How Can High Blood Sugar Levels In The Morning Be Controlled
Once you and your doctor determine how your blood sugar levels are behaving at night, he or she can advise you about the changes you need to make to better control them. Options that your doctor may discuss depend on the cause of the morning high blood sugars.
For dawn phenomenon:
- Changing the timing or type of your diabetes medications
- Eating a lighter breakfast
- Increasing your morning dose of diabetes medication
- If you take insulin, switching to an insulin pump and programming it to release additional insulin in the morning
For Somogyi effect:
How Is It Determined If The Dawn Phenomenon Or Somogyi Effect Is Causing The High Blood Sugar Levels
Your doctor will likely ask you to check your blood sugar levels between 2 a.m. and 3 a.m. for several nights in a row. If your blood sugar is consistently low during this time, the Somogyi effect is suspected. If the blood sugar is normal during this time period, the dawn phenomenon is more likely to be the cause.
Some additional clues that the Somogyi effect may be the cause include nightmares, restless sleep and overnight sweating as these are all signs of low blood sugar levels.
Does Blood Sugar Rise If You Dont Eat
Skipping a meal is typically no big deal. But if youre a person with diabetes, skipping meals or a lack of meal structure could result in dangerously low or high blood sugar levels. It is important to know your numbers especially when taking certain medications to lower blood sugar levels. 4
Recommended Reading: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Eat Each Day
If My A1c Is Normal My Glucose Is Good
An A1C result thatâs below 5.7% is normal âs standards, but having a result below that number isnât the end of the story. Pregnancy, hemoglobin variants, anemia, liver disease, and certain medications can cause inaccurate A1C results.
Additionally, the A1C test is measuring your average glucose value over the past 3 months, but averages inherently do not capture highs and lows. So, you could have a normal average while also having abnormal glucose spikes. The A1C test should only supplement your regular blood sugar testing, not replace it completely.
How Do I Know If I’m At Risk
Testing your urine with a urine test strip will reveal the presence of ketones in your urine high levels of these chemicals are a potential signal of diabetic ketoacidosis. Your doctor will tell you when you should perform the test, but the ADA says that, in general, you may want to check your urine for ketones when your blood sugar levels hit more than 240 mg/dL.
Other symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis include nausea, difficulty breathing, an altered mental state and a fruity odor on the breath.
“In our clinic, if a person has blood sugar levels of over 300 mg/dL, we will check for urine ketones,” says Susan Spratt, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine. “If their blood sugar levels are over 300 mg/dL and certainly over 400 mg/dL we’re concerned that they may be going into diabetic ketoacidosis.”
If your urine test reveals that ketones are present, call your doctor, who can give you further instructions. You may need to go to the emergency room to seek treatment right away. The ADA says that if you have ketones present in the body, you shouldn’t exercise. In this case, exercise can cause your blood sugar levels to spike even higher.
Warning
Don’t Miss: A1c Range For Non Diabetic
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
When the body doesn’t have enough insulin, glucose stays in the blood and can’t get into the body’s cells to be used for energy. This can happen, for example, when someone skips doses of insulin or when the need for insulin suddenly increases and the doses are not adjusted.
When the body can’t use glucose for fuel, it starts to use fat. When this happens, chemicals called ketones are released into the blood. Some of these ketones, like extra glucose, pass out of the body through the urine.
High levels of ketones in the blood can be a problem because they cause the blood to become acidic. Too much acid in the blood throws off the body’s chemical balance and causes the symptoms listed below. In people with diabetes, this problem is called diabetic , or DKA. DKA is a very serious condition that can lead to coma or death if it’s not treated. The good news, though, is that it’s preventable and can be treated.
DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but can sometimes also happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome : A Complication Of Severe Hyperglycemia In Type 2 Diabetes
In people with type 2 diabetes, extreme hyperglycemia can lead to a very rare but serious condition called hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome, or HHNS). HHNS is most likely to occur when you’re sick particularly if you aren’t able to drink enough fluids or keep fluids down. It happens most often in elderly people and, like ketoacidosis, can result in a coma.
You May Like: What Type Of Hormone-receptor Action Allows Insulin To Move Glucose Into Cells
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Many people with diabetes must check their blood sugar levels daily with a glucose meter. This device takes a drop of blood, usually from a finger, and displays the sugar level within a few seconds.
People with type 1 diabetes will need to take insulin as their doctor recommends, usually several times a day.
Those with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes may need to change their diet and exercise habits. They may also need to take oral medications or insulin.
A number of strategies can help prevent hyperglycemia.
People should:
- check their blood sugar levels as their doctor advises and take the correct amount of insulin, if they have type 1 diabetes
- speak to their healthcare provider or dietitian about which foods to eat or avoid, how much to eat, and how often
- take precautions to avoid infections, for example, through regular hand washing, as illness, such as a cold, can trigger a rise in blood pressure
- plan their food intake and exercise to balance blood sugar levels
- minimize stress, as far as possible, for example, through exercise, getting enough sleep, and stress-reducing activities such as meditation or yoga
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can happen when a person:
- has certain medical conditions
- does a lot of exercise
- skips meals or eats too little
It can also be a side effect of diabetes medicines. Taking too much insulin can result in low blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
- visit a doctor regularly
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Children
Younger than 6 years oldmg/dL
| Bedtime | 100-140 |
Adults who are 20 years or older will have blood sugar levels that range between less than 100-180 mg/dL over the course of a day. When you wake up in the morning, your fasting blood sugar should be at its lowest because you havent consumed food for about eight hours. If youre an adult and struggling with glucose control, your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan to manage your blood sugar better.
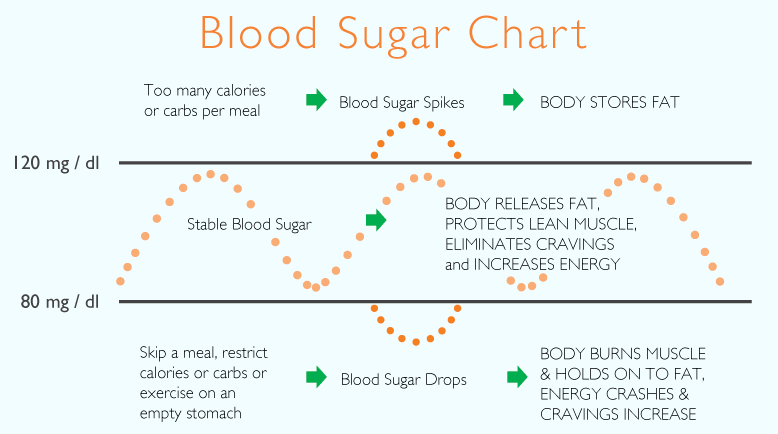
Blood glucose levels outside the ranges listed above are categorized as either high or low blood sugar. Blood sugar levels are considered high if theyre over 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL within one to two hours after a meal. Many people wont start to experience symptoms from high blood sugar until their levels are at 250 mg/dL or higher. The highest blood sugar level thats considered safe will depend on the person and whether they have diabetes, but will typically be between 160 to 240 mg/dL.
Don’t Miss: Hypoglycemia Turning Into Diabetes
Carbohydrates And Blood Sugar
When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood.
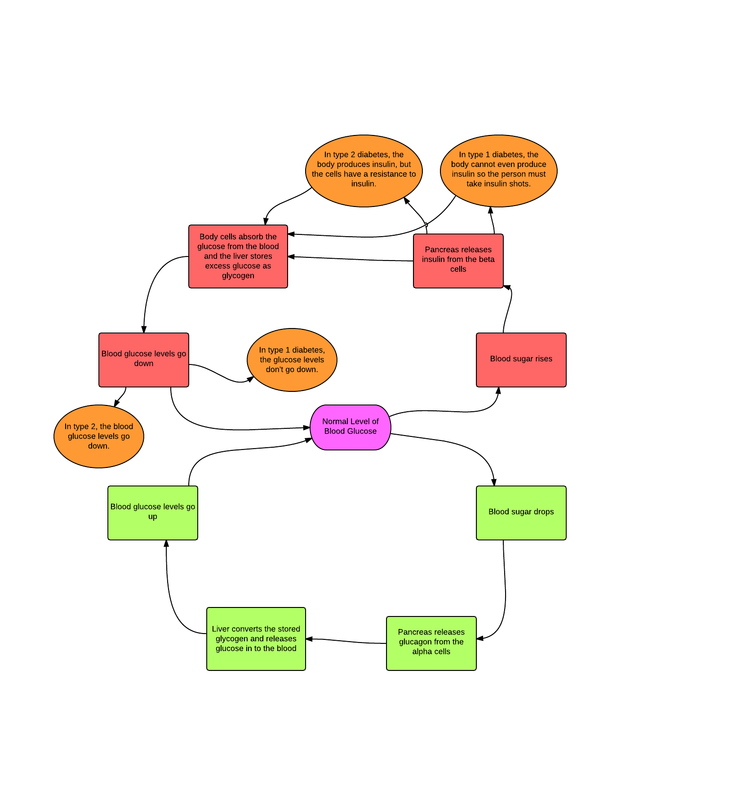
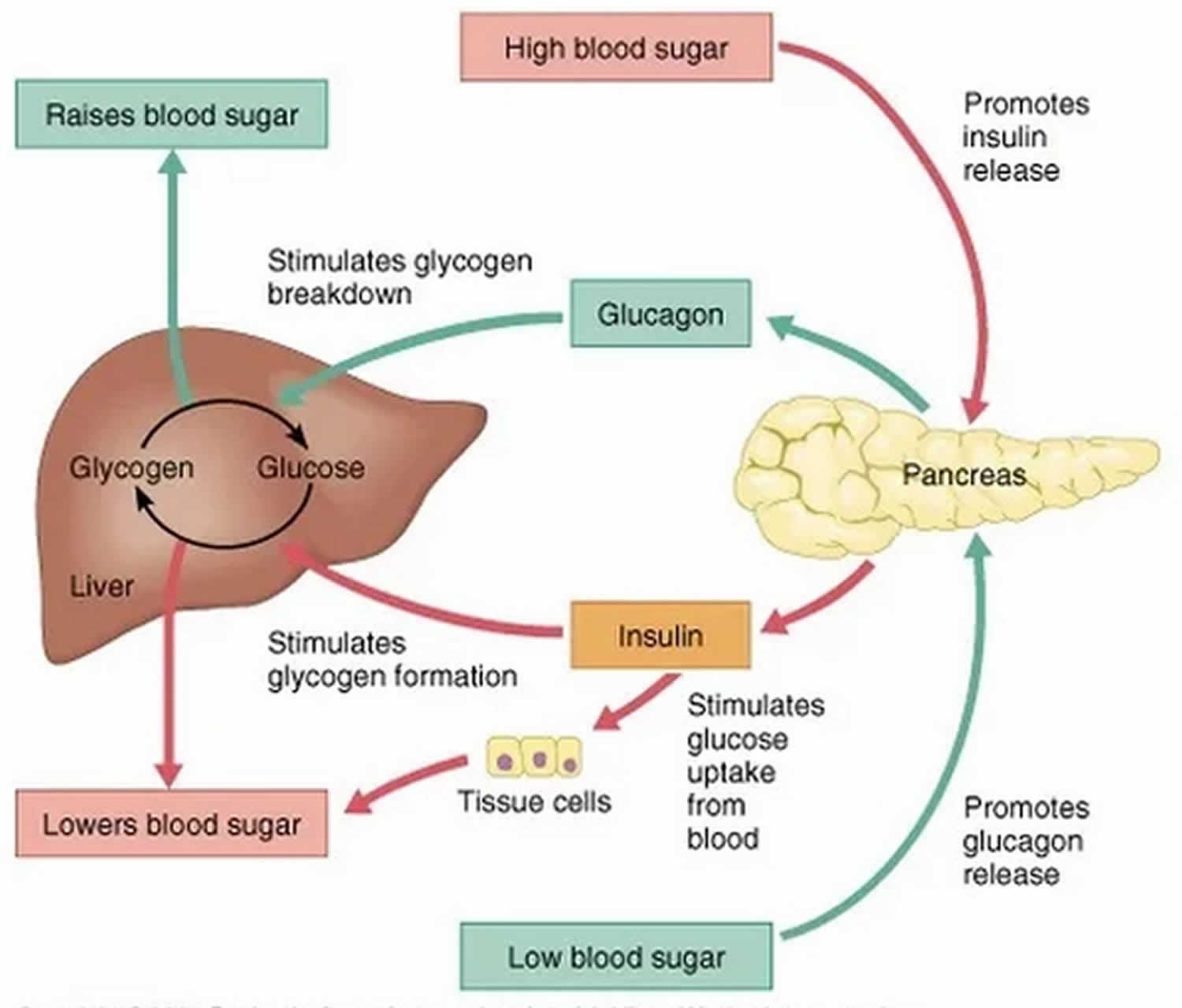
- As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage.
- As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fall.
- When this happens, the pancreas start making glucagon, a hormone that signals the liver to start releasing stored sugar.
- This interplay of insulin and glucagon ensure that cells throughout the body, and especially in the brain, have a steady supply of blood sugar.
Carbohydrate metabolism is important in the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body cant make enough insulin or cant properly use the insulin it makes.
- Type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually over a number of years, beginning when muscle and other cells stop responding to insulin. This condition, known as insulin resistance, causes blood sugar and insulin levels to stay high long after eating. Over time, the heavy demands made on the insulin-making cells wears them out, and insulin production eventually stops.
What Is The Dawn Phenomenon
Dr. Parilo explains that its a natural surge of hormones produced by your body growth hormone, cortisol, adrenaline, and others typically between 2 and 8 a.m.
People without diabetes can handle this extra hormonal activity. But if you have diabetes, dawn phenomenon can suppress production of the hormone insulin, which is essential for controlling blood sugar. Insulin enables sugar, or glucose, to enter cells to fuel the body.
When less insulin enters your bloodstream, the level of sugar in your blood is more likely to rise. About half of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes experience this morning increase in blood sugar.
About half of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes experience this morning increase in blood sugar.
Also Check: List Of Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Type 2
Causes Related To Lifestyle
Physical inactivity
Exercising prompts your body to burn more energy than usual, and, as a result, consume more glucose. Maintaining a low level of physical activity, on the other hand, means more glucose will remain in the bloodstream. This raises your overall blood glucose values in the process.
Exercise also makes our body more insulin sensitive, which means we will require less insulin for the rest of the day to control glucose levels.
Stress
Part of the bodyâs fight-or-flight response to stress is to produce additional glucose. Another facet of that response is an increase in the hormone cortisol. High cortisol can reduce the bodyâs sensitivity to insulin. As a result, blood glucose levels may also increase.
Poor sleep
A lack of quality sleep can inhibit how much insulin your body can release. It can also cause the production of cortisol, which makes it harder for insulin to work. When your bodyâs insulin cannot properly metabolize the glucose in your blood, the glucose remains there and your glucose levels rise.
Get better insight into your glucose levels
Want to gain a better understanding of how your body responds to glucose? Try monitoring your glucose levels in real time with the Nutrisense Continuous Glucose Health Program.
Diabetes Medication That Can Help You Control Your Blood Sugar
If youve been diagnosed with diabetes, your doctor will likely discuss medication options to help bring your blood sugar down. If you have prediabetes, on the other hand, youll probably rely on diet and lifestyle changes to help stabilize your numbers, though in some cases, you may need medication, Dodell says.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is treated with emergency insulin and fluids administered intravenously. But the goal with blood sugar control is to prevent this type of medical emergency from happening in the first place. If your blood glucose readings are consistently higher than usual, you may not be getting enough insulin. Talk to your doctor about adjusting your dosage. You should also tell them about any other prescription or over-the-counter medication you take, as these could affect your blood sugar, too. Corticosteroids for inflammation are just one example.
Read Also: Average Dosage Of Metformin
Hyperglycemia: What Happens If Your Blood Sugar Is Too High For Too Long
Hyperglycemia means high blood sugar, and is one of the defining characteristics of diabetes, and means that the body does not make or use insulin properly. The body needs glucose to function properly, as the cells rely on it for energy. Glucose comes from the foods that are eaten. Fruit, milk, potatoes, bread, and rice are all carbohydrates and the biggest sources of glucose in a normal diet. The carbohydrates are broken down into glucose and then transported to the cells through the bloodstream.
Make Some Small Changes
You might try to get more exercise, or limit carbs at your next meal, but don’t go crazy. “One blood sugar that’s high doesn’t indicate a need for major changesthat should only be done on a pattern,” says Rice, such as “continuing highs despite following a doctor’s instructions.” If a pattern continues for two to three days or more, then you might want to let your health-care provider know.
Also Check: Metformin Interactions With Supplements
Blood Sugar Spike Symptoms
Learning to recognize the symptoms of hyperglycemia can help you keep your diabetes in control. Some people with diabetes immediately feel the symptoms of high blood sugar, but others go undiagnosed for years because their symptoms are mild or vague.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia typically begin when your blood glucose goes above 250 milligrams per deciliter . Symptoms get worse the longer you go untreated.
Symptoms of a blood sugar spike include:
- frequent urination
Headaches And Difficulty Concentrating
Acute hyperglycemia can cause headaches and difficulty concentrating in a fashion similar to polyphagia in which starving cells send out hunger signals because they cant access the glucose circulating in the blood.
Your brain is the biggest glucose hog around. If you dont believe it, consider that while the brain represents about 2 percent of your body weight, it devours fully 25 percent of the glucose you consume. And when brain cells have difficulty getting the fuel they need, they function poorly. This can cause problems with thinking, reasoning, and remembering, difficulty staying focused on tasks, and headaches.
Chronic high blood glucose can also lead to headaches, but by a different route. These headaches are often related to various types of nerve damage. Examples include occipital neuropathy, or damage to the optic nerve from elevated glucose levels, and a variety of diabetic mononeuropathies, which can affect specific cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, or nerve roots all of which can lead to headaches of varying intensities.
Read Also: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
How Do I Prevent Hyperglycemia
- Exercise to help lower blood sugar. Work with your healthcare provider to make a daily activity plan.
- Follow your meal plan if you have one. Learn how carbohydrates impact your blood sugar, and work with your diabetes care team to find the best meal plan for you.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Dont smoke.
- Limit drinking alcohol. Alcohol can raise blood sugar levels, but can also cause dangerously low blood sugar levels. Work with your provider to determine how much is safe to drink.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/12/2020.
References
Also Check: What Are The First Signs Of Diabetes
Sick Day Rules For Diabetes
Developing sick day rules is an important part of diabetes management and can help you recover from sickness. Talk to your healthcare provider and share any concerns you may have about properly caring for yourself during times of illness. This includes sicknesses like the common cold and flu and infections, as well as physical stress related to any surgeries and times of heightened emotional stress.
Recommended Reading: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Eat A Day
Eat As You Normally Would
Your diabetes diet is designed to help you manage your blood glucose and keep you feeling well. You should do your best to continue eating as you normally would, even when you dont feel well. Consuming carbohydrate-rich drinks and snacks can help you prevent having low blood sugar .
Eating normally means:
- Consuming the same types and combinations of foods you generally eat
- Balancing your meals as you typically do, whether thats by the plate method, carb counting, or another plan
- Eating the same quantity of food during meals and snack times
Avoiding High Blood Sugar And Dka
No matter how well they take care of themselves, people with diabetes will sometimes have high blood sugar levels. But the best way to avoid problems is to keep your blood sugar levels as close to your desired range as possible, which means following your diabetes management plan. Checking your blood sugar levels several times a day will let you know when your blood sugar level is high. Then you can treat it and help prevent DKA from happening.
High blood sugar levels don’t always cause symptoms, and a person who isn’t testing regularly might be having blood sugar levels high enough to damage the body without even realizing it. Doctors may use the HbA1c test to find out if someone has been having high blood sugar levels over time, even if the person has not had obvious symptoms.
Here are some other tips for avoiding high blood sugar levels and preventing DKA:
- Try to eat all your meals and snacks on time and not skip any.
- Take the right amount of insulin.
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly and your ketone levels when your diabetes management plan recommends it.
- Stick to your diabetes management plan.
Don’t Miss: How Much Metformin Is Fatal
How Does Lack Of Sleep Raise Your Risk
Itâs hard to know for certain. Many studies have suggested that short sleepers have irregular eating habits, snack more, and are more likely to eat unhealthy foods.
Other research has found that shortchanging sleep can directly affect how the body makes other hormones, which in turn affect blood sugar. For example, when you stay up late, your body makes more of the hormone cortisol, which affects how insulin works.
Also, growing evidence shows that disrupting your bodyâs biological clock by being awake at night can make your cells more resistant to insulin. In one study, researchers altered the circadian rhythms of 16 healthy volunteers by allowing only 5 hours of sleep each night for 5 nights, much like a sleep-deprived workweek. When those volunteers ate food at night — a time when the body isnât biologically prepared for a spike in blood sugar — their bodies didnât use insulin normally.

