What Should I Do After I Check My Blood Glucose
Write the blood glucose number in a log book or on a log sheet , and:
- Include all of your blood glucose numbers.
- Write a comment if there is a reason the blood glucose is above or below target.
- Take your blood glucose meter with you when you are away from home.
- Know your blood glucose numbers when you call the clinic or the doctor.
- Bring your blood glucose meter and blood glucose records to all your appointments.
- Bring a list of any questions that you may have.
Low Blood Sugar: What To Watch Out For
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes who:
- Take too much medication or insulin
- Are late eating a meal or snack
- Have increased physical activity
- Drink too much alcohol
Symptoms of low blood sugar include feeling weak, sweaty or clammy, confused, hungry and/or irritable. Sometimes people experience a fast heartbeat and some symptoms may make a person appear to be drunk. A severely low blood sugar can result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma or death especially when a low occurs during the night.
Low blood sugar affects many parts of the body, but the most frustrating part can be that hypoglycemia can happen anytime and anywhere even when you think you are closely following the plan for your diabetes care. If low blood sugar is severe, people may need to go to the hospital to help raise their glucose level or miss work due to the side effects.
It can happen during a date, during a business meeting, or even while driving, which is the most dangerous scenario if there is confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel. Its important to use your blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others safe. Frequent testing with your blood sugar meter and taking action when blood sugar is trending low can prevent a severe low and keep your life on track.
What Is The Correct Sugar Level After Eating And Temporarily
After eating
Consumption of a meal significantly raises blood sugar levels. After eating, an average blood sugar level means that carbohydrate burning is occurring correctly. Glucose levels should drop to about 150 mg/dL after about two hours in a healthy person.
If a glucose measurement taken at any time during the day approaches or exceeds 200 mg/dl, it indicates diabetes. Sugar, after eating, is broken down into glucose, the primary source of energy .
Fasting
Normal fasting blood sugar levels should be between 70-99 mg/dl in a healthy person. When the concentration is higher but does not exceed
125 mg/dl is glucose intolerance and is only treated with a diet. However, if it exceeds 125 mg/dl, additional tests are recommended to diagnose diabetes.
Blood sugar testing when should it be done?
Blood glucose levels should be tested when :
- when there are symptoms of hypoglycemia or overdiagnosis
- Routinely, as part of laboratory tests especially for people at risk for diabetes
- regularly diabetics measure their sugar several times a day
- Every pregnant woman between 24th and 28th week .
- Every healthy person over 45 should have their fasting blood glucose checked at least once every 3 years. Diabetics test their blood glucose levels at home with a glucometer. To determine their glucose metabolism.
How do I prepare for a blood sugar test?
Prepare for your blood sugar test as directed. Glucose testing can be done:
Readers Also Read & Shared
Recommended Reading: Therapeutic Effect Of Insulin
How To Save On Metformin Hcl
Because Metformin Hcl is an inexpensive generic, the manufacturers do not offer any Metformin Hcl manufacturer coupons, Metformin Hcl patient assistance, or copay savings cards at this time.
With a free SingleCare savings card, Metformin Hcl costs only $2.34 for 60, 1000MG Tablet of generic Metformin Hcl. You can use your SingleCare discount card at major retailers , pharmacies , or grocery store pharmacies , and many others.
How To Lower Blood Sugar Level
A patient with diabetes is at a 5 times greater risk of developing cardiovascular disease than patient without diabetes. One third of all cardiovascular diseases also affect people with diabetes.
Three quarters of diabetics die from cardiovascular disease. Women with diabetes have a 4 times greater risk of death from cardiovascular disease. People suffering from diabetes usually have high cholesterol levels as well.
Disturbances in the metabolism of blood sugar levels are mainly the consequence of heredity , age , poor diet, excessive body weight and physical inactivity. Disturbances in the metabolism of blood sugar were present in 20% of adult Europeans during 2002-2005 a study showed.
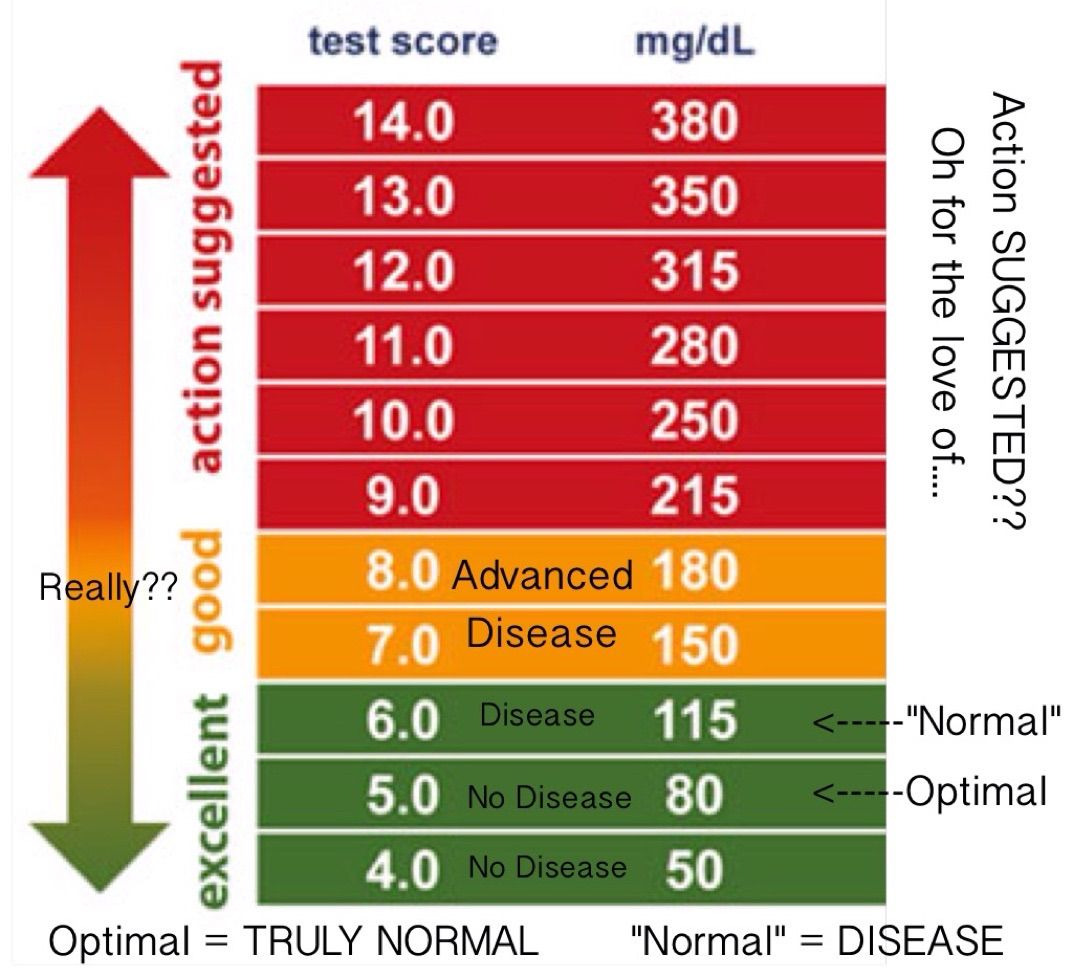
RECOMMENDATIONS to decrease elevated blood sugar:Blood sugar level is determined in the fasting state. In a healthy person, a normal blood glucose level is less than 108 mg/dL or 6 mmol/L on an empty stomach.
Possible values are
- normal blood sugar level ,
- disruption of glycemia ,
- diabetes .
What can you do to lower the chance of developing diabetes:
- lose weight be fit,
- sleep more, be rested.
- have a healthy diet with as many vegetables and fruits, a lot of fiber, consume less calories, less fat, less alcoholic beverages and no simple sugars,
- workout at least 30 minutes per day.
Useful resource: blood sugar levels chart:
Don’t Miss: Metformin Dosage Forms
How Food Affects Blood Sugar
When you eat food, your body breaks it down into essential parts:
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Vitamins and minerals
All parts are necessary in a healthy diet, but the three types of carbohydrates are particularly important when it comes to your blood glucose level. While the general rule is that the more carbohydrates you eat, the higher your blood sugar level, not all three types of carbohydrates convert to blood sugar at the same rate.
The foods that fit into each carb category include:
- Starches, or complex carbohydrates: Starchy vegetables, dried beans, and grains
- Sugars: Fruits, baked goods, beverages, and processed food items like cereals or granola bars
- Fiber: Whole wheat products, chickpeas, lentils, berries, pears, and brussels sprouts
The glycemic index helps you find out which foods can increase or help decrease blood sugar levels. Based on a scale ranging from 0 to 100, high-indexed foods are rapidly digested, absorbed, and metabolized, resulting in marked fluctuations in blood sugar levels, while low-indexed foods produce smaller fluctuations in your blood glucose.
The American Diabetes Association advises adding lean sources of protein and heart-healthy fats to help reduce the overall glycemic impact of a meal or snack.
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
Read Also: Do Type 1 Diabetics Take Insulin
What Is Blood Glucose Anyway
Blood glucose, or sugar, is sugar that is in your blood . It comes from the food that you eat foods that contain carbohydrate, such as bread, pasta and fruit are the main contributors to blood glucose. The cells in our bodies need glucose for energy and we all need energy to move, think, learn and breathe. The brain, which is the command center, uses about half of all the energy from glucose in the body.
What You Can Drink With Meals
Add a low-calorie, low-sugar drink or choose water. Proper hydration is essential to helping your body remove excess sugar.
Some drinks that are good for keeping your blood sugar level low include:
- Unsweetened tea
- Unsweetened coffee
- Sparkling water or club soda
- Flavored water or sparkling water without added sugar
- Diet soda or other diet drinks
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Nph Insulin Take To Work
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person’s needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals. A general guideline is:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
In general, before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
Remedies For Low Blood Sugar Levels
If you experience any of the low sugar symptoms, immediately test your blood glucose levels. For levels between 60 to 80 mg/dL, consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbs. Repeat the test after 15 minutes and eat till sugar levels settle to normal.
But if the levels are below 50 mg/dL and if the patient is conscious and able to eat, give 15 gm. of fast-acting carbs. But if the patient is unable to speak, dont give anything to eat. Call emergency services immediately. If possible, administer glucagon via injection.
Also Check: Metformin Max Dose Per Day
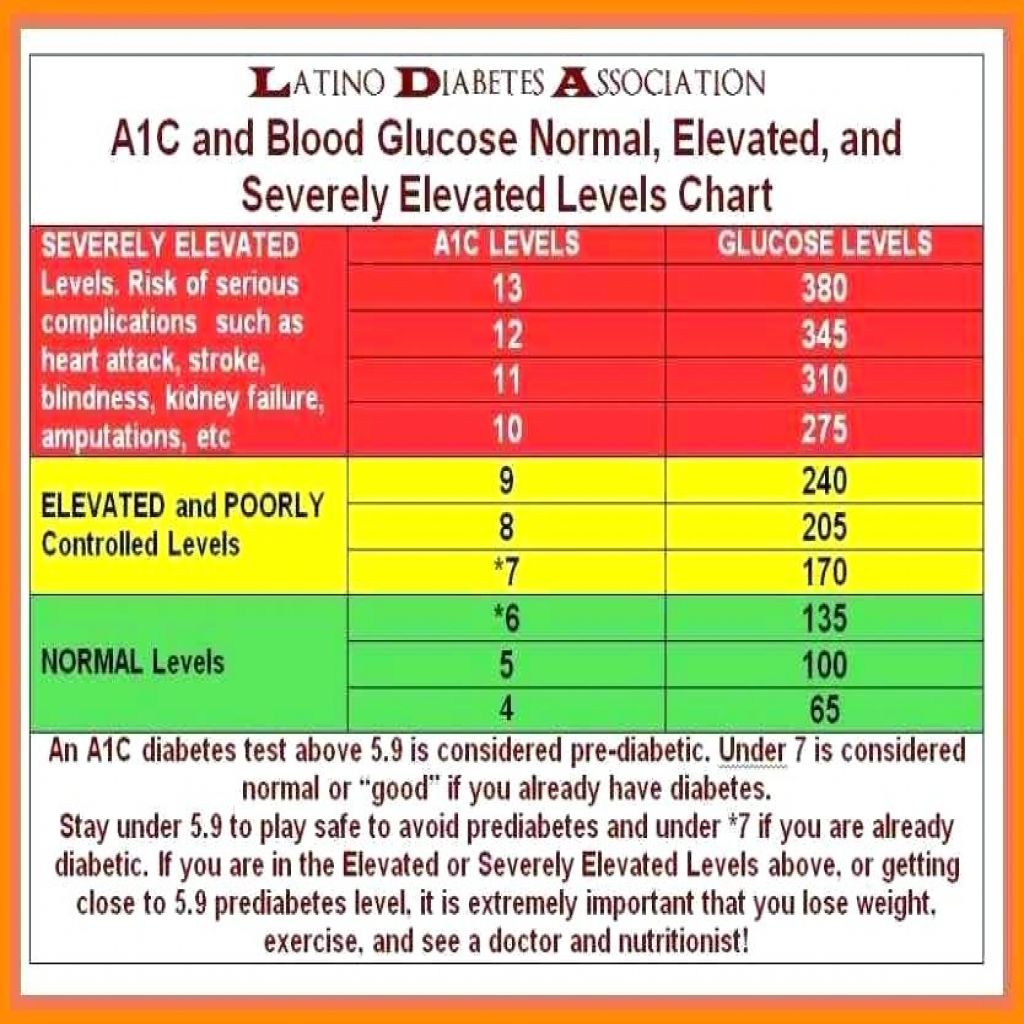
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood sugar levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink. It tells the doctor how your body processes sugar.
- Diabetes is diagnosed at 2 hour blood sugar of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl
|
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
|
| Normal | |
| 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl | |
| Diabetes | 200 mg/dl or higher |
Is Hyperglycaemia Serious
The aim of diabetes treatment is to keep blood sugar levels as near to normal as possible. But if you have diabetes, no matter how careful you are, you’re likely to experience hyperglycaemia at some point.
It’s important to be able to recognise and treat hyperglycaemia, as it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated.
Occasional mild episodes aren’t usually a cause for concern and can be treated quite easily or may return to normal on their own. However, hyperglycaemia can be potentially dangerous if blood sugar levels become very high or stay high for long periods.
Very high blood sugar levels can cause life-threatening complications, such as:
- diabetic ketoacidosis a condition caused by the body needing to break down fat as a source of energy, which can lead to a diabetic coma this tends to affect people with type 1 diabetes
- hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state severe dehydration caused by the body trying to get rid of excess sugar this tends to affect people with type 2 diabetes
Regularly having high blood sugar levels for long periods of time can result in permanent damage to parts of the body such as the eyes, nerves, kidneys and blood vessels.
If you experience hyperglycaemia regularly, speak to your doctor or diabetes care team. You may need to change your treatment or lifestyle to keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
You May Like: Best Candy For Diabetics
When Things Go Awry
When we eat food, the pancreas goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose . If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis. Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, its all about the blood glucose.
Factors That Can Affect Blood Sugar Levels
If you have prediabetes or diabetes, you may have insulin resistance or an inability to produce insulin. This means your body has difficulty regulating blood sugar levels on its own.
Its a delicate balance to maintain, so the following list can help you familiarize yourself with factors that can cause your blood glucose levels to go up or down.
Read Also: Max Dosage Of Metformin
Levels After Youve Eaten
Many foods have types of carbohydrates called starches and sugars. When you eat foods with these types of carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which is a type of simple sugar, and releases the glucose into your bloodstream. Aside from glucose produced by your liver, food is the main source of plasma glucose.
Two hours after eating, your blood sugar levels rise. They rise more when you eat more carbohydrates, when you do not eat fiber, fat, or protein with your carbs, and when you eat certain types of carbohydrates, such as refined sugars and starches.
These are target values from The Joslin Diabetes Center, which include levels for people with diabetes:
| When Measured |
|---|
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Also Check: Normal A1c For Non Diabetic
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart For Diabetic Adults Age Wise
| Chart of Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetic Adults |
|---|
| Age |
| 100 to 140 mg/dL |
Healthy blood sugar levels in diabetic adults age wise:
Summary
Healthy diabetic adults should maintain a blood sugar level of 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after 2 hours of meals. Pregnant women should maintain a blood sugar level of 95-140 mg/dL to avoid complications. This can be done with the right habits in place that help you maintain your sugar level without getting stressed about it.
Controlling Blood Glucose Levels
Uncontrolled blood sugar can result in regular episodes of hyperglycemia . This can cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms are uncomfortable to experience but there are things you can do at home to reduce your blood sugar. In terms of drinks, water is the best as it will help to maintain hydration and dilute excess sugar in the blood. Also, try to add more fiber to your diet to reduce your blood sugar apples, bananas, oranges, and strawberries are all fibrous fruits.
However, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also lead to more severe, long term disease. Poorly managed diabetes leads to vision loss, kidney problems, nerve damage, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, if your blood sugar level reaches 16.7mmol/L, this could be dangerous and you need to seek immediate medical attention.
Read Also: Metformin How Long To Work
Achieving Normal Blood Sugar/blood Glucose Levels
For most people with diabetes, keeping blood sugar levels in check is all about being mindful of what and how much they eat and drink. Making healthy choices and watching portion sizes can help you control your weight and your blood sugar levels.
But dont worry, you dont have to navigate this road alone. When you have nutritionists who specialize in managing diabetes by your side, you can learn to choose the right foods, such as:
- Smart carbohydrates Instead of white or flour-based bread, rice or pasta, choose whole grains, barley, brown rice, non-starchy vegetables and fresh fruit. These foods can be efficiently converted to energy.
- Lean proteins Limit or avoid red meats and go for chicken, turkey, low-fat dairy, fish and shellfish.
- Healthy fats Skip the cream sauces, butter, lard and processed foods, and start cooking with canola or olive oil. Like to snack? Munch on nuts like almonds, cashews, pecans and peanuts.

