What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal blood values for a 3-hour 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test are:
- Fasting: greater than 95 mg/dL
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour: greater than 155 mg/dL
- 3 hour: greater than 140 mg/dL
ONE-STEP TESTING
Abnormal blood values for a 2-hour 75-gram oral glucose tolerance test are:
- Fasting: greater than 92 mg/dL
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour: greater than 153 mg/dL
If only one of your blood glucose results in the oral glucose tolerance test is higher than normal, your provider may simply suggest you change some of the foods you eat. Then, your provider may test you again after you have changed your diet.
If more than one of your blood glucose results is higher than normal, you have gestational diabetes.
How To Lower Your Blood Glucose Level
You have gestational diabetes, your single blood reading is abnormal, or you have normal sugar levels, monitoring and controlling sugar levels is vital for your and your babys long-term health. Here are some simple habits you can adopt and follow diligently.
References:
How To Control Fasting Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
This article was medically reviewed by Erik Kramer, DO, MPH. Dr. Erik Kramer is a Primary Care Physician at the University of Colorado, specializing in internal medicine, diabetes, and weight management. He received his Doctorate in Osteopathic Medicine from the Touro University Nevada College of Osteopathic Medicine in 2012. Dr. Kramer is a Diplomate of the American Board of Obesity Medicine and is board certified.There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 21,250 times.
If you have gestational diabetes or are at risk for developing it, your doctor will monitor your blood sugar. To determine how effectively your body processes sugar, they’ll check your blood sugar levels before you eat. If it’s above 95 milligrams per deciliter , you may need to make changes to your diet and everyday habits. Although this might seem overwhelming, there are lots of things you can do and medications you can take to control your blood sugar levels.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Dosage For Diabetes
Blood Sugar Testing At Home
A person can test their blood sugar levels at home.
In most cases, doctors ask people to measure fasting blood sugar immediately upon waking and before they have anything to eat or drink. It may also be appropriate to test blood sugar before eating or sometimes 2 hours after a meal when blood sugar has returned to normal levels.
The right time to test is dependant on treatment goals and other factors. For example, most people with diabetes do not need to test between meals unless they are using a diabetes drug that can lower blood sugar. Other people may test between meals if they feel their sugar levels may be low.
Since they do not make any insulin, some people with type 1 diabetes need to test several times a day. They do this because they need to check their levels regularly in order to adjust their insulin dose at that time.
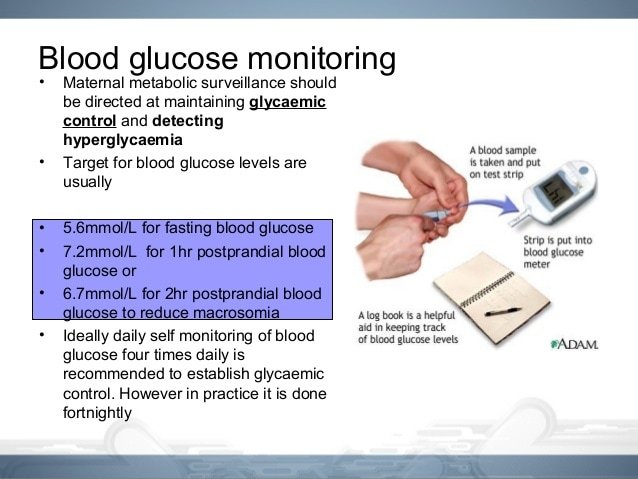
To do the blood sugar test, a person will:
- Prepare the testing strip and glucose monitor to be ready for the blood sample.
- Clean the testing area, usually the side of a fingertip, using an alcohol swab.
- Lance the testing area. Bracing against a firm surface can help with the impulse to pull away.
- Squeeze the testing area around the wound to maximize blood flow.
- Squeeze a drop of blood onto the test strip.
- Put the strip into the monitor.
- Record the time, blood sugar reading, and recent food intake in a log.
Blood glucose monitoring kits for use at home are available for purchase online.
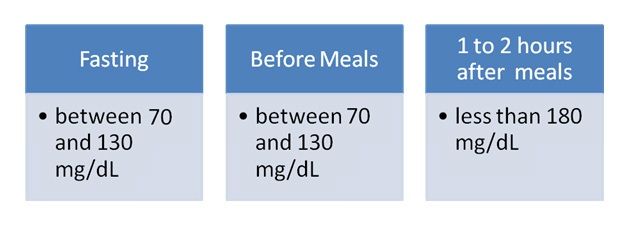
What Should Your Numbers Look Like
Ideally, you want your numbers to be as follows:
- Fasting blood glucose below 83 mg/dL
- Pre-meal reading-below 90 mg/dL, or at fasting level
- 1 hour reading- under 140 mg/dL
- 2 hour reading-under 120 mg/dL
- 3-hour reading-back to pre-meal level
- No readings above 140 mg/dL
If you have readings higher than this, your body is not processing glucose optimally and you likely have some level of insulin resistance. Reduce the amount of carbs in your diet and remove processed foods entirely. Make sure you are getting good fats and proteins as well. Implement the Seven Steps above.
If you have readings on the high end of the pre-diabetic range or in the diabetic range consider consulting with a specialist in addition to implementing the Seven Steps above.
Even if you dont have any underlying glucose issues, testing your blood sugar occasionally will help you pin point which carbohydrates you tolerate well and which you dont. It can help you have a better understanding of your bodys reaction to foods and take control of your health. It is also an accurate alternative to the pregnancy test for gestational diabetes, so talk to your doctor if youd prefer to test yourself, though you may have to explain your reasons!
Note: I am not a doctor and cannot take the place of your doctor. Before making any changes, especially to medication, consult your doctor or health care professional.
Do you struggle with diabetes? Have you overcome it?
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Screening And Diagnosis Of Gdm
Early screening. Screening for diabetes in the first trimester should be considered for diagnosing overt diabetes in women who are at risk , including those with a history of previous GDM. The ability to predict abnormal results on glucose screening tests at 24 to 28 weeks and risk of continued dysglycemia postpartum are other, but less compelling, reasons cited to screen in the first trimester.
The test of choice for early screening should be based primarily on the ability to predict poor obstetrical outcomes, which may be modifiable by lifestyle or pharmacological intervention. There are 2 strategies for testing glucose levels in early pregnancyusing the nonpregnancy-recommended screening tests or using the typical 24- to 28-week gestational diabetes screening criteria . To apply nonpregnant FPG or A1C criteria in early pregnancy does not take into account that both decrease early in pregnancy and may lead to underdiagnosis in women with pre-existing diabetes. On the other hand, there has been no rigorous validation that criteria accepted for the diagnosis of GDM in the second or third trimester are appropriate for use in the first trimester.
Elevated Fasting Blood Sugar In Pregnancy Linked To Harmful Outcomes For Mothers Babies
Issues persist even when drug treatments for gestational diabetes are given, U of A study shows.
Women with gestational diabetes who have elevated blood sugar levels before eating are at higher risk for complications than those whose blood sugar is only elevated after mealseven when their diabetes is treated, according to a new study.
Pregnant women diagnosed with diabetes who have elevated fasting blood sugar levels are more likely to face complications than those who have only elevated post-meal glucose levels, according to a new study by a University of Alberta research team.
“The women who had elevated fasting glucose, adjusted for all other risk factors, were almost three times more likely to have a big baby than women who had normal fasting glucose levels but elevated postprandial sugar levels,” said cardiology professor Padma Kaul, who is also an adjunct professor in the School of Public Health.
The women with high fasting blood sugars were also found to be at 1.5 times higher risk for high blood pressure during pregnancy, and had a higher likelihood of needing an induced labour, having a caesarean section or having a preterm birth.
Kaul said large babies are at risk for complications during birth and obesity later in life, and high blood pressure during pregnancy can place extra stress on the heart and kidneys of a mother.
Also Check: Does Crystal Light Raise Blood Sugar
Myth #: Cut Back On Carbohydrates But Not Less Than 175g Of Carbohydrates/day
The conventional nutrition advice for gestational diabetes is mind-numbingly nonsensical. Youre given the diagnosis of GD, aka carbohydrate intolerance, yet told to eat a bunch of carbohydrates. You fail a 50 or 75 gram glucose tolerance test, yet are told to eat 45-60 grams of carbohydrates at almost EVERY MEAL. Its no wonder roughly 40% of women will require insulin and/or medication to lower their blood sugar when theyre consistently filling up their carbohydrate-intolerant body with lots of carbohydrates.
Perhaps not-so-shocking is that researchers have shown that eating a lower-glycemic diet reduces the chance a women will require insulin by HALF. Its common sense, friends.
Unfortunately, theres oodles of misinformation low-carb diets. Women are warned not to eat low-carb because they might go into ketosis . Plus, theres entirely no acknowledgement that ketosis can exist outside of diabetic ketoacidosis. Sadly, few healthcare professionals have fully investigated the details and continue to fear-monger based on false information.
Im one of the few that has done the research and Im the first dietitian to scientifically defend the safety of a lower-carbohydrate diet to manage gestational diabetes .
Timing And Route Of Delivery
In gestational diabetes, shoulder dystocia is the complication most anticipated at the time of delivery. In one study,36 this complication occurred in 31 percent of neonates weighing more than 4,000 g who were delivered vaginally to unclassified mothers with diabetes. No prospective data support the use of cesarean delivery to avoid birth trauma in women who have gestational diabetes. One remaining limiting factor is the 13 percent error rate in estimating fetal weight by ultrasonography.37
A decision analysis38 that evaluated the cost and efficacy of a policy of elective cesarean delivery for an estimated fetal weight of 4,500 g in mothers with diabetes found that 443 cesarean deliveries would need to be performed to prevent one case of brachial plexus injury, at a cost of $930,000. A reasonable approach is to offer elective cesarean delivery to the patient with gestational diabetes and an estimated fetal weight of 4,500 g or more, based on the patient’s history and pelvimetry, and the patient and physician’s discussion about the risks and benefits. There are no indications to pursue delivery before 40 weeks of gestation in patients with good glycemic control unless other maternal or fetal indications are present.
Read Also: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Have In One Day
Prevention And Risk Factors
The incidence of GDM is increasing worldwide. The global prevalence of hyperglycemia during pregnancy has been estimated at 16.9% using the World Health Organization criteria . A higher proportion of women entering pregnancy at an older age and/or with obesity contribute to this increase in prevalence, along with changes in screening strategies and diagnostic criteria. There is a need for an effective and acceptable intervention that will prevent the development of GDM. Such an approach has the potential to improve maternal and child health, with significant savings to the health-care system.
Understanding the pathophysiology of GDM and its risk factors is important for the development of preventive strategies. The GDM population includes a heterogeneous group of women with different metabolic profiles when exposed to pregnancy hormones. Various presentations include:
- Hyperglycemia that likely preceded the pregnancy , elevated first trimester fasting glucose, overt diabetes in pregnancy, monogenic diabetes)
- Reduced and/or falling insulin secretory capacity
- Significant insulin resistance from early pregnancy
- A combination of factors ).
Why The Test Is Performed
This test checks for gestational diabetes. Most pregnant women have a glucose screening test between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. The test may be done earlier if you have a high glucose level in your urine during your routine prenatal visits, or if you have a high risk for diabetes.
Women who have a low risk for diabetes may not have the screening test. To be low-risk, all of these statements must be true:
- You have never had a test that showed your blood glucose was higher than normal.
- Your ethnic group has a low risk for diabetes.
- You do not have any first-degree relatives with diabetes.
- You are younger than 25 years old and have a normal weight.
- You have not had any bad outcomes during an earlier pregnancy.
You May Like: Glyburide Metformin Side Effects
Gestational Diabetes: Testingfor Ketones
DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is notintended and should not be construed as medical advice. Consultyour health provider. This particular web section isdesigned to present more than one view of a controversialsubject, pro and con. It should be re-emphasized that nothingherein should be considered medical advice.
Contents
Ketones are formed when your body’s fat stores have to beaccessed for energy. Normally, you eat food and then the bodyconverts it to glucose/blood sugar for use as energy by yourcells. Your insulin is then like a key, unlocking the door to thecell so it can access this blood sugar. In pregnancy, placentalhormones make you more resistant to your own insulin and make it harder to get thatglucose from your blood into your cells. So while your bloodremains high in blood sugar, your cells can be starving. Thefetus absolutely must have energy, so if your pancreas cannotmake enough insulin to overcome the hormone-caused resistance,the cells start accessing other sources of energy, like fatstores. The by-product of this is ketones.
Ketones may be dangerous when pregnant, although thisis controversial and still being studied and disputed. There wereseveral studies that showed that babies exposed to a lot ofketones had learning problems and reduced IQ later in life. Thesehave since been disputed by other studies, but just in case,everyone plays it safe during pregnancy, which is very prudent.
How To Reduce Blood Sugar
You can take steps to reach your blood sugar goals as soon as you find out that it is high. This is how to reduce blood sugar if you have a single high reading that may be dangerous:
- Ask your doctor what to do if you missed a dose of insulin or another diabetes medication
- Ask your doctor if your medication types and doses are still appropriate for you
- Drink water to dilute the sugar
- Exercise for 15 minutes
- Eat a small protein snack, such as a hard-boiled egg, ½ ounce of peanuts or pistachios or other nuts, ½ cup of beans, or ½ cup of plain yogurt or cottage cheese
If you have chronically high blood sugar in prediabetes or diabetes, you can follow this treatment plan:
- Exercise regularly, assuming your doctor approves it
- Lose weight if you are overweight or obese
- Eat a higher proportion of vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fruit
- Limit sugary foods and beverages, fried foods, refined starches, and processed and fatty red meats
- Beware of starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes, which can spike your blood sugar. Check out our guide of which veggies to avoid!
Read Also: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Monitoring The Problem As It Improves
Anyone with diagnosed Diabetes should consult a physician before making any changes to a diabetes regimen, and especially before changing medication dosages. That being said, improving your diet and eating the foods to help your body heal is your prerogative and your right. For the 65% of America that is overweight, including the 37% that are clinically obese, there is a good chance that many are operating in a pre-diabetic state, or may even have undiagnosed diabetes. Even those without any signs of disease can figure out their insulin levels by at home glucose monitoring.
Ive done this for years and I do it each time Im pregnant in place of the glucose test. It is an easy way to keep insulin levels in check and see how your body responds to certain foods. While I can offer general advice on the amount of carbohydrates that should be consumed, at home glucose monitoring allows you to know exactly what your body will and wont handle.
Future Risks Post Birth
A 2002 publication19 from Diabetes Care comparing 28 studies found that elevated fasting levels during pregnancy was the most common risk factor associated with future risk of type 2 diabetes:
Cumulative incidence of type 2 diabetes increased markedly in the first 5 years after delivery and appeared to plateau after 10 years. An elevated fasting glucose level during pregnancy was the risk factor most commonly associated with future risk of type 2 diabetes.
References
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication

