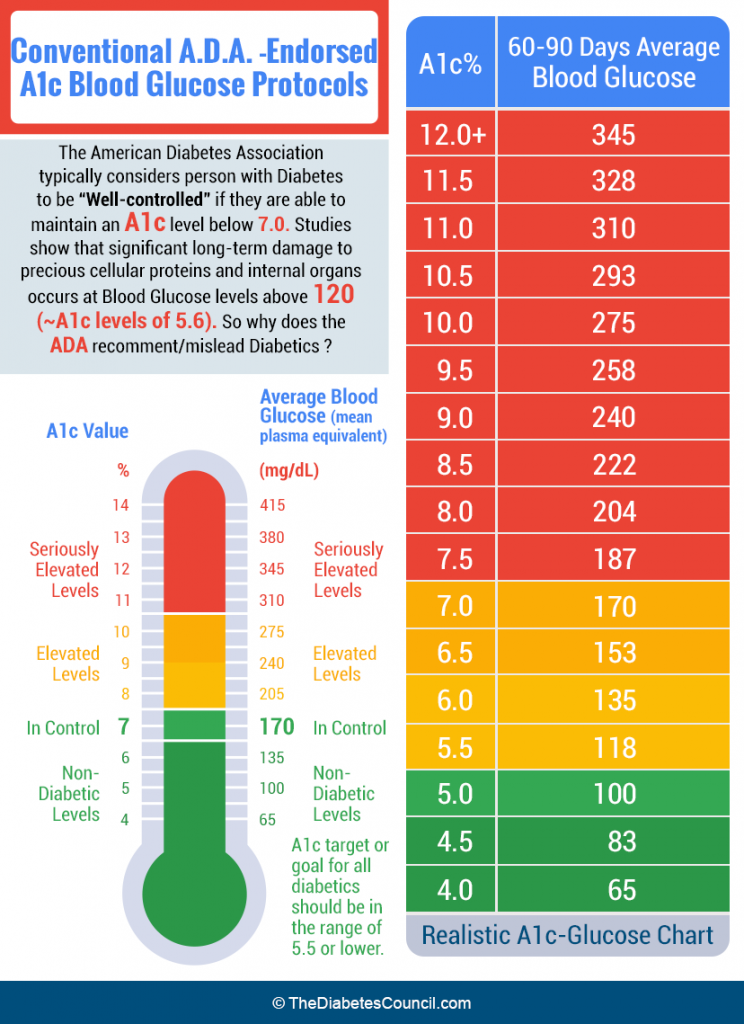
What Are Normal A1c Levels For People Who Don’t Have Diabetes
Generally, high A1c values indicate high average blood sugar levels and that a person might be at risk for or may have diabetes. The American Diabetes Association has established the following cutoffs:
|
A1c Level |
|
|
Prediabetes, meaning at risk for developing type 2 diabetes |
|
|
6.5% or greater |
Diagnosed diabetes |
Make sure you get a regular A1c test, especially if you think you might be at risk for diabetes.
How Does Age Affect A1c
A1c is a measure of diabetes management, so your A1c won’t naturally shift as you get older. However, as you age your diabetes management strategies and A1c goals may change for example, younger people may be more focused on reducing long-term health complications, while older people may concentrate on avoiding severe lows. Talk with your healthcare professional if you’re curious about how your age may affect your A1c levels.
Back To The Basics: What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Nurse Practitioner, NorthBay Center for Diabetes & Endocrinology So, what is your number? As someone with diabetes, do you ever find yourself comparing your number with your friends or family members who also have diabetes? What should that number be and what does it mean? What is an A1C? This is a blood test that measures your average blood sugar control for the past three months. It shows how well your blood sugars have been controlled over time. How often should this be measured? It should be measured every three months if your blood sugar is not at goal. Why the fuss about A1C numbers? Lowering the A1C makes a difference in diabetes management. Just a small drop in your Hemoglobin A1C number say by 1 percent — can mean a 37 percent lowering of your risk of diabetes problems that affect the small blood vessels, in the eyes, kidneys and nerves, for example. What should my A1C be? This is an individual target that is best set with you and your health care provider. For many years the recommendation has been a Hemoglobin A1C of 7 percent or less. However, recent studies suggest that the best recommendation is an individual goal, taking into consideration many factors, such as your age, associated diabetes complications and your risks of having low blood sugars. These are all important factors to consider when setting your personal A1C goal. For more information regarding the blood test A1C go to:Continue reading > >
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Prediabetes Diagnosis As An Older Adult: What Does It Really Mean
- By A. Enrique Caballero, MD, Contributor
As our bodies age, the risk of type 2 diabetes increases. It is estimated that 25% of adults older than 65 have type 2 diabetes, while half of people over 65 have prediabetes. We know that having type 2 diabetes as an older adult requires proper lifestyle, and sometimes medications, to control the disease and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, but the implications of having prediabetes at this age are not totally clear.
How Often Do You Need To Take An A1c Test
If your blood sugar levels have remained stable, the American Diabetes Association recommends getting the A1C test two times each year. If your therapy has changed or you are not meeting your glycemic targets, the ADA recommends getting the test four times per year. This simple blood draw can be done in your doctor’s office.
The A1C test results provide insight into how your treatment plan is working, and how it might be modified to better control the condition. Often your blood sample is sent out to a lab for your results though some doctors can use a point-of-care A1C test, where a finger stick can be done in the office, with results available in about 10 minutes. Such an in-office test can be used to monitor your condition.
Nonetheless, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases notes that point-of-care tests should not be used for diagnosis, which can only be done by lab tests certified by the NGSP. Any results pointing to a change in your health should be confirmed by conventional lab tests.
RELATED: 9 Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Out of Control
Also Check: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
Medication And Regular Monitoring
A1C is an important tool for managing diabetes, but it doesnt replace regular blood sugar testing at home. Blood sugar goes up and down throughout the day and night, which isnt captured by your A1C. Two people can have the same A1C, one with steady blood sugar levels and the other with high and low swings.
If youre reaching your A1C goal but having symptoms of highs or lows, check your blood sugar more often and at different times of day. Keep track and share the results with your healthcare provider so you can make changes to your treatment plan and medications if needed.
What Does An A1c Of 61 Mean
An A1C of 6.1 means that you have prediabetes, which puts you at risk for developing diabetes.
The A1c test measures blood sugar over the last three months by looking at the percentage of hemoglobin saturated with sugar. An A1c of 6.1 means that 6.1% of the hemoglobin in your blood are saturated with sugar.
While there are no signs or symptoms of prediabetes, the damage diabetes can have on your heart, blood vessels and kidneys may have already begun.
A score of 6.1 doesnt automatically mean that you will get diabetes. However, you should focus on reducing your A1c score and improving your overall health.
Don’t Miss: Which Blood Glucose Lowering Hormone Is Produced By The Pancreatic Islet Cells
What Is A Dangerous Level Of A1c
When levels rise to 9.0, the risk of kidney and eye damage and neuropathy increases. Some people who are newly diagnosed could have levels over 9.0. Lifestyle changes and possibly medication can lower levels quickly. For someone who has long-standing diabetes, levels rise above 9.0 could signal the need for a change in their treatment plan.
Some labs estimate average blood glucose , which corresponds to home glucose meter readings , allowing patients to understand the results better.
What Is A1c And Why Is It Used
A1c estimates a persons average blood sugar levels over a 2 to 3-month span. It is the best measure we have of how well blood glucose is controlled and an indicator of diabetes management.
Though A1c doesnt provide day-to-day information, keeping A1c low has been proven to lower the risk of microvascular complications like kidney disease , vision loss , and nerve damage . The relationship between A1c and macrovascular complications like heart disease is harder to show in clinical trials, but having high blood sugar is a major risk factor for heart disease.
A1c is usually measured in a lab with routine blood work, or with a countertop machine in a doctors office using a fingerstick.
A1c measures the quantity of glycated hemoglobin, which refers to sugar attached to a red blood cell protein called hemoglobin. The number is reported as a percentage of the total hemoglobin in the blood. If a person consistently has higher blood glucose levels over time, A1c levels go up because more red blood cells are coated with sugar. The test is representative of a 2 to 3-month average because once a red blood cell becomes coated with sugar, the link is irreversible. It is only when the red blood cell is “recycled” that the sugar coating disappears.
Recommended Reading: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Accurate Are A1c Tests
A1C levels rise well before the clinical onset of diabetes, making early diagnosis possible according to the 2017 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes by the American Diabetes Association . Sometimes, however, in the early stages of diabetes, blood sugar levels are not high enough to show up as problematic. Testing environments, such as temperature in the lab, equipment used, and handling of samples, can affect the results however, this is more common in the fasting plasma glucose and the OGTT than in the A1C. Strict quality controls and advancements in testing have made the A1C test more precise than in the past, according to the NIDDK. Doctors should be aware of laboratories that use an NGSP-certified method of testing for A1C levels. The NIDDK warns that blood samples taken at home or analyzed in a healthcare providers office should not be used for diagnosis.
There are some health conditions and situations that might skew the results of the test. These include:
- Anemia
- Dialysis
- Blood loss or blood transfusions
Also, the test can be unreliable for people of African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian descent, people with a family member with sickle cell anemia, and those with thalassemia. For those who fall into these groups, a healthcare provider might suggest a different test or a specialized A1C.
Follow The Diabetes Treatment Plan Your Healthcare Team Recommends
Diabetes treatment is very individualized, noted an article published in May 2014 in Diabetes Spectrum. After all, factors including how long youve lived with the disease, your socioeconomic status, and any other conditions youre living with can play a role in the best treatment approach for you.
Your healthcare team will help you determine the steps you need to take to successfully manage diabetes. Always talk to your doctor before making any changes, such as starting a very-low-carbohydrate diet or beginning a new exercise regimen, and especially before making any medication or insulin changes.
RELATED: 6 Top Diabetes Exercise Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Also Check: How Much Can Metformin Lower A1c
Ways To Lower Your A1c
A1C is a blood test that shows how well your diabetes management plan is working. Here’s how to reach a healthy A1C number and avoid diabetes complications.
For some, home blood sugar testing can be an important and useful tool for managing your blood sugar on a day-to-day basis. Still, it only provides a snapshot of whats happening in the moment, not a full picture of whats happened in the long term, says Gregory Dodell, MD, assistant clinical professor of medicine, endocrinology, diabetes, and bone disease at Mount Sinai Health System in New York City.
For this reason, your doctor may occasionally administer a blood test that measures your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. Called the A1C test, or the hemoglobin A1C test, this provides another lens on how well your type 2 diabetes management plan is working.
Hemoglobin A1c Not Reliable In Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes
With Maria Mercedes Chang Villacreses, MD, and Elena Christofides, MD, FACE
The test that doctors most often rely on to detect a persons risk for prediabetes and type 2 diabetesthe hemoglobin A1c blood testtoo often delivers a poor reading, thereby missing the diagnosis in nearly three out of four at-risk individuals,1 according to research presented at the Endocrine Society meeting in New Orleans, Louisiana.
The investigators compared the accuracy of the A1c test with the other screening method used to assess patients risk of diabetesthe oral glucose tolerance test to arrive at this startling conclusion.1
The common use of the hemoglobin A1c test to screen for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes should be skipped in place of more reliable tests. Photo: 123rf
“The A1c missed almost 73% of the people with diabetes in comparison to the oral glucose tolerance test,” says Maria Mercedes Chang Villacreses, MD, a clinical endocrinology fellow at the City of Hope Diabetes and Metabolism Research Institute in Duarte, California, who introduced the findings at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society but are considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed medical journal.
Since the fasting blood test requires a person to fast, the OGTT measures the body’s response to sugar it requires a person to fast overnight. First, blood is taken, then the person drinks a sugary drink. Blood is taken again two hours later.
You May Like: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin is a protein that sits inside red blood cells and is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout your body. Interestingly, hemoglobin can also attach to glucose traveling in your blood, and that hemoglobin-glucose combination is known as glycosylated hemoglobin, hemoglobin A1C, or HbA1C. The higher your blood sugar levels are, the higher your hemoglobin A1C levels will be.
Large Trial Compared Usual Tools For Assessing For Diabetes In Adults
The researchers looked at data from 9,000 adults, ages 20 years and older, from the 2005-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey . The information collected by the research team included body weight and blood test results.
Based on the fasting blood glucose test and the OGTT, 765 patients were diagnosed as having type 2 diabetes . However, only about 27% of these individuals were classified as having diabetes based on their A1c levels, which is how Dr. Villacreses and her team determined that nearly three-quarters of those at risk for diabetes were not aware that they had this chronic disease, and therefore were not receiving treatment.1
“Most worrisome, 73 % of patients would have missed out on early intervention and treatment,” she tells EndocrineWeb. While the A1c test is convenient, ”we recommend that we do not rely solely on this number,” Dr. Villacreses says.
The guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes from the American Diabetes Association already advise against relying solely on A1c,3 she says. While the American Diabetes Association guidelines specify that diabetes can be diagnosed based on fasting plasma glucose , the OGTT, or the A1c, our findings confirm that reliance on A1c remains the least reliable method for assessing diabetes risk.
You May Like: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
What Does Hba1c Mean
HbA1c is whats known as glycated haemoglobin. This is something thats made when the glucose in your body sticks to your red blood cells. Your body cant use the sugar properly, so more of it sticks to your blood cells and builds up in your blood. Red blood cells are active for around 2-3 months, which is why the reading is taken quarterly.
A high HbA1c means you have too much sugar in your blood. This means youre more likely to develop diabetes complications, like serious problems with your eyes and feet.
Knowing your HbA1c level and what you can do to lower it will help you reduce your risk of devastating complications. This means getting your HbA1c checked regularly. Its a vital check and part of your annual review. Youre entitled to get this test at least once a year. But if your HbA1c is high or needs a little more attention, itll be done every three to six months. It’s really important not to skip these tests, so if you haven’t had one in over a year contact your healthcare team.
Once you know your HbA1c level, its important that you understand what the results mean and how to stop them from getting too high. Even a slightly raised HbA1c level makes you more at risk of serious complications, so get all the facts here and be in the know about HbA1c.
What Is An A1c Test
The hemoglobin A1c test tells you your average level of blood sugar over the past 2 to 3 months. It’s also called HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin test, and glycohemoglobin. Itâs a lot like a baseball player’s season batting average. A single game doesn’t tell you how a player is performing in their career. And 1 day’s test results don’t give you the complete picture of how your treatment is working.
People who have diabetes need this test regularly to see if their levels are staying within range. It can tell if you need to adjust your diabetes medicines. The A1c test is also used to diagnose diabetes.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Blood Glucose Levels Move Up And Down
Your results can vary because of natural changes in your blood glucose level. For example, your blood glucose level moves up and down when you eat or exercise. Sickness and stress also can affect your blood glucose test results. A1C tests are less likely to be affected by short-term changes than FPG or OGTT tests.
The following chart shows how multiple blood glucose measurements over 4 days compare with an A1C measurement.
Blood Glucose Measurements Compared with A1C Measurements over 4 Days
The straight black line shows an A1C measurement of 7.0 percent. The blue line shows an example of how blood glucose test results might look from self-monitoring four times a day over a 4-day period.
Whole Blood Donation Affects The Interpretation Of Hemoglobin A1c
Abstract Several factors, including changed dynamics of erythrocyte formation and degradation, can influence the degree of hemoglobin A1c formation thereby affecting its use in monitoring diabetes. This study determines the influence of whole blood donation on HbA1c in both non-diabetic blood donors and blood donors with type 2 diabetes. In this observational study, 23 non-diabetic blood donors and 21 blood donors with type 2 diabetes donated 475 mL whole blood and were followed prospectively for nine weeks. Each week blood samples were collected and analyzed for changes in HbA1c using three secondary reference measurement procedures. Twelve non-diabetic blood donors and 10 blood donors with type 2 diabetes had a significant reduction in HbA1c following blood donation . All non-diabetic blood donors with a normal ferritin concentration predonation had a significant reduction in HbA1c. In the non-diabetic group the maximum reduction was -11.9%, in the type 2 diabetes group -12.0%. When eligible to donate again, 52.2% of the non-diabetic blood donors and 41.2% of the blood donors with type 2 diabetes had HbA1c concentrations significantly lower compared to their predonation concentration . Patients with type 2 diabetes contributing to whole blood donation programs can be at risk of falsely lowered HbA1c. This could lead to a wrong interpretation of their glycemic control by their general practitioner or internist.Continue reading > >
Also Check: What Happens If A Diabetic Doesn T Eat

