When Should I Call My Doctor
If you havent been diagnosed with diabetes, you should see your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of diabetes. If you already have been diagnosed with diabetes, you should contact your provider if your blood glucose levels are outside of your target range, if current symptoms worsen or if you develop any new symptoms.
How Are Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus Similar
Both types are similar in that they can cause complications if not treated properly. Blindness, kidney failure, and amputations are just some of the possible complications of diabetes when it is left untreated. In addition, both types are monitored in a similar manner and both can be treated with insulin when necessary. Care must be taken with all diabetic patients to keep blood sugar levels consistent.
What Types Of Healthcare Professionals Might Be Part Of My Diabetes Treatment Team
Most people with diabetes see their primary healthcare provider first. Your provider might refer you to an endocrinologist/pediatric endocrinologist, a physician who specializes in diabetes care. Other members of your healthcare team may include an ophthalmologist , nephrologist , cardiologist , podiatrist , neurologist , gastroenterologist , registered dietician, nurse practitioners/physician assistants, diabetes educator, pharmacist, personal trainer, social worker, mental health professional, transplant team and others.
Also Check: Does Insulin Raise Blood Pressure
What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
You May Like: Metformin Common Side Effects
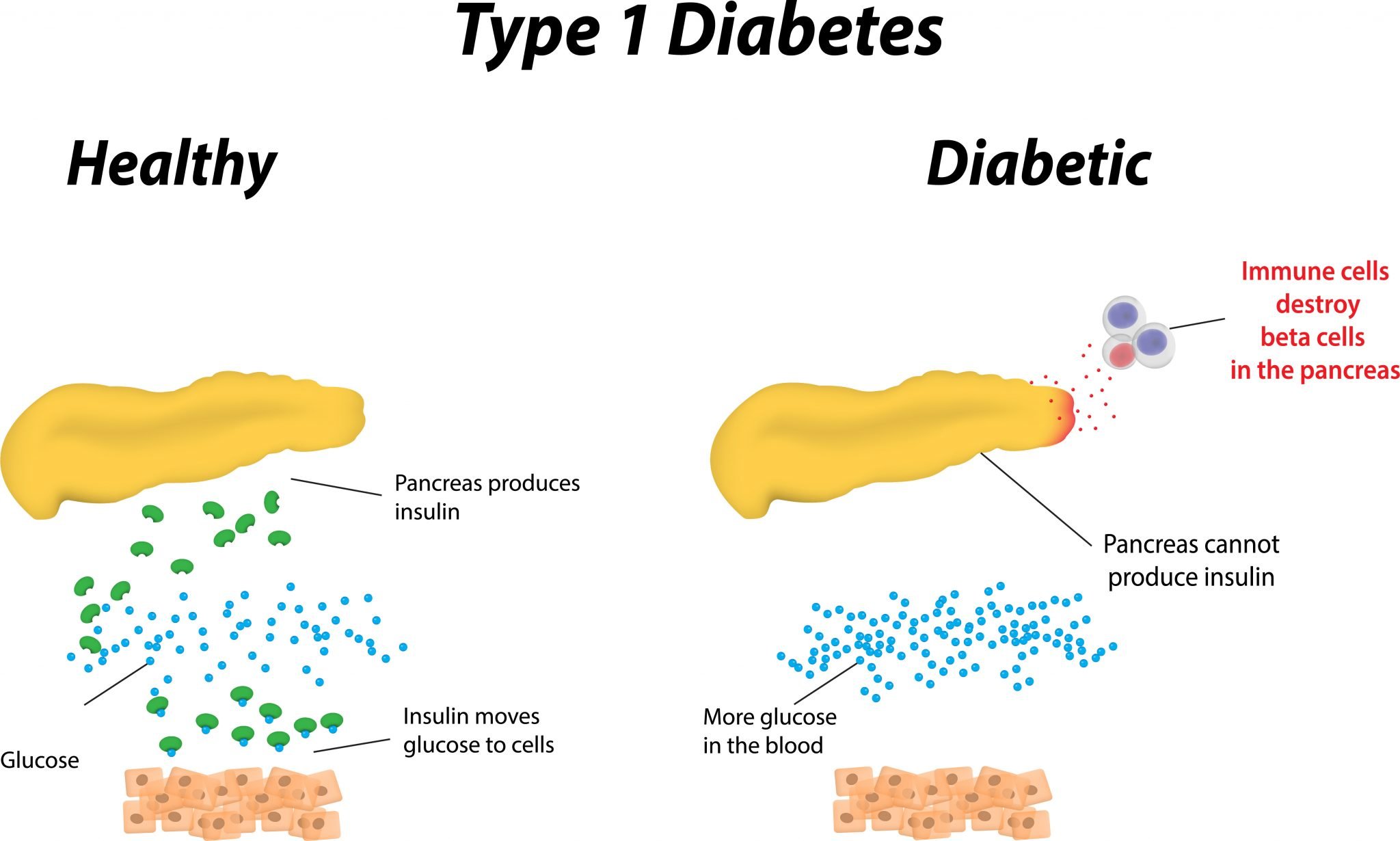
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
People of all ages can develop type 1 diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make insulin or makes very little insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps blood sugar enter the cells in your body where it can be used for energy. Without insulin, blood sugar cant get into cells and builds up in the bloodstream. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and causes many of the symptoms and complications of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults, but it can develop at any age.
Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2approximately 5-10% of people with diabetes have type 1. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes, but it can be managed by following your doctors recommendations for living a healthy lifestyle, managing your blood sugar, getting regular health checkups, and getting diabetes self-management education and support.
How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.
Read Also: Does Steroid-induced Diabetes Go Away
Eating A Healthy Balanced Diet
What you eat can make a difference to how you feel and how you manage your condition. Thats why weve got a huge range of tasty and nutritious recipes ready for you to try.
Whether youre cooking up a feast for dinner, or looking for something lighter for lunch, weve got you covered. Simply search by ingredient, meal type or dietary requirement and enjoy eating with diabetes.
Diagnosis And Prognosis Of Type 1 Diabetes
People at risk of developing type 1 diabetes should be screened regularly, especially for family members having diabetes.
For diagnostics purposes, doctors look for antibodies against the beta cells of the pancreas. The antibodies in beta cells predict the appearance of DMT1.
The diagnosis is made after a medical examination and subsequent investigations examinations. The doctor first of all inquiries about the signs, familiarity, and other risk factors of type 1 diabetes.
He then investigates the presence of symptoms and prescribes diagnostic tests to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of DMT1. The tests are:
We cannot cure type 1 diabetics, but keeping it under control is possible. Life expectancy for people with type 1 diabetes is about ten years shorter than for other people, and this is because the disease exposes you to cardiovascular problems.
People with diabetes have a five times greater risk of suffering from heart disease than non-diabetic people. However, following a correct lifestyle and the prescribed therapy makes it possible to lead an utterly everyday life.
Read Also: Blood Sugar Too High Symptoms
Pathogenesis Of T1d Immune And Islet Perspectives
The pathological features of T1D, although often definitively stated , in reality has many unknowns, unproven assumptions, and knowledge gaps . It is widely assumed that a triggering event or events initiate the celldirected autoimmunity, but these events or events remain unknown despite sustained efforts over many years. Many environmental agents have been postulated, including virus infection , diet, intestinal microbiota, cleanliness of the environment, and gene-environmental interactions . The search continues in the TEDDY study, which is prospectively and systematically investigating potential environmental triggers.
Studies by a number of investigators have provided critical insight by collecting and studying the human pancreas from the few individuals who die at T1D onset, after a relatively short duration of T1D , or who were found to have islet-related autoantibodies at the time of organ donation . Some of the pathological findings in the pancreas in recent-onset T1D include modest, patchy, variable insulitis some pseudoatrophic, insulin-negative islets and some islets with normal-appearing cells . The clinical features of T1D and biomarkers mostly correlated with these pathological features of T1D , thus providing an important connection between peripheral measurements and pancreas pathology.
Pancreatic changes and immune abnormalities in T1D.
Diabetes: Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
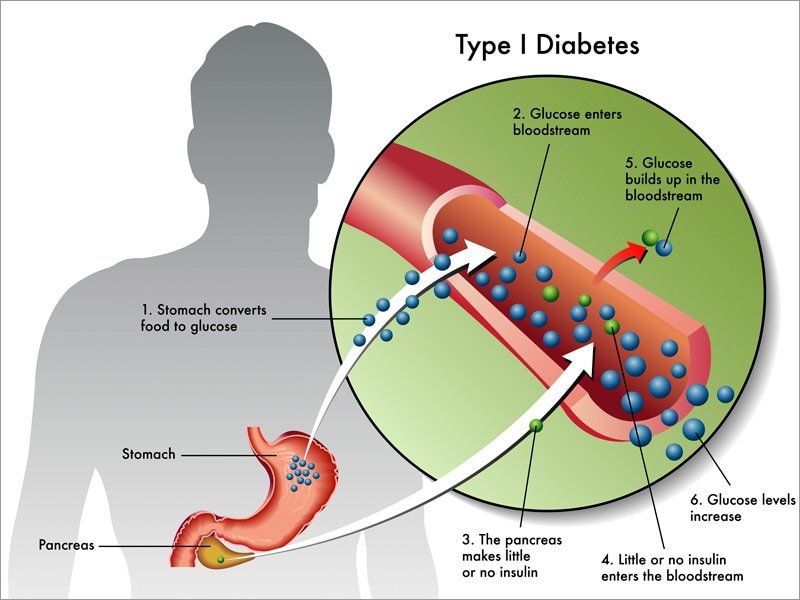
Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus , also known as type 1 diabetes, usually starts before 15 years of age, but can occur in adults also. Diabetes involves the pancreas gland, which is located behind the stomach . The special cells of the pancreas produce a hormone called insulin.
The body is made up of millions of cells. All cells need glucose from the food we eat for energy. Just as a car cant run without gasoline, the body cant work without glucose. Insulin is the key that allows glucose to enter the cells. Without this key, glucose stays in the bloodstream and the cells cant use it for energy. Instead, the glucose builds up in the blood and spills over into the urine. When a person develops type 1 diabetes, the pancreas stops making insulin. To help the bodys cells use the glucose, a child with type 1 diabetes mellitus must receive insulin by injection .
You May Like: What Can You Eat With Diabetes
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Type 1 diabetes is a systemic disorder with diverse presentations and very high morbidity for this reason, the condition is best managed by an interprofessional team of healthcare professionals.
Type 1 diabetes is a serious disorder with very high morbidity and mortality. Over the long term, the vast majority of patients with this disorder will develop blindness, adverse cardiac events, end-stage renal disease, neuropathy, and in some cases, premature death. Data indicate that for those patients who manage to control their blood sugars without developing serious complications tend to have a good quality of life.
The key factor in preventing complications is patient compliance with their medications, follow up with the specialists and educators. At every patient encounter, the pharmacist, nurse, and clinicians should emphasize the importance of blood glucose control, long-term complications, and management goals. The patient should be encouraged to modify the lifestyle to reduce the risk of complications. In addition, all patients with diabetes should be made aware of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and ways of managing it. Patients should be educated about resources that are available and the benefits of joining support groups. A dietitian should educate the patient about foods that can be consumed, and the nurse should educate the patient on blood glucose monitoring at home.
Current Therapy For T1d
Current T1D therapy focuses on matching exogenous insulin and food intake while incorporating daily activities such as exercise and sleep. Remarkable advances have been made in insulin formulation and diabetes technology, including methods for insulin delivery and glucose monitoring . Additionally, T1D clinical care is evolving to incorporate mobile technology and provide greater emphasis on behavioral and psychosocial aspects, the social determinants of health, and health care access/cost. The goal is near normoglycemia while avoiding hypoglycemia and allowing for normal daily activities. Traditionally, the glycemic goal in T1D has been an A1C of 7.0 or lower, with this target individualized for age, comorbidities, and lifestyle . Importantly, hypoglycemia, a major adverse effect of intensive glycemic control, is a substantial, lifelong burden of current therapy for T1D .
Don’t Miss: Metformin Low Blood Pressure
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Type 1 Diabetes
Health care professionals usually test people for type 1 diabetes if they have clear-cut diabetes symptoms. Health care professionals most often use the random plasma glucose test to diagnose type 1 diabetes. This blood test measures your blood glucose level at a single point in time. Sometimes health professionals also use the A1C blood test to find out how long someone has had high blood glucose.
Even though these tests can confirm that you have diabetes, they cant identify what type you have. Treatment depends on the type of diabetes, so knowing whether you have type 1 or type 2 is important.
To find out if your diabetes is type 1, your health care professional may test your blood for certain autoantibodies. Autoantibodies are antibodies that attack your healthy tissues and cells by mistake. The presence of certain types of autoantibodies is common in type 1 but not in type 2 diabetes.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can come on over time or suddenly. Sometimes, kids dont have diabetes symptoms yet and the condition is discovered when blood or urine tests are done for another reason. Kids who show symptoms may:
- need to pee a lot
- start to wet the bed after having been dry at night
- be thirstier and drink more than usual
- feel tired often
- lose weight
Read Also: Diabetic Reaction To Too Much Sugar
How Can Parents Help
Now is the perfect time to help your child to create healthy habits for life. Heres how:
- Get involved with daily care. Help your child put their care plan into action every day. From counting carbs, to calculating insulin doses, and giving injections, theres a lot to learn at first. Share the responsibilities with your child. Over time, theyll be able to take on more on their own. Turn to your childs care team with any questions about the care plan or daily care.
- Learn all you can about diabetes. The more you know about type 1 diabetes, the more confident youll feel about helping your child manage it day to day. And a solid understanding of diabetes lets you advocate for your child. You can share your knowledge with important people in your childs life, like grandparents, teachers, coaches, and babysitters. Doing so helps you build a community of support for your child.
- Encourage your child. It can take a while to adjust to the new responsibilities that come with type 1 diabetes. Remind your child that many kids their age have type 1 diabetes, and they follow a similar care plan. If your child has concerns that youre not sure how to handle, ask the care team. Theyll connect you with the right resources.
Having a child with type 1 diabetes may seem overwhelming at times, but you’re not alone. If you have questions or problems, reach out to your childs diabetes care team they can help with all kinds of issues, and will guide your family through this journey.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus affects around 85% of people with diabetes, and is usually diagnosed at a later age than type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes is often, but not always, associated with excess body weight and lack of exercise. Type 2 diabetes mellitus affects people of different ethnicities to a different degree.
For instance, people of South Asia, Polynesia, African, African-Caribbea, Middle-Eastern and American-Indian ancestry may face a greater risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. At an early stage, type 2 diabetes mellitus is controlled using diet and exercise, but many people with type 2 diabetes mellitus eventually require insulin.
You May Like: Can Someone With Diabetes Get A Tattoo
Are There Other Treatment Options For Diabetes
Yes. There are two types of transplantations that might be an option for a select number of patients who have Type 1 diabetes. A pancreas transplant is possible. However, getting an organ transplant requires taking immune-suppressing drugs for the rest of your life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs. However, if the transplant is successful, youll likely be able to stop taking insulin.
Another type of transplant is a pancreatic islet transplant. In this transplant, clusters of islet cells are transplanted from an organ donor into your pancreas to replace those that have been destroyed.
Another treatment under research for Type 1 diabetes is immunotherapy. Since Type 1 is an immune system disease, immunotherapy holds promise as a way to use medication to turn off the parts of the immune system that cause Type 1 disease.
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option thats an indirect treatment for diabetes. Bariatric surgery is an option if you have Type 2 diabetes, are obese and considered a good candidate for this type of surgery. Much improved blood glucose levels are seen in people who have lost a significant amount of weight.
Of course other medications are prescribed to treat any existing health problems that contribute to increasing your risk of developing diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high cholesterol and other heart-related diseases.
Important Facts About Diabetes
People do not outgrow type 1 diabetes, but they can learn to control it by insulin shots, blood glucose testing, diet and exercise.
Diabetes is not contagious .
About 14.6 million Americans have diabetes.
About 1 out of 10 people with diabetes have type 1 DM.
Another type of diabetes is type 2, non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus . Type 2 diabetes is more common than type 1. About 9 out of 10 people with diabetes have type 2. Type 2 DM used to occur mostly in adults, but is becoming increasingly more common in children. It is associated with obesity. NIDDM usually starts after 40 years of age. People with type 2 diabetes usually produce enough of their own insulin, but their bodies dont use it right. Type 2 may be controlled by weight loss or with insulin and/or oral medicine.
Recommended Reading: Side Effect Of Insulin

