Are There Other Treatment Options For Diabetes
Yes. There are two types of transplantations that might be an option for a select number of patients who have Type 1 diabetes. A pancreas transplant is possible. However, getting an organ transplant requires taking immune-suppressing drugs for the rest of your life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs. However, if the transplant is successful, youll likely be able to stop taking insulin.
Another type of transplant is a pancreatic islet transplant. In this transplant, clusters of islet cells are transplanted from an organ donor into your pancreas to replace those that have been destroyed.
Another treatment under research for Type 1 diabetes is immunotherapy. Since Type 1 is an immune system disease, immunotherapy holds promise as a way to use medication to turn off the parts of the immune system that cause Type 1 disease.
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option thats an indirect treatment for diabetes. Bariatric surgery is an option if you have Type 2 diabetes, are obese and considered a good candidate for this type of surgery. Much improved blood glucose levels are seen in people who have lost a significant amount of weight.
Of course other medications are prescribed to treat any existing health problems that contribute to increasing your risk of developing diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high cholesterol and other heart-related diseases.
Treatment For Each Type Of Diabetes
Regardless of the type of diabetes you have, it is still necessary to keep it under control and to do that you need to work together with your doctor. The primary goal of diabetes treatment is to maintain your blood sugar levels within the target range, as prescribed by your doctor. These target ranges vary from person to person, depending on the diabetes type, your age, overall health, as well as the presence of any complications.
In the case of gestational diabetes, blood glucose targets are typically lower than people suffering from type-1 or type-2 diabetes.
Management of any type of diabetes places a lot of importance on physical activity or exercise. You should definitely inquire from your doctor about how many minutes per week you should be devoting to aerobic exercise along with what kind of exercise will be the best fit for you. Diet is also another important factor for controlling your blood sugar and you will need to maintain a healthy diet and a healthy lifestyle in order to control your blood sugar levels in any type of diabetes.
Mature Onset Diabetes Of The Young
Mature Onset Diabetes of the Young is a rare form of diabetes which is different from both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but is genetic and runs in families.
MODY is caused by a mutation in a single gene. If a parent has this gene mutation, their children have a 50% chance of inheriting the gene for MODY from them.
If a child inherits the MODY gene, they are likely to develop this form of diabetes before they turn 25, despite any lifestyle changes they may make.
MODY is often treated with oral diabetes medications or insulin, and some forms may not require any treatment at all. There are four types of MODY:
Also Check: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.
Also Check: Is Greek Yogurt Good For Diabetics
Who Is More Likely To Develop Type 2 Diabetes
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight. Physical inactivity, race, and certain health problems such as high blood pressure also affect your chance of developing type 2 diabetes. You are also more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes or had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant. Learn more about risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Different Types Of Diabetes & Its Causes Symptoms Treatment Complications
Diabetes has become a very common lifestyle disease of today. Almost every third person one meets has one or the other type of diabetes. Diabetes is also the most commonly occurring disorder of the endocrine system. Diabetes occurs when the blood sugar levels in the body persistently start staying well above normal .
Diabetes is a disease is brought on by the bodys inability to either manufacture insulin, known as type-1 diabetes or by the bodys inability to respond to the effects of insulin, known as type-2 diabetes. Diabetes can also affect women during pregnancy and then disappear never to be seen again. As you can see, there are many types of diabetes and today we will make an effort to understand the different types of diabetes that affect people around the world.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
What Insulin Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
There are many types of insulins for diabetes. If you need insulin, you healthcare team will discuss the different types and if they are to be combined with oral medications. To follow is a brief review of insulin types.
- Rapid-acting insulins: These insulins are taken 15 minutes before meals, they peak at one hour and work for another two to four hours. Examples include insulin glulisine , insulin lispro and insulin aspart .
- Short-acting insulins: These insulins take about 30 minutes to reach your bloodstream, reach their peak effects in two to three hours and last for three to six hours. An example is insulin regular .
- Intermediate-acting insulins: These insulins reach your bloodstream in two to four hours, peak in four to 12 hours and work for up to 18 hours. An example in NPH.
- Long-acting insulins: These insulins work to keep your blood sugar stable all day. Usually, these insulins last for about 18 hours. Examples include insulin glargine , insulin detemir and insulin degludec .
There are insulins that are a combination of different insulins. There are also insulins that are combined with a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication .
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Best Yogurt For Diabetics
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
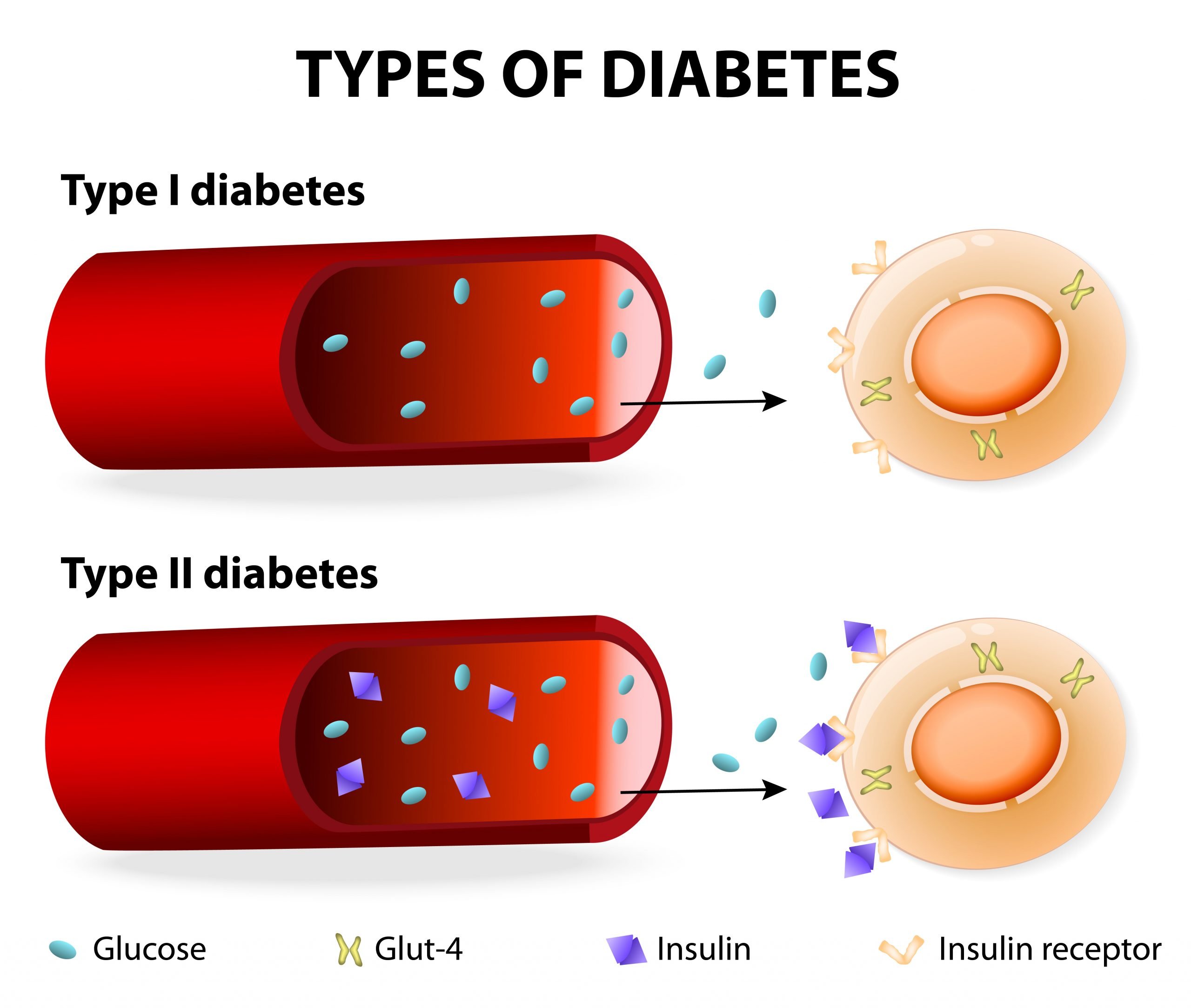
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
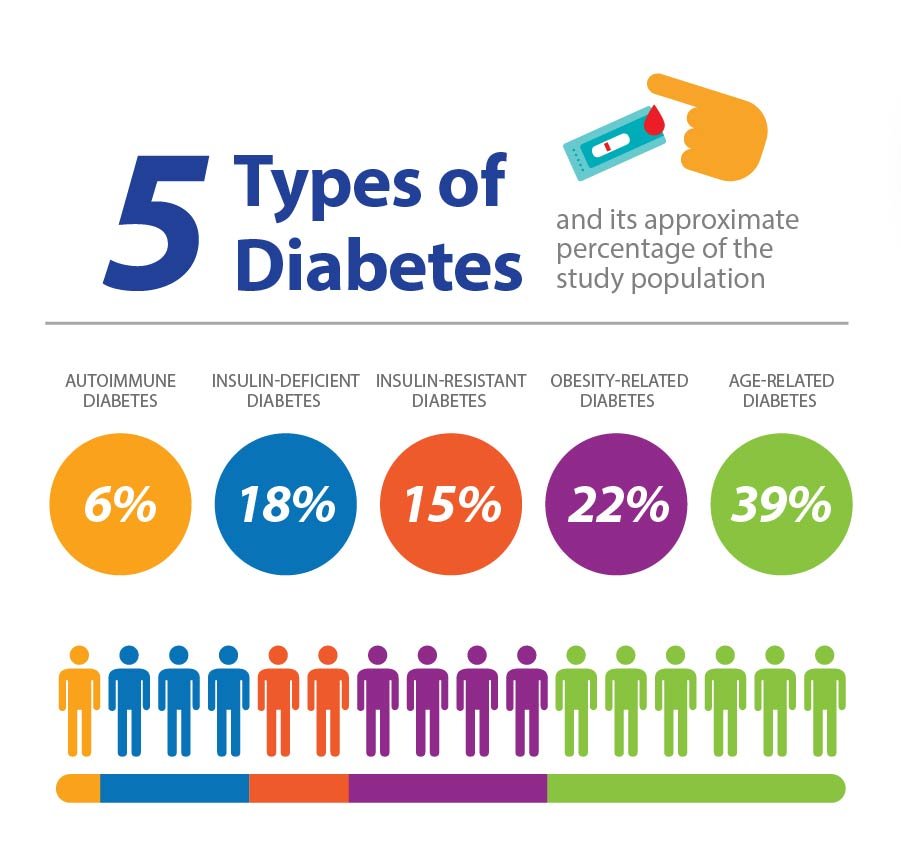
What Are The Main Types Of Diabetes
Typically, the medical world considers there to be three major types of diabetes that affect people. These include :
When a person has diabetes, the body either does not produce sufficient or any insulin altogether, or the body is not able to properly use the insulin that is being produced. There can also be a possibility that the body exhibits a combination of both circumstances. When any of these situations arises, the body fails to get sugar from the bloodstream into the cells. This causes higher levels of blood sugar, which can lead to many health problems.
Let us look at the causes of each type of diabetes.
Read Also: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that impacts 1.25 million American children and adults. For type 1, the immune system destroys the cells that release insulin, eventually leading to the complete inability to produce insulin in the body. Type 1 generally manifests at a young age and lasts a lifetime.
Type 2 diabetes has multiple contributing factors including genetics and lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. The disease generally arises during adulthood and oftentimes can be reversed or controlled through diet and exercise. 90-95% of those diagnosed with diabetes have type 2.
Recommended Reading: Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat Bananas
What Does It Mean If Test Results Show I Have Protein In My Urine
This means your kidneys are allowing protein to be filtered through and now appear in your urine. This condition is called proteinuria. The continued presence of protein in your urine is a sign of kidney damage.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Theres much you can do to prevent the development of diabetes . However, if you or your child or adolescent develop symptoms of diabetes, see your healthcare provider. The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the sooner steps can be taken to treat and control it. The better you are able to control your blood sugar level, the more likely you are to live a long, healthy life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/28/2021.
References
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Advancements in technology have given us another way to monitor glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitoring uses a tiny sensor inserted under your skin. You don’t need to prick your finger. Instead, the sensor measures your glucose and can display results anytime during the day or night. Ask your healthcare provider about continuous glucose monitors to see if this is an option for you.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
In autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly manufactures antibodies and inflammatory cells that are directed against and cause damage to patients’ own body tissues. In persons with type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas, which are responsible for insulin production, are attacked by the misdirected immune system. It is believed that the tendency to develop abnormal antibodies in type 1 diabetes is, in part, genetically inherited, though the details are not fully understood.
Exposure to certain viral infections or other environmental toxins may serve to trigger abnormal antibody responses that cause damage to the pancreas cells where insulin is made. Some of the antibodies seen in type 1 diabetes include anti-islet cell antibodies, anti-insulin antibodies and anti-glutamic decarboxylase antibodies. These antibodies can be detected in the majority of patients, and may help determine which individuals are at risk for developing type 1 diabetes.
Read Also: Insulin Drug Classification
Categories Of Increased Risk For Diabetes
Recommendations
-
Testing to assess risk for future diabetes in asymptomatic people should be considered in adults of any age who are overweight or obese and who have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes. For all patients, particularly those who are overweight or obese, testing should begin at age 45 years. B
-
If tests are normal, repeat testing carried out at a minimum of 3-year intervals is reasonable. C
-
To test for prediabetes, the A1C, FPG, and 2-h PG after 75-g OGTT are appropriate. B
-
In patients with prediabetes, identify and, if appropriate, treat other cardiovascular disease risk factors. B
-
Testing to detect prediabetes should be considered in children and adolescents who are overweight or obese and who have two or more additional risk factors for diabetes. E
Testing for type 2 diabetes or prediabetes in asymptomatic children*
How Are Different Types Of Diabetes Treated
No matter what type of diabetes you have, youll need to work closely with your doctor to keep it under control.
The main goal is to keep blood glucose levels within your target range. Your doctor will let you know what your target range should be. Targets vary with the type of diabetes, age, and presence of complications.
If you have gestational diabetes, your blood sugar targets will be lower than people with other types of diabetes.
Physical activity is an important part of diabetes management. Ask your doctor how many minutes per week you should devote to aerobic exercise. Diet is also crucial to good control. Youll also need to monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol.
You May Like: Does Type 2 Diabetes Need Insulin
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
Type 1 And Type 2 Differences

Below is a guide to some of the main differences between type 1 and type 2.
|
Your body attacks the cells in your pancreas which means it cannot make any insulin. |
Your body is unable to make enough insulin or the insulin you do make doesnt work properly. |
|
|
We dont currently know what causes type 1 diabetes. |
We know some things can put you at risk of having type 2 like weight and ethnicity. |
|
|
The symptoms for type 1 appear more quickly. |
Type 2 symptoms can be easier to miss because they appear more slowly. |
|
|
Type 1 is managed by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. |
You can manage type 2 diabetes in more ways than type 1. These include through medication, exercise and diet. People with type 2 can also be prescribed insulin. |
|
|
Currently there is no cure for type 1 but research continues. |
Type 2 cannot be cured but there is evidence to say in many cases it can be prevented and put into remission. |
Recommended Reading: Obesity And Diabetes: Pathophysiology

