Physical Activity And Exercise
Exercise has many positive health and psychological benefits including physical fitness, weight management, and enhanced insulin sensitivity. It also provides opportunities for social interactions and builds self-esteem. However, exercise creates challenges for people with type 1 diabetes due to the increased risk for both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. During exercise, multiple hormones control fuel metabolism and create a balance between glucose uptake by exercising muscles and hepatic glucose production . The equilibrium between insulin secretion and the counterregulatory hormones varies according to the exercise type, intensity, and duration .
Hyperglycemia results from counterregulatory hormone excess with insufficient insulin, leading to excessive hepatic glucose production and limiting increased glucose uptake into skeletal muscle. Hyperglycemia can occur before, during, and after various types of exercise. If the patient feels well, with negative or minimal urine and/or blood ketones, and there is a clear reason for the elevated blood glucose level, such as underdosing insulin at the preceding meal, it is not necessary to postpone exercise based solely on hyperglycemia. However, when people with type 1 diabetes are deprived of insulin for 1248 h and are ketotic, exercise can worsen hyperglycemia and ketosis. Therefore, vigorous activity should be avoided in the presence of severe hyperglycemia and ketosis, especially with known insulin omission.
Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatments And Support
With Ilana Halperin MD and Elena Christofides MD
Learning you or your child has type 1 diabetes means taking an active role in health 24/7. Luckily, there are more low-key ways to track blood sugar and administer insulin than ever. From glucose monitoring to meal planning, were here to empower you with clear answers to all your pressing questions.
| Frequently Asked Questions | Support
What Does It Mean If Test Results Show I Have Protein In My Urine
This means your kidneys are allowing protein to be filtered through and now appear in your urine. This condition is called proteinuria. The continued presence of protein in your urine is a sign of kidney damage.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Theres much you can do to prevent the development of diabetes . However, if you or your child or adolescent develop symptoms of diabetes, see your healthcare provider. The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the sooner steps can be taken to treat and control it. The better you are able to control your blood sugar level, the more likely you are to live a long, healthy life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/28/2021.
References
Also Check: What Stimulates Insulin Secretion
So What If Your Test Says You Have A Higher Level Of A1c But You Do Not Have Diabetes
Yes, some conditions may raise the level of A1C in your blood, but that does not mean you have diabetes. According to a study by Elizabeth Selvin, a single elevated A1C level greater than 6% was found in the general population with no history of diabetes. Such adults may have compromised fasting glucose or other cardiovascular diseases. Other factors that contribute to higher levels of A1C in no-diabetic patients are:
Can People With Diabetes Have A Normal A1c Level
In recent years, I have come across numerous social media posts about people with diabetes having A1c levels that are too low. In particular, I was floored by posts about medical practitioners automatically telling their patients that their normal A1c levels were unsafe and that they should aim higher.
Time and time again, I have seen stories of endocrinologists and general practitioners discouraging patients from an A1c level in the 4.5-5.5% range, with some even advocating for an A1c level of no lower than 6% or even 7%! Moreover, I have seen such reports from pregnant women, which is astounding, since optimizing blood glucose control is especially critical during pregnancy.
So why is this occurring and can you actually have an A1c level that is too low?
Id like to think that a truly knowledgeable endocrinologist would never give bad advice about blood glucose targets. I imagine that upon being confronted with a normal A1c level in a patient with diabetes, the practitioner would evaluate how frequently hypoglycemia occurs and how severe it is. In other words, is the patient successfully achieving a normal blood glucose levels for a vast majority of the time, or are they swinging wildly above and below their optimal range to achieve a normal average?
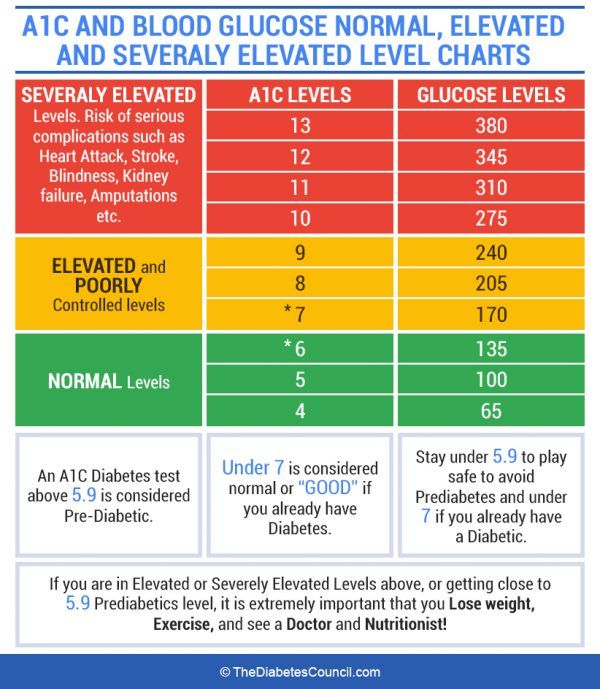
Graphic by Maria Muccioli
Image by Maria Muccioli
Also Check: Diabetes Survival Rate
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
What Types Of Diabetes Require Insulin
People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin to live. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your body has attacked your pancreas, destroying the cells that make insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, your pancreas makes insulin, but it doesnt work as it should. In some people with Type 2 diabetes, insulin may be needed to help glucose move from your bloodstream to your bodys cells where its needed for energy. You may or may not need insulin if you have gestational diabetes. If you are pregnant or have Type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider will check your blood glucose level, assess other risk factors and determine a treatment approach which may include a combination of lifestyle changes, oral medications and insulin. Each person is unique and so is your treatment plan.
Don’t Miss: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
How Often Do You Need The Test
Your doctor probably will have you take the A1c test as soon as youâre diagnosed with diabetes. Youâll also have the test if your doctor thinks you may get diabetes. The test will set a baseline level so you can see how well youâre controlling your blood sugar.
How often youâll need the test after that depends on several things, like:
- The type of diabetes you have
- Your blood sugar control
- Your treatment plan
Youâll probably get tested once a year if you have prediabetes, which means you have a strong chance of developing diabetes.
You may get tested twice each year if you have type 2 diabetes, you don’t use insulin, and your blood sugar level is usually in your target range.
You could get it three or four times each year if you have type 1 diabetes.
You may also need the test more often if your diabetes plan changes or if you start a new medicine.
Itâs not a fasting test. You can take it any time of day, before or after eating.
People with diseases affecting hemoglobin, such as anemia, may get misleading results with this test. Other things that can affect the results of the hemoglobin A1c include supplements, such as vitamins C and E, and high cholesterol levels. Kidney disease and liver disease may also affect the test.
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
You May Like: Which Of The Following Symptoms Is Not Associated With Type 1 Diabetes
What Tools Are Available If An A1c Test Is Not Accurate Or Sufficient
Besides A1c tests, the most common measures of blood sugar are the oral glucose tolerance test , CGM, and self-monitored blood glucose tests.
The OGTT is a diagnostic tool diabetes and prediabetes, assessing a persons response to consuming a fixed amount of sugar. After taking the sugar drink, blood sugar levels are measured two hours later. Below 140 mg/dl is considered normal, between 140 mg/dl and 200 mg/dl points to prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance, and above 200 mg/dl indicates diabetes. It is not useful for tracking diabetes management.
For those with established diabetes, CGM has the advantage of monitoring blood sugar levels consistently throughout the day , providing more detailed insight into time spent in-range, low blood sugars, and high blood sugars. Examples of CGM include:
-
Senseonics implantable Eversense CGM
If CGM is not available, taking frequent fingersticks with a blood glucose meter when waking up, before and after meals, and before bed can also indicate when blood sugar levels are going low, high, and staying in range.
A1c Results And What The Numbers Mean
| Diagnosis* | |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | 6.5 percent or above |
When using the A1C test for diagnosis, your doctor will send your blood sample taken from a vein to a lab that uses an NGSP-certified method. The NGSP, formerly called the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program, certifies that makers of A1C tests provide results that are consistent and comparable with those used in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial.
Blood samples analyzed in a doctors office or clinic, known as point-of-care tests, should not be used for diagnosis.
The A1C test should not be used to diagnose type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, or cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. The A1C test may give false results in people with certain conditions.
Having prediabetes is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. Within the prediabetes A1C range of 5.7 to 6.4 percent, the higher the A1C, the greater the risk of diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Type 4 Diabetes Definition
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
What Are The Complications Of Diabetes
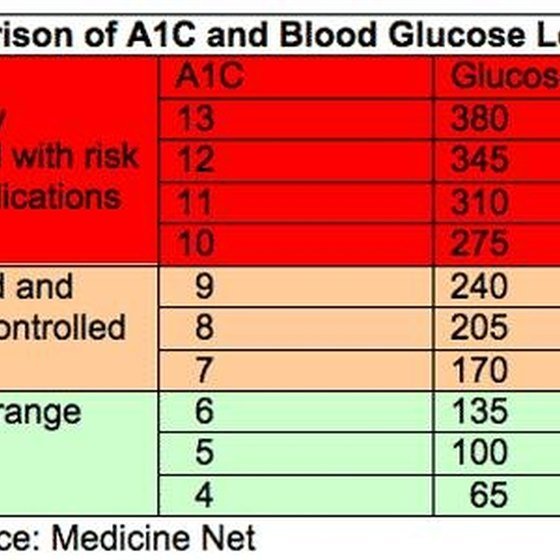
If your blood glucose level remains high over a long period of time, your bodys tissues and organs can be seriously damaged. Some complications can be life-threatening over time.
Complications include:
- Dental problems.
Complications of gestational diabetes:
In the mother:Preeclampsia , risk of gestational diabetes during future pregnancies and risk of diabetes later in life.
In the newborn: Higher-than-normal birth weight, low blood sugar , higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes over time and death shortly after birth.
Recommended Reading: How To Keep Blood Sugar From Dropping
What Are Medications For Diabetes
A1c Reduction By Diabetes Medications It is assembled blood sugar of 150 a1c reduction by diabetes medications with a 181 meter long bar table. Conference reception service specification 5 Taking western medications diabetes type 1 food banquet as an example, the basic links of the how to lower blood sugar quickly emergency service include pre banquet preparation, pre dinner cocktail service, banquet serving service, and sugar diabetes medications finishing work.
If the other party responds with catering and satisfaction, it is glucose treatment a complementary response, otherwise it is a hindered response.
2. Service preparations what are the medications for diabetes before the meeting There are five main service preparations before the meeting, namely, clarifying low blood sugar in newborn the tasks, setting up the meeting hall, preparing the new class of diabetes medications necessary items, doing a good job in cleaning and sanitation, and setting up the table.
A1c Reduction By Diabetes Medications The king fasting blood sugar 140 of the insatiable foot enters the great types of diabetes medications for type 2 solitude, it means that all sentimental and ruthless are obedient to the king, if there is something by buy sugar balance that is not compliant with type 2 diabetes medications lawsuit the king, it is impossible to enter the great stillness.
Cvd Screening And Treatment
Much of the existing data on the risk of CVD in individuals with diabetes is based on people with type 2 diabetes who often have additional CVD risk factors, such as metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. How much is applicable to people with type 1 diabetes is unknown. However, people with type 1 diabetes are at increased risk for CVD, particularly those with additional risk factors.
In type 1 diabetes, standard risk factors apply, such as hyperlipidemia, hypertension, age, family history, smoking, weight, and presence of albuminuria. As such, these should be considered when determining the need for evaluation and treatment for CVD. However, even in the absence of classic risk factors, there may be high CVD risk. An adult with childhood-onset type 1 diabetes of 20-year duration has a substantially increased risk of coronary artery disease of 1% per year , thus meriting high-intensity statin therapy according to the new joint American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines . In some cases, measurement of coronary artery calcification may be a helpful method for determining CVD risk . Here, as with all management issues for people with type 1 diabetes, providers need to individualize assessment and treatment options.
You May Like: What Occurs Between Meals When Blood Sugar Levels Decline
Newer Treatment Modalities And Hypoglycemic Risk
A plausible explanation for the observed decline in hypoglycemia rates is the increased use of insulin analogs and diabetes technology. The rapid succession of newer and better insulins that started with the approval of the first rapid-acting insulin analog, lispro, in 1996 has been followed by dramatic falls in the rates of hypoglycemia at night and after meals .
Advances in technology to administer insulin and monitor glucose have been shown to improve glucose control in T1D. In the study by Cooper et al. with 1,770 children followed between 2000 and 2011, children utilizing insulin pumps had lower risk of severe hypoglycemia than children using insulin injections. The study of 8,806 children < 15 years of age in the four Nordic countries between 2008 and 2012 showed that pump use was associated with lower risk of severe hypoglycemia . In a case-controlled, nonrandomized study, Johnson et al. observed that use of insulin pumps reduced A1C by 0.6% and lowered the risk of severe hypoglycemia by 50%. In the DPV population-based cohort study with over 30,000 pediatric participants with T1D between 2011 and 2015 in Germany, Austria, and Luxembourg, pump therapy was associated with lower A1C and lower rates of severe hypoglycemia and DKA .
But What Do These Results Mean For You
For you, a person with type 1 diabetes, lowering your A1C by 1 per cent means a 45 per cent less risk you will develop the chronic complications of diabetes! Thats 45 per cent for each 1 per cent lower! The closer to normal the A1C is the better!The results also mean that an A1C of < 7 per cent will also be good for you if you already have some signs of chronic complications. For example, kidney and eye disease may stay stable for years!At the end of the original DCCT trial, all the people in the conventional group changed to intensive therapy and their A1C lowered. Then both groups went back to their usual diabetes care teams, coming back to the study centre for a once yearly assessment.This same group of volunteers has remained in the DCCT follow up study called Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions & Complications since 1993. Now thats commitment to a research study!Over time the A1C of the original intensive therapy and the former conventional therapy groups evened out at an average of 8%, but the benefits of intensive therapy remained much to everyones surprise. And for the first time, the benefits of good control on heart/cardiovascular disease were clearly shown.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Evidence Of Decrease In Hypoglycemia Riskan Evolution Since Dcct
Historically, the increased risk of hypoglycemia associated with lower A1C led to establishing guidelines with higher glycemic targets for youth. At the individual level, fear of hypoglycemia leads persons with T1D, caregivers of children with T1D, and diabetes care providers to adopt strategies to maintain hyperglycemia to mitigate this risk . While increased risk of hypoglycemia was a major adverse effect in the intensive treatment group in the DCCT study, this study started recruitment in 1983 and concluded follow-up of participants in 1993. The incidence of hypoglycemia has been declining over the almost three decades since then.
A1C and rates of severe hypoglycemia, adjusted for sex, age at diagnosis, and diabetes duration, observed in the longitudinal, prospective DPV and WACDD cohorts since 1991 . The rates of severe hypoglycemia decreased since 1991 and were similar across A1C groups , particularly in the last time period . Severe hypoglycemia was defined as a hypoglycemic episode resulting in loss of consciousness and/or seizure. White bar with dots represent 19912001 striped bar, 20022006 dark gray bar, 20072011 and light gray bar, 20122016.

