Understanding Oral Diabetes Medications
Today, almost 21 million Americans have diabetes, and more than 90 percent of those have type 2, or insulin resistant diabetes. Doctors often prescribe oral medications to treat type 2 diabetes, either alone or combination with insulin therapy. This article provides a guide to those oral medications.
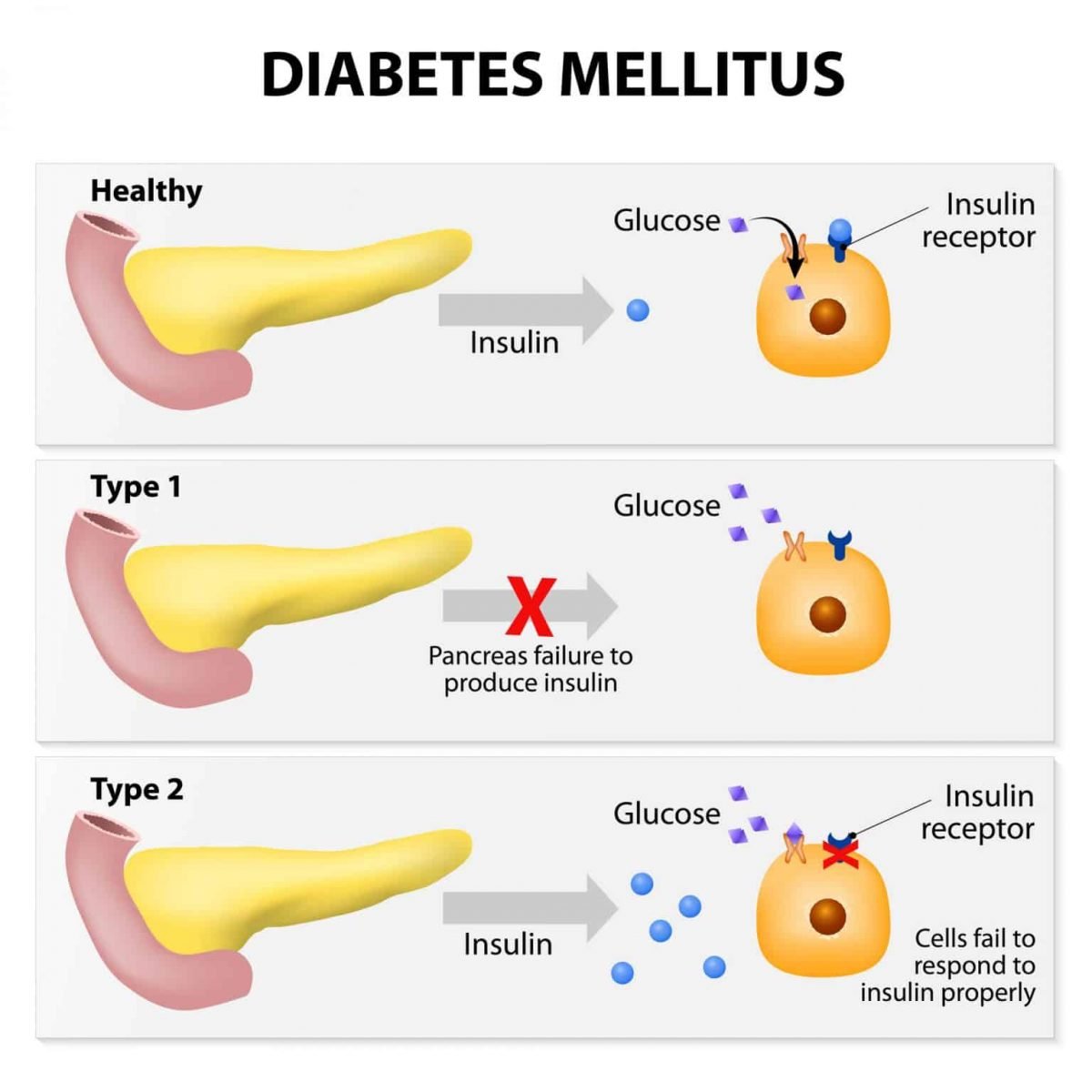
Which Diabetics Use Pills? With a few exceptions, diabetes comes in two types. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin on its own. To treat type 1, you must restore the proper amount of insulineither by taking insulin , or by receiving a transplant, either of an entire pancreas or of specialized pancreas cells, called islet cells. Type 1 cannot be treated with oral medications.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body produces enough insulin, but gradually becomes insulin resistantthat is, loses the ability to process insulin. Type 2 is usually controlled first through diet and exercise, which improve your bodys ability to process its insulin. For most type 2 diabetics, however, diet and exercise changes are not enough. The next step is oral diabetes medication. Moreover, most type 2 diabetics eventually stop producing enough insulin, and often cease insulin production altogether. As a result, many type 2 diabetics will ultimately need insulin therapy in combination with their pills.
How Do the Different Pills Work? Oral diabetes medications attack the problem in three ways.
| Brand name |
What Happens If I Have Too Little Insulin
People with diabetes have problems either making insulin, how that insulin works or both. The main two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although there are other more uncommon types.
People with type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin at all. This condition is caused when the beta cells that make insulin have been destroyed by antibodies , hence they are unable to produce insulin. With too little insulin, the body can no longer move glucose from the blood into the cells, causing high blood glucose levels. If the glucose level is high enough, excess glucose spills into the urine. This drags extra water into the urine causing more frequent urination and thirst. This leads to dehydration, which can cause confusion. In addition, with too little insulin, the cells cannot take in glucose for energy and other sources of energy are needed to provide this energy. This makes the body tired and can cause weight loss. If this continues, patients can become very ill. This is because the body attempts to make new energy from fat and causes acids to be produced as waste products. Ultimately, this can lead to coma and death if medical attention is not sought. People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin in order to survive.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If youve been diagnosed with insulin resistance, it may be helpful to ask your healthcare provider the following questions:
- Whats causing my insulin resistance?
- What can I do to increase my insulin sensitivity?
- Whats my risk of developing prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes?
- Is there any medication I can take?
- Should I see a specialist for insulin resistance?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Insulin resistance is a complex condition that can affect your health in several ways. Since it doesnt have any symptoms until it turns into prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes, the best thing you can do is try to prevent and reverse insulin resistance by maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Unfortunately, though, not all causes of insulin resistance can be prevented or treated. If you have any questions about your risk of developing insulin resistance or conditions associated with it, talk you your healthcare provider. Theyre there to help you.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/16/2021.
References
Read Also: Low Diabetes Symptoms
Why Is This Medication Prescribed
Lixisenatide injection is used along with diet and exercise to treat type 2 diabetes . Lixisenatide injection is not used to treat type 1 diabetes . Lixisenatide is not used instead of insulin to treat people with diabetes who need insulin. Lixisenatide injection is in a class of medications called incretin mimetics. It works by stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin when blood sugar levels are high. Insulin helps move sugar from the blood into other body tissues where it is used for energy. Lixisenatide injection also slows the emptying of the stomach and causes a decrease in appetite.
Over time, people who have diabetes and high blood sugar can develop serious or life-threatening complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, nerve damage, and eye problems. Using medication, making lifestyle changes , and regularly checking your blood sugar may help to manage your diabetes and improve your health. This therapy may also decrease your chances of having a heart attack, stroke, or other diabetes-related complications such as kidney failure, nerve damage , eye problems, including changes or loss of vision, or gum disease. Your doctor and other healthcare providers will talk to you about the best way to manage your diabetes.
The Exocrine Function Of The Pancreas
The exocrine function of the pancreas is responsible for secreting the substances required to digest the food we eat, so that it can be absorbed by the body. The organ secretes around one liter of fluid per day into the small intestine as a direct response to the bodys signal that food has arrived.
This fluid includes enzymes, which are proteins that help break down other substances like carbohydrates , fats, and proteins into nutrients that can be absorbed into the blood and carried to all parts of the body.
This pancreatic function is important because without it, we would have trouble digesting all the different components of our food.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Not Taking Insulin
Carbohydrates And Blood Sugar
When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood.
- As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage.
- As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fall.
- When this happens, the pancreas start making glucagon, a hormone that signals the liver to start releasing stored sugar.
- This interplay of insulin and glucagon ensure that cells throughout the body, and especially in the brain, have a steady supply of blood sugar.
Carbohydrate metabolism is important in the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body cant make enough insulin or cant properly use the insulin it makes.
- Type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually over a number of years, beginning when muscle and other cells stop responding to insulin. This condition, known as insulin resistance, causes blood sugar and insulin levels to stay high long after eating. Over time, the heavy demands made on the insulin-making cells wears them out, and insulin production eventually stops.
Understanding The Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index is an index that ranks carbohydrate-containing foods by high, medium, and low glucose levels. Understanding where foods fall on the GI scale can help you make smart eating and food purchasing decisions to help support insulin resistance.
Youll want to eat foods that generally fall low on the GI scale. Low GI foods include whole grains, sweet potatoes, and non-starchy veggies. If youre looking for sweet stuff, youll want to try low-GI, non-nutritive sweeteners, such as monk fruit and Stevia. A wise move: Download a GI app, such as Glycemic Index Load, for your phone to help you make healthy grocery-shopping decisions.
Don’t Miss: Nph Insulin Side Effects
Lixisenatide Injection May Cause Side Effects Tell Your Doctor If Any Of These Symptoms Are Severe Or Do Not Go Away:
- nausea
- very dry mouth or skin or extreme thirst
Lixisenatide injection may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online or by phone .
Gpcrs And Insulin Changes During Pregnancy
A variety of genetic studies suggested that another class of GPCRs plays an important role in islet function. Pregnancy is characterized by an increase in insulin resistance specifically, the effect of insulin at the level of the cell is decreased. Because of this, scientists reasoned that pregnancy would serve as a good model for understanding how beta cells adapt to insulin resistance. During pregnancy, islets respond by secreting more insulin to overcome this resistance. This is accomplished largely via an increase in the size and number of beta cells in the pancreas. As type 2 diabetes is a disorder in which islets do not fully adapt to insulin resistance, the implications of these studies may be applicable to understanding the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. To address this question, Kim et al. compared the level of expression of genes in islets from pregnant and nonpregnant female mice. These studies identified serotonin and its receptors as being important in regulating islet function during pregnancy. More specifically, these researchers observed that pancreatic beta cells express higher levels of serotonin receptors 2b and 1d during pregnancy, and signaling through these receptors mediates, in part, the pregnancy-induced increase in the number of pancreatic beta cells.
Read Also: Low Blood Sugar Diarrhea
How Well Is Your Pancreas Functioning
Lets review a host of symptoms that might indicate youve got a poorly functioning pancreas.
Impaired pancreatic function is implicated in indigestion, gas, constipation, heart disease, arteriosclerosis, allergies, diabetes, immune dysfunction, prostate problems, susceptibility to infection, and many other illnesses.
Sticky stool indicates a weak pancreas. Floating stool may a sign that fats in your diet are not sufficiently digested, or that the dietary fat consumed are of poor quality .
In addition to sugar and pesticide exposure, the following factors also cause the pancreas to be stressed, impairing its function:
- Alcohol, coffee, and packaged commercial teas and juices
- Emotional stress
- Eating too fast, not chewing your food
- Poor food combining
- Trace mineral deficiencies .
- Many prescriptions and over-the-counter medications.
- Allergies people with allergies have a poorly functioning pancreas, resulting in reduced production of digestive enzymes amylase, lipase, and protease which are needed to digest the starches, fats, and proteins that we consume.
How Is Insulin Resistance Diagnosed
Insulin resistance is difficult to diagnose because there isnt routine testing for it, and as long as your pancreas is producing enough insulin to overcome the resistance, you wont have any symptoms.
As theres no single test that can directly diagnose insulin resistance, your healthcare provider will consider several factors when assessing insulin resistance, including your:
- Medical history.
- Test results.
You May Like: Is Instant Oatmeal Good For Diabetics
What Is The Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen of the body. Specifically, it sits behind the stomach and close to the spine. It is considered an accessory organ to the digestive tract. This means that, unlike the stomach and intestine, the pancreas does not come into direct contact with the food you eat. Instead, the pancreas helps the digestive process move forward smoothly.
Its function is to release fluids, hormones, and other components that aid digestion and absorption of food. The function of the pancreas can be broken down into two parts: exocrine and endocrine.
Fatty Acids Acutely Enhance Insulin Secretion Ocr And Ecar From Human Islets At Fasting Glucose Concentrations With Mufas Being More Potent Than Sfas
Insulin secretion rate from statically incubated human islets in the presence of 5.5 mmol/l glucose was 1.48±0.24 fmol/min/g protein. When fatty acids were added to the incubation containing 5.5 mmol/l glucose, insulin secretion was significantly raised . The rise was around 1.5-fold in the presence SFA palmitate or stearate , and significantly higher reaching 2 to 2.5-fold when exposed to MUFA palmitoleate or oleate . Chain length played no significant role in the effects of fatty acids on insulin secretion. The observations that fatty acids stimulated insulin secretion from human islets in the presence of fasting glucose concentration and that MUFAs were more potent than SFAs made us study the secretory response dynamically by perifusing human islets. Perifused human islets secreted insulin at 2.09±0.12 fmol/min/g protein in the presence of 5.5 mmol/l glucose . When SFA palmitate or stearate was acutely added to the perifusion medium insulin release was enhanced equally by approximately 2-fold by either of the SFAs . MUFAs were significantly more potent with palmitoleate causing 4-fold and oleate 3-fold rise in insulin secretion . The rises in insulin secretion caused by SFAs and MUFAs were accounted for by rises in both first and second phases of insulin secretion.
Fig. 1
Don’t Miss: Glucagon Inhibits Insulin
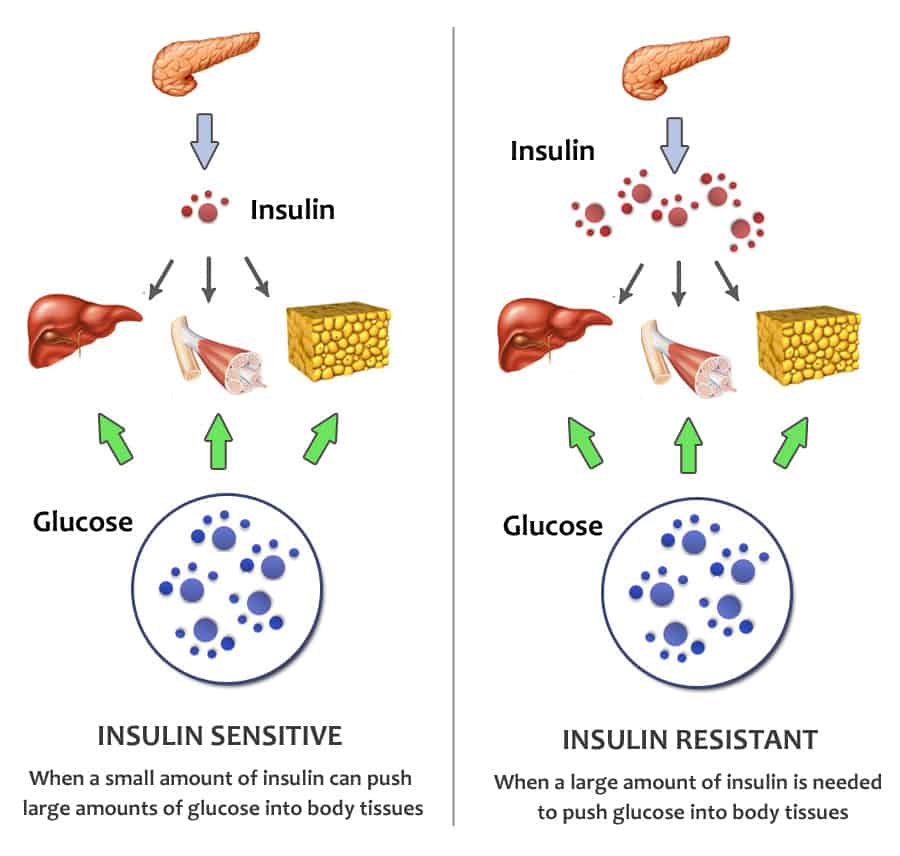
What Is Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, also known as impaired insulin sensitivity, happens when cells in your muscles, fat and liver dont respond as they should to insulin, a hormone your pancreas makes thats essential for life and regulating blood glucose levels. Insulin resistance can be temporary or chronic and is treatable in some cases.
Under normal circumstances, insulin functions in the following steps:
- Your body breaks down the food you eat into glucose , which is your bodys main source of energy.
- Glucose enters your bloodstream, which signals your pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps glucose in your blood enter your muscle, fat and liver cells so they can use it for energy or store it for later use.
- When glucose enters your cells and the levels in your bloodstream decrease, it signals your pancreas to stop producing insulin.
For several reasons, your muscle, fat and liver cells can respond inappropriately to insulin, which means they cant efficiently take up glucose from your blood or store it. This is insulin resistance. As a result, your pancreas makes more insulin to try to overcome your increasing blood glucose levels. This is called hyperinsulinemia.
As long as your pancreas can make enough insulin to overcome your cells weak response to insulin, your blood sugar levels will stay in a healthy range. If your cells become too resistant to insulin, it leads to elevated blood glucose levels , which, over time, leads to prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
Body Can Regain The Ability To Produce Insulin
Researchers have discovered that patients with type 1 diabetes can regain the ability to produce insulin. They showed that insulin-producing cells can recover outside the body.
Hand-picked beta cells from the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Photo: Oskar Skog, Uppsala University.
Type 1 diabetes is a serious disease that affects many children and adolescents. The disease causes the pancreas to stop producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
When blood sugar levels are too high, the smallest blood vessels in the body eventually become damaged. This can lead to serious health problems further down the line, including heart attacks, stroke, blindness, kidney failure and foot amputations.
Professor Knut Dahl-Jørgensen and doctoral student Lars Krogvold are leading a research project, , in which they want to ascertain among other things whether a virus in the pancreas might cause type 1 diabetes.
They have previously discovered viruses in hormone-producing cells, the so-called islets of Langerhans, in the pancreas. Now their research has generated some new and surprising results.
Lars Krogvold, doctoral student at the University of Oslo and paediatrician at Oslo University Hospital. Photo: Private
Don’t Miss: What Color Is The Type 1 Diabetes Ribbon
Fasting Diet ‘regenerates Diabetic Pancreas’
Health and science reporter, BBC News website
The pancreas can be triggered to regenerate itself through a type of fasting diet, say US researchers.
Restoring the function of the organ – which helps control blood sugar levels – reversed symptoms of diabetes in animal experiments.
The study, , says the diet reboots the body.
Experts said the findings were “potentially very exciting” as they could become a new treatment for the disease.
People are advised not to try this without medical advice.
In the experiments, mice were put on a modified form of the “fasting-mimicking diet”.
It is like the human form of the diet when people spend five days on a low-calorie, low-protein, low-carbohydrate but high unsaturated-fat diet.
It resembles a vegan diet with nuts and soups, but with around 800 to 1,100 calories a day.
Then they have 25 days eating what they want – so overall it mimics periods of feast and famine.
Previous research has suggested it can slow the pace of ageing.
This Trick Can Stimulate The Pancreas Into Producing Insulin Again
Home Latest Research This Trick Can Stimulate the Pancreas into Producing Insulin Again This Trick Can Stimulate the Pancreas into Producing Insulin Again Is it possible that an intense four day fast can regenerate pancreas cells and stimulate insulin production? Well, Valter Longo, from the University of Southern California and director of the Longevity Institute who authored of the research believes a fasting diet can reprogram non-insulin producing cells into cells that produce insulin. By activating pancreatic cell regeneration, we have been able to rescue mice from both types of diabetes, and we have also reactivated insulin production in human pancreatic cells of patients with type 1 diabetes. The study published on February 23 in the journal Cell is the latest in a series of papers demonstrating promising health benefits that occur as a consequence of a brief periodic diet that mimics the effects of fasting. The pancreas of a person with type 1 and late stage of type 2 diabetes, is unable to produce beta cells. That lack of production increases the instability of blood sugar levels. But, Longos study showed a remarkable reversal of diabetes in mice who followed a fast for four days each week. The rodents regained sound insulin production, reduced insulin resistance and demonstrated more stable levels of blood glucose. This was the case even for mice suffering the later stages of the disease.Continue reading > >
Read Also: Is Macaroni And Cheese Bad For Diabetics

