Urine Testing For Diabetes
Urine tests arent always used to diagnose diabetes. Doctors often use them if they think you may have type 1 diabetes. The body produces ketone bodies when fat tissue is used for energy instead of blood sugar. Laboratories can test urine for these ketone bodies.
If ketone bodies are present in moderate to large amounts in the urine, this could indicate your body is not making enough insulin.
What Is An Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
This is the test used for diagnosing gestational diabetes in the UK & ROI.
The test involves fasting from the previous night, having a fasting blood test taken on arrival, drinking 75g of glucose , then a subsequent post glucose blood test taken after 2 hours.
You should check with your hospital when you should fast from and whether you are allowed to drink water during this time.
All hospitals can vary the targets used for diagnosis of the OGTT. Some will take three blood tests , where as others will take two .
In some areas they may use a fasting glucose test alone or a HbA1c blood test instead of a OGTT.
Are Some Women At A Higher Risk Of Getting Gestational Diabetes Than Others
You have an increased risk of gestational diabetes if:
- your body mass index is 30 or more
- you have previously had a baby who weighed 4.5kg or more at birth
- you had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- you have PCOS
- you have a family history of diabetes one of your parents or siblings has diabetes
- your family origins are South Asian, black Caribbean or Middle Eastern
- you are aged 35 or older
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
What Is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It happens when your body is not able to produce enough insulin to keep the amount of glucose in your blood at proper levels. Untreated GD increases the likelihood of having a large baby, and is associated with birth complications as well as health risks for the newborn . Untreated GD also increases the risk of stillbirth late in pregnancy . Women who develop GD are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. However, there is excellent treatment for GD, and most women diagnosed with GD have normal deliveries and healthy babies.
Reducing The Risk Of Gestational Diabetes
Recent research has shown that diet and exercise in those that have a high BMI before pregnancy, could reduce the risks of developing gestational diabetes and a further article published in BJOG stated:
Analysis of 13 trials, involving more than 2,800 women, found that exercise reduced the risk of gestational diabetes by more than 30% for women who exercised throughout pregnancy this was even greater . This effect was strongest for women who combined toning, strength, flexibility and aerobic exercise.
Recommended Reading: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
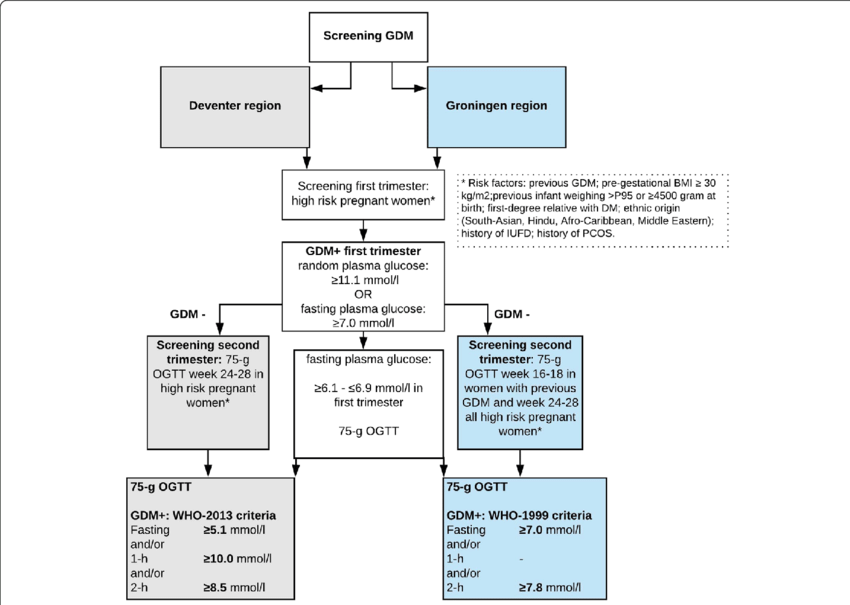
The Postcode Lottery In Diagnosing Gestational Diabetes
Depending on where you live you may or may not be screened for gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
In Cambridgeshire, they screen all pregnant women for gestational diabetes and offer a blood glucose test at 8-12 weeks of pregnancy, but this is not the case across the rest of the UK and Ireland.
In the majority of areas, only women who have known risk factors are screened and the risk factors can also be different.
Different target levels are used for diagnosing which also poses problems too.
Some women may be referred for testing if they have symptoms of gestational diabetes, but unfortunately this is not the case for all.
Diagnosis test target levels England & Wales:
NICE guidelines for diagnosis are the following:
1.2.8 Diagnose gestational diabetes if the woman has either:
- a fasting plasma glucose level of 5.6 mmol/litre or above or
- a 2hour plasma glucose level of 7.8 mmol/litre or above.
Diagnosis test target levels Scotland:
SIGN guidelines for diagnosis are the following:
- The adoption of internationally agreed criteria for gestational diabetes using 75 g OGTT is recommended: fasting venous plasma glucose 5.1 mmol/l, or one hour value 10 mmol/l, or two hours after OGTT 8.5 mmol/l.
- Women with frank diabetes by non-pregnant criteria should be managed within a multidisciplinary clinic as they may have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and be at risk of pregnancy outcomes similar to those of women with pre-gestational diabetes.
Diagnosis test target levels Ireland:
How Does Gestational Diabetes Affect Any Future Pregnancies
If you have had gestational diabetes you are more likely to have it again in future pregnancies. For that reason, a test for gestational diabetes will be performed early in any future pregnancy. If this test gives a result within the recommended range, then another pregnancy OGTT will be done again later in the pregnancy to make sure your blood glucose levels are still in the recommended range.
Also Check: Glipizide Vs Metformin
While We Cover A Lot One Of The Key Points We Discuss Are The Three Ways To Diagnose Gestational Diabetes
I get a lot of questions about how to diagnose gestational diabetes and what screening method is best. There are pros and cons for each screening method, but my unique background in both gestational diabetes public policy and clinical practice might give you a more complete perspective than what youve read elsewhere online. I break it all down in this interview.
Heres a recap of what we cover:
- Does pregnancy really trigger gestational diabetes or are there other things that can put you at risk? Is this something that was going on before pregnancy?
- Does gestational diabetes go away after delivery?
- Why I moved away from the traditional gestational diabetes diet and how my real food gestational diabetes diet is different
- How the traditional gestational diabetes diet was formulated
- How most research on high fat diets during pregnancy misses the point
- Three ways to diagnose gestational diabetes what screening method I recommend and why
- The frustrating medical bias against women diagnosed with gestational diabetes and why it needs to stop
- The three different types of ketosis and which one is dangerous during pregnancy
- Top 3 tips for managing gestational diabetes
Obstetric And Perinatal Considerations
The presence of fasting hyperglycemia may be associated with an increase in the risk of intrauterine fetal death during the last 48 weeks of gestation. Although uncomplicated GDM with less severe fasting hyperglycemia has not been associated with increased perinatal mortality, GDM of any severity increases the risk of fetal macrosomia. Neonatal hypoglycemia, jaundice, polycythemia, and hypocalcemia may complicate GDM as well. GDM is associated with an increased frequency of maternal hypertensive disorders and the need for cesarean delivery. The latter complication may result from fetal growth disorders and/or alterations in obstetric management due to the knowledge that the mother has GDM.
Read Also: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Listen To This Interview On Stitcher Or Itunes
In other news, you might like to hear some updates from the gestational diabetes world:
1. For the first time ever, my real food approach to gestational diabetes will be used in a research study. Ive just finished recording my portion of the training program that will be part of a gestational diabetes pilot study through the University of Kentucky. The principal investigator, Rebecca Dekker, who you may know from her popular blog, Evidence Based Birth, sought my help on this project after reading my book. This is a HUGE milestone for women with gestational diabetes everywhere!
2. Im excited to announce Ill be interviewed for ReachMD this week, a highly trafficked website for medical professionals that offers a streaming radio station to help doctors and other providers stay abreast of the latest research . Its humbling and reassuring to see medical companies, such as this one, seek alternative opinions on gestational diabetes. Clearly, those in the prenatal nutrition industry have noticed that the conventional gestational diabetes diet doesnt offer the results theyre looking for and are ready to think outside of the box. Bravo!
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will test your blood sugar during pregnancy. The test may have two parts:
- Glucose challenge test: You drink a sweet liquid. After about an hour, youll have a blood test to check your blood sugar level. If your blood sugar is high, your healthcare provider will do a glucose tolerance test.
- Glucose tolerance test: An oral glucose tolerance test is only done if your challenge test results are unusual. You fast before the tolerance test. Your healthcare provider draws your blood before and after you drink a sweet liquid. The tolerance test can confirm a diagnosis of gestational diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Diabetes Type 1
What Is The Evidence On Different Ways To Diagnose Gdm
The Cochrane review on this topic included seven trials , and the researchers found disappointing results . The studies in the review were of poor quality, had small sample sizes, did not study the best time during pregnancy to test for GDM, and often did not report important infant or maternal outcomes, such as higher birth weight. Because the evidence was so limited, the Cochrane reviewers could not recommend one strategy over another. They concluded that large, randomized trials are needed before we can establish the best way to identify people with GDM.
Testing For Gestational Diabetes
Breadcrumb
There are some risk factors that increase your chance of developing gestational diabetes. Your midwife will ask you about these at your booking appointment, which happens around 8-12 weeks of pregnancy. If you have any of the risk factors, youll be offered a test for gestational diabetes when you’re between 24 and 28 weeks pregnant.
Gestational diabetes does not usually cause any symptoms, but some women may have some if their blood glucose levels get too high. Speak to your midwife if you have any concerns. Talk to your midwife if you think you are at risk of developing gestational diabetes, but you havent been offered a screening test.
You dont have to take the test if its offered, but there are a few things to keep in mind:
- if you have gestational diabetes, you will be offered more care during both pregnancy and labour, to help reduce the risk of problems
- for some women, gestational diabetes can be improved by changes in diet and doing more exercise
- if changes in diet and doing more exercise don’t improve gestational diabetes, youll be offered medication or insulin.
“I wasnt obviously skinny, but I wasnt massively obese either I had no symptoms whatsoever. I had no expectation that the test would be anything other than a formality.”
Beth, mum of two
Don’t Miss: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
So What Is Gestational Diabetes
GDM is diabetes of pregnancy. That means once you have birthed, you are no longer considered diabetic.
That being said, history of GDM is linked to higher risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life, so it is important to have diabetes follow-up with your GP at 6-8 weeks post birth and ongoing.
The hormones produced by the placenta are vital in helping a baby grow and develop.
However, these hormones also block the action of insulin, which lowers blood glucose levels.
In pregnancy, the need for insulin is 2-3 times higher because of this insulin resistance.
In the case of GDM, the body isnt coping with the extra demand for insulin and the blood glucose levels are therefore higher.
Gestational Diabetes Test Alternatives
This post may contain affiliate links. Please read my disclosure and privacy policy.
If youre looking for an alternative to the traditional Gestational Diabaetes Test for pregnancy, I hope that sharing my own experience below might help. Keep in mind that I am not a doctor, so be sure to work with your own certified practitioner to develop a plan that is best for you.
Read Also: What Happens If You Take Glipizide And Don T Eat
What Are The Risk Factors
The people who would be most at risk for gestational diabetes are women who:
Women who have one or more of these risk factors are usually encouraged to test.
What Can I Do To Make Living With Gestational Diabetes Easier
Make diabetes management part of your daily routine. Create a schedule and stick to it. Try to:
- Check your blood glucose levels at the same time each day.
- Choose three days each week to get 30 minutes of light exercise.
- Plan small, balanced meals ahead of time.
- Talk with your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator about other tips for daily diabetes management.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women when theres too much glucose in their blood. GD is usually diagnosed during the middle stage of pregnancy with a few simple blood tests. If left untreated, GD can cause health complications for the mother and the baby. Most women can manage gestational diabetes with diet and exercise. Some will need medication. Gestational diabetes increases your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to reduce your risk of diabetes before, during and after pregnancy.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/14/2021.
References
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Gestational Diabetes Diagnosis & Treatment
Gestational diabetes is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that is first recognized during pregnancy. The condition occurs in approximately 4% of all pregnancies.
Do I Wish I Wouldnt Have Eaten
Kind of. Part of me wishes I would have just had eggs and toughed it out so I wouldnt have had to sit through 3 hours of starvation at the hospital, but on the other hand, I didnt want to try and trick a test that is put in place for the sake of my and Baby Ds health. If I had GD, I didnt want to dupe the test and put our health at risk.
Read Also: What Are The Side Effects Of Glucophage
When Is The Best Time During Pregnancy To Screen For Gdm
One of the challenges in diagnosing gestational diabetes is that many people are not screened for diabetes before pregnancy, so it can be difficult for the provider to tell if GDM is undiagnosed, pre-existing type 2 diabetes or new onset GDM. Currently, ACOG recommendations suggest that providers test people with risk factors for type 2 diabetes at their first prenatal visit . People diagnosed with diabetes in the first trimester are classified as having pregestational type 2 diabetes, instead of GDM. There is disagreement about the best test for type 2 diabetes in early pregnancy. Some providers use the one-part diagnostic method, others use the two-part screening and diagnostic method, and others measure hemoglobin A1c. We wont be covering the evidence on type 2 diabetes screening in this article, as our focus is on GDM.
Right now, researchers are conducting studies to evaluate early testing for GDM, and its possible they may discover that GDM can be identified in the first or second trimester. But as weve already mentioned, most guidelines today recommend that GDM be diagnosed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. In 2014, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded that there is not enough evidence on the benefits and harms of screening for GDM before 24 weeks of pregnancy .
Gestational Diabetes Just Causes A Bigger Baby
Anyone who is under the assumption that gestational diabetes will just cause a bigger baby chubby babies are cute, bouncy babies! and that this is the only concern, should learn about the associated complications. There is a difference between a larger sized baby and a baby who is swollen and very poorly as a result of undiagnosed or poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
Please read more here on the complications caused by gestational diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes UK is dedicated to offering support and evidence based research to women diagnosed with gestational diabetes in the UK and Republic of Ireland.
If you have been diagnosed, or are going to be tested for gestational diabetes and want a support network and community for help, advice and to discuss all things related to gestational diabetes, then please join our Facebook support group, Gestational Diabetes UK Mums.
National guidelines for diabetes in pregnancy:-
Read Also: When Do Diabetics Need Insulin
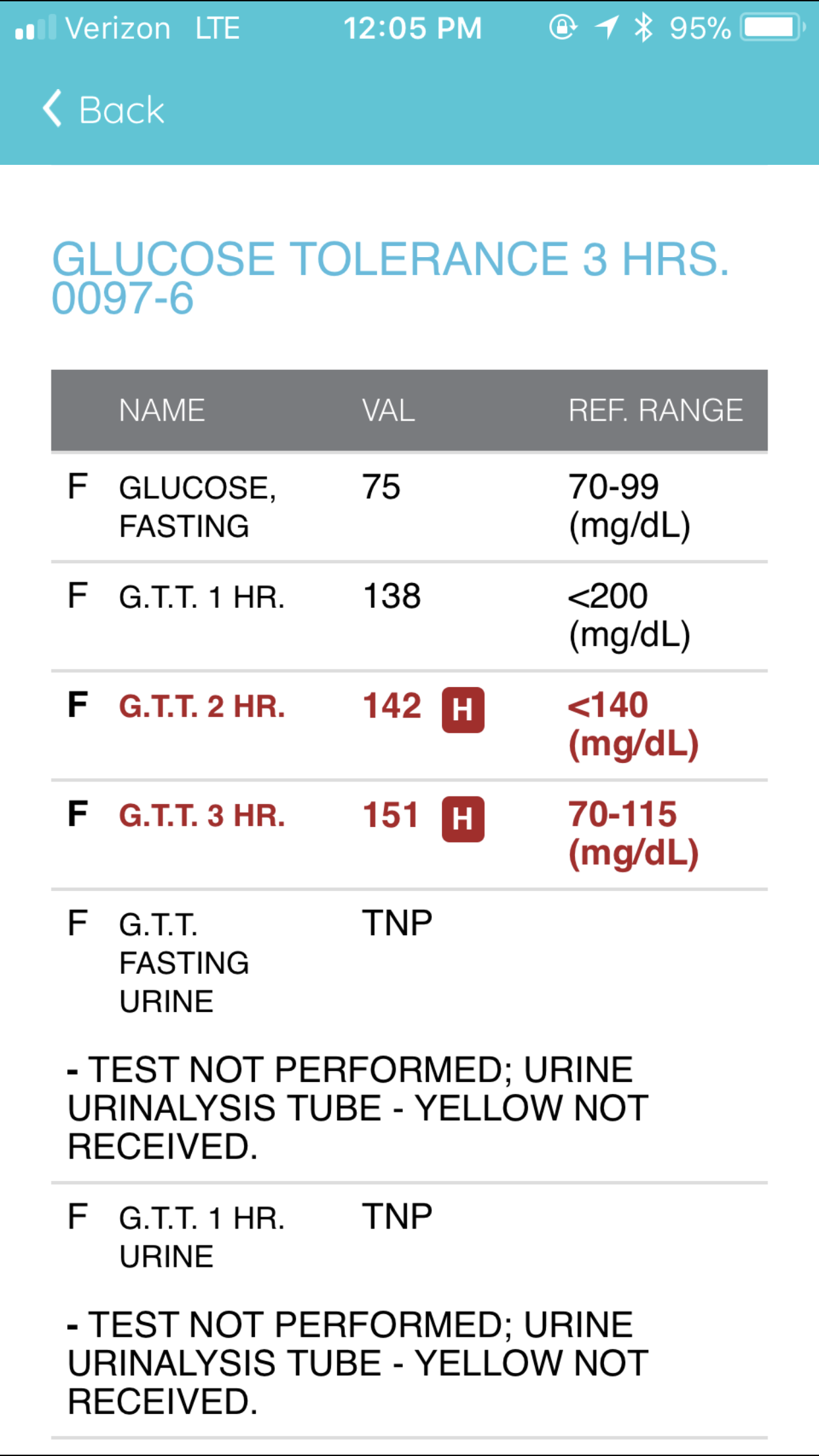
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal blood values for a 3-hour 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test are:
- Fasting: greater than 95 mg/dL
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour: greater than 155 mg/dL
- 3 hour: greater than 140 mg/dL
ONE-STEP TESTING
Abnormal blood values for a 2-hour 75-gram oral glucose tolerance test are:
- Fasting: greater than 92 mg/dL
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour: greater than 153 mg/dL
If only one of your blood glucose results in the oral glucose tolerance test is higher than normal, your provider may simply suggest you change some of the foods you eat. Then, your provider may test you again after you have changed your diet.
If more than one of your blood glucose results is higher than normal, you have gestational diabetes.

