How Can Continuous Glucose Monitoring Help You Maintain Optimal Glucose Levels
It is not uncommon for your glucose levels to increase after a meal: you just ate food that may contain glucose, and now your body is working on getting it out of the bloodstream and into the cells. We know that we want to prevent excessive spiking of glucose levels because studies show that high post-meal glucose spikes over 160 mg/dl are associated with higher cancer rates. Spikes are also associated with heart disease. Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain. Additionally, the data shows that the big spikes and dips in glucose are more damaging to tissues than elevated but stable glucose levels. Therefore, you should strive to keep your glucose levels as steady as possible, at a low and healthy baseline level, with minimal variability after meals.
Keeping your glucose levels constant is more complicated than just following a list of eat this, avoid that foods. Each person has an individual response to food when it comes to their glucose levels studies have shown that two people can have different changes in their glucose levels after eating identical foods. The difference can be quite dramatic. One study found that some people had equal and opposite post-meal glucose spikes in response to the same food.
Blood Sugar Chart: Summary
The fasting blood sugar, 2-hour post-meal blood sugar, and HbA1C tests are important ways to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, as well as indicate how well a persons diabetes is being managed. If you think you have diabetes, its important to not try and diagnose yourself by doing a finger-stick with a home blood glucose meter. There are strict standards and procedures that laboratories use for diagnosing diabetes therefore, you should get tested at your doctors office or at a laboratory.
Its also important to talk with your doctor to make sure you understand a) how often you should have certain tests, such as a fasting blood glucose or HbA1C test b) what your results mean and c) what your blood sugar and HbA1C targets are.
If you have not been previously diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes but your results are above normal, your doctor may recommend other tests and should discuss a plan of treatment with you. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, a healthy eating plan, and regular physical activity. You may need to start taking diabetes medications, including insulin. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, its recommended that you learn how to check your blood sugars with a meter so that you and your healthcare team can determine how your treatment plan is working for you.
What Is The Meaning Of Fasting Blood Sugar
Fasting blood glucose: A test to determine how much glucose is in a blood sample after an overnight fast. Levels between 100 and 126 mg/dl are referred to as impaired fasting glucose or pre-diabetes. Diabetes is typically diagnosed when fasting blood glucose levels are 126 mg/dl or higher.
Subsequently, one may also ask, what is fasting blood sugar normal range?
Fasting blood sugar test.A fasting blood sugar level less than 100 mg/dL is normal. A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL is considered prediabetes. If it’s 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests, you have diabetes.
Beside above, what is a good blood sugar level in the morning? What we call fasting blood sugar or blood glucose levels is usually done six to eight hours after the last meal. So it’s most commonly done before breakfast in the morning and the normal range there is 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter.
Then, is fasting sugar 110 normal?
Until 2003, a fasting blood glucose level under 110 mg/dl was considered to be normal and fasting blood glucose in the range of 110 to 125 mg/dl indicated impaired fasting glucose , or prediabetes. A blood glucose level 200 mg/dl or higher two hours after the drink indicates diabetes.
How fasting blood sugar test is done?
You May Like Also
Don’t Miss: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Fasting Vs Nonfasting Blood Sugar
Fasting blood sugar is a test that measures blood sugar and is used to determine if an individual has diabetes. When a person takes this test, they are not to eat or drink for at least eight hours prior to the test. The results determine whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic.
The results are measured in milligrams per deciliter or mg/dL. The following results indicate whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
To test nonfasting blood sugar, an A1C test is administered to determine the average blood sugar level of an individual over a period of two to three months. There is no need to fast prior to taking this test. The following results indicate whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
- Normal: 5.7%
- Diabetes: 6.5%
Managing Blood Sugar When Youre Ill
When you get sick, your blood sugar levels may fluctuate and become unpredictable.
If youre sick, its very important that you:
- drink plenty of water or sugar-free fluids
- check your blood sugar levels more often than usual
- take 15 grams of carbohydrate every hour if you are not able to follow your usual meal plan
- replace food with fluids that contain sugar if you cant eat solid food
- continue to take your insulin or other diabetes medication
If you have a cold or flu and want to use a cold remedy or cough syrup, ask your pharmacist to help you make a good choice. Many cold remedies and cough syrups contain sugar, so try to pick sugar-free products.
As an extra precaution, you should always check with your health-care team about guidelines for insulin adjustment or medication changes during an illness.
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
What Is Normal Fasting Blood Sugar
Includes Diseases:Diabetes mellitus type 1
Then, what is a good blood sugar level in the morning?
What we call fasting blood sugar or blood glucose levels is usually done six to eight hours after the last meal. So it’s most commonly done before breakfast in the morning and the normal range there is 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter.
Similarly, is fasting sugar 110 normal? Until 2003, a fasting blood glucose level under 110 mg/dl was considered to be normal and fasting blood glucose in the range of 110 to 125 mg/dl indicated impaired fasting glucose , or prediabetes. A blood glucose level 200 mg/dl or higher two hours after the drink indicates diabetes.
Secondly, what is the normal range for blood sugar?
Normal blood sugar levels are less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least eight hours. And they’re less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. During the day, levels tend to be at their lowest just before meals.
What should your blood sugar be after fasting for 12 hours?
Fasting blood glucose measures blood glucose levels after a 12– to 14-hour fast. While levels normally decrease during fasting, they remain persistently high in people with diabetes. A fasting glucose value above 125 mg/dL on at least 2 tests indicates diabetes.
You May Like Also
Eat Healthy Foods And Follow A Regular Eating Schedule
Following a healthy diet as recommended by your diabetes team, watching portion sizes, and not skipping meals can help to prevent side effects like low blood sugar that can occur while taking glipizide. Notify your healthcare providers if you are not able to eat because you are sick or because you will be having a surgery or procedure done.
Don’t Miss: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Low Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar that is too low can cause symptoms such as:
- shaking and sweating
- headache
- tiredness
As with low blood sugar, high blood sugar may cause loss of consciousness or seizures if people leave them untreated. Persistent high levels can increase the risk of serious complications that doctors relate to diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Diabetics
The American Diabetes Association recommends that the blood sugar 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal be less than 180 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. This is typically the peak, or highest, blood sugar level in someone with diabetes. Again, this target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
Also Check: Is Raisin Bran Cereal Good For Diabetics
Who Should Do The Test
According to the American Diabetes Association, screening for diabetes is recommended in people over 45 , or at any age if you have certain risk factors, including :
- Being overweight, obese, or physically inactive
- Having a close relative with diabetes
- Belonging to a certain race/ethnic group
- Having signs of insulin resistance or conditions associated with insulin resistance, such as high blood pressure , low good cholesterol and/or high triglycerides , and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Having had diabetes in pregnancy
Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. Having prediabetes puts you at greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but participating in the program can lower your risk by as much as 58% .
Also Check: Can You Be Born With Type 1 Diabetes
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
Blood Sugar Level Chart
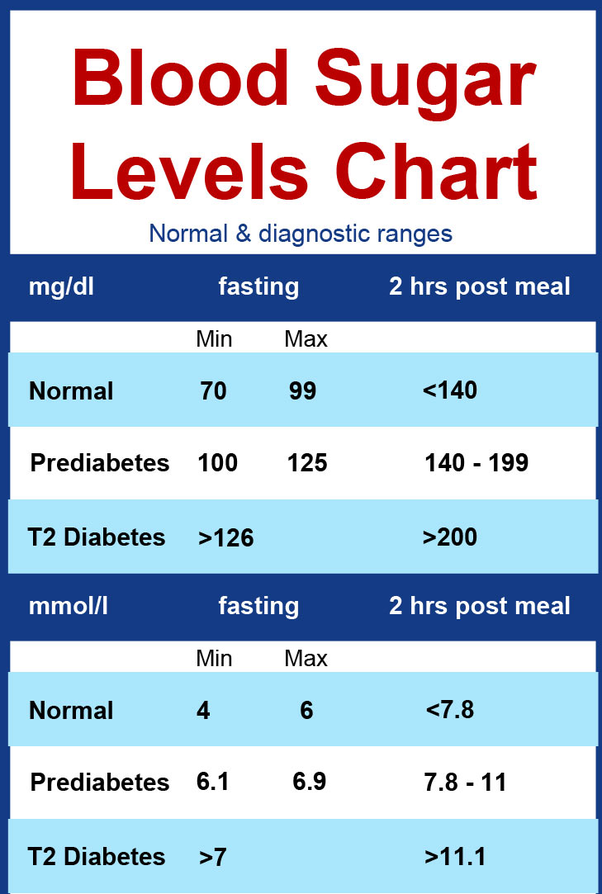
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = 7099 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 80130 mg/dl
Two hours after a meal
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 140 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = Below 180 mg/dl
HbA1c
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 5.7%
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 7% or less
**My Med Memo The measurement mmol is the abbreviation for millimole.
Read Also: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
Risks Of Abnormal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
As suggested earlier, the normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70-100mg/dl.
- If your blood sugar level is below 70mg/dl then you may have hypoglycemia or low blood sugar.
- A blood sugar level of 100 suggests prediabetes or borderline diabetes.
- A blood sugar of 120 mg/dl is an indication of diabetes.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Beyond Normal Goals: Whats An Optimal Glucose Level And Why Does It Matter
Exact numbers for what is considered optimal glucose levels to strive for while using CGM to achieve your best health are not definitively established this is a question that is individual-specific and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. With that said, research shows that there is an increased risk of health problems as fasting glucose increases, even if it stays within the normal range, making finding your optimal glucose levels all the more important.
While the International Diabetes Federation and other research studies have shown that a post-meal glucose spike should be less than 140 mg/dL in a nondiabetic individual, this does not determine what value for a post-meal glucose elevation is truly optimal for your health. All that number tells us is that in nondiabetics doing an oral glucose tolerance test, researchers found that these individuals rarely get above a glucose value of 140 mg/dL after meals.
So, while this number may represent a proposed upper limit of whats normal, it may not indicate what will serve you best from a health perspective. Many people may likely do better at lower post-meal glucose levels. Similarly, while the ADA states that a fasting glucose less than 100 mg/dL is normal, it does not indicate what value is optimal for health.
The following is a summary of insights from our review of research. You should consult with your doctor before setting any glucose targets or changing dietary and lifestyle habits.
What Abnormal Results Mean
If you had a fasting blood glucose test:
- A level of 100 to 125 mg/dL means you have impaired fasting glucose, a type of prediabetes. This increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A level of 126 mg/dL or higher usually means you have diabetes.
If you had a random blood glucose test:
- A level of 200 mg/dL or higher often means you have diabetes.
- Your provider will order a fasting blood glucose, A1C test, or glucose tolerance test, depending on your random blood glucose test result.
- In someone who has diabetes, an abnormal result on the random blood glucose test may mean that the diabetes is not well controlled. Talk with your provider about your blood glucose goals if you have diabetes.
Other medical problems can also cause a higher-than-normal blood glucose level, including:
- Weight loss after weight loss surgery
- Vigorous exercise
Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Before having the test, tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking.
For some thin young women, a fasting blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL may be normal.
Also Check: Banana And Diabetes Type 2
When To See A Doctor
If a persons blood sugar levels are high more than three times in a 2-week period without an apparent reason, the National Institute for Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases recommend that they seek medical help.
Any significant change in blood sugar patterns warrants a visit to a doctor. People with diabetes and those at risk of diabetes should also consult a doctor if:
- blood sugar levels become unusually high or low
- well-managed blood sugar levels are suddenly start fluctuating
- people have new or worsening symptoms of diabetes
- they change their medication or stop using it
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
Don’t Miss: Metformin And Low Blood Sugar

