturns to baseline, but insulin levelsremain elevated, leading to furtherhypoglycemia.
Use of beta-agonist tocolyticagents such as terbutaline also isassociated with hyperinsulinemia inthe newborn, especially if the agentwas used for more than 2 weeks andwas discontinued less than 1 weekprior to delivery. Affected infantsalso appear to have reducedglycogen stores, which further aggravatesthe hyperinsulinemia and its effectson decreasing glucoseconcentrations.
Low Blood Sugar In Babies Prevention
If you have diabetes during pregnancy, work with your healthcare provider to control your blood sugar level. Be sure that your newborn’s blood sugar level is monitored after birth. A study by Joshi et al 2) suggested that in women with pregestational type 1 or type 2 diabetes, neonatal hypoglycemia can be avoided by aiming at an intrapartum blood glucose level of 72 – 126 mg/dl .
Fasting Blood Glucose Level Test Preparation
What should you do if your doctor orders a fasting blood sugar test? The preparation is the same as when you take a fasting test for cholesterol. First, be sure to find out if you need to schedule an appointment for your test . Ask your doctor what time is best to take it.
Then:
- Schedule your test if necessary
- Ask your doctor if you need to change any of the medications you take on the morning of the test
- If you normally drink coffee or have caffeine, ask your doctor if that is okay. It may not be, since it affects blood sugar levels
- Fast for at least 8 hours before your test. Usually, an overnight fast is most convenient
- You can drink water
How Can Diabetes Affect My Baby
A baby’s organs, such as the brain, heart, kidneys, and lungs, start forming during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. High blood glucose levels can be harmful during this early stage and can increase the chance that your baby will have birth defects, such as heart defects or defects of the brain or spine.
High blood glucose levels during pregnancy can also increase the chance that your baby will be born too early, weigh too much, or have breathing problems or low blood glucose right after birth.
High blood glucose also can increase the chance that you will have a or a stillborn baby.1 Stillborn means the baby dies in the womb during the second half of pregnancy.
Why Is My Babys Blood Sugar Abnormal
-
Low blood sugar is common in many babies right after birth. The baby’s body is getting used to controlling its blood sugar level without help from the mother’s body.
-
Mothers with diabetes have babies who are more likely to have low blood sugar. Babies who are either larger or smaller than the normal range for their age may also have low blood sugar.
-
High blood sugar can be caused by illness or stress. It’s also common in preemies born very early. That’s because the organ that makes insulin is not fully developed.
Findings Reinforce Current Treatment Guidelines For Hypoglycemia
- Date:
- NIH/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- Summary:
- Researchers have shown that treating hypoglycemia, or low blood glucose, in newborns according to current recommendations is safe and appears to prevent brain damage.
Researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health have shown that treating hypoglycemia, or low blood glucose, in newborns according to current recommendations is safe and appears to prevent brain damage.
Glucose levels that are too low–or too high–could maylead to brain injury in newborns and possibly result in severe intellectual and developmental disabilities. Until now, the threshold for blood sugar had only been an estimate, never having been verified by a research study in people. According to the latest study, infants treated for hypoglycemia at the recommended threshold level were no more likely to experience neurological problems by two years of age than those in a comparable group who did not need treatment.
“These findings are extremely reassuring,” said Tonse Raju, M.D., chief of the Pregnancy and Perinatology Research Branch at NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which funded co-funded the study. “There is now firm evidence that physicians can provide an essential treatment to prevent brain damage without concern that there might be any unforeseen increase in risk to the newborn.”
Story Source:
What Should You Do If Your Babys Blood Glucose Is Low
The baby will be checked for certain diseases. It will need extra food if it doesn’t level up by itself. You can continue breastfeeding:
- from the breast,
- with ASIP,
- Formula milk.
If the supplementary food does not increase the blood glucose level, a glucose gel may be given to increase blood sugar. But if the baby’s blood sugar remains low or if the baby is not feeding properly, they will need intravenous care .
The most natural way to feed your baby and keep blood glucose levels normal is to breastfeed early and often. Talk to your doctor about the most appropriate treatment for your baby’s condition.
Low blood glucose levels in babies need to be watched out, especially if you and your baby have symptoms as mentioned. Hope this information is helpful, Ma!
What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is a sugar that moves through the bloodstream and provides energy to all the cells in the body. It is one of your baby’s most important sources of energy.
Babies with normal blood glucose levels have all the energy they need for healthy growth and development. However, in rare cases, blood glucose levels can fall too low and cause a baby to become sick.
How Will My Babys Blood Glucose Be Checked
Blood glucose can be checked with just a few drops of blood, usually taken from your baby’s heel.
If your baby is in one of the above at-risk groups and is well, blood glucose will be checked at 2 hours of age and then again before your baby feeds, about three to five times during the first and second days of life.
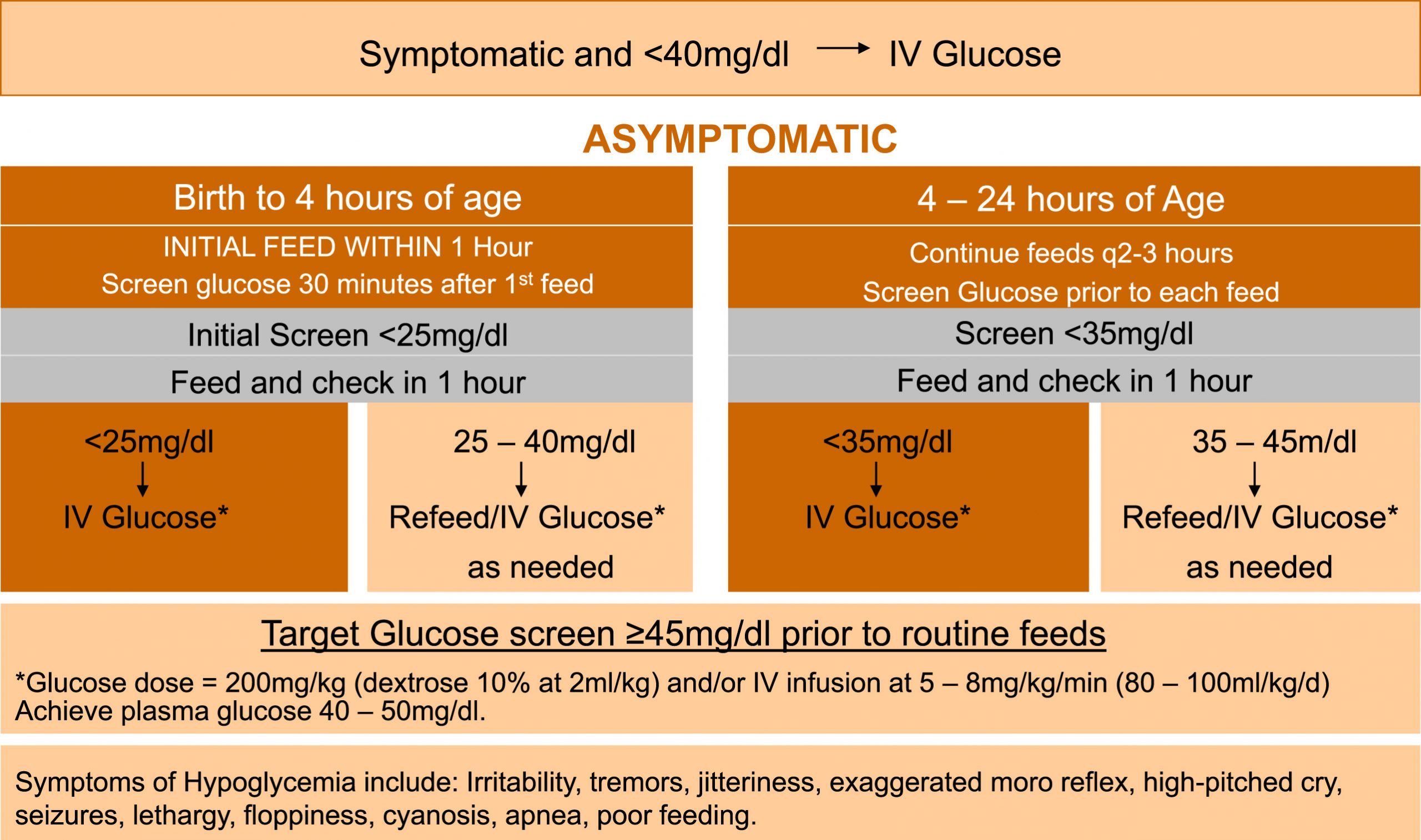
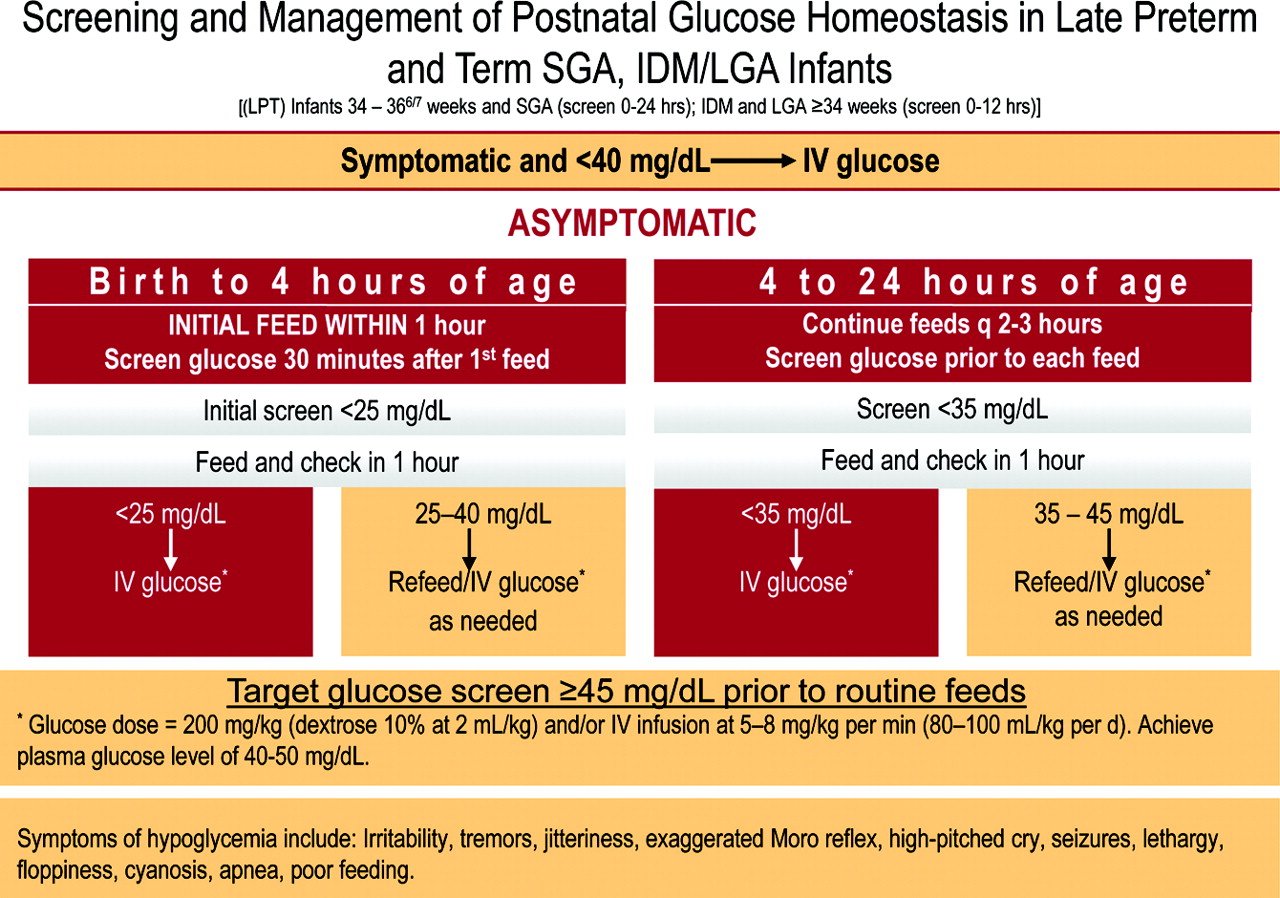
Screening For Neonatal Hypoglycemia
The American Academy of Pediatrics that screening for neonatal hypoglycemia be limited to at-risk infants , and infants who experience birth injury. The AAP also recommends that the frequency and duration of screening be based on the infant’s risk level. In other words, medical necessity should determine the need for NH screening and treatment.
A summary of the guidelines follow:
What Do I Do If My Baby Has Low Blood Glucose Levels
Your baby will be checked for signs of illness. He will need extra feedings if his levels don’t rise on their own. The extra feeds can be given:
- from the breast,
- as expressed breast milk, or
- as formula.
If the extra feedings don’t raise the blood glucose level, glucose gel can be provided with a feed to raise the blood sugar. This can be repeated once, but if your baby’s blood sugar remains low or if your baby is not able to feed well, they will need intravenous treatment . Preterm babies or babies with low birth weight often have an intravenous started when they are born.
Prevention Of Hypoglycemia In The Newborn:
There may not be any way to prevent hypoglycemia, only to watch carefully for the symptoms and treat as soon as possible. Mothers with diabetes whose blood glucose levels are in tight control will have lower amounts of glucose that go to the fetus. This will lower the fetal insulin production and reduce the risk of neonatal hypoglycemia.
How To Diagnose Low Blood Sugar In Newborns
Newborns will have blood tests to know the sugar level for a few hours. A heel stick is used for this. The healthcare professionals will keep continuing the test until the glucose level comes to normal for nearly 12 to 24 hours.
Some other tests may include screening for metabolic disorders and urine tests.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
How Can I Prepare For Pregnancy If I Have Diabetes
If you have diabetes, keeping your blood glucose as close to normal as possible before and during your pregnancy is important to stay healthy and have a healthy baby. Getting checkups before and during pregnancy, following your diabetes meal plan, being physically active as your health care team advises, and taking diabetes medicines if you need to will help you manage your diabetes. Stopping smoking and taking vitamins as your doctor advises also can help you and your baby stay healthy.
How To Test Your Blood Sugar Levels
After you wake up in the morning, check your fasting blood sugar levels using a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor . Before you use a blood glucose meter, the recommends washing your hands and using the lancing device to get a drop of blood. After you hold the test strip against the drop of blood, your blood sugar levels should appear on the meter.
Is Low Blood Sugar In Newborns Common
Approximately about 15% of newborns are suffering from low blood sugar levels called neonatal hypoglycemia in medical terms. And this is the only condition that can be prevented to stop the brain damage in infants. Let us have a look at what causes low blood sugar levels in newborns and how low blood sugar in newborns can be addressed.
Inborn Errors Of Metabolism
Inborn errors of metabolism mayaffect either the availability ofgluconeogenic precursors or thefunction of the enzymes required forproduction of hepatic glucose.Metabolic defects that may present withhypoglycemia include some formsof glycogen storage disease,galactosemia, fatty acid oxidation defects,carnitine deficiency, several of theamino acidemias, hereditary fructoseintolerance , and defects ofother gluconeogenic enzymes.Finally, endocrine disorders such ashypopituitarism and adrenal failurealso can result in hypoglycemiabecause of the absence of theappropriate hormonal response tohypoglycemia and subsequent failure toactivate hepatic glucose production.However, these conditions are veryrare and should be considered afterruling out more common etiologies.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels

You might want to measure your blood sugar before meals to get a baseline, and then two hours after your meal to measure your “normal blood sugar level”. Your doctor might also suggest measuring blood sugar before bed to be sure you have been eating well throughout the day and can go to sleep with peace of mind.
These are considered within the range of “normal”:
- Less than 140 mg/dl if you do not have diabetes.
- Less than 180 mg/dl if you have diabetes.
What Health Problems Could I Develop During Pregnancy Because Of My Diabetes
Pregnancy can worsen certain long-term diabetes problems, such as eye problems and kidney disease, especially if your blood glucose levels are too high.
You also have a greater chance of developing preeclampsia, sometimes called toxemia, which is when you develop high blood pressure and too much in your during the second half of pregnancy. can cause serious or life-threatening problems for you and your baby. The only cure for preeclampsia is to give birth. If you have preeclampsia and have reached 37 weeks of pregnancy, your doctor may want to deliver your baby early. Before 37 weeks, you and your doctor may consider other options to help your baby develop as much as possible before he or she is born.
What Should A Newborn’s Blood Sugar Level Be
4.1/5newbornblood glucose levelwhich willblood glucose levelnewborn
Of the infants, 216 had blood glucose levels less than 47 milligrams per deciliter , which is a well-accepted threshold for hypoglycemia.
Additionally, what is a good blood sugar score? Normal blood sugar levels are less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least eight hours. And they’re less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
In this manner, is low blood sugar in a newborn dangerous?
Low blood sugar in newborns, known as “neonatal hypoglycemia,” is the most common preventable cause of brain damage in infancy. Those at risk of low blood sugar include babies born prematurely, those small or large for their gestational age, and those born to mothers with diabetes.
How long does neonatal hypoglycemia last?
Usually, low blood glucose levels will only last for a few hours, but can last up to 24-72 hours. Once your baby’s levels become normal, he shouldn’t have further problems with hypoglycemia . In very rare cases, low blood sugar can be severe or last a long time.
Blood Sugar Level Chart By Age
Blood sugar levels tend to rise with age due to an increase in insulin resistance and decrease in insulin sensitivity. In one study by the National Health Institute , each extra decade of age was linked to a 2.7 mg/dl increase in fasting glucose, and a 4.5 mg/dl increase in 2-hour post-prandial glucose levels.
Causes Of Neonatal Hypoglycemia
The causes of neonatal hypoglycemia include the following :
- An excess of insulin in the baby’s blood: Insulin is a hormone that decreases the amount of glucose in the blood. When a baby has an excess of insulin, one condition is called persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy .
- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- Limited storage of glycogen: Before glucose is broken down into its simple form, it is stored in the form of glycogen. Decreased glycogen storage can happen as a result of prematurity or intrauterine growth restriction , and can cause hypoglycemia.
- Increased glucose use: A baby may need to utilize more glucose than usual due to the following medical conditions:
- Hyperthermia
- Polycythemia
- Growth hormone deficiency
How Would You Treat This Infant
An intravenous infusion of 10% dextrose or Neonatalyte must be started immediately at a rate to give 60 ml/kg/day. Add 2 ml/kg of 10% dextrose as a bolus. Repeat the reagent strip measurement after 15 minutes. If it is still low give a dose of 5 mg hydrocortisone intravenously. Start milk feeds every 2 hours as soon as possible. If the milk feeds are tolerated and the blood glucose concentration returns to normal, then the rate of the 10% dextrose infusion can be slowly reduced. Monitor the blood glucose concentration carefully.
What To Expect From Your Blood Sugar In The Morning
After an overnight fast, a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 milligrams per deciliter , according to the American Diabetes Association . But, according to Susan Spratt, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, not everyone with type 1 or type 2 diabetes has to shoot for “normal” levels.
“If you’re young, the goal may be to get your fasting blood sugar levels to less than 120 mg/dL,” Dr. Spratt says. But if you’re older and have other health conditions, that number may be higher, she says.
The points out that not everyone will have the same blood sugar level goals. Instead, your endocrinologist or doctor will calculate your target number based on your age, how long you’ve had diabetes, whether you have health conditions like heart disease and other factors.
Keep in mind, too, that your fasting blood sugar levels can be too low. For example, a morning blood sugar reading below 70 mg/dL can indicate a , or low blood sugar.
Read more:Which Helps You More in the Morning: Tea, Water or Coffee?

