Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin Production
Type 1 diabetes
The ways in which insulin production is impaired differs between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where antibodies attack the pancreas and destroy its ability to produce insulin, says Romy Block, M.D., endocrinologist and co-founder of Vous Vitamin. Essentially, the body is not able to produce insulin. These patients require insulin as a lifesaving medication.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, however, has two main parts: 70% is related to a decreased functioning pancreas, and 30% is related to insulin resistance, Dr. Block says. So, the insulin you have doesn’t work as well. In those with type 2 diabetes, the pancreas ability to produce insulin gets less effective over time. Some patients can be controlled with lifestyle changes and pills, while other patients require insulin, he says.
According to Dr. Block, more than 90% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes, while around only 10% of those with diabetes have type 1. Read on for the main similarities and differences between the two conditions
What You Need To Know
-
In patients with new onset hyperglycaemia where the type of diabetes is ambiguous, diabetes specific autoantibodies are the diagnostic test of choice to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
-
Patients with newly diagnosed diabetes who are over 40 and respond well to oral anti-hyperglycaemic therapy do not need to undergo testing to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
-
Glycated haemoglobin is not recommended as a diagnostic test for patients with possible or suspected type 1 diabetes because it may not reflect a recent rapid rise in blood glucose and results take longer than with serum glucose testing
A 33 year old man with no notable medical history attends his general practitioner reporting two months of fatigue, with no other symptoms. His mother has hypothyroidism. His body mass index is 25 kg/m2 and he has a pulse rate of 72 beats/min and blood pressure 135/88 mmHg with no postural drop. Examination is unremarkable. A random blood glucose test shows 14 mmol/L . Urinalysis is normal. The next day the patient returns, and a repeat fasting glucose test finds 14 mmol/L.
This article is intended to help primary care doctors to differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes when first diagnosing diabetes in a patient where the distinction is unclear.
Which Type Of Diabetes Is Most Common
Type 1 diabetes is much less common and affects about 1.25 million people. It is further estimated that of the 29.1 million people affected with diabetes, about 8.1 million people are undiagnosed, meaning that they have diabetes but are not aware of it. There has been an increase in the number of Americans with prediabetes. In 2010, 79 million people were estimated to have prediabetes. In 2012, this number was 86 million.
Don’t Miss: Lower Blood Sugar Fast
What Is Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
Many doctors consider LADA the adult form of type 1 diabetes because its also an autoimmune condition.
As in type 1 diabetes, the islet cells in the pancreas of people with LADA are destroyed. However, this process occurs much more slowly. Once it starts, it can take several months up to several years for the pancreas to stop being able to make insulin.
Other experts consider LADA somewhere in between type 1 and type 2 and even call it type 1.5 diabetes. These researchers believe that diabetes can occur along a spectrum.
Researchers are still trying to figure out the details, but in general, LADA is known to:
- develop in adulthood
- have a slower course of onset than type 1 diabetes
- often occur in people who arent overweight
- often occur in people who dont have other metabolic issues, such as high blood pressure and high triglycerides
- result in a positive test for antibodies against the islet cells
The symptoms of LADA are similar to those of type 2 diabetes, including:
- excessive thirst
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2
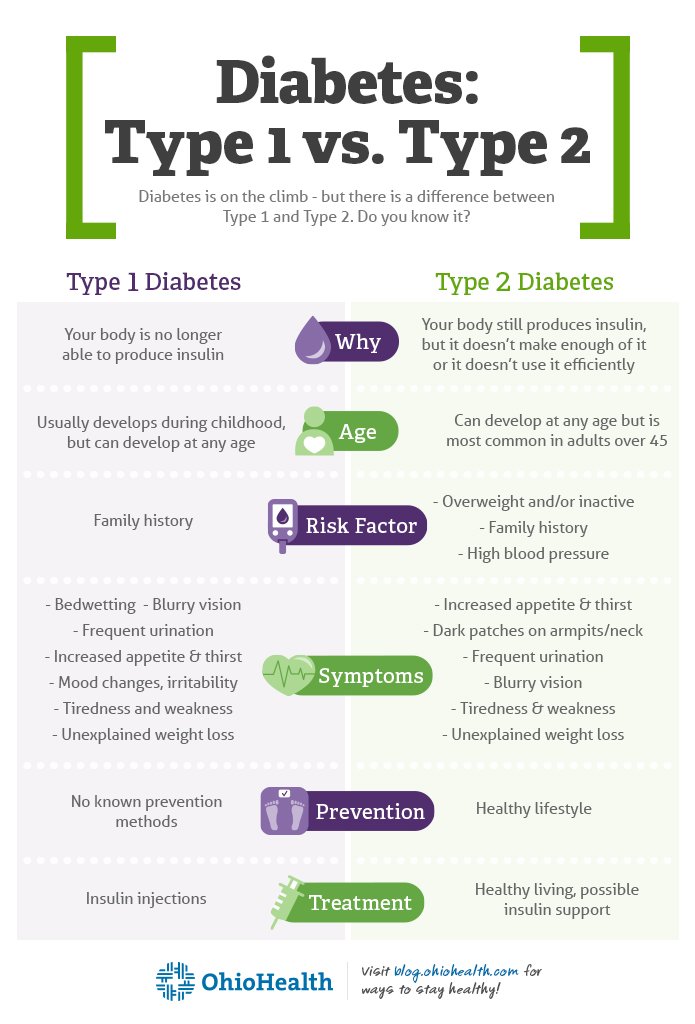
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share common symptoms. They are:
- going to the toilet a lot, especially at night
- being really thirsty
- feeling more tired than usual
- losing weight without trying to
- genital itching or thrush
- cuts and wounds take longer to heal
- blurred vision.
But where type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different in symptom is how they appear. Type 1 can often appear quite quickly. That makes them harder to ignore. This is important because symptoms that are ignored can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis .
But type 2 diabetes can be easier to miss. This is because it develops more slowly, especially in the early stages. That makes it harder to spot the symptoms. That is why it is important to know your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some people have diabetes and dont know it. They can have it for up to 10 years without knowing.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Joint Pain Side Effects
What Are The Risks And Complications Of Diabetes
Chronic high blood sugars lead to complications in all types of diabetes.
In a nutshell: the higher your blood sugars are, the more damage occurs to the nerve-endings in your fingers, toes, eyes, and kidneys, along with increased inflammation and stress throughout your body.
Perfection isnt necessary to live a long, healthy life with diabetes. Working with your healthcare team to find the right balance of medications and changes in diet and exercise to achieve the best blood sugar levels for you requires patience, persistence, and a great deal of self-discipline. Dont give up!
Type 1 Diabetes Definition
Type 1 diabetes used to go by different names, including juvenile-onset diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes. This type of diabetes is a condition that causes the immune system to destroy islet cells, cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Over time, this causes the body to stop producing insulin. The body needs insulin, a hormone, because it helps turn blood glucose into energy for cells. Type 1 diabetes is less common than Type 2 diabetes about 5% of people with diabetes have Type 1. However, about 85% to 90% of children and adolescents with diabetes have Type 1.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Onset Peak Duration
Peace Of Mind With Life Line Screening
At Life Line Screening, we have years of experience helping people prevent major medical issues with vital early detection services, including A1C screenings. In fact, screenings are our specialty. We partner with community centers to help people get quick, easy access to the screenings they want to stay on top of their health. No lengthy doctors visits, no complicated insurance to deal with, just convenient screenings for health-conscious people conducted by trained professionals.
Learn more or schedule a screening today at lifelinescreening.com or give us a call at . Wed love to help.
In Type 2 Diabetes Your Body Produces Insulin But It Doesn’t Work Properly
“In type 2 diabetes, you produce insulin, but the main issue is that the rest of your body does not listen to it,” O’Malley explains. “We call this insulin resistance.” When blood sugar is high and insulin is released, your body ignores it. Just like in type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar stays high, your liver releases even more glucose, and other cells don’t get the energy they need.
“With time, some patients with type 2 diabetes may start to produce less insulin, but not to the same extent as with type 1,” O’Malley says.
Although some people are genetically predisposed to developing type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors also play a role. According to the NIDDK, a person is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if they are overweight or obese, have high blood pressure, have high cholesterol or are not physically active. People over the age of 45, or with a history of heart attack or stroke, are also more likely to develop the disease.
Although people with type 2 diabetes sometimes experience the same symptoms as those with type 1 diabetes prior to diagnosis, many have no symptoms at all . Doctors routinely test for diabetes using blood glucose tests in patients over 45, or patients with two or more other risk factors, according to the NIDDK. As in type 1 diabetes, glucose levels of 126 or above for the fasting plasma glucose test, or 200 or above for the oral glucose tolerance or random plasma glucose tests, are indicative of diabetes.
Also Check: Optimal A1c For Non Diabetic
What Is A Diabetes Meal Plan
There’s no “magic” diabetes diet. However, there are dietary recommendations for people with diabetes. Diet methods for managing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes include:
- Carbohydrate counting
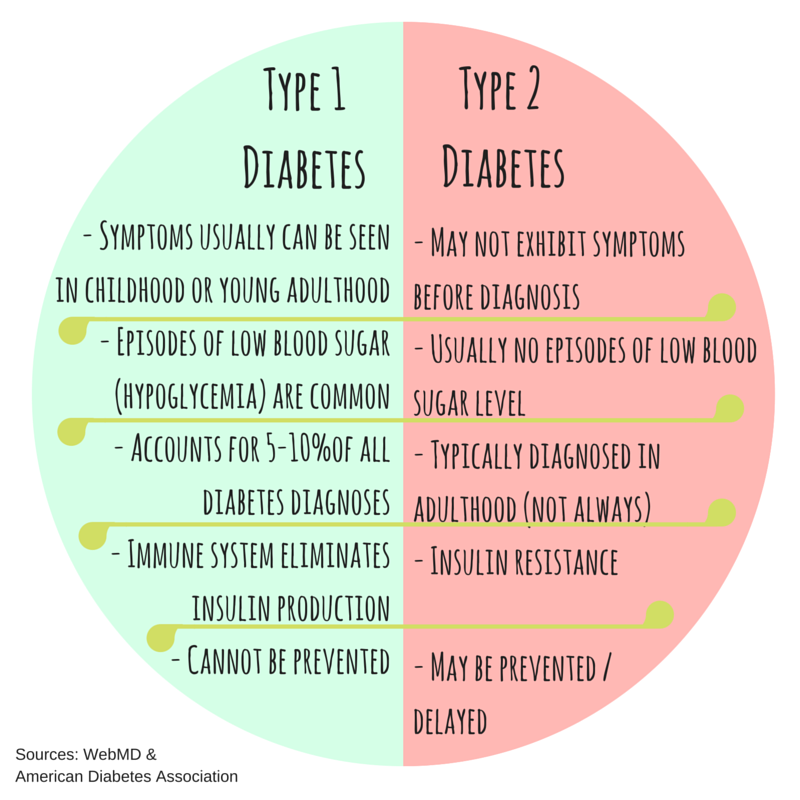
Signs and symptoms of diabetes, whether type 1 or type 2, do not differ.
- Early diabetes may not produce any symptoms at all.
- When symptoms do occur, the age of onset is typically different, with type 1 diabetes being diagnosed most often in younger people , while type 2 diabetes is diagnosed more commonly in adults. However, this is not always the case.
- The increasing incidence of obesity among children and adolescents has caused a rise in the development of type 2 diabetes in young people.
- Further, some adults with diabetes may be diagnosed with a form of late-onset type 1 diabetes.
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
Diagnosing diabetes is very straight-forward for both types, but type 1 diabetes comes on so quickly that patients generally get to the hospital quickly. Type 2 diabetes, however, comes on so slowly that it can easily go undiagnosed for years if you arent going to your primary care doctor regularly for check-ups.
TYPE 1: Type 1 diabetes is easy to diagnose once a doctor has a chance to test your urine and prick your finger for a blood sample, but the symptoms can easily be overlooked for the flu, so its important to always have your child or yourself as an adult tested for type 1 diabetes at that time as well.
Testing the urine for ketones and the blood for a blood glucose reading is very fast and easy at the doctors office or in an emergency room.
Type 1 diabetes used to be considered a disease that was always diagnosed during childhood but the rates of adult diagnoses has climbed dramatically, and is very common now.
An uninformed doctor may dismiss a type 1 diagnosis just because of the patients age, and misdiagnose them as a type 2. In this case, the patient can ask for an autoantibodies test to clearly determine which type they have.)
TYPE 2: Type 2 diabetes is also straight-forward to diagnose based on an A1c test and a blood glucose test, but there are a couple of stages.
-
Pre-diabetes: A1c above 5.6 percent
-
Type 2 diabetes: A1c above 6.5 percent
-
Pre-diabetes: fasting blood sugar above 100 mg/dL
-
Type 2 diabetes: fasting blood sugar above 126 mg/dL
Also Check: Type 1 Diabetes Tips And Tricks
How To Treat Type 2 Diabetes:
Unlike type 1, people with type 2 diabetes often do not need to take insulin, because their bodies still produce a small amount of it. Though there are medications like Metformin available to assist in lowering blood sugar, the primary ways to treat type 2 diabetes are:
- A balanced diet. Eating fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins while avoiding more than the occasional high-fat, high-sugar food is the first and most essential step to treating type 2 diabetes.
- Exercise. Staying active is also very important. There are so many ways to get exercise. Try different activities to find a type of exercise you enjoy and work it into your weekly routine.
- Weight loss. Of course, if you work toward eating healthier and exercising, this may be a byproduct. Losing weight is less about the number on the scale and more about taking care of your body and reducing the strain on your pancreas.
- Blood glucose monitoring. Checking your blood sugar regularly will become a part of your daily routine. Its important to stay up-to-date on how your levels are doing throughout the day and adjust your food and activities accordingly. After a while youll figure out the regimen and balance that works best for you.
Men Are At Higher Risk
Men are more likely to develop both types than women. Both sexes are equally affected by type 1 in childhood, but the incidence is higher in males than in females in adulthood, says Marina Basina, MD, clinical associate professor at Stanford University Medical Center, and an advisory board member for Beyond Type 1, a philanthropic foundation focusing on educating, advocating, and eventually curing type 1, and CarbDM, an online community for people with type 1 diabetes. Men are at slightly higher risk of developing type 2 than women, which is possibly due to lifestyle factors, body weight, and the fat distribution in the bodyabdominal versus in the hips.
Both types of the disease can develop at any age, but while there is no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes can be preventedor at least delayedwith diet and lifestyle changes, according to research in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of High Or Low Blood Sugar
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
The Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2 Are Different
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, which means that your immune system mistakenly attacks your body. In the case of type 1 diabetes, immune-system cells go after the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, which causes insulin production to suddenly turn off.
No one knows exactly why your body goes on the offensive, but there are probably many contributing factors. “We don’t completely understand why this happens but there is some data that a viral infection can trigger the process if you already have a predisposition,” says Dr. Vouyiouklis Kellis. “You may already have antibodies but the second hit is a viral infection.” That predisposition could also be genetic.
With type 2 diabetes, genetics, including family history, can also play a role, but here the main risk comes from being obese or overweight, as well as other lifestyle factors, such as not being active and eating unhealthy foods, Jasmine D. Gonzalvo, PharmD, director of the Center for Health Equity and Innovation at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, tells Health. “The body still has some ability to produce insulin, but the body has a resistance to the insulin.” In type 2 diabetes, the cells may also have difficulty using the insulin effectively, called insulin resistance.
RELATED: What Causes Type 1 Diabetes? 3 Things You Need to Know, According to Doctors
Also Check: What Is The Normal A1c Level For A Nondiabetic
How Is Diabetes Treated
TYPE 1: A person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will need to begin taking insulin immediately. Depending on the severity of ketone levels, a short stay in the hospital may be necessary to get saline through an IV to flush out the ketones, rehydrate the body, and stabilize fully before heading home.
Type 1 diabetes requires constant, 24/7 attention to the balancing act of food, activity, insulin, and some non-insulin diabetes medications.
Other variables such as hormones, stress, weight-gain or weight-loss, age and growth, and menstruation all impact blood sugar levels and insulin needs. Perfection is neither expected nor reasonable to demand of any patient with type 1 diabetes, but encouraging patients to do the best they can with the medications, technology, and knowledge available today is crucial.
Thanks to many advancements in technology, people with type 1 diabetes have a variety of choices when it comes to how they take their insulin with pumps, pods, and insulin pens.
Every person living with type 1 diabetes needs their own glucose meter to check your blood sugar at least 4x per day. Many patients today are also using continuous glucose monitors .
TYPE 2:Treating type 2 diabetes comes with many more medication options than type 1 diabetes because not all type 2 patients will need to start taking insulin.
Only Type 2 Diabetes Can Be Prevented
There’s no way to prevent type 1 diabetes, but you can help prevent type 2 with lifestyle modifications. “We’re talking about making healthier food choices, engaging in physical activity, and taking medication,” says Dr. Gonzalvo.
To get our top stories delivered to your inbox, sign up for the Healthy Living newsletter
- Tags
You May Like: Normal A1c For Non Diabetic

