Clearing Glycogen Stores And Increasing Glycogen Accumulation After Exercise
When you deplete your glycogen stores through exercise, you increase your available storage space for future incoming glucose. This increased availability is something that you can take advantage of. You can replenish your glycogen stores by eating carbohydrates while minimizing your glucose responses and fat gain.
You may have had a sports coach or trainer tell you to eat carbohydrates immediately after exercise. Thatâs because by doing this, you stabilize your blood sugar levels and enhance muscle glycogen recovery. This is a great technique for athletes, but also a great trick for us to have more flexibility in our diets.
Choose the correct type of training to deplete your glycogen stores to take full advantage of the increased storage space and improve your metabolic flexibility.
According To What Was Published By The New York Times Why
The study, conducted in rodents and humans, showed that eating a diet rich in sugar and processed foods.
which may pave the way for poor blood sugar control.
can impair long-term health in part by changing how our bodies respond to diabetes.
It is medically known that high blood sugar is unhealthy on more than one level:
First, the weight of people with high blood sugar tends to increase.
Second, it increases the rates of heart disease.
Third: It increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Fourth, these people tend to be less fit.
In epidemiological studies, people with high blood sugar levels were usually less fit.
and in studies of mice bred to low tolerance, they showed diabetes-related problems early in their lives.
This interrelationship between sugar and fitness is in one respect causal.
Because low athletic fitness is closely related to the risk of dying at an early age.
However, most previous studies on glycemia and fitness have been epidemiological studies.
meaning that they have examined links between the two conditions but not their sequences or mechanisms.
Previous studies have not shown whether high blood sugar usually precedes.
and leads to poor fitness, or vice versa, or how either condition can influence the other.
How Exercise Lowers Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
If you stick with it, exercise can reduce your need for blood-sugar-lowering drugs.
You may consider exercise a nuisance, a chore, or simply a bore. But if you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, you need to look at physical activity in a whole new light. Now it’s a tool. Just like taking a drug or altering your diet, exercise can lower blood sugar on its own, even if you don’t lose weight.
“Exercising is the most underused treatment and it’s so, so powerful,” said Sharon Movsas, RD, a diabetes nutrition specialist at the Clinical Diabetes Center at Montefiore Medical Center in New York City.
For most people with diabetes, exercise is a safe and highly recommended way to reduce the risk of complications. However, check with your doctor to make sure you don’t have heart problems, nerve damage, or other issues that need special consideration when you are working out.
How exercise affects blood sugar
In general, blood sugar drops after exercise and is lower for the next 24 to 48 hours, says Movsas. “If I take a blood sugar reading after aqua-aerobics, I usually notice it’s down,” says David Mair, 79, of Marquette, Mich.
When you exercise, your muscles become more sensitive to insulin and absorb more glucose from the blood. However, like many aspects of type 2 diabetes, the response can be highly personal. Exercise can sometimes boost blood sugar. At first, you’ll need to test your blood sugar before, after, and sometimes during exercise, to see how your body responds).
You May Like: Can Skinny People Get Diabetes
The Benefits Of Any Kind Of Exercise
Sure, there are more things to think about and prepare for when exercising with type 1 diabetes. But there are also extra benefits! In addition to getting stronger, improving heart health, decreasing stress, aiding weight management and loss and improving general mental health, those with type 1 diabetes can see these benefits:
- Muscles are better at absorbing glucose when they are contracted. This increased glucose uptake by your muscles increases insulin sensitivity the opposite of insulin resistance, a problem when the body requires more insulin to process glucose.
- Exercise slows carbohydrate absorption, better using the glucose it has and reducing the insulin you need. This counteracts after-meal hyperglycemia.
Type 1 diabetes should never hold you back from your fitness goals. There are no exercises specifically for people with diabetes, any workout you want to do is possible. There will be highs and lows as you figure out what works for you, but dont let them get you down! Youve got this!
T1D athlete Maddie Maloney uses a combination of yoga and meditation to get in the right headspace for exercise. Watch her explain how she does it.
What Is The Best Type Of Exercise For Type 2 Diabetes
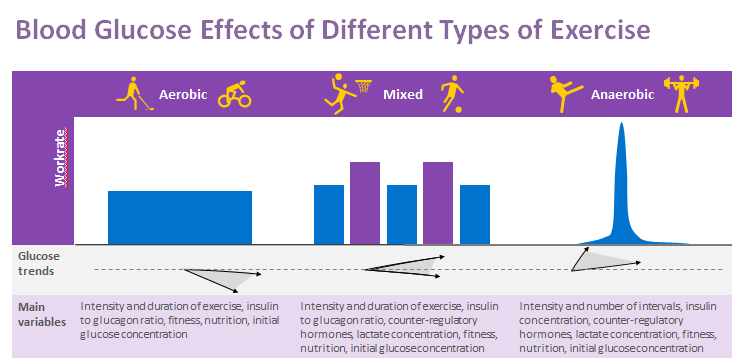
Choosing the right type of exercise is CRUCIAL, and this is also where most people go wrong.
Most clinical studies have compared the effects of aerobic exercise to strength training exercise .
But on this subject, our opinion is a bit different from what the research found.
At Type2Diet we believe that the best possible exercise you can do to improve your diabetes is….
*DRUMROLL PLEASE*
You May Like: Can Diabetics Eat
Move More Facebook Live With Our Experts
Watch our Senior Physical Activity Advisor, Neil Gibson, and Senior Clinical Advisor, Emma Elvin, talk about moving more when you have diabetes. As well as answering questions from viewers, they cover topics ranging from checking your blood sugar levels when exercising, to what you should eat and how we can support you to get active.
The thought of being more active might be overwhelming, but once you start people have told me how great it makes them feel. You wont just see the benefits now. Its about building a healthier future too – we know being active helps protect your body against diabetes complications and can help you lead a happier and healthier life.” Emma Elvin, our Senior Clinical Advisor
Is Your Blood Sugar Undermining Your Workouts
Eating a diet high in sugar and processed foods could dent our long-term health in part by changing how well our bodies respond to exercise.
- Read in app
People with consistently high levels of blood sugar could get less benefit from exercise than those whose blood sugar levels are normal, according to a cautionary new study of nutrition, blood sugar and exercise. The study, which involved rodents and people, suggests that eating a diet high in sugar and processed foods, which may set the stage for poor blood sugar control, could dent our long-term health in part by changing how well our bodies respond to a workout.
We already have plenty of evidence, of course, that elevated blood sugar is unhealthy. People with hyperglycemia tend to be overweight and face greater long-term risks for heart disease and Type 2 diabetes, even if, in the early stages, their condition does not meet the criteria for those diseases.
They also tend to be out of shape. In epidemiological studies, people with elevated blood sugar often also have low aerobic fitness, while, in animal studies, rats bred with low endurance from birth show early blood-sugar problems, as well. This interrelationship between blood sugar and fitness is consequential in part because low aerobic fitness is closely linked to a high risk of premature death.
Other animals remained on their normal chow, as a control group.
Let Us Help You Pick Your Next Workout
You May Like: Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Blood Sugar Levels Before Exercise
If you check your blood sugars yourself, whether thats using diabetes technology or test strips, try doing this more often around the time youre starting to exercise.
Trial and error can help you to spot patterns, but remember to stay safe. If you begin exercising when your blood sugar levels are high, you may experience dehydration and tiredness. This can make it harder for you to do your activity, so its important to drink more and keep hydrated.
To help you get started, weve put together a set of general guidelines around blood sugar levels and moving more for people who test their blood sugars. You may find them useful to refer to when you are preparing to get active.
These recommendations are only guidance, and your individual experience when exercising may differ. You should speak to your healthcare team about what’s best for you.
How Exercise Improves Insulin Health
Exercise helps manage prediabetes and type 2 diabetes by lowering blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity throughout the body. Heres how:
Taking Up Excess Glucose An immediate benefit of exercise is lowering excessively high blood sugar levels, Dr. Kazlauskaite says. Exercise triggers the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into the working muscles and organs. This is one reason experts agree that people with elevated blood sugar levels can benefit from walks after meals.
Building Muscle When it comes to blood sugar management, muscle is consistently underrated. After you eat, 70 to 80 percent of the glucose in your body goes to your muscles, she says. The lower our muscle mass is, the more we hinder our capacity to clear glucose from the bloodstream. On the flip side, the more muscle we maintain throughout the aging process, the more insulin receptors we have and the greater our glucose sink, Occhipinti says.
RELATED: The Health Benefits of Strength Training for People With Type 2 Diabetes
RELATED: Animal Study Sheds Light on How Strength Training Reduces Insulin Resistance
Recommended Reading: Does Low Blood Sugar Cause High Blood Pressure
How To Benefit From Physical Activity
The goal is to get at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity physical activity. One way to do this is to try to fit in at least 20 to 25 minutes of activity every day. Also, on 2 or more days a week, include activities that work all major muscle groups .
Examples of moderate-intensity physical activities include:
- Walking briskly
- Bicycling
- Playing Sports
These activities work your large muscles, increase your heart rate, and make you breathe harder, which are important goals for fitness. Stretching helps to make you flexible and prevent soreness after being physically active. Find out more by reading tips for being active with diabetes pdf icon.
On Average Each Mouse Ran About 480 Kilometers During That Time
But not all mice gain the same fitness The mice in the control group ran longer on the wheel before they fell ill.
and had significantly higher fitness.
The mice with the highest sugar level showed less improvement in their fitness, and barely increased their physical fitness.
Because lab mice are not humans, the researchers examined glucose levels and stamina in a group of 24 adults.
None of them had diabetes, although some had elevated blood sugar levels, and they might be categorized as prediabetes.
During the running test, the fitness of those who had problems controlling sugar levels was the least.
and when the scientists later tested their muscle tissue under a microscope.
they found a high activity of proteins that may hinder the acquisition of physical fitness.
Overall, the results of this study, both in mice and humans, suggest that constantly stuffing your tissues with sugar is not a good idea,.
and may deprive you of any benefits from exercise, says Sarah Lessard.
assistant professor at Joslin Diabetes Center and Harvard Medical School, which supervised the new study.
Don’t Miss: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Benefits Of And Recommendations For Reduced Sedentary Time
Recommendations
-
All adults, and particularly those with type 2 diabetes, should decrease the amount of time spent in daily sedentary behavior. B
-
Prolonged sitting should be interrupted with bouts of light activity every 30 min for blood glucose benefits, at least in adults with type 2 diabetes. C
-
The above two recommendations are additional to, and not a replacement for, increased structured exercise and incidental movement. C
Sedentary behaviorwaking behaviors with low energy expenditure is a ubiquitous and significant population-wide influence on cardiometabolic health . Higher amounts of sedentary time are associated with increased mortality and morbidity, mostly independent of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity participation . In people with or at risk for developing type 2 diabetes, extended sedentary time is also associated with poorer glycemic control and clustered metabolic risk . Prolonged sitting interrupted by brief bouts of standing or light-intensity ambulation every 2030 min improves glycemic control in sedentary overweight/obese populations and in women with impaired glucose regulation. In adults with type 2 diabetes, interrupting prolonged sitting with 15 min of postmeal walking and with 3 min of light walking and simple body-weight resistance activities every 30 min improves glycemic control. The longer-term health efficacy and durability of reducing and interrupting sitting time remain to be determined for individuals with and without diabetes.
Physical Activity In Youth With Type 2 Diabetes

Randomized trials evaluating exercise interventions in youth with type 2 diabetes are limited and inconclusive, although benefits are likely similar to those in adults. In the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth study , youth aged 1017 years with type 2 diabetes were stabilized on metformin and then randomized to metformin plus placebo, metformin plus rosiglitazone, or metformin plus lifestyle intervention and followed for a mean of 3.86 years. The lifestyle intervention included modest weight loss achieved through dietary energy restriction and increased physical activity , along with metformin use. The rate of glycemic failure was not significantly reduced in the lifestyle plus metformin group compared with metformin only or metformin plus rosiglitazone. Given the limited data in youth with type 2 diabetes, it is recommended that children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes meet the same physical activity goals set for youth in general : a minimum 60 min/day of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, including strength-related exercise at least 3 days/week.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar Levels At Night
Exercise & Glucose: Why Fitness Impacts Your Glucose Levels
Exercising is one of the most common recommendations health experts give for reducing your blood sugar levels. But, they also say that exercise can cause your blood sugar levels to spike. So, which statement is true?
Both, actually. Understanding why this is the case, though, is a key part of managing your metabolic health. Itâs especially important if you have prediabetes or a strong family history of diabetes. Thatâs because exercise has the power to help prevent or delay prediabetes from progressing into type 2 diabetes, making it a reversible condition!
Exactly how exercise alters glucose levels can be different for everyone. The effect can change depending on the type, duration, and intensity of the physical activity as well as your diet and overall health status. So, when it comes to blood sugar and exercise, the relationship is complex.
Our goal is to help you find a signal in the noise that will guide you toward taking control of your blood sugar levels. Because when you do, you can reap the benefits of optimal metabolic health.
The best way to understand exercise and blood sugarâs relationship is to jump right into the science.
Being Physically Active Helps Your Mind And Body In Many Ways
Exercise has so many benefits, but the most critical one is that it makes it easier to control your blood glucose level. People with type 2 diabetes have too much glucose in their blood, either because their body doesnt produce enough insulin to process it, or because their body doesnt use insulin properly .
In either case, exercise can reduce the glucose in your blood. Muscles can use glucose without insulin when youre exercising. In other words, it doesnt matter if youre insulin resistant or if you dont have enough insulin: when you exercise, your muscles get the glucose they need, and in turn, your blood glucose level goes down.
If youre insulin resistant, exercise actually makes your insulin more effective. That isyour insulin resistance goes down when you exercise, and your cells can use the glucose more effectively.
Exercise can also help people with type 2 diabetes avoid long-term complications, especially heart problems. People with diabetes are are likely to develop blocked arteries , which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Exercise helps keep your heart healthy and strong. Plus, exercise helps you maintain good cholesteroland that helps you avoid high cholesterol and the build up of plaque that may block the blood from passing easily through your arteries.
- Lower blood pressure
- Increased level of good cholesterol
- Leaner, stronger muscles
- Stress management
But Before You Begin ExercisingYou should talk to your doctor
Don’t Miss: What Diabetic Supplies Are Covered By Medicaid
The Effect Of Blood Sugar Level On Exercise
So, in this new study published in September 2021 in the journal Nature Metabolism.
researchers at Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston, USA.
and other institutions decided to raise the blood sugar levels of mice and monitor the effect when they exercise.
At first, they worked on adult mice, and switched them from their normal diet to one that contains a high percentage of sugar and saturated fat.
similar to the Western diet rich in burgers, pizza, and others.
The mice quickly gained weight and their blood sugar levels rose.
The researchers injected other mice with a substance that reduces their ability to produce insulin.
the hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar levels, just as it does in people with a certain type of diabetes.
These mice did not gain weight, but their blood sugar levels rose to levels similar to those of the first group of mice.
As for the mice in the third group, they were left on their traditional diet as the control group.
After four months, the researchers tested each rats fitness by measuring the time it could spend.
on a running machine before it fell ill.
Then they put a running wheel in each mouses cage and let it run whenever it wanted for six weeks.
What Is The 15
The American Diabetes Association recommends people who feel their blood glucose has gotten too low follow the 15-15 rule:2
You May Like: Does Type 2 Diabetes Need Insulin

