Research Design And Methods
The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study is an epidemiologic study of the relationships among insulin resistance, cardiovascular disease, and its known risk factors in three ethnic groups and different states of glucose tolerance . The design and methods of this study have been described previously . In brief, the study was conducted at four clinical centers: Oakland and Los Angeles, California, San Antonio, Texas, and San Luis Valley, Colorado. A total of 1,625 individuals were enrolled between October 1992 and April 1994 . After an average of 5.2 years , follow-up examinations were conducted using the same baseline protocol. The response rate was 81%, and those who attended the follow-up examination were similar to those who did not in terms of ethnicity, sex, baseline glucose tolerance status, and BMI . The IRAS protocol was approved by local institutional review committees, and all participants provided written informed consent.
Subjects described in this study have been part of many previous reports. Among 1,065 participants who were free of diabetes , 22 died during the follow-up period and 890 returned to the follow-up examination. We excluded 13 participants because of treatment with glucose-lowering agents and 22 others because of missing information. This report is limited to 855 of 1,030 eligible participants who attended the follow-up examination, because A1C was only measured at this time point .
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood sugar levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink. It tells the doctor how your body processes sugar.
- Diabetes is diagnosed at 2 hour blood sugar of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl
|
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
|
| Normal | |
| 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl | |
| Diabetes | 200 mg/dl or higher |
A1c Tests Can Be Affected By Changes In Red Blood Cells Or Hemoglobin
Conditions that change the life span of red blood cells, such as recent blood loss, sickle cell disease, erythropoietin treatment, hemodialysis, or transfusion, can change A1C levels.
A falsely high A1C result can occur in people who are very low in iron for example, those with iron-deficiency anemia. Other causes of false A1C results include kidney failure or liver disease.
If youre of African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian descent or have family members with sickle cell anemia or a thalassemia, an A1C test can be unreliable for diagnosing or monitoring diabetes and prediabetes. People in these groups may have a different type of hemoglobin, known as a hemoglobin variant, which can interfere with some A1C tests. Most people with a hemoglobin variant have no symptoms and may not know that they carry this type of hemoglobin. Health care professionals may suspect interferencea falsely high or low resultwhen your A1C and blood glucose test results dont match.
Not all A1C tests are unreliable for people with a hemoglobin variant. People with false results from one type of A1C test may need a different type of A1C test to measure their average blood glucose level. The NGSP provides information for health care professionals about which A1C tests are appropriate to use for specific hemoglobin variants.
You May Like: Instant Oatmeal And Diabetes
Insulin Blood Sugar And Prediabetes
Prediabetes can develop when the system goes awry and your blood sugar levels increase. This happens due to resistance to a hormone called insulin, which is produced by an organ called the pancreas. Your pancreas release insulin when your blood sugar levels rise after a meal. Insulin helps sugar get out of your blood and into your fat, muscle, and some other cells so that they can use the sugar for fuel, and so that the extra sugar leaves your bloodstream.
Prediabetes happens when your cells become less sensitive, or more resistant, to the effects of insulin. You progressively need more insulin to get the sugar out of your blood and into your cells. Eventually, possibly after years or decades, your body cannot produce enough insulin to keep up with demand.
This is when blood sugar rises to the levels that are seen in prediabetes. At this point, your doctor might diagnose you with prediabetes after taking a blood glucose test. Even higher levels, which can happen if you do not treat prediabetes, indicate diabetes.
Recommended Tests For Identifying Prediabetes
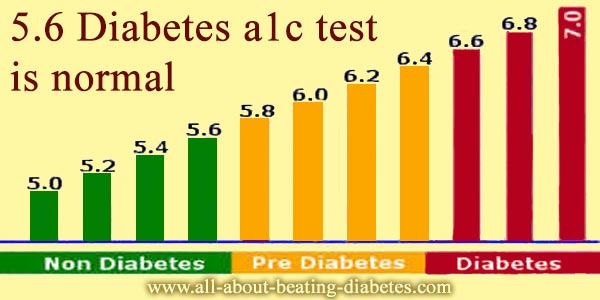
There are three recommended blood testing methods to identify or diagnose prediabetes: A1C, fasting plasma glucose, and 2-hour post 75 g oral glucose challenge. These are the same tests currently recommended to identify undiagnosed type 2 diabetes. The A1C test offers advantages for patients and providers because it removes the burden of fasting and/or lengthy lab visits.
Any of the following results will confirm a diagnosis of prediabetes:
- A1C 5.7%6.4% or
- Fasting plasma glucose 100125 mg/dL or
- 2-hour post 75 g oral glucose challenge 140199 mg/dL
Although the future development of type 2 diabetes is possible when blood test results are below these ranges, the risk for progression becomes higher for individuals with these more elevated test results.
Important Note: These different test options do not always identify the same patients. For example, some individuals may yield a normal fasting glucose test but a simultaneous A1C test in the prediabetes range. If the suspicion for prediabetes is high but the initial screening test is normal, it is reasonable to consider repeat testing in a shorter period of time or confirming the normal result with one of the other two screening test options.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
The good news is that more than half of all cases of type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed! Taking steps now to improve your lifestyle can make a huge difference and lead to a healthier future.
If you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes, reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by:
- following a healthy diet
- exercising regularly
- losing weight
What Does A1c Stand For
Hemoglobin A1C , commonly called A1C, stands for glycosylated hemoglobin. An A1C test provides information on how well-controlled a persons diabetes is. It does this by measuring the percentage of red blood cell hemoglobin protein that has sugar stuck to it and provides a three-month average of your blood glucose levels, explains , MD, a board-certified endocrinologist at the Center for Endocrinology at Mercy Medical in Baltimore. The higher blood sugar levels are, the more glucose attaches to hemoglobin. The results provide patients and their healthcare providers with information on how well their treatment, diet, and medication is working and whether adjustments are necessary.
There are a few reasons a doctor might suggest an A1C test:
- To make a diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes
- To test for prediabetes
- To monitor blood sugar levels
- To determine if treatment adjustments are needed
The A1C blood test is not for diagnosing Type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, or cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases .
Don’t Miss: Life Expectancy Of Dialysis Patients With Diabetes
Prediabetes Diagnosis As An Older Adult: What Does It Really Mean
- By A. Enrique Caballero, MD, Contributor
As our bodies age, the risk of type 2 diabetes increases. It is estimated that 25% of adults older than 65 have type 2 diabetes, while half of people over 65 have prediabetes. We know that having type 2 diabetes as an older adult requires proper lifestyle, and sometimes medications, to control the disease and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, but the implications of having prediabetes at this age are not totally clear.
You Have Hemoglobin Type C D Or E
Did you know there were various variants of hemoglobin? Itâs not common to know your type, but if youâre wondering whatâs leading to elevated A1C levels, you may want to check. The most common is Hemoglobin A.
According to research by the government in British Columbia, Canada, there are 350 varieties. Type C, for example, doesnât carry oxygen very well, which can affect A1C levels. Then thereâs Type E, an inherited blood disorder most common among people of Southeast Asian descent. It can also record false high levels of A1C in your system. To find out what types you have, itâs a good idea to take a blood test called the hemoglobin electrophoresis test.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Why Is My A1c High
As blood sugar level rises, so do A1C levels. A high A1C indicates that blood sugar control is not optimal. This in itself is not an emergency, but it gives your healthcare provider a picture of how blood glucose has, or has not, been controlled, says Dr. Williams.
Poor diabetes control or a need for medication adjustments might cause higher A1C. Diet changes, daily exercise, or medication adjustments might quickly lower A1C. Because Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease, adjustments to ones treatment might be a part of the process of controlling diabetes. Poor diabetes control does not always mean a patient is doing something wrong. But there are other reasons why levels might be high.
As previously mentioned, other health conditions can cause skewed results. These include kidney disease, anemia, liver disease, asplenia, blood loss, hypothyroidism, uremia, and sickle cell anemia. Other factors that might lead to a high A1C level include increased age, pregnancy, and gestational diabetes.
You Have Low Thyroid Levels
Quick review: thyroid hormones regulate the rate at which your body burns calories. The number of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream can affect your A1C level. This will cause the reading to fluctuate or give you false results. For example, hypothyroidism, or a low thyroid hormone levels, can lead to an elevated level of A1C.
Also Check: Max Dose Of Metformin
What Are The Consequences If High A1c Levels Are Left Untreated
There can be serious consequences if a high A1c isnt treated. Higher than healthy levels of glucose in the bloodstream can damage blood vessels.
The problems that can happen with large blood vessels are called macrovascular disease. And the problems that can happen with small blood vessels are called microvascular disease.
Macrovascular disease: These complications are similar to what we see when someone has high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
-
Heart attacks
-
Poor blood flow to limbs
Microvascular disease: These complications are more specific to diabetes.
-
Vision loss
-
Nerve damage
-
Kidney damage
High glucose levels also make it more difficult for the immune system to work correctly. Elevated glucose also increases the risk of developing infections.
If I Have Prediabetes Can I Avoid Developing Diabetes
If you have prediabetes, the best way to avoid developing type 2 diabetes is by making changes in your lifestyle.
- Lose weight. If you are overweight, losing just 7 percent of your starting weight can help delay or prevent diabetes. That means if you weigh 200 pounds, losing 14 pounds can make a difference. Weight loss also helps lower your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise is an important part of diabetes prevention. Your exercise routine should include 30 minutes of moderate physical activity at least 5 times a week. This could include brisk walking, riding a bike, or swimming. Ask your doctor what exercise level is safe for you.
- Follow a healthy diet. Eat foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins such as fish or chicken, and low-fat dairy. Dont eat a lot of processed, fried, or sugary foods. Eat smaller portions to reduce the number of calories you take in each day. Drink water instead of sweetened drinks.
Your doctor might refer you to a dietitian or diabetes educator to help you change your eating and exercise habits.
Some people take medicine to help prevent or delay diabetes. Ask your doctor if this is a good option for you.
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Small Changes In Temperature Equipment Or Sample Handling
Even when the same blood sample is repeatedly measured in the same lab, the results may vary because of small changes in temperature, equipment, or sample handling. These factors tend to affect glucose measurementsfasting and OGTTmore than the A1C test.
Health care professionals understand these variations and repeat lab tests for confirmation. Diabetes develops over time, so even with variations in test results, health care professionals can tell when overall blood glucose levels are becoming too high.
What About Exercise And Prediabetes
All exercise helps reverse prediabetes by using up sugar in the bloodstream and improving insulin sensitivity. An exercise plan should focus on two things:
Increasing muscle strength makes the cells of the muscle “hungrier , and that equals a healthier metabolism. You can build muscle by using weights, your own body weight, or resistance bands. If you choose weight training start slowly, and ask for help using the equipment safely and properly. Begin with low weights, and gradually work up to heavier weights. Lifting one round of heavy weights for only 6-8 repetitions has more benefit than one round of light weights for 10 or more repetitions. If you can do more than 10 repetitions, add more weight.
This plan also is great if you are in a hurry. You can complete a full workout in just 20 minutes twice a week. Work up to this gradually to avoid injury.
And, as always check with your health-care professional before starting any exercise program and get help using equipment properly to avoid injury.
Recommended Reading: Which Jonas Brother Has Juvenile Diabetes
How To Lower A1c
Your A1C levels are lowered when you reduce your average blood-glucose levels. This can be done through lifestyle changes and medication.
With a multidisciplinary approach including optimal nutrition, implementing an exercise regimen, and diabetic medication, most patients can lower the hemoglobin A1C, Richardson says.
Here are a few of the most effective ways to lower your A1C levels:
You Can Help Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
You can help decrease your childs risk of getting diabetes. Work with your childs healthcare provider on the following:
-
Healthy eating. Make sure your child is eating many different kinds of foods. Focus on fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meats, whole grains, and low-fat dairy. Limit sugars and fats. And limit processed, prepackaged foods and fast foods, such as burgers, fries, and shakes. Stay away from sugary drinks, such as nondiet soda, sports drinks, lemonade, and sweet tea. These foods are high in calories, fat, and sodium. They are also low in nutrition.
-
Physical activity. Being active helps your childs body use glucose. Try for at least 60 minutes of active playtime every day. It doesnt have to be all at once. A few playtimes of 10 to 20 minutes add up.
-
Weight loss. Ask your healthcare provider for a referral to a lifestyle intervention program. This program will help your child get to and stay at a 7% weight loss and increase physical activity. Even a loss of 5% to 7% of body weight may help your childs body use glucose better
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Reasons Your A1c Might Be High When Youre Not Diabetic
Are you worried youâre at risk of diabetes because of high blood sugar levels on your A1C test? Does your blood sugar spike even when youâre eating healthy foods like apples and pears?
While high blood sugar is a common sign of diabetes, itâs not exclusive to those with the health condition. In fact, people often encounter high levels even if they donât have a history of diabetes.
You Have High Triglyceride Levels
Your triglycerides are a type of fat in your blood, serving as an energy source for your body. Your body can convert energy it doesnât need to burn right away into triglycerides. It then uses them as an energy source between meals.
The NIH has found that A1C levels can be an indicator of your triglyceride count. If one is high, the other most likely is as well. This is especially true if your diet is high in added sugars.
You May Like: Candy For Diabetics Type 2
Whos At Risk For Prediabetes
If you have risk factors for prediabetes, talk to your healthcare provider about getting your blood sugar checked regularly. These prediabetes checks are essential because prediabetes often has no symptoms. You can have it for years and not know it.
You may also be at higher risk of prediabetes due to:
- Age .
- Parent or sibling with Type 2 diabetes.
- Ethnicity. Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or a Pacific Islander.
Do You Have To Fast For An A1c Blood Test
Unlike the fasting plasma glucose and the OGTT tests, there is no need to fast before having the A1C test. If A1C test results indicate a person has or might have diabetes, a healthcare provider might suggest one of these tests to confirm the results. Another test, the random plasma glucose test, which does not require fasting, can also be used. If the results are borderline or if the results of the different tests do not match, a doctor might suggest repeating the test in several weeks or months.
You May Like: Metformin And Glipizide Not Working
Some Medications Such As Opioids Can Cause High A1c Levels
Several different medications can interfere with A1C test results. Some can even cause errors in readings or bring up inaccurate results. Some opiates and even over-the-counter drugs can increase your A1C levels. According to a study by the NIH, common drugs like aspirin also cause high or low A1C levels.
Of course, taking the occasional aspirin wonât affect your levels too much. It usually only starts to skew the results of an A1C test if you are taking these medications at regular, larger doses over a long period. This isnât a one size fits all rule, though. For example, among those with type 2 diabetes, aspirin didnât show any elevated levels at all.

