What Abnormal Results Mean
If you had a fasting blood glucose test:
- A level of 100 to 125 mg/dL means you have impaired fasting glucose, a type of prediabetes. This increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A level of 126 mg/dL or higher usually means you have diabetes.
If you had a random blood glucose test:
- A level of 200 mg/dL or higher often means you have diabetes.
- Your provider will order a fasting blood glucose, A1C test glucose tolerance test , depending on your random blood glucose test result.
- In someone who has diabetes, an abnormal result on the random blood glucose test may mean that the diabetes is not well controlled.
Other medical problems can also cause a higher-than-normal blood glucose level, including:
- Overactive thyroid gland
- Swelling and inflammation of the pancreas ( pancreatitis
- Stress due to trauma, stroke, heart attack, or surgery
- Rare tumors, including
- Weight loss after weight loss surgery
- Vigorous exercise
Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Before having the test, tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking.
For some thin young women, a fasting blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL may be normal.
Blood Sugar Levels In Prediabetes
Blood sugar levels in prediabetes are higher than normal, but not as high as in diabetes. A fasting blood glucose or fasting plasma glucose test or an oral glucose tolerance test can assess your blood sugar and can be used to diagnosis prediabetes.
You take the FPG after an overnight fast, without eating or drinking anything with calories. Then you get your blood drawn and wait for your results to come in, which could take hours to weeks depending on your lab and healthcare provider.
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner than age 45.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 and then every 3 years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
Read Also: Metformin Max Dose Per Day
Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Diabetics
The American Diabetes Association recommends that the blood sugar 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal be less than 180 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. This is typically the peak, or highest, blood sugar level in someone with diabetes. Again, this target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Recommended Reading: Can A Diabetic Eat Pasta
What Is Blood Sugar
When you eat, the carbohydrate in your food is broken down into a usable form of energy called glucose. Glucose also known as sugar enters the bloodstream and a hormone called insulin helps move it into our cells.
This process lowers the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. When this process works efficiently, your muscles and organs have the fuel they need without there being too much glucose remaining in the blood.
Remedies For Low Blood Sugar Levels
If you experience any of the low sugar symptoms, immediately test your blood glucose levels. For levels between 60 to 80 mg/dL, consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbs. Repeat the test after 15 minutes and eat till sugar levels settle to normal.
But if the levels are below 50 mg/dL and if the patient is conscious and able to eat, give 15 gm. of fast-acting carbs. But if the patient is unable to speak, dont give anything to eat. Call emergency services immediately. If possible, administer glucagon via injection.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Using Insulin
Target Glucose Ranges For Adults
- Fasting glucose range: 72-90 mg/dL or 4.0-5.0 mmol/L
- Before eating: Depends on what you ate, what you did, and what you plan to eat
- Glucose range 1-2 hours after eating: < 120 mg/dL or 6.7 mmol/L
Most blood sugar charts show recommended levels as a range, allowing for differences between individuals. People with diabetes will often have higher blood sugar targets or âacceptableâ ranges than those without the condition, although a standard treatment goal in diabetes is to keep your blood glucose in a normal range as much as possible.
For type 1 diabetics and type 2 diabetics, blood sugar ranges are higher than the averages and targets listed above. According to the American Diabetes Association, average blood sugar levels for diabetics are:
- Fasting plasma glucose: 126 mg/dL or higher
- Before eating: 80â130 mg/dL
- One to two hours after eating: < 180 mg/dL
Diabetes occurs when the pancreas cannot make enough insulin to clear glucose out of the blood. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that moves glucose from what we consume from the bloodstream and into the cells to make energy.
Abnormal blood sugar occurs when thereâs either too much or too little sugar in the blood.
- Hypoglycemia is 70 mg/dL or less .
- Hyperglycemia is 180 mg/dL or more.
Blood Sugar Basics: What Is Blood Sugar
The term blood sugar refers to the sugar, or glucose, that is floating around in your bloodstream at any given time. Blood sugar, or blood glucose is the main source of sugar found in your blood, and comes from the food you eat. I
f you are monitoring your blood sugar, it is important to keep these numbers in check according to the American Diabetes Association .
Your blood sugar needs to be in the right range for you to be healthy. At least some glucose is necessary for your muscle, liver, and some other cells to use as fuel so they can function.
At least some sugar is necessary for your cells and organs to function properly. When our blood sugar levels get too low, it is called hypoglycemia. Without enough glucose as fuel, we lose the ability to function normally. This can make us feel weak, dizzy, and sweaty. And it can even lead to loss of consciousness.
On the other hand, blood sugar levels that get too high are also harmful, this is called hyperglycemia. Our blood sugar levels can get too high when we dont have enough insulin, or when our insulin isnt working well. This is the case for people who have prediabetes or diabetes. If it isnt treated, high blood sugar can lead to serious problems that can be deadly
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention explains that keeping blood sugar levels in the target range is vital. It can help us prevent serious health concerns like heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease, for example.
Also Check: Metformin Should Be Used With Caution For Patients Who Have
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. The following is a list of healthy blood sugar levels.
If an individual has type 1 diabetes the blood sugar should be the following:
- Before meals: From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- After meals : Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
- At bedtime: From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
If an individual has type 2 diabetes, levels should be the following:
- Before meals: From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- After meals : Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
The Big Picture: Checking Your Blood Sugar
Blood sugar monitoring is the primary tool you have to find out if your blood glucose levels are within your target range. This tells you your blood glucose level at any one time.
Its important for blood sugar levels to stay in a healthy range. If glucose levels get too low, we can lose the ability to think and function normally. If they get too high and stay high, it can cause damage or complications to the body over the course of many years.
The logging of your results is vital. When you bring your log to your healthcare provider, youll have a good picture of your body’s response to your diabetes care plan. To help keep track of your levels, we have a glucose log. We also have a blood glucose log available for purchase that is smaller so you can carry it with you.
Also Check: Bad Effects Of Insulin
Who Should Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, monitoring your blood sugar regularly will help you understand how medication like insulin, food, and physical activity affect your blood glucose. It also allows you to catch rising blood sugar levels early. It is the most important thing you can do to prevent complications from diabetes such as heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Other people who may benefit from checking their blood glucose regularly include those:
- Taking insulin
What Is Considered A Normal Blood Sugar Level
![25 Printable Blood Sugar Charts [Normal, High, Low] á? ... 25 Printable Blood Sugar Charts [Normal, High, Low] á? ...](https://www.livingwithdiabetes.info/wp-content/uploads/25-printable-blood-sugar-charts-normal-high-low-a.jpeg)
The normal blood sugar level for a healthy, non-diabetic adult is determined by when and how blood sugar levels are tested.
The below information describes what normal blood sugar levels are prior to and after meals and what the recommended HbA1c and Haemoglobin A1c levels are for those with and without diabetes.
If you are diabetic, it is advisable to consult with your doctor in order for appropriate blood sugar level targets to be set based on your age, the severity of your condition, medications taken and overall health status.
Don’t Miss: Low Blood Pressure High Blood Sugar
What Are Satisfactory Blood Glucose Meter Readings
As of 2007, 7.8 percent of the U.S. population has diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association. Although this condition can lead to life-threatening complications if not controlled, monitoring your blood sugar with a blood glucose meter can help you maintain healthy glucose levels and avoid complications. If you have diabetes, consult a health care provider about the glucose meter readings that are ideal for you.
Video of the Day
How To Prevent Hyperglycaemia
There are simple ways to reduce your risk of severe or prolonged hyperglycaemia:
- Be careful what you eat be particularly aware of how snacking and eating sugary foods or carbohydrates can affect your blood sugar level.
- Stick to your treatment plan remember to take your insulin or other diabetes medications as recommended by your care team.
- Be as active as possible getting regular exercise can help stop your blood sugar level rising, but you should check with your doctor first if you’re taking diabetes medication, as some medicines can lead to hypoglycaemia if you exercise too much.
- Take extra care when you’re ill your care team can provide you with some “sick day rules” that outline what you can do to keep your blood sugar level under control during an illness.
- Monitor your blood sugar level your care team may suggest using a device to check your level at home so you can spot an increase early and take steps to stop it.
Page last reviewed: 08 August 2018 Next review due: 08 August 2021
You May Like: Is Pasta Good For Diabetics
Controlling Your Glucose Levels
Getting satisfactory readings on your blood glucose meter requires controlling your diet. If you have hypoglycemia not related to diabetes, eat frequent meals and snacks with a balanced amount of complex carbohydrates, protein and fat. If you have diabetes, base your diet on grains, vegetables and fruits and aim to get 10 to 20 percent of your calories from protein, recommend University of Maryland experts. Limit high carbohydrate foods including starchy vegetables and sweets. Insulin injections may also be necessary.
What Should My Blood Sugar Level Be
When you’re first diagnosed with diabetes, your diabetes care team will usually tell you what your blood sugar level is and what you should aim to get it down to.
You may be advised to use a testing device to monitor your blood sugar level regularly at home.
Or you may have an appointment with a nurse or doctor every few months to see what your average blood sugar level is. This is known as your HbA1c level.
Target blood sugar levels differ for everyone, but generally speaking:
- if you monitor yourself at home with a self-testing kit a normal target is 4 to 7mmol/l before eating and under 8.5 to 9mmol/l 2 hours after a meal
- if your HbA1c level is tested every few months a normal HbA1c target is below 48mmol/mol
The Diabetes UK website has more about blood sugar levels and testing.
Read Also: Diabetes Stomach Pain Treatment
When Things Go Awry
When we eat food, the pancreas goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose . If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis. Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, its all about the blood glucose.
Know Your Body Mass Index
Being overweight or obese puts you at risk for developing type 2 diabetes. BMI is an easy way to estimate excess fat. Even a small change in body weight can reduce your risk of diabetes.
If your score is:
25.029.9 = Overweight/Pre-obese 30.0 and over = Obese
To calculate your BMI, you can use the BMI chart or the formulas at the bottom of this page or complete the Canadian diabetes risk questionnaire.
Read Also: Metformin Cause Hypoglycemia
Other Tips For Checking:
- With some meters, you can also use your forearm, thigh, or fleshy part of your hand.
- There are spring-loaded lancing devices that make sticking yourself less painful.
- If you use your fingertip, stick the side of your fingertip by your fingernail to avoid having sore spots on the frequently used part of your finger.
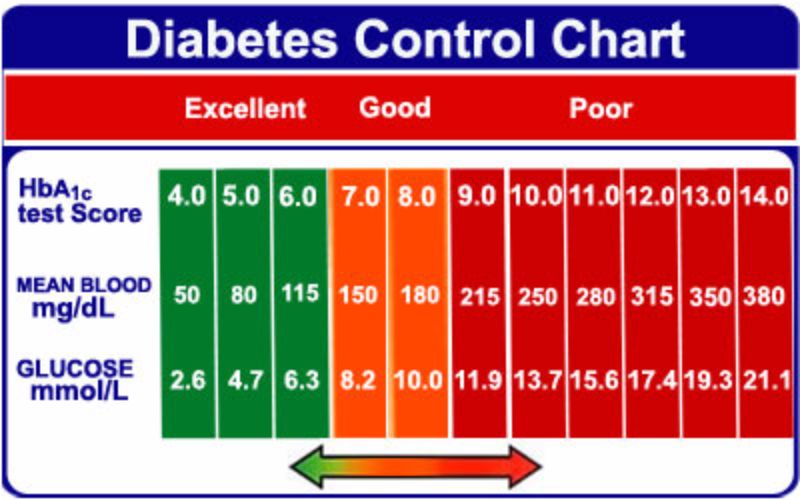
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
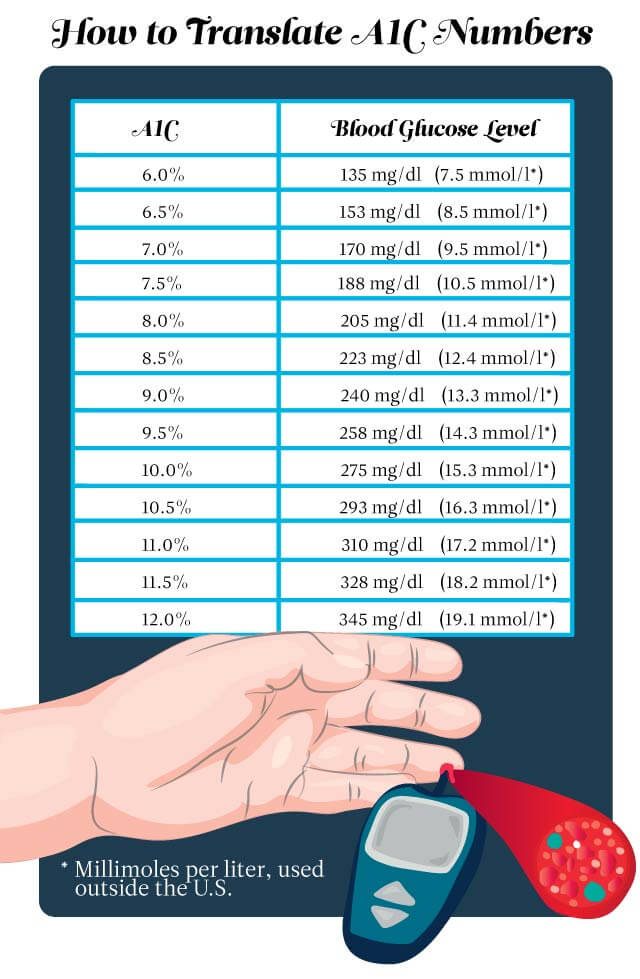
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
Also Check: How Much Blood Sugar Is Too High
When Should You Check Your Blood Sugar Levels
Its important that people who suspect they have diabetes or pre-diabetes monitor their glucose levels regularly, checking at least once daily and charting the results in order to know what is normal for themselves. If it seems like something isnt quite right with ones blood glucose. It may be time to talk to a doctor about getting a diabetes diagnosis. Its also important that parents make sure their children are well aware of any symptoms of high or low blood sugar. So they know when they need to alert an adult about what might be going on if their parents are not around.
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
Read Also: Dangers Of Low Blood Sugar

