Why Am I Having Lows
If you are experiencing low blood sugar and youre not sure why, bring a record of blood sugar, insulin, exercise and food data to a health care provider. Together, you can review all your data to figure out the cause of the lows.
The more information you can give your health care provider, the better they can work with you to understand what’s causing the lows. Your provider may be able to help prevent low blood sugar by adjusting the timing of insulin dosing, exercise and meals or snacks. Changing insulin doses or the types of food you eat may also do the trick.
Glucagon May Help Fight Obesity
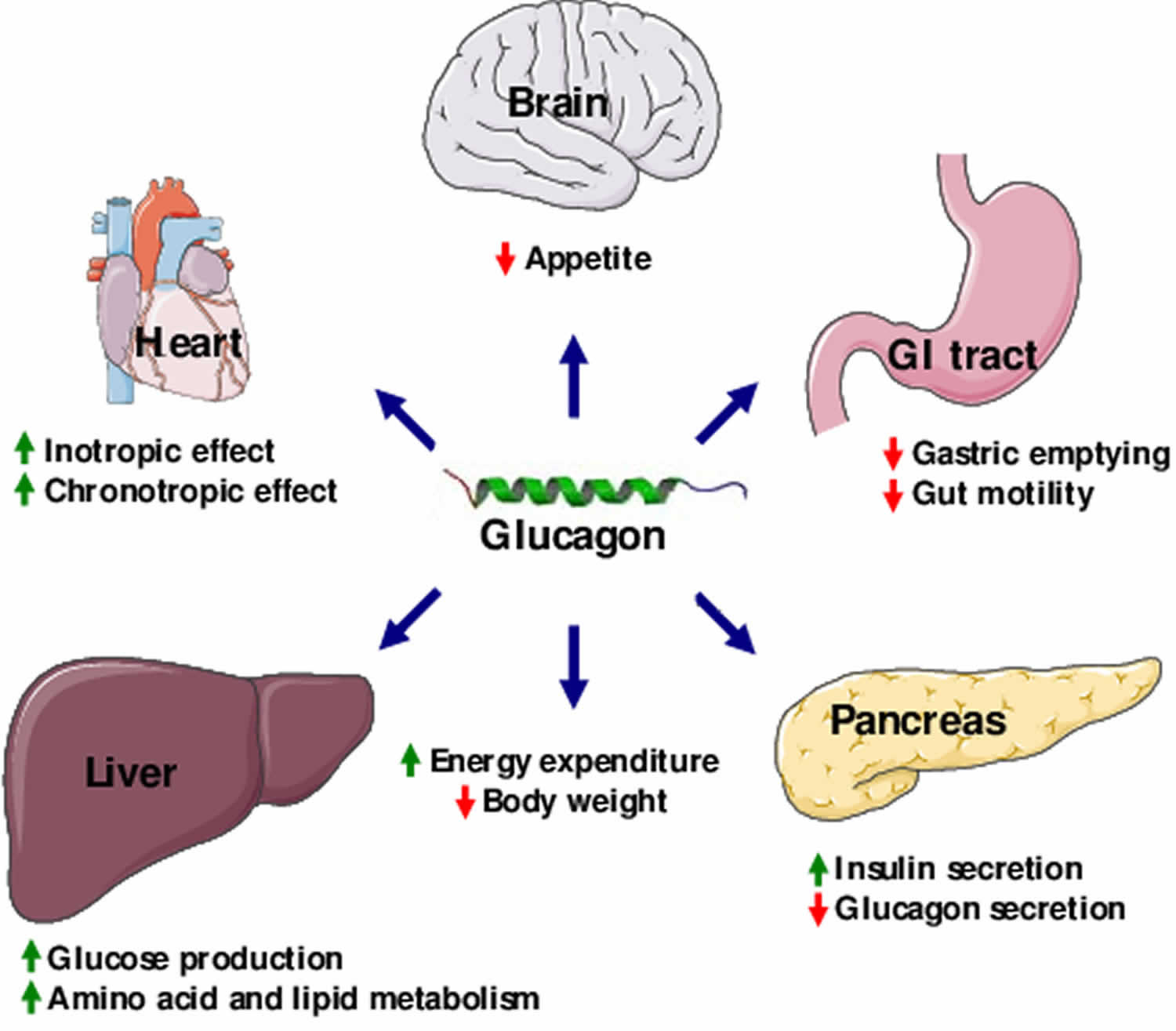
Glucagon and glucagon-like substances are being investigated as weight-loss therapies. Thats because glucagon may increase satiety and may help burn fats. Scientists are designing drugs which would have these beneficial effects of glucagon without raising blood sugar levels. This would potentially help with metabolic syndrome, obesity, or high blood cholesterol .
Hormones Of The Pancreas
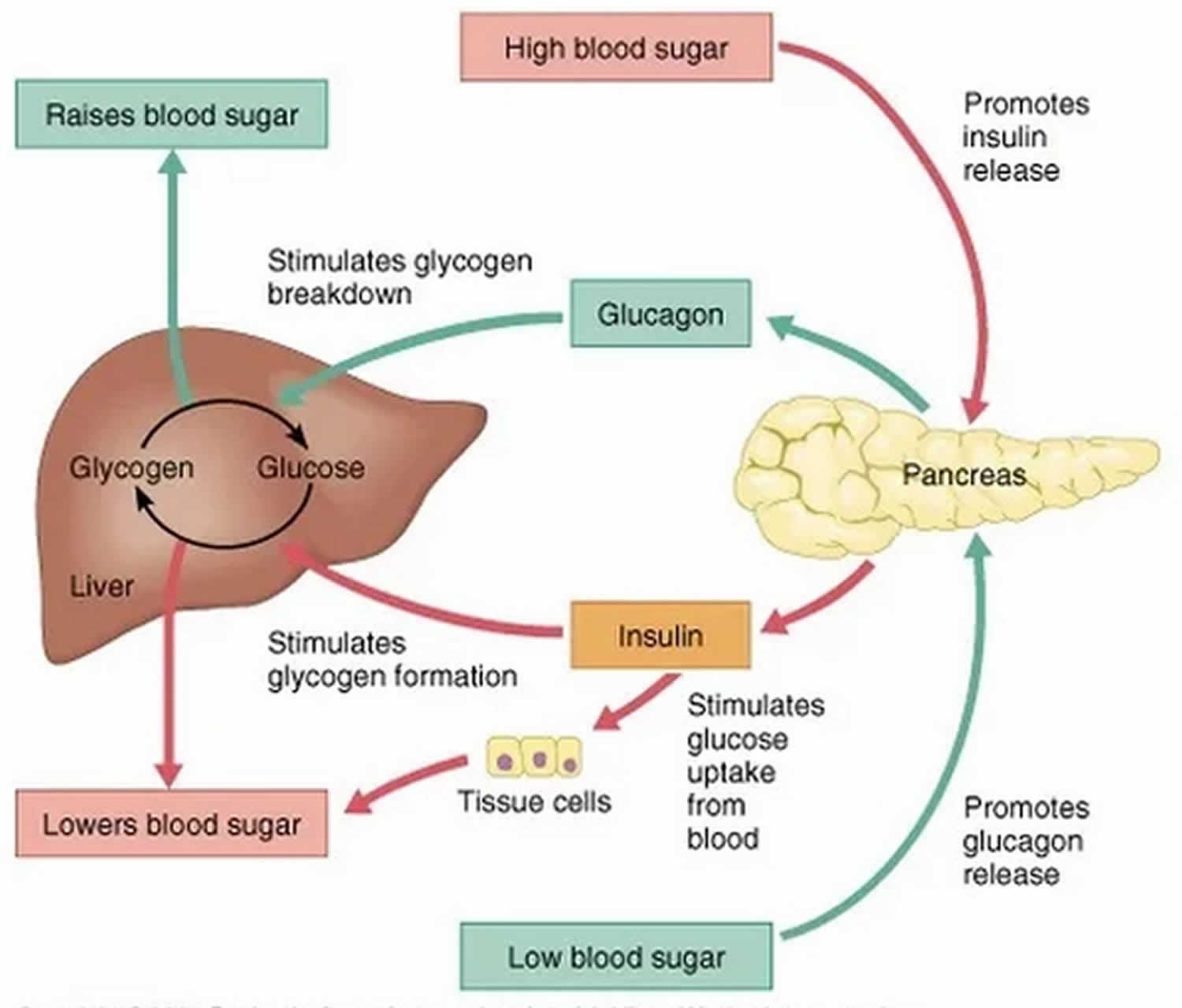
Regulation of blood glucose is largely done through the endocrine hormones of the pancreas, a beautiful balance of hormones achieved through a negative feedback loop. The main hormones of the pancreas that affect blood glucose include insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and amylin.
Insulin lowers BG levels, whereas glucagon elevates BG levels.
Somatostatin is formed in the delta cells of the pancreas and acts as the pancreatic policeman, balancing insulin and glucagon. It helps the pancreas alternate in turning on or turning off each opposing hormone.
Amylin is a hormone, made in a 1:100 ratio with insulin, that helps increase satiety, or satisfaction and state of fullness from a meal, to prevent overeating. It also helps slow the stomach contents from emptying too quickly, to avoid a quick spike in BG levels.
In a healthy liver, up to 10% of its total volume is used for glycogen stores. Skeletal muscle cells store about 1% of glycogen. The liver converts glycogen back to glucose when it is needed for energy and regulates the amount of glucose circulating between meals. Your liver is amazing in that it knows how much to store and keep, or break down and release, to maintain ideal plasma glucose levels. Imitation of this process is the goal of insulin therapy when glucose levels are managed externally. Basalbolus dosing is used as clinicians attempt to replicate this normal cycle.
Test Your Knowledge
Apply Your Knowledge
Online Resource
Don’t Miss: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Treating Low Blood Sugar When Glucagon Isnt Needed
If low blood sugar is treated promptly, it wont usually drop low enough to be considered severe. Glucagon is only needed in cases of severe hypoglycemia, when a person isnt able to treat the condition themselves.
In most cases, a person with diabetes can treat low blood sugar on their own or with minimal help. The treatment is to consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as:
- ½ cup juice or soda that contains sugar
- 1 tablespoon honey, corn syrup, or sugar
- glucose tablets
Following treatment, its important to wait 15 minutes and then recheck your blood sugar levels. If your blood sugar levels are still low, consume another 15 grams of carbohydrates. Continue doing this until your blood sugar is above 70 mg/dL .
Why The Test Is Performed

Glucagon stimulates the liver to release glucose. As the level of blood sugar decreases, the pancreas releases more glucagon. And as blood sugar increases, the pancreas releases less glucagon.
The provider may measure glucagon level if a person has symptoms of:
- Diabetes
- Glucagonoma with symptoms of a skin rash called necrotizing migratory erythema, weight loss, mild diabetes, anemia
- Growth hormone deficiency in children
- Liver
- Low blood sugar — most common reason
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type I
- Pancreatitis
You May Like: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
Glucagon Concentrations In The Circulation
In normal physiology, circulating glucagon concentrations are in the picomolar range. In the fasting state with plasma glucose levels around 5 mmol/l, glucagon is secreted in basal levels resulting in plasma concentrations below 20 pmol/l . Basal glucagon secretion balances the effect of basal insulin secretion resulting in a steady-state between glucose uptake and endogenous glucose production in the fasted state i.e. stable blood glucose concentrations. During exercise or in case of hypoglycemia, circulating glucagon levels may increase dramatically to 3-4 times basal levels increasing the glucagon to insulin ratio .
Regulation Of Blood Glucose Levels By Thyroid Hormones
The basal metabolic rate, which is the amount of calories required by the body at rest, is determined by two hormones produced by the thyroid gland: thyroxine, also known as tetraiodothyronine or T4, and triiodothyronine, also known as T3. These hormones affect nearly every cell in the body except for the adult brain, uterus, testes, blood cells, and spleen. They are transported across the plasma membrane of target cells and bind to receptors on the mitochondria resulting in increased ATP production. In the nucleus, T3 and T4activate genes involved in energy production and glucose oxidation. This results in increased rates of metabolism and body heat production, which is known as the hormones calorigenic effect.
Disorders can arise from both the underproduction and overproduction of thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism, underproduction of the thyroid hormones, can cause a low metabolic rate leading to weight gain, sensitivity to cold, and reduced mental activity, among other symptoms. In children, hypothyroidism can cause cretinism, which can lead to mental retardation and growth defects. Hyperthyroidism, the overproduction of thyroid hormones, can lead to an increased metabolic rate and its effects: weight loss, excess heat production, sweating, and an increased heart rate. Graves disease is one example of a hyperthyroid condition.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Effects Of Autonomic Nerves
The islets of Langerhans receive both parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation. The activation of the parasympathetic system during meals stimulates insulin secretion at the same time that gastrointestinal function is stimulated. The activation of the sympathetic system, by contrast, stimulates glucagon secretion and inhibits insulin secretion. The effects of glucagon, together with those of epinephrine, produce a stress hyperglycemia when the sympathoadrenal system is activated.
What Does Glucagon Do To Blood Sugar
Severe Hypo and Zegalogue: A Conversation with Dr. David Kendall and Dr. Danilo Verge David Kendall and Danilo Verge of Zealand Pharma spoke with diaTribe about Zegalogue , a new emergency glucagon injection used to treat severe hypoglycemia in people with diabetes over.
Be sure to always have a fast-acting carbohydrate with you, such as juice or glucose tablets so that you can treat a falling blood sugar level before it dips dangerously low. But too much insulin or other diabetes medications may cause your blood sugar level to drop too low, causing hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia can also occur if you eat less than usual after taking diabetes medication, or if you exercise more than you normally do. If you have diabetes, you might not make enough insulin or you might be less responsive to it . As a result, glucose tends to build up in the bloodstream and can reach dangerously high levels. To correct this problem, you might take insulin or other drugs to lower blood sugar levels. What Provides The Fuel Your Body Needs
For people with diabetes, routinely monitoring your blood sugar can be the key to feeling properly and functioning usually. Even if your diabetes is under control, for the most element, spikes can happen, and youll need to make sure that you are.
The pharma massive is now acquiring the relaxation of Protomer that it does now not already.
A smart glucagon. Injectable glucagon is a rescue remedy used while blood sugar tiers fall dangerously.
Read Also: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
When To Use Your Glucagon Emergency Kit
You need glucagon if your blood sugar level is less than 50 mg/dl and you are:
- Unable to eat or drink safely because youre confused or disoriented
- Unconscious
- Having seizures
If possible, someone will need to check your blood sugar level to make sure its low. This is because having high blood sugar can also make you unconscious. In that case, glucagon wont help. Instead, get medical attention right away by calling 911. If you cannot find the blood glucose kit, and the person is showing the symptoms above, skip this step.
Regulation Of Glucagon Secretion By Glucose
The most potent regulator of glucagon secretion is circulating glucose. Hypoglycemia stimulates the pancreatic alpha cell to release glucagon and hyperglycemia inhibits glucagon secretion . The cellular mechanism behind this glucose-dependent regulation of glucagon secretion involves uptake of glucose by the glucose transporter 1 in the cell membrane of pancreatic alpha cells and subsequent glycolysis which ultimately generates adenosine triphosphate in the mitochondria of the alpha cell. Thus, the intracellular ATP level in the alpha cell reflects plasma glucose levels. Hypoglycemia and resulting low intracellular ATP levels in the alpha cell close ATP-sensitive potassium channels whereby the efflux of potassium is reduced. This causes a depolarization of the cell membrane which, in turn, opens voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels allowing influx of Ca2+. This increases intracellular Ca2+ levels, the primary trigger for exocytosis of glucagon granules from the alpha cells . Conversely, increasing circulating glucose levels increase glucose influx to the alpha cell generating an increase in intracellular ATP concentration, which opens KATP-channels. This leads to a membrane potential that closes voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels thereby preventing Ca2+ influx and glucagon secretion .
Recommended Reading: What To Do If A Diabetic Feels Dizzy
How Does Insulin And Glucagon Regulate Glycolysis
insulinwillcanGlucagon doeswill
Insulin helps the cells absorb glucose, reducing blood sugar and providing the cells with glucose for energy. When blood sugar levels are too low, the pancreas releases glucagon. Glucagon instructs the liver to release stored glucose, which causes blood sugar to rise.
Additionally, does insulin increase glycolysis? Insulin has the opposite effect on these enzymes. Thus the phosphorylation of phosphofructokinase inhibits glycolysis, whereas its dephosphorylation through the action of insulin stimulates glycolysis.
Similarly, you may ask, how does insulin regulate glycolysis?
Glycolysis is regulated by a key bifunctional enzyme, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 1 . Insulin dephosphorylates phosphorylated-PFKFB1 and activates its kinase activity, thereby promoting glycolysis .
Why does glucagon inhibit glycolysis?
Glucagon generally elevates the concentration of glucose in the blood by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Glucagon turns off glycolysis in the liver, causing glycolytic intermediates to be shuttled to gluconeogenesis. Glucagon also regulates the rate of glucose production through lipolysis.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About A Glucagon Blood Test
A glucagon blood test and a test called a glucagon stimulation test are both often called glucagon tests. But they are not the same thing. A glucagon blood test is used to check conditions related to glucose levels. A glucagon stimulation test checks for problems with growth hormones. It is most often used for infants and children.
Read Also: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Regulation Of Blood Glucose Levels By Insulin And Glucagon
Glucose is required for cellular respiration and is the preferred fuel for all body cells. The body derives glucose from the breakdown of the carbohydrate-containing foods and drinks we consume. Glucose not immediately taken up by cells for fuel can be stored by the liver and muscles as glycogen, or converted to triglycerides and stored in the adipose tissue. Hormones regulate both the storage and the utilization of glucose as required. Receptors located in the pancreas sense blood glucose levels, and subsequently the pancreatic cells secrete glucagon or insulin to maintain normal levels.
How Can I Increase Glucagon In My Body
TheglucagonTheglucagonthe
. Likewise, people ask, what happens if you don’t have enough glucagon?
Glucagon helps your liver break down the food you eat to make glucose. If your blood sugar drops too low, you can get hypoglycemia. This can make you feel dizzy or sluggish or even pass out.
Subsequently, question is, what happens when glucagon levels are high? Glucagon balances the effects of insulin by regulating the amount of sugar in your blood. If you have too much glucagon, your cells don’t store sugar and instead sugar stays in your bloodstream. Glucagonoma leads to diabetes-like symptoms and other painful and dangerous symptoms, including: high blood sugar.
In this way, what causes glucagon deficiency?
Glucagon deficiency is one of the major causes of hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by diminished levels of glucose in the blood. Glucagon deficiency can produce a variety of symptoms, but the principal problems arise from an inadequate supply of glucose in the brain and resulting impairment of function.
Where should glucagon be injected?
Glucagon is given just like an injection of insulin and can be given in the buttock, upper arm, or thigh. Follow these steps to give the injection: Follow the instructions on the glucagon kit to mix the powder and the liquid. Choose a clean site for the shot on the buttock, upper arm, or thigh.
Read Also: Antiglycemic Definition
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may indicate that the person may have a condition described above under Why the Test is Performed.
Some experts now believe that high glucagon levels in the blood contribute to the development of diabetes instead of just a low level of insulin. Medicines are being developed to decrease glucagon levels or block the signal from glucagon in the liver.
When your blood sugar is low, the level of glucagon in your blood should be high. If it is not increased, this can help identify people that are at higher risk of severe hypoglycemia that can be dangerous.
Glucagon can be increased by prolonged fasting.
The Role Of Glucagon In The Pathophysiology And Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
- Center for Diabetes Research, Gentofte Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Hellerup, DenmarkFaculty of Health and Medical Sciences, Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, DenmarkNovo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
- Tina VilsbøllCorrespondenceCorrespondence: Address to Tina Vilsbøll, MD, DMSc, Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen, University of Copenhagen, Niels Steensens Vej 2, DK-2820 Gentofte, Denmark.Center for Diabetes Research, Gentofte Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Hellerup, DenmarkSteno Diabetes Center Copenhagen, University of Copenhagen, Gentofte, DenmarkFaculty of Health and Medical Sciences, Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
Also Check: What Happens If You Take Glipizide And Don’t Eat
Got It Whats Glucagon
Glucagon is similar to insulin: Its another hormone your pancreas releases that controls the levels of glucose in your blood.
Glucagon works with your liver to prevent your blood sugar level from dropping too low. It also helps convert glycogen into glucose and releases it into your blood so your body can use it for energy.
Ever the multitasker, glucagon also works to keep your liver from consuming too much glucose in order to keep your blood sugar stable throughout your body.
Response To An Increase In Blood Glucose
In the absorptive state, an increase in blood glucose is detected by the beta cells of the pancreatic islets, causing them to increase the release of insulin into the blood. Insulin stimulates cells, especially adipose and muscle cells, to take up glucose from the blood.
Insulin and the transport of glucose into cells – To enter cells, glucose requires trans-membrane transporters and there is a family of these called GLUT . The most numerous is GLUT4, which is found on muscle and fat cells.
When insulin binds to insulin receptors on the cell membrane, cells are stimulated to increase the number of glucose transporters. The more transporters are produced, the more glucose is transported into cells – with a corresponding drop in blood glucose.
The precise mechanism whereby insulin binds to receptors causing translocation is still to be determined .
Not all tissues require insulin to take up glucose, for example brain and liver cells use GLUT transporters that are not dependent on insulin.
Further effects of insulin – The hormone also has other effects on the bodys cells, all of which contribute to an increase in glucose usage and storage – and therefore a reduction in blood glucose. These include:
– The promotion of glycolysis, a process that breaks down glucose for cellular energy
– The promotion of glycogenesis, a process that converts glucose into glycogen for storage
– The inhibition of lipolysis, a process that breaks down lipids to release energy.
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Medications Which Affect Glucagon Secretion
A number of medications have been developed to help modify the release of glucagon in type 2 diabetes.
Two different classes of diabetes drugs , DPP-4 inhibitors and incretin mimetics, act in response to the presence of meals to stimulate the increase of insulin and to inhibit the release of glucagon.
What Can Cause Low Blood Sugar Levels
Some things that can make low blood sugar levels more likely are:
- skipping meals and snacks
- not eating enough food during a meal or snack
- exercising longer or harder than usual without eating some extra food
- getting too much insulin
- not timing the insulin doses properly with meals, snacks, and exercise
Also, some things may increase how quickly insulin gets absorbed into the bloodstream and can make hypoglycemia more likely. These include:
- taking a hot shower or bath right after having an insulin injection increases blood flow through the blood vessels in the skin, which can make the insulin be absorbed more quickly than usual
- injecting the shot into a muscle instead of the fatty layer under the skin
- injecting the insulin into a part of the body used a lot in a particular sport .
All of these situations increase the chances that a person may get hypoglycemia.
page 1
You May Like: Insulin-degrading Enzyme

