How Does Insulin Help Glucose Get Into The Cells
The carbohydrates in the foods we eat are broken down into sugars which enter the bloodstream. The body releases insulin in response to the blood glucose. Insulin opens up the cells to allow the glucose to enter, thus providing nutrients and energy to the body.
In diabetics, however, there’s not enough insulin or else the cell receptors don’t respondas they normally would. In either case, the glucose cannot enter the cells.
Due to this impaired function in the body, diabetics need tocontrol their blood sugar levels through a combination of things. First, a healthy and nutritious diet with “diabetes-friendly”foods and regular meal times will help. Second, if you’re overweight, a weight lossof even just 10 or l5 pounds can help because it reduces insulinresistance. Third, a regular exercise program can help you feel better while also improving your body’s response to insulin control cholesterol and high blood pressure and improve circulation.
For some people, these lifestyle measures are enough to control diabetes without the need for medication.This isn’t always the case, though if these measures are not enough, diabetesmedicine or insulin may be prescribed by your doctor. These should be taken as prescribed even if you think you feel well enough to skip them. All of these steps can help to improve how your body reacts to insulin and help to move glucose into your body’s cells.
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
In dogs, diabetes mellitus is caused by the failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar. This is insulin dependent diabetes mellitus . This type of diabetes usually results from destruction of most or all of the beta-cells that produce insulin in the pancreas. As the name implies, dogs with this type of diabetes require insulin injections to stabilize blood sugar levels.
How Do You Take Insulin Without A Syringe
- Insulin pens look like large writing pens and can help prevent under- and overdosing. They also dont require refrigeration, are conveniently prefilled, and are more durable than syringes.
- Insulin pumps are attached to a thin tube thats implanted under your skin. Pumps are computerized or motorized, and some models also act as glucose monitors. They deliver insulin before each meal along with small amounts through the course of the day. In the US, about 60% of people with diabetes use some form of insulin pump.
- Jet injection devices are a good option if you hate needles. A jet injector holds several doses of insulin. After placing it against your skin, you press a button, and the insulin is pushed through.
- Inhalable insulin comes in a premeasured inhaler and was first approved in 2014. Its short-acting and usually not covered by insurance, which makes it more cost prohibitive than other types of insulin for most people with diabetes.
Unless you have an insulin pump that also works as a glucose monitor, insulin dosing is based on self-monitoring your blood glucose levels. You can check them by doing finger pricks or wearing a device that continuously monitors them for you.
Recommended Reading: High Blood Sugars Symptoms
Insulin Is Produced By The Beta Cells Of The Pancreas Glucagon By The Alpha
Both insulin and glucagon are produced in the pancreas, and more specifically in what are known as islets of Langerhans, clusters of cells that are especially abundant in the tail and body of the pancreas. Even so, the cell type that produces them are different. While insulin is synthesized by the beta cells of these islets, glucagon is produced by the alpha cells..
Insulin And Type 1 Diabetes
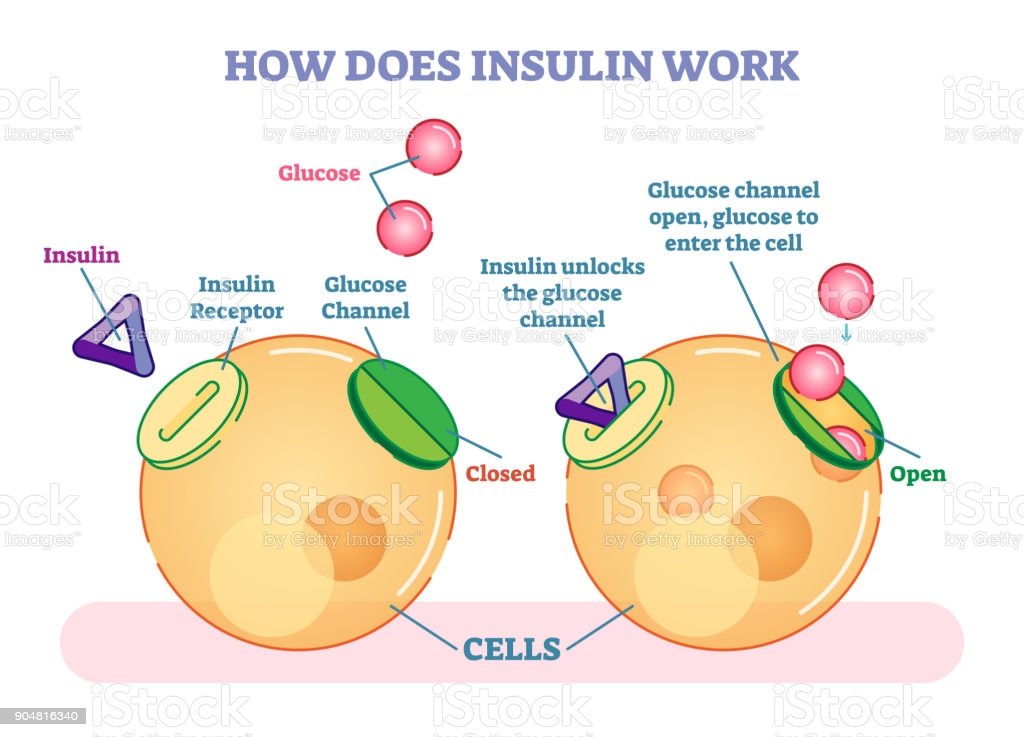
In type 1 diabetes, the body produces insufficient insulin to regulate blood glucose levels.
Without the presence of insulin, many of the bodys cells cannot take glucose from the blood and therefore the body uses other sources of energy.
Ketones are produced by the liver as an alternative source of energy, however, high levels of the ketones can lead to a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis.
People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin to compensate for their bodys lack of insulin.
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Stopping Diabetes Medication
What Are Alternative Medications For People With Diabetes That Arent Insulin
- Metformin a pill that stops sugar production in the liver
- Glitazones pills that remove sugar from the bloodstream
- Sufonylureas and glinides pills that increase the release of insulin from your pancreas
- Starch blockers pills that slow starch absorption
- Incretin therapies and amvlin analogs pills and injections that reduce sugar production in the liver and slow food absorption. Types of the former include DPP4 inhibitors and GLP1 analogs .
- SGLT2 inhibitors pills that are taken before meals that prevent the reabsorption of glucose
Measurement Of Insulin And Insulin Resistance
There are a variety of approaches to the laboratory assessment of insulin resistance. Over the years the limited specificity of older radio-immunoassays that cross-react with proinsulin have reduced the credibility of measuring insulin resistance in clinical settings. Current assays have improved specificity and precision. A comprehensive review of insulin assays is beyond the scope of this review and the reader is encouraged to consult Sapin in this regard. Insulin resistance may be measured by looking directly at insulin mediated glucose uptake in the basal or post-stimulated state, by inference from the relative concentrations of glucose and insulin, or by looking at surrogate markers of insulin action.
You May Like: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Insulin Lowers Glucose Levels Glucagon Increases Them
The most important difference and, without a doubt, the one with which we must stay. Both are hormones that regulate blood sugar levels, but in their role they are antagonists. Insulin is produced and released at times of hyperglycemia, when blood glucose is high, in order to reduce blood sugar levels.
Instead, glucagon is produced in just the opposite scenario. In times of hypoglycemia , when blood glucose is too low, glucagon stimulates blood sugar levels to increase so that the cells have fuel at their disposal. what do you need.
Exercise & Physical Activity
Since Chauveu & Kaufmans remarkable observation in 1887 that When a horse chews on hay the concentration of glucose in the blood draining its masseter muscle substantially decreases a large body of evidence supports the role of exercise in improving insulin sensitivity and its beneficial outcomes in insulin resistant states. Epidemiological studies such as the US Physicians Health Study have reported substantial decreases in the relative risk of type 2 diabetes with lifelong regular physical activity. Large scale randomised controlled clinical trials such as the Diabetes Prevention Program and the Finnish Prevention Study demonstrate a 58% reduction in progression of impaired glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes by intensive lifestyle modification which included a minimum of 2030 minutes of exercise per day. Acute exercise increases GLUT 4 translocation to sarcolemmal membrane, whereas chronic exercise training increases Glut 4 mRNA expression. In addition to this insulin-dependent mechanism, enhanced glucose uptake into exercising muscle occurs by multiple insulinin dependent mechanisms. Exercise training appears to enhance insulin sensitivity by increased post-receptor insulin signalling increased insulin-mediated glucose transport appears to be related to enhanced signal transduction at the level of IRS proteins and PI 3-kinase.
You May Like: Maximum Daily Dose Of Metformin
What Are The Different Types Of Insulin
The American Diabetes Association characterizes insulin by how fast it works. But everyones body is different. If you have diabetes, you should expect deviations in the amount of time any medication takes to reach your bloodstream.
Here are 8 different types of Insulin and how they work.
- Onset is defined as the length of time before insulin hits your bloodstream and begins to lower blood glucose.
- Peak is the time during which insulin is at its maximum effectiveness at lowering your blood glucose levels.
- Duration is the length of time insulin continues to lower your blood glucose levels.
- Rapid-acting insulin begins to affect blood glucose approximately 15 minutes after injection. It peaks in about an hour, and then continues to work for a few more.
- Short-acting insulin reaches your bloodstream within 30 minutes of injection. It peaks in the 2-3-hour range and stays effective for 3-6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting insulin includes NPH insulin which helps control glucose for 10-12 hours. A protamine is a type of protein that slows the action of this insulin.
- Long-acting insulin enters the bloodstream 1-2 hours after injection and may be effective for as long as 24 hours. An advantage to long-acting insulin is there is no pronounced peak, and it works more like typical pancreatic insulin.
- Premixed/combination insulin contains a mix of rapid- or short-acting insulin combined with an intermediate-acting insulin. This eliminates the need to draw insulin from more than one bottle.
Symptoms Of Insulin Resistance
You can’t tell that you have insulin resistance by how you feel. You’ll need to get a blood test that checks your blood sugar levels.
Likewise, you wonât know if you have most of the other conditions that are part of insulin resistance syndrome without seeing your doctor.
Some signs of insulin resistance include:
- A waistline over 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Glucaphage
So What Affects My Blood Sugar Levels
It is important to understand what can make your blood sugar rise or fall, so that you can take steps to stay on target.
Things that can make blood sugar rise include:
- A meal or snack with more food or more carbohydrates than usual
- Inactivity
- Changes in hormone levels, such as during menstrual periods
- Stress
Pharmacological Influences On Insulin Action And Insulin Resistance
A wide range of pharmacological agents have been associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Antihypertensive agents such as diuretics and -blockers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, nicotinic acid and antipsychotic agents have been reported to impair glucose tolerance, as have the anti-retroviral protease inhibitors used to treat human immunodeficiency virus infection. The mechanisms vary -blockers impair insulin secretion from the pancreas by blockade of -adrenoceptors, thiazide diuretics are thought to act by depleting potassium levels, corticosteroids and oral contraceptives have counter-regulatory hormonal activity, and the HIV-1 protease inhibitors result in partial lipodystrophy with loss of peripheral subcutaneous fat and accumulation of truncal adipose tissue leading to insulin resistance.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Disadvantages Of Using A Diabetes Insulin Pump
Although there are many good reasons as to why using an insulin pump can be an advantage, there are some disadvantages.
The disadvantages of using an insulin pump are that it:
- Can cause weight gain
- Can cause diabetic ketoacidosis if your catheter comes out and you dont get insulin for hours
- Can be expensive
- Can be bothersome since you are attached to the pump most of the time
- Can require a hospital stay or maybe a full day in the outpatient center to be trained
There are pluses and minuses to using an insulin pump. Even though using an insulin pump has disadvantages, most pump users agree the advantages outweigh the disadvantages.
Getting Started With An Insulin Pump
Once you have talked with your diabetes care team and have become comfortable with all of the options on your insulin pump, you and your team will need to do the following in order to get you started.
Don’t Miss: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
The Relationship Between Insulin And Potassium
Shortly after insulin was discovered, scientists revealed that insulin had something to do with the potassium levels in both the cells and in the blood. The insulin is the hormone in the body that keeps the potassium level in the blood within the normal range. When insulin is decreased, the potassium level rises and can rise even further if you eat something high in potassium, such as salt substitutes and bananas.
When the potassium level is high, it causes the pancreas to release insulin in order to counteract the effects of high potassium levels. When you eat something that is high in potassium, the potassium enters the blood stream, increases the potassium level, stimulates insulin to be released, and then is put into the cells along with glucose. When all of this works normally, most of the potassium in the body is inside the cells and very little of it is circulating in the bloodstream.
Patients with diabetes often have high potassium levels. Type 1 diabetics have extremely low levels of insulin secreted by the pancreas and are at risk for having hyperkalemia . Without the insulin, the potassium cannot enter the cells and more of the potassium is allowed to float around in the blood.
Other research, however, disputes this and indicates that the uptake of glucose doesnt have to be related to the uptake of potassium, even though both require adequate amounts of insulin in order to be put into the cells.
What Is Insulin What About Glucagon
Before going in depth and analyzing the most important differences between these hormones synthesized by the pancreas, it is interesting that we put ourselves in context and understand, individually, the physiological bases and functions of each of them. So lets see what is insulin and what is glucagon.
Read Also: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Have In One Day
Insulin Basics: How Insulin Helps Control Blood Glucose Levels
Insulin and glucagon are hormones secreted by islet cells within the pancreas. They are both secreted in response to blood sugar levels, but in opposite fashion!
Insulin is normally secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas. The stimulus for insulin secretion is a HIGH blood glucose…it’s as simple as that! Although there is always a low level of insulin secreted by the pancreas, the amount secreted into the blood increases as the blood glucose rises. Similarly, as blood glucose falls, the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreatic islets goes down.
As can be seen in the picture, insulin has an effect on a number of cells, including muscle, red blood cells, and fat cells. In response to insulin, these cells absorb glucose out of the blood, having the net effect of lowering the high blood glucose levels into the normal range.
Glucagon is secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreatic islets in much the same manner as insulin…except in the opposite direction. If blood glucose is high, then no glucagon is secreted.
When blood glucose goes LOW, however, more and more glucagon is secreted. Like insulin, glucagon has an effect on many cells of the body, but most notably the liver.
What Does Insulin Do In My Body
Diabetes mellitus , often referred to as diabetes, is characterized by high blood glucose levels that result from the bodys inability to produce enough insulin and/or effectively utilize the insulin. Diabetes is a serious, life-long condition and the sixth leading cause of death in the United States. Diabetes is a disorder of metabolism . There are three forms of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that accounts for five- to 10-percent of all diagnosed cases of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes may account for 90- to 95-percent of all diagnosed cases. The third type of diabetes occurs in pregnancy and is referred to as gestational diabetes. Left untreated, gestational diabetes can cause health issues for pregnant women and their babies. People with diabetes can take preventive steps to control this disease and decrease the risk of further complications.Continue reading > >
Read Also: Does Metformin Make You Hungry
The Insulin Resistance Syndrome
The insulin resistance syndrome describes the cluster of abnormalities which occur more frequently in insulin resistant individuals. These include glucose intolerance, dyslipidaemia, endothelial dysfunction and elevated procoagulant factors, haemodynamic changes, elevated inflammatory markers, abnormal uric acid metabolism, increased ovarian testosterone secretion and sleep-disordered breathing. Clinical syndromes associated with insulin resistance include type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, essential hypertension, polycystic ovary syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, certain forms of cancer and sleep apnoea.
What Are Normal Glucose Levels
Depending on how much glucose is in a bodys system, blood sugar levels might be normal, high, or low. It is a simple sugar that is always present in the bloodstream. When someone fasts, eats, or has eaten, normal blood glucose levels can be monitored.
Adults without diabetes with a fasting blood glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL have a normal blood glucose level. Two hours after eating, a normal level for persons without diabetes is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Maintaining your blood sugar levels in the normal range is crucial for your body to function properly and healthily. Diabetes patients must keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels. A safe range before eating is 90130 milligrams per deciliter . It should be less than 180 mg/dL after an hour or two.
Blood sugar levels might trigger a variety of causes. The following are some examples of triggers:
- Heavy meal
Also Check: What Do Diabetics Eat

