How To Do A Finger
Your healthcare team will show you how to do it the first time, but these are the key steps:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water. Dont use wet wipes as the glycerine in them can affect the test result. Make sure your hands are warm so its easier to get blood and wont hurt as much.
- Take a test strip and slot it into the meter to turn it on. Some meters will have tests strips built in.;
- Remove the cap from your finger prick device and put in a new lancet. Then put the cap back on and set the device by pulling or clicking the plunger.
- Choose which finger to prick but avoid your thumb or index finger . And dont prick the middle, or too close to a nail. Place the device against the side of your finger and press the plunger. Use a different finger each time and a different area.
- Take your meter with the test strip and hold it against the drop of blood. Itll tell you if the test strip is filled, usually by beeping.
- Before you look at your reading, check your finger. Use a tissue to stop bleeding, then use it to take out the lancet and throw it away in your sharps bin.
- You can use the same tissue to take out the test strip and throw that away too. Taking out the strip will usually turn the meter off.
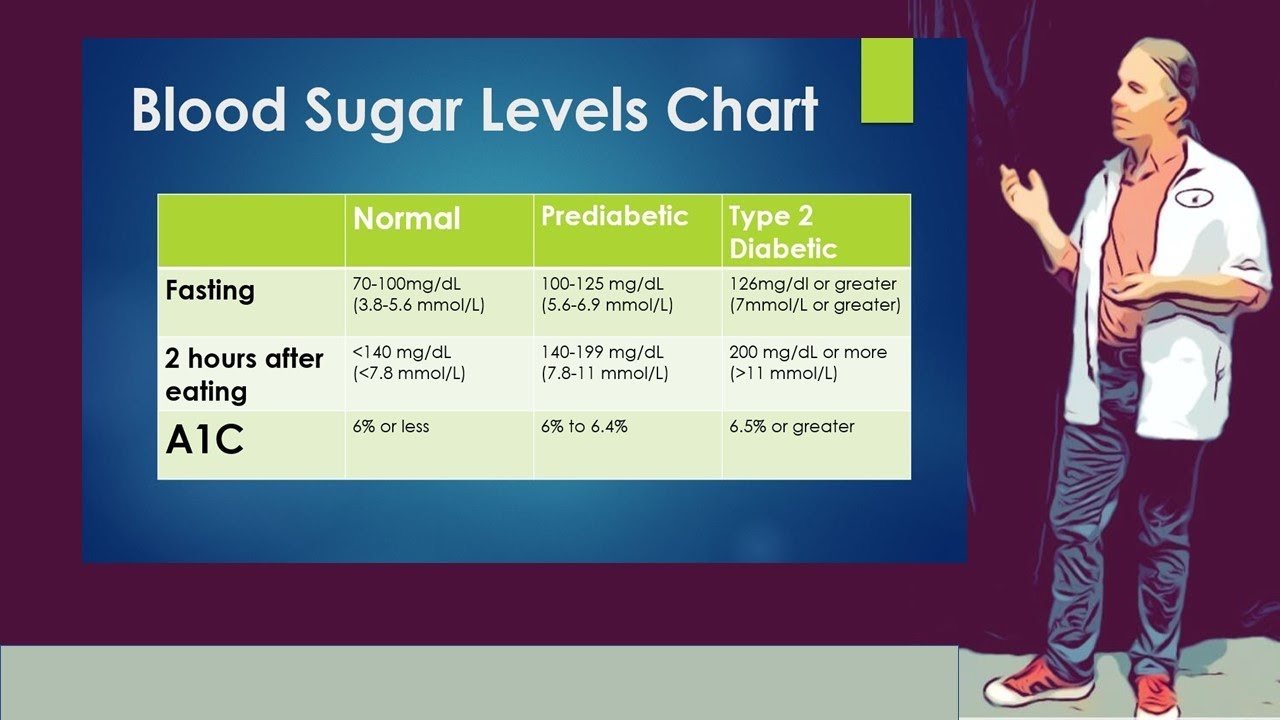
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.;;;
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods;
- Alcohol;
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.;;;
What Should I Aim For
Effective management of diabetes is all about aiming for a careful balance between the foods you eat, how active you are and the medication you take for your diabetes. Because this is a delicate balance, it can be quite difficult to achieve the best possible blood glucose management all the time.
The ranges will vary depending on the individual and an individuals circumstances. While it is important to keep your blood glucose levels as close to the target range of target range between 4 to 6 mmol/L as possible to prevent complications, it is equally important to check with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator for the range of blood glucose levels that are right and safe for you. Therefore the following information should be treated only as a general guide.
You May Like: Skinny Diabetes
Avoid Excessive Exercise Late At Night
Try to avoid any exercise late at night before going to bed. If your blood sugar is less than 5.6 mmol/L or 100 mg/DL before sleeping and you do want to exercise make sure you double your food portion. If you do excessive exercise late at night this can lead to increased blood sugar during the next day.;
Why Is It So Important To Check My Blood Levels
Regular checking and recording of your blood glucose level can reinforce your healthy lifestyle choices as well as inform you of your response to other choices and influences.
Importantly, blood glucose level pattern changes can alert you and your health care team to a possible need for a change in how your diabetes is being managed.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Improving Blood Sugar Control
Good blood sugar control can help you avoid the symptoms and complications of going too high or low. Youll also feel better and have more energy, says Rasa Kazlauskaite, MD, medical director of the Rush University Prevention Center in Chicago, Illinois, and associate professor in the department of preventive medicine and internal medicine.
Get started with these 10 tips to help you rein in your blood sugar and better manage type 2 diabetes:
1. Stick to your medication plan. There are many drugs to help control blood sugar, Reddy says. Taking your medication as directed is vital don’t skip doses.
2. Eat on schedule. Eating healthy meals at about the same time every day helps keep blood sugar steady. Also, meal routines and consistency help to avoid severe hunger and help medications work better, Dr. Kazlauskaite says.
3. Distribute carbohydrates throughout the day. Make it a goal to eat two to four carbohydrate servings about 30 to 60 grams per meal, says Margaret Powers, PhD, RD, CDE, president-elect of health care and education for the American Diabetes Association and a research scientist at Park Nicollet Health Services International Diabetes Center in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Because carbohydrates raise your blood sugar, spacing them out can help keep your levels in a healthy range.
9. Make it a family affair. Reddy suggests recruiting family members to eat healthy and exercise with you so it feels more like fun than a task.
Why Check Blood Sugar Levels
If you take certain medication, like insulin or sulphonylureas, checking your blood sugars is a vital part of living with diabetes. It can help you work out when you need to take more medication, when you need to eat something or for when you want to get up and move around more.
Routine checks can help you know when you might be starting to go too low; or too high . Its a way of getting to know your body and how it works. It can help you and your healthcare team spot patterns too. Do you write your results down? You might find that helpful.
But importantly, it will help you stay healthy and prevent serious diabetes complications now and in the future. By complications, we mean serious problems in places like your feet and your eyes. This happens because too much sugar in the blood damages your blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow around your body. This can lead to very serious problems like sight loss and needing an amputation.
The higher your blood sugar levels are and the longer theyre high for, the more at risk you are.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Fasting Before A Blood Test: Drinking Coffee Eating And More
Certain blood tests require fasting beforehand. If your healthcare provider has instructed you to fast before your upcoming test, it means that you should not eat or drink anything for the specified amount of time before having your blood drawn.
Understanding why fasting is important and how to properly fast before a blood test can be helpful for eliminating pre-test anxiety and simplifying the testing process. Below, learn how to fast for a blood test correctly to help make sure that your test results are accurate.;
Blood Sugar Level Immediately After Eating:
Blood sugar level changes rapidly according to the intake of the meal. The normal blood sugar level before eating or during fasting is between 3.5 to 6.1 mmol/L.
Normal blood sugar right after eating rises drastically as the digestive tract acts quickly to digest the food through mechanical actions, digestive enzymes and different hormones. So the blood glucose rises sharply during this time. The rate at which the blood sugar rises depends on the type of food, the amount is taken, the metabolic condition of the individual, etc.
You May Like: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Also Watch For High Blood Sugar
If youre not eating due to an acute illness like the flu or an infection, its also common for your blood sugars to rise.
When you have diabetes and are acutely ill, you should check your blood sugars up to four times per day, drink plenty of fluids and contact your doctor if your blood sugars are consistently over 250, Garvey says.
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Target Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes
It’s possible for diabetes to cause problems during pregnancy. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who have uncontrolled blood sugar levels could experience an increased risk of having a premature baby, needing a C-section and more.
Gestational diabetes a type of diabetes that occurs in a pregnant woman who has never been diagnosed with diabetes before can also cause complications. These include giving birth to a baby who is larger than average and an increased risk of needing a C-section. The ADA suggests that pregnant women shoot for a target fasting blood sugar level of 95 mg/dL or less before a meal.
Read more:Do Oranges Raise Your Blood Sugar?
Times To Check More Often
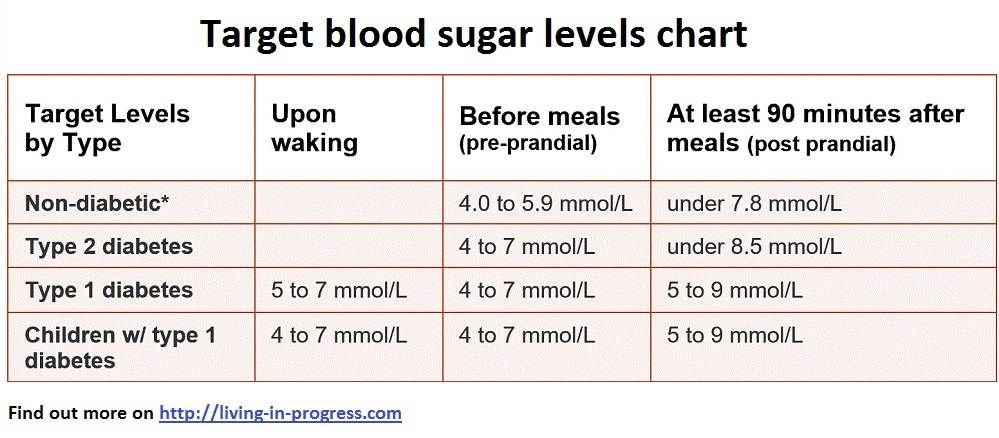
There will be times when you need to check more often, however you should first discuss this with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator. Example of these times include when you are:
- Being more physically active or less physically active
- Sick or stressed
- Experiencing changes in routine or eating habits, e.g. travelling
- Changing or adjusting your insulin or medication
- Experiencing symptoms of hypoglycaemia
- Experiencing night sweats or morning headaches
- A female planning pregnancy or are pregnant.
- Pre/post minor surgical day procedures
- Post dental procedures
Your Credentialled Diabetes Educator can help you work out self-monitoring approach especially for you.
Recommended Reading: Cloudy Before Clear Insulin
What Is Normal Blood Sugar Reading After Eating
What is normal blood sugar reading after eating? What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels? Theyre less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least 8 hours. And theyre less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating. During the day, levels tend to be at their lowest just before meals.
What should blood sugar be 1 hour after eating?;1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL. 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL. 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL.
What is a dangerous level of blood sugar after meal?;Blood sugar levels are considered high if theyre over 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL within one to two hours after a meal. Many people wont start to experience symptoms from high blood sugar until their levels are at 250 mg/dL or higher.
Is 200 blood sugar normal after eating?;Less than 140 mg/dL is normal. 140 to 199 mg/dL is diagnosed as prediabetes. 200 mg/dL or higher after two hours suggests diabetes.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About Fasting Before A Blood Test
Be sure to talk to your health care provider if you have any questions or concerns about fasting.
You should talk to your provider before taking any lab test. Most tests donât require fasting or other special preparations. For others, you may need to avoid certain foods, medicines, or activities. Taking the right steps before testing helps ensure your results will be accurate.
Also Check: How Do Doctors Check For Diabetes
Don’t Miss: Banana Raise Blood Sugar
Easy Before Bed Routines For People With Diabetes
You might be surprised to learn what your blood sugar should be at bedtime. The range is usually 5.0-8.3 mmol/L , and its important to check what yours is before going to bed. Checking your blood sugar before you go to sleep will give you information about what caused any spikes or dips in the day that you might not have noticed. For instance, if your nighttime reading were high, this would tell us that something may have happened during the day that could affect your diabetes management plan.
Creating a bed routine can also be helpful if your blood sugar at bedtime is higher than what youd like it to be. For instance, rather than eating or drinking anything sweet before bedtime and then checking how what should happen next for diabetes management will depend on what the readings are in the morning, try adding this into a routine:
- Eat dinner earlier in the evening
- Don’t drink sugar-sweetened beverages before bedtime
- Eating a nitrile snack before bed helps maintain your blood sugar normal and prevents your liver from releasing excess glucose
- Limit alcoholic beverages to the extent they disturb sleep
- Too close to bed exercises often can cause poor sleeping habits
- Avoid eating caffeine within several hours of going to bed
- Take medicine if needed to lower your blood sugar levels, but dont take too much insulin so you wont have a low reading in the morning.
Always consult with your doctor before changing anything to your diet, insulin plan, or diabetes management.
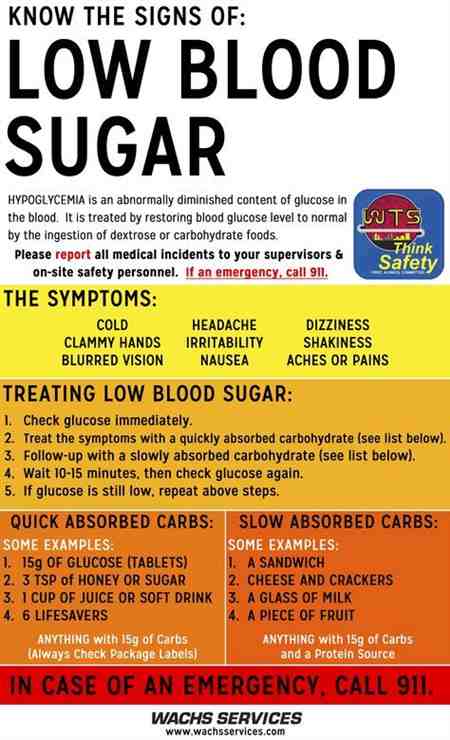
Low Blood Sugar: What To Watch Out For
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes who:
- Take too much medication or insulin
- Are late eating a meal or snack
- Have increased physical activity
- Drink too much alcohol
Symptoms of low blood sugar include feeling weak, sweaty or clammy, confused, hungry and/or irritable. Sometimes people experience a fast heartbeat and some symptoms may make a person appear to be drunk. A severely low blood sugar can result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma or death especially when a low occurs during the night.
Low blood sugar affects many parts of the body, but the most frustrating part can be that hypoglycemia can happen anytime and anywhere even when you think you are closely following the plan for your diabetes care. If low blood sugar is severe, people may need to go to the hospital to help raise their glucose level or miss work due to the side effects.
It can happen during a date, during a business meeting, or even while driving, which is the most dangerous scenario if there is confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel. Its important to use your blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others safe. Frequent testing with your blood sugar meter and taking action when blood sugar is trending low can prevent a severe low and keep your life on track.
You May Like: How To Mix Insulin
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
Support Groups And Counseling For High Blood Sugar
You or family members may wish to join a support group with other people to share your experiences. The American Diabetes Association and the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation are both excellent resources. Your health care provider will have information about local groups in your area. The following groups also provide support:
American Association of Diabetes Educators100 W Monroe, Suite 400Chicago, IL 60603
Don’t Miss: Can A Diabetic Drink Milk
Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
People with diabetes have difficulty creating or using enough insulin, which is the hormone that helps convert glucose into energy. Although there is no universal blood sugar chart for everyone with diabetes, clinical organizations like the ADA and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists offer guidelines on target blood sugar levels as a starting point.
Healthcare providers typically tailor normal blood sugar target ranges to an individual diabetes care plan. This includes considering your:
- Age
Diabetes And The Blood Glucose Test
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and teenagers whose bodies arent able to produce enough insulin. Its a chronic or long-term condition that requires continuous treatment. Late-onset type 1 diabetes has been shown to affect people between the ages of 30 and 40.
Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed in overweight and obese adults, but it can develop in younger people as well. This condition occurs when your body doesnt make enough insulin or when the insulin you produce doesnt work properly. The impact of type 2 diabetes may be reduced through weight loss and healthy eating.
Gestational diabetes occurs if you develop diabetes while youre pregnant. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after you give birth.
After receiving a diagnosis of diabetes, you may have to get blood glucose tests to determine if your condition is being managed well. A high glucose level in a person with diabetes may mean that your diabetes isnt being managed correctly.
Other possible causes of high blood glucose levels include:
- hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid
Also Check: What Is The Lowest Dose Of Metformin You Can Take

