What Happens With Diabetes
With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt produce insulin, which is a hormone that helps cells in your body absorb glucose from your blood. Without insulin, the cells cant absorb sugar properly, and your blood sugar levels get too high. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin to survive.
With type 2 diabetes, cells in your body become resistant to the effects of insulin. This means they dont absorb sugar from your blood as well as they should. As a result, your blood sugar levels can start to get too high. Over time, your pancreas can also stop producing insulin. If that happens, you need to take insulin to help manage your blood sugar.
Taking Mealtime Insulin When You Cant Eat
Flu, , and food reactions can all make it hard to eat. Work with your doctor on a mealtime insulin schedule for when youre sick. Often, doctors recommend continuing the same schedule as if you were eating. Your insulin dose may even increase. Check your blood sugar levels often and keep the lines of communication open with your doctor, especially if you feel your levels are uncontrolled.
Heres the big takeaway: mealtime insulin for diabetes isnt just about the medication itself. It requires some education and planning, but it also helps keep controlling your blood sugar levels at the top of the priority list. Keep in mind you and your doctor chose your current diabetes treatment plan because you both felt it was the best one for you. Stay confident in your ability to see it through, but if its simply not working out, have an honest conversation with your doctor about that, too. Your doctor will have tips and strategies for sticking to mealtime insulin and can work with you to make adjustments if you need. If you take mealtime insulin as prescribed, learn how to make up for missed doses, consistently refill your prescription, and be honest with your doctor, youll be in control of your blood sugar levels and your .
How To Cope With Side Effects
What to do about:
- cold-like symptoms – try taking paracetamol or ibuprofen regularly for a few days. If the symptoms return when you stop taking the painkillers, ask your doctor for advice.
- headaches – make sure you rest and drink plenty of fluids. Do not drink too much alcohol. Ask your pharmacist to recommend a painkiller. Talk to your doctor if they last longer than a week or are severe.
- stomach ache or indigestion – tryto restand relax. It can help to eat and drink slowly and have smaller and more frequent meals. Puttingaheat pad or covered hotwater bottle on yourtummymay also help. If you’re in a lotof pain, speakto your pharmacistor doctor.
- diarrhoea – drink lots of fluids, such as water or squash, to avoid dehydration. Signs of dehydration include peeing less than usual or having dark strong-smelling pee. Do not take any other medicines to treat diarrhoea without speaking to a pharmacist or doctor.
- rash or itchy skin – it may help to take an antihistamine, which you can buy from a pharmacy. Check with the pharmacist to see what type is suitable for you. If your rash gets worse or lasts for more than a week, make an appointment to see your doctor.
Read Also: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Missed An Insulin Shot
Take for example the case of a juvenile with diabetes. As such, adolescence is turbulent with hormonal changes, the transition to adulthood, and peer pressure. A child in this stage needs much more support in terms of treatment compliance.
For parents of such patients, the horror of a missed insulin shot is unimaginable. Reasons stated by children for intentionally skipping insulin shots were that it was an interference in their activities, it was an embarrassment, or rarely had injection-related issues.
When it comes to skipping the shot unknowingly, the reasons commonly stated were oversleeping, forgetting, and not carrying the injection kit along with them.
Is insulin pump an answer for this? Talk to our expert diabetologists to consider this option!
Facts about missing insulin injections.
|
|
Patients often are clueless about the next course of action after missing out on an insulin injection. Do I have to compensate for the missed injection by taking another shot? Do I just take it easy and wait for the nest dosage?
What Happens If I Miss A Dose Of Insulin

Using insulin exactly as instructed by your doctor is vital to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, so you should try not to miss a dose. If you vary the dose or schedule of taking this medication, your blood sugar may become either too low or too high, both of which can be very dangerous. Ask your doctor for specific instructions if you miss or delay a dose.
Don’t Miss: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
How To Take Tresiba
You should take Tresiba according to your doctors or healthcare providers instructions.
Tresiba is taken as a subcutaneous injection . Youll usually take it once a day. When you first get your Tresiba prescription, your healthcare provider or pharmacist will explain how to inject the medication.
Step-by-step instructions for giving an injection using the Tresiba FlexTouch pen or the Tresiba vial are provided in the leaflet that comes with your medication. Theres also a step-by-step instruction video for using the FlexTouch pens on the manufacturers website.
Youre Forgetting Your Dose Because You Have Too Many Pills To Take Each Day
If youre missing doses because you just have too many pills to take each day and its difficult to keep track of them, see a doctor to discuss your options.
Your doctor may be able to prescribe a combination pill that contains multiple medications. This will reduce the number of pills you have to take each day.
It can be difficult to keep track of your medications, especially if you take multiple drugs to manage type 2 diabetes and other health conditions. Here are a few tips and tricks to help you remember to take your medication.
- Organize your medications in pill boxes with separate compartments for each day of the week.
- Set reminders on your smart phone or other smart device.
- Log your medication on a chart attached to a wall or your refrigerator, or on a phone app. Search your app store for medication reminders.
- Take your medications at the same time each day while you do another routine habit, like brushing your teeth, making breakfast, or at bedtime.
- Leave your pill box on the bathroom counter in plain sight.
- Ask for help from a friend or family member.
You should also ask your doctor if taking the oral diabetes medication with a meal will reduce GI side effects. Fewer side effects can help you stick to your treatment regimen.
Also Check: Obesity And Diabetes: Pathophysiology
How To Monitor Your Insulin & Glucagon Levels
Although you canât directly monitor your insulin and glucagon levels at home, you can monitor your glucose levels with a continuous glucose monitor , providing you with the data you need to understand if there is a problem with these hormones.
Continuous glucose monitoring enables you to track your glucose levels in real-time. It can help you to identify if your glucose levels are significantly high or low and take the right steps to find out why. Wearing a CGM helps you take charge of your metabolic health and make positive changes to ensure your glucose levels remain stable.
It can seem a bit daunting to start monitoring your own glucose levels, but the NutriSense Continuous Glucose Health Program simplifies it. It provides you with a CGM, accompanying CGM phone app, and personalized support from Registered Dietitians to help you decipher your data. If you have any concerns about your glucose levels, why not give it a try?
When Do I Take Rapid
You should inject rapid-acting insulin no more than 15 minutes before you eat. Your doctor will tell you how much insulin to inject. Remember, you should not wait more than 15 minutes to eat after you take this insulin shot.
Rapid-acting insulin can be more convenient to take than regular insulin. With regular insulin, you inject the insulin and then wait 30 to 60 minutes before eating. Many people find it hard to time their meals around regular insulin injections. Sometimes they end up eating too soon or too late. Then they dont achieve the best blood sugar control. Since rapid-acting insulin is taken so close to mealtime, it may help you control your blood sugar more effectively.
Read Also: Hypoglycemia And Prediabetes
Detrimental Combination Of Hyperinsulinemia With Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is defined as an attenuated effect of insulin on blood glucose homeostasis, primarily by less efficient export of glucose from the blood into skeletal muscle, adipose, and liver tissue. Permanently elevated insulin concentrations in the blood are often considered as an attempt to overcome insulin resistance. Indeed, induction of insulin resistance by genetic disruption of insulin signaling, as well as by increased growth hormone levels or an inflammatory milieu, causes hyperinsulinemia . The opposite causality is of more relevance. Hyperinsulinemia during insulin infusion in humans leads to systemic insulin resistance , while in vitro, high ambient insulin concentrations cause an increase in insulin resistance in isolated adipocytes . A summary analysis of nine studies in rodents and seven trials in humans confirmed that the first detectable change in the fasting state, after feeding a high caloric diet for several days, is an increase of basal insulin concentrations, but not of blood glucose concentrations or insulin resistance . Both increased secretion of insulin by ß cells and decreased insulin clearance in the liver contribute to elevated insulin levels post-meal, the latter being of primary importance in the case of carbohydrate-rich food .
Fig. 4Fig. 5
You can also search for this author inPubMed
Who Can And Cannot Take Alogliptin
Alogliptin can be taken by adults .
Alogliptin is not suitable for some people. To make sure it’s safe for you, tell your doctor if you:
- have had an allergic reaction to alogliptin or any other medicines in the past
- have kidney disease or liver disease
- have heart failure
- have problems with your pancreas
- are pregnant or breastfeeding, or trying to get pregnant
This medicine is not used to treat type 1 diabetes .
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Elevated Insulin Concentrations Impair Cellular Functionsinsulin Toxicity
There is ample evidence that transient increases of metabolic or immune mediator levels are benign physiological responses to biochemical challenges, such as the rise of systemic glucose or cytokines following meals. However, chronic elevations of such mediators, even when modest in amplitude, are usually detrimental to cellular functions . In the case of glucose, the term glucose toxicity was coined to describe this phenomenon . Prolonged conditions of elevated glucose concentrations cause dysfunction of numerous cell types in the body, including beta cells, neurons, and the endothelium, via several pathways, including increased oxidative stress and activation of the sorbitol pathway . As described below, there seems to be a similar detrimental outcome of long-term elevated insulin concentrations on cellular functions, a corresponding term would be insulin toxicity.
Fig. 3
Articles On Type 1 Diabetes Complications
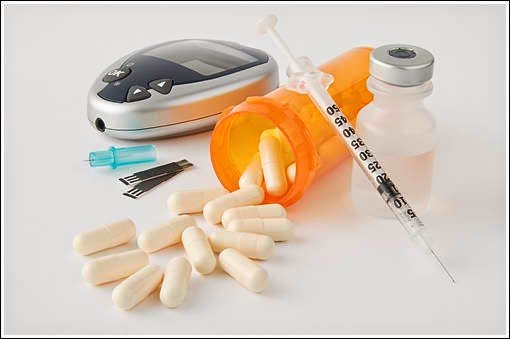
Cold sweats, trembling hands, intense anxiety, a general sense of confusion — these are signs of low blood sugar. Your doctor may call it hypoglycemia. It often happens when you take too much insulin.
Hypoglycemia happens to many people with diabetes. It can be serious. Thankfully, most insulin problems can be avoided if you follow a few simple rules.
Read Also: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Do Rotate The Place Where You Inject Insulin
Try not to inject your insulin in the same exact place on your body every time. This is to prevent a condition called lipodystrophy. In lipodystrophy, the fat under the skin either breaks down or builds up and forms lumps or indentations that can obstruct insulin absorption.
Instead, rotate injection sites. The best places for injecting insulin are your abdomen, front or side of thighs, upper buttocks, and upper arms due to their higher fat content. Each injection should be at least two inches from the previous site. Try not to inject too close to your belly button or into any moles or scars.
For mealtime insulin, its best to consistently use the same part of the body for each meal. For example, you can inject in your stomach prior to breakfast, your thigh prior to lunch, and your arm prior to dinner.
Clean your skin with cotton dipped in alcohol or an alcohol pad before you inject yourself. Wait 20 seconds for the area to dry before you inject. This helps avoid infections.
You should also wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water before you handle any needles.
Dont Wait More Than 15 Minutes To Eat After Taking A Mealtime Insulin
Rapid-acting insulins were designed to be taken right before you eat to help you control your blood sugar more effectively.
As the name suggests, rapid-acting insulin starts to work rapidly in the bloodstream. If you wait too long to eat, your blood sugar can actually end up getting too low. This puts you at risk for hypoglycemia.
If, for some reason, you cant eat a meal after youve already taken your mealtime insulin, you should carry around glucose tablets, juice, non-diet soda, raisins, or hard candies to avoid hypoglycemia.
Calculating the right dose of mealtime insulin can be complicated at first, especially if you dont know how many carbohydrates youre going to be eating at your next meal.
Try not to panic if you realize you took too much or too little insulin.
If you think youve taken too much insulin, eat some rapidly-absorbed carbs, like juice or glucose tabs. Also, you may want to call your doctor.
If youve taken a lot more than you need , have a friend or family member get you to a hospital. You may need to be observed for severe low blood sugar.
If you think youve taken too little insulin, or you completely forgot to take it at all before your meal, measure your blood sugar. If it gets too high, you may need to take a short or rapid-acting insulin as a corrective measure to lower your blood glucose levels. If youre at all unsure about the dose, seek advice from your doctor or diabetes care team.
Don’t Miss: Acceptable A1c Levels
What Is High Blood Sugar
The is the amount of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a sugar that comes from the foods we eat, and its also formed and stored inside the body. Its the main source of energy for the cells of our body, and its carried to each cell through the bloodstream.
Hyperglycemia is the medical word for high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels happen when the body either cant make insulin or cant respond to insulin properly . The body needs insulin so glucose in the blood can enter the cells of the body where it can be used for energy. In people who have developed diabetes, glucose builds up in the blood, resulting in hyperglycemia.
Having too much sugar in the blood for long periods of time can cause serious health problems if its not treated. Hyperglycemia can damage the vessels that supply blood to vital organs, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve problems. These problems dont usually show up in kids or teens who have had the disease for only a few years. But they can happen in adulthood in some people with diabetes, particularly if they havent managed or controlled their diabetes well.
Blood sugar levels are considered high when theyre above your target range. Your diabetes health care team will let you know what your target blood sugar levels are.
page 1
How To Prevent Insulin Overdoses
- Take care when calculating meal time insulin. Taking an extra couple of minutes to be sure of your dose will save the time and hassle of an overdose.
- Never be tempted to delay your meal or snack if you have injected.
- Dont inject whilst doing other tasks, such as watching the TV, holding a conversation or performing another task as this raises the chance that you may forget your injection has been done. Concentrate solely on giving the injection
- Be careful of injecting insulin when you are hypo as mistakes are more likely to be made. Ideally, ensure your blood glucose has risen to safe levels and then put in your scheduled insulin dose.
- Ask for help if you have difficulty seeing the numbers or gradations on your insulin pen or syringe. See also our page on diabetes and visual impairment which lists a number of injection aids for people that have visual impairments
- Nightmares or crying out during sleep
Severe hypoglycemia from an insulin overdose can lead to:
- Being unable to talk, chew, or swallow
- Losing consciousness because your brain isnt getting the glucose it needs to function
- Seizures because your brain isnt getting the glucose it needs to function
- Death because every part of your part requires glucose in order to function
Recommended Reading: What Is The One Food That Kills Diabetes

