What Is A Dangerous Level Of A1c
When levels rise to 9.0, the risk of kidney and eye damage and neuropathy increases. Some people who are newly diagnosed could have levels over 9.0. Lifestyle changes and possibly medication can lower levels quickly. For someone who has long-standing diabetes, levels rise above 9.0 could signal the need for a change in their treatment plan.;
Some labs estimate average blood glucose , which corresponds to home glucose meter readings , allowing patients to understand the results better.;
Normal Vs Optimal Blood Sugar Ranges
Ive written extensively about the difference between normal and optimal blood markers here, and the same applies to your blood sugar ranges.;
From the perspective of conventional medicine, a fasting blood sugar level of 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes.
Two consecutive fasting glucose levels of 126 mg/dL indicates diabetes, as well as a random glucose reading of 200 mg/dL , and a 2-hour post-meal reading of 200 mg/dL .
But much of the data in conventional medicine comes from populations who are not enjoying optimal health.
So what does a healthy daily glucose response look like from the perspective of preventative medicine?
On waking: Research indicates that your optimal glucose after waking in the morning should be between 82-88 mg/dL . This level is associated with optimal aging, the lowest risk of chronic disease, and the lowest mortality risk.
After meals: Blood sugar peaks between 1 and 2 hours after the meal and should be back down to fasting levels by 3 hours post-meal. From the perspective of optimal health, you should avoid regularly eating foods that raise your blood sugar over 100 mg/dl .
One strategy to test the impact of your diet on your long-term health is to measure your blood sugar before and after meals.;
How To Lower Blood Sugar Level
A patient with diabetes is at a 5 times greater risk of developing cardiovascular disease than patient without diabetes. One third of all cardiovascular diseases also affect people with diabetes.
Three quarters of diabetics die from cardiovascular disease. Women with diabetes have a 4 times greater risk of death from cardiovascular disease. People suffering from diabetes usually have high cholesterol levels as well.
Disturbances in the metabolism of blood sugar levels are mainly the consequence of heredity , age , poor diet, excessive body weight and physical inactivity. Disturbances in the metabolism of blood sugar were present in 20% of adult Europeans during 2002-2005 a study showed.
RECOMMENDATIONS to decrease elevated blood sugar:Blood sugar level is determined in the fasting state. In a healthy person, a normal blood glucose level is less than 108 mg/dL or 6 mmol/L on an empty stomach.
Possible values are
- normal blood sugar level ,
- disruption of glycemia ,
- diabetes .
What can you do to lower the chance of developing diabetes:
- lose weight be fit,
- sleep more, be rested.
- have a healthy diet with as many vegetables and fruits, a lot of fiber, consume less calories, less fat, less alcoholic beverages and no simple sugars,
- workout at least 30 minutes per day.
Useful resource: blood sugar levels chart:
You May Like: Glucophage Weight Loss Dosage
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
What Is The A1c Test

The A1C test; is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure;below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol;levels.
- s: Stop smoking;or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
Read Also: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
My Perspective On A1c As A Person Living With Diabetes
I have a very ambivalent relationship with my A1c myself. Ive been living with type 1 diabetes for over 20 years, and my A1c is not something I think about in my daily life. However, every three months when I see my endo, I get a little anxious because receiving your A1c can feel a lot like getting your diabetes report card.
And, quite honestly, thats really silly. My A1c number doesnt reflect whats been going on in my life for the last three months. It doesnt tell me how much effort Ive put into managing my diabetes and it does not define me as a person. Its a good source of information, nothing more.
Still, we tend to look at it and judge, good or bad, how weve done with our diabetes management. But we really shouldnt!
That doesnt mean that I think we shouldnt get our A1c checked. I absolutely think we should, but we also need to understand what it means as well as why we should look beyond the A1c number. I hope this guide has given you the knowledge and tools to do so!
If you liked this guide on how to lower your A1c, please sign up for our newsletter in the form below. We send out a weekly newsletter with the latest posts and recipes from Diabetes Strong.
Suggested next posts:
If you found this guide to lowering your A1c useful, please sign up for our newsletter using the form below. We send out a weekly newsletter with the latest posts and recipes from Diabetes Strong.
Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Blood sugar levels rise and drop during the day. This is normal. However, dramatic fluctuations in your blood glucose levels may indicate problems.
Dramatic changes of blood sugar levels have significant physical symptoms and will increase your risk of diabetes-related complications.
and keep track of your results write down all of your measured values.
Blood sugar levels chart for non-diabetics
| Glucose mg/dL or mmol/L |
|---|
- headache,
- visual disturbances
Symptoms may vary different people might experience different symptoms. In some cases symptoms can even remain unrecognized .
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
How Can Continuous Glucose Monitoring Help You Maintain Optimal Glucose Levels
It is not uncommon for your glucose levels to increase after a meal: you just ate food that may contain glucose, and now your body is working on getting it out of the bloodstream and into the cells. We know that we want to prevent excessive spiking of glucose levels because studies show that high post-meal glucose spikes over 160 mg/dl are associated with higher cancer rates. Spikes are also associated with heart disease. Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain. Additionally, the data shows that the big spikes and dips in glucose are more damaging to tissues than elevated but stable glucose levels. Therefore, you should strive to keep your glucose levels as steady as possible, at a low and healthy baseline level, with minimal variability after meals.
Keeping your glucose levels constant is more complicated than just following a list of eat this, avoid that foods. Each person has an individual response to food when it comes to their glucose levels; studies have shown that two people can have different changes in their glucose levels after eating identical foods. The difference can be quite dramatic. One study found that some people had equal and opposite post-meal glucose spikes in response to the same food.
Controlling Blood Glucose Levels
Uncontrolled blood sugar can result in regular episodes of hyperglycemia;. This can cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms are uncomfortable to experience but there are things you can do at home to reduce your blood sugar. In terms of drinks, water is the best as it will help to maintain hydration and dilute excess sugar in the blood. Also, try to add more fiber to your diet to reduce your blood sugar; apples, bananas, oranges, and strawberries are all fibrous fruits.;
However, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also lead to more severe, long term disease. Poorly managed diabetes leads to vision loss, kidney problems, nerve damage, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, if your blood sugar level reaches 16.7mmol/L, this could be dangerous and you need to seek immediate medical attention.;
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
How To Avoid Diabetic Ketoacidosis
It might have been a really long time since youve been in diabetic ketoacidosis , or maybe youve never had it.
But if you have Type 1 diabetes, you are at risk. Sometimes when you havent recently experienced a situation, you kind of forget about what you were told to do for prevention or treatment. Thats why a refresher might be a great idea!
How Often Is A1c Tested
To keep A1C levels in check, patients should have the test repeated regularly. If the A1C is less than 5.7, indicating you dont have diabetes, you should have it checked every three years, according to Robert Williams, MD, a family doctor and geriatrician in Lakewood, Colorado, and a medical advisor for eMediHealth. If it is between 5.7 and 6.4, indicating you are at risk of developing diabetes, you should have it rechecked every one to two years. If you have a confirmed diabetes diagnosis, and your blood sugar is well-controlled, you should have an A1C test every six months. If you already have diabetes and your medications change, or your blood sugar is not well-controlled, you should have an A1C test every three months.;
Read Also: Normal A1c Level
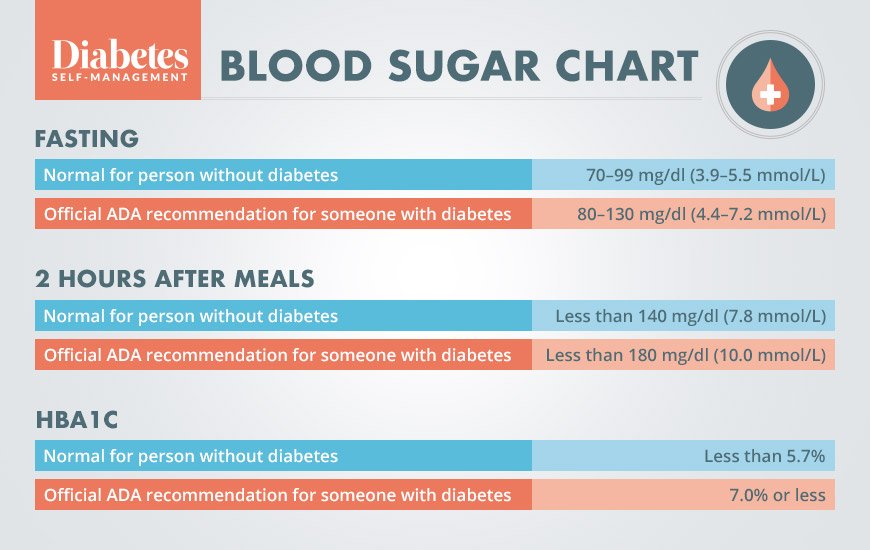
Official Fasting Blood Sugar Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting blood sugar target of 80 to 130 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. However, the fasting blood sugar target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
Keeping Your Levels In Range
If you have diabetes, keeping your blood glucose within normal range after a high-carbohydrate meal can be difficult. The type of carbohydrates you choose can make a difference in your blood sugar. Complex carbohydrates, which must be broken down into simple sugars before your body can absorb them, slow the absorption process and help stabilize your blood sugars. The glycemic index defines carbohydrates by their absorption rate. Carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, less than 45, cause a slow steady rise in blood glucose. Whole grains such as oats, wheat, barley, brown rice and lesser known grains such as quinoa help keep your levels within range. Foods high in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables, also slow digestion and help stabilize blood glucose after meals. Exercise can also help slow digestion and stabilize peaks in glucose.
Recommended Reading: Late Onset Type 1 Diabetes Life Expectancy
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.;;
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.;;;;;;;;
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.;;;;;;;;;
What Should My Blood Sugar Level Be 4 Hours After Eating
aftereatingforhourshours after eatingthelevelsmealsFordiabetesblood sugar levelsmeals
Normal and diabetic blood sugar ranges
| BLOOD SUGAR CHART | |
|---|---|
| Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes | 80130 mg/dl |
| 1 to 2 hours after meals | |
| Normal for person without diabetes | Less than 140 mg/dl |
| Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes | Less than 180 mg/dl |
what should blood glucose be 3 hours after eating? Blood sugar chart
| Time of check | Target blood sugar levels for people without diabetes |
|---|---|
| Before meals | |
| 12 hours after the start of a meal | less than 140 mg/dl |
| Over a 3-month period, which an A1C test can measure | less than 5.7% |
Consequently, what is a normal blood sugar level 5 hours after eating?
Blood sugar levels in diagnosing diabetes
| Plasma glucose test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Below 11.1 mmol/l Below 200 mg/dl | N/A | |
| Below 5.5 mmol/l Below 100 mg/dl | 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l 100 to 125 mg/dl | |
| 2 hour post-prandial | Below 7.8 mmol/l Below 140 mg/dl | 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l 140 to 199 mg/dl |
What is a normal blood sugar level 1 hour after eating?
Normal blood sugar levels are less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least eight hours. And they’re less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
Read Also: How Much Vitamin B12 Should A Diabetic Take
How To Lower Your A1c Levels
Its important to get your hemoglobin A1C levels as close to normal as possible, says Dr. Bellatoni, Decreasing your hemoglobin A1C decreases your risk of having complications from diabetes. Even if you cannot get your A1C back to the normal range, any improvement lowers your risk of diabetes complications.
Are You Suffering From Untreated Hyperglycemia
Untreated hyperglycemia leads to serious complications. Signs are hard to identify, but self-monitoring and early treatment lowers these risks and improves quality of life.
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, affects people who have diabetes. Since the symptoms are difficult to feel and easily go unnoticed, the condition often goes untreated. Prolonged hyperglycemia is the main cause of almost all the complications associated with diabetes but good blood sugar control can prevent them. The more you know about high blood sugar, the more likely you are to recognize it, treat it, and hopefully take steps to prevent it.
Also Check: Can Skinny People Have Diabetes
The Best Healthcare Options To Prevent Diabetes
Health care is expensive.; Canada spent an estimated $253.5 billion in 2018, and as the cost of health care increases, so does the cost to you. Pre-existing medical conditions, family history, and BMI are all factors that increase the cost of health care. These factors also increase your risk of diabetes, so;you must be covered.;
Of course, as a Canadian, you are entitled to some free and subsidized health care, which is great. But many people opt for private healthcare and for diabetes prevention this can be very useful. If you’re shopping around for private healthcare, it’s important to choose the right package.;
Basic health insurance will usually cover health care, medical services, and prescriptions, but they tend to lack customizations.;If you opt for a premium/guaranteed health insurance you have the bonus of a custom plan based on your needs; if you are worried about your risk of diabetes this is like gold dust.;
Private healthcare plans can cover the cost of many expenses related to diabetes such as blood tests, blood sugar monitors, specialist referrals, hospital stays, and much more! The most important thing to note about private health care is that it covers costs for preventative care, not just treatment for diseases.;
There are many different options available, so make sure you search for the best quotes.
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
Read Also: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication

