Blood Sugar And Pregnancy With Pre
Brian Levine, MD, MS, is board-certified in obstetrics and gynecology as well as in reproductive endocrinology and infertility.
Blood sugar needs extra attention when a woman with pre-existing diabetes gets pregnant. Diabetes brings with it certain added pregnancy risks, so the goal is to maintain a blood sugar average that is as far below the normal level as you can without greatly increasing your risk for hypoglycemia or restricting the growth of your baby in the womb. It is important that this is done throughout the entire nine months of pregnancy.
Average blood sugar levels can be found with an A1c test. This test provides an idea of what your blood sugar average has been for the prior two to three months.
Because blood sugar has to be kept under tight control, it is useful to know if your doctor’s target ranges are in whole blood or plasma measurements and what type of result your glucometer provides.
S To Controlling Blood Sugar
Most women who have gestational diabetes will give birth to perfectly healthy babies. But, in order to do so, you may need to make changes to your lifestyle to promote a healthy pregnancy and avoid any risks to your baby .
The management of gestational diabetes involves making healthy choices. This involves five key steps:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Knowing your blood sugar level and keeping it under control
- Taking insulin, if needed
What If Gestational Diabetes Develops
If you do get gestational diabetes, your doctor will monitor it throughout your pregnancy because it can cause problems for both you and your baby.
Since your bodys insulin supply cannot keep up, extra glucose stays in your blood and the baby receives more sugar than it needs and stores it as fat. Possible outcomes include a large baby, more chance of a cesarean delivery, and a slightly higher risk of fetal and neonatal death.
Babies born to mothers with diabetes need their blood sugar levels monitored after birth. Low blood sugars can result in newborn babies from mothers with any type of diabetes, and this can lead to problems for your baby, including seizures, Dr. Chapa says.
However, you can still have a healthy baby if you focus on good habits. To ensure stable blood sugar levels:
- Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly.
- Limit the amount of carbohydrates and simple sugars in your diet.
- Exercise regularly.
For most women, blood sugar levels return to normal after delivery, but your doctor will likely check them during the postpartum period. About 10% of women with gestational diabetes have type 2 diabetes without knowing it.
If a woman has gestational diabetes, she also has a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. About half of women with gestational diabetes will have type 2 diabetes in 10 years, so it is important for your primary care physician to closely monitor your blood sugars.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
Random Blood Sugar Test
A physician takes a blood sample at any time, and not necessarily when fasting. People who have serious diabetes symptoms may have this test. If blood glucose levels are 200 mg/dL at any time, this indicates that diabetes is present.
People with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose levels regularly, using a home testing kit or continuous glucose monitor.
Risk Factors For Developing Diabetes During Pregnancy
There is an increased risk of diabetes during pregnancy if:
- The woman is overweight
- The woman is a smoker or around smokers more than average
- The woman is older
- There is a family history of diabetes
- The woman is from an ethnic minority
- There is previous history of the birth of a large baby
There is a routine antenatal test used to measure glucose levels in urine; however it has been noted it is relatively unreliable for diagnosing diabetes.
Therefore blood sugar levels are checked between 26 and 30 weeks of gestation. This is done of two separate occasions using one of two tests, either the fasting glucose test or the random glucose test. In addition to this if there are any abnormal results of these tests or there is a family history of diabetes, or a woman is regarded as obese she will be offered a glucose tolerance test.
Often with gestational diabetes, the woman is advised to take a number of steps to change their diet and exercise habits to ensure the best possible pregnancy.
It is reportedly advisable to increase participation in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, yoga and pilates. In addition to this it is advisable to eat regular meals watching the amount of fat being eaten, remembering it is controlling the amount of fat not cutting it out of the diet completely.
Also reducing the amount of salt in the diet and ensuring that plenty of fruit and vegetables are included in the diet.
Recommended Reading: Nph Drug
Foods To Avoid With Gestational Diabetes
Some other things that I noticed is that I got my highest readings that were out of the target range after eating a high fat, high sugar combo.
The two meals that elevated my blood sugar the most were when I ate brie cheese with cranberry sauce on three rice crackers after eating oatmeal. My other highest reading was after I ate half of a big vegan chocolate bar before my dinner. When I looked back at the chocolate bar, I realized that it had 20 grams of fat plus sugar plus my dinner.
I would also get my highest post-meal blood sugar reading after dinner. Generally, I eat a late dinner after a 5 pm snack. I focused on eating a lighter and earlier dinner since I wasnt doing much physical activity after dinner.
A trend I noticed is that I would get my highest fasting blood sugar levels following a previous dinner that contained high amounts of saturated fats or refined fats such as fries, red meat, and coconut cream.
Processed fats, saturated fats and refined sugar are foods that should be avoided with gestational diabetes.
How To Walk More Each Day
Below are some tips on how you can incorporate more walking into your life. It is important never to exert yourself.
- Walking to the local shops instead of driving.
- Start a walking group with family or friends perhaps meet at a regular time and day. This will help make sure youre committed and help you stay in touch with your loved ones.
- Take the stairs instead of the elevator.
- Stand and move while on the phone.
- Garden.
- Buy a pedometer , a small device you can clip to yourself that counts your daily steps. This will help you measure just how much walking youre doing.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
Why Are Fasting Levels Important
Fasting levels give an indicator of our baseline blood sugar levels. This shows an picture of what our levels are returning to when they are not complicated by;the foods we are eating.
High fasting levels have been associated with increased adverse pregnancy outcomes in many research studies1416
A large Canadian study published in Nov 201915 of 257,547 pregnancies between 2008 -2014 found that those diagnosed with high fasting blood sugar levels following the GTT resulted in the highest rates of adverse pregnancy outcomes .
elevated FPG was significantly associated with a higher risk of LGA and HDP outcomes compared to postload elevation in GDM pregnancies. We also found that the use of pharmacological treatment was highest in pregnancies with elevated FPG and treatment rates increased with increasing dysglycaemia . After adjusting for other maternal factors, FPG was associated with an increased risk of LGA and HDP outcomes in GDM pregnancies with and without pharmacological intervention.
Elevated fasting plasma glucose in women with gestational diabetes is a stronger predictor of largeforgestationalage and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy outcomes than elevated postload glucose
Higher fasting levels in the first trimester has been linked to increased risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes17,18
How To Monitor Your Blood Glucose Levels
Watch this film from Diabetes UK or read the instructions below.
Tip
There is less sensation in the sides of your fingers than the tips or the underneath. Try to prick the side of your finger, near the tip.
To monitor your glucose, you will be given a blood glucose monitor. This is designed for you to measure your own blood glucose levels at home, or wherever you happen to be, by checking a drop of your blood. You produce the blood by using a finger pricker.
To monitor your glucose, you will be given a blood glucose monitor. This is designed for you to measure your own blood glucose levels at home, or wherever you happen to be, by checking a drop of your blood. You produce the blood by using a finger pricker.
There are many different brands of meter on the market, but they all work in similar ways:
Step 1; Wash your hands.
Step 2;;Set up a finger pricker with a clean needle.
Step 3;;Insert one end of a test strip into the meter.
Step 4; Use the finger pricker to prick the side of your finger.
Step 5; When a spot of blood appears where you pricked you finger, place it onto the end of the testing strip that is sticking out of the meter to transfer the blood.
Step 6; After a few seconds, the meter will display your blood glucose level.
Step 7; Clean the blood off your finger.
Step 8; Record the results in your blood glucose diary or diabetes journal, or you may have a phone app that you use.
Step 9;;Throw away the test strip.
Read Also: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Target Blood Glucose Levels Before Pregnancy
When youre planning to become pregnant, your daily blood glucose targets may be different than your previous targets. Ask your health care team which targets are right for you.
You can keep track of your blood glucose levels using My Daily Blood Glucose Record. You can also use an electronic blood glucose tracking system on your computer or mobile device. Record the results every time you check your blood glucose. Your blood glucose records can help you and your health care team decide whether your diabetes care plan is working. You also can make notes about your insulin and ketones. Take your tracker with you when you visit your health care team.
Keeping Active With Gestational Diabetes
For women with gestational diabetes, moderate intensity physical activity can help to manage blood glucose levels. Moderate means a slight but noticeable increase in breathing and heart rate. If there are no specific obstetric or medical conditions, you should be able to safely exercise during pregnancy.
However, it is best to discuss this with your obstetrician or midwife prior to commencing any exercise regime in pregnancy.
You May Like: Normal A1c For Type 2 Diabetes
Problems Of Gestational Diabetes In Pregnancy
Blood sugar that is not well controlled in a woman with gestational diabetes can lead to problems for the pregnant woman and the baby:
An Extra Large Baby
Diabetes that is not well controlled causes the babys blood sugar to be high. The baby is overfed and grows extra large. Besides causing discomfort to the woman during the last few months of pregnancy, an extra large baby can lead to problems during delivery for both the mother and the baby. The mother might need a C-Section to deliver the baby. The baby can be born with nerve damage due to pressure on the shoulder during delivery.
C-Section
A C-section is an operation to deliver the baby through the mothers belly. A woman who has diabetes that is not well controlled has a higher chance of needing a C-section to deliver the baby. When the baby is delivered by a C-section, it takes longer for the woman to recover from childbirth.
High Blood Pressure
When a pregnant woman has high blood pressure, protein in her urine, and often swelling in fingers and toes that doesnt go away, she might have preeclampsia. It is a serious problem that needs to be watched closely and managed by her doctor. High blood pressure can cause harm to both the woman and her unborn baby. It might lead to the baby being born early and also could cause seizures or a stroke in the woman during labor and delivery. Women with diabetes have high blood pressure more often than women without diabetes.
audio icon
Low Blood Sugar
Infant Mortality And Birth Defects

There is a slight increase in the risk of infant mortality or birth defects in babys of mother with diabetes than without, however preconception care can reduce this risk by ensuring the mother is as healthy as possible before and through out pregnancy
In addition to this if a woman has diabetes before pregnancy, diabetes related complications can worsen; this includes things like hypertensio, kidney disease, nerve damage and retinopathy which is a form of diabetic eye disease.
Recommended Reading: Can A Diabetic Drink Milk
How To Reduce Fasting Blood Sugar Level During Pregnancy
Last Updated on February 1, 2019 | RD, Payal Banka
Lately , I have been receiving a lot of queries and comments from my readers. They all want to know How to reduce fasting blood sugar level during pregnancy ? So here is a post on;How to reduce fasting blood sugar level during pregnancy. Read on ..
Image :Copyright: norgal / 123RF Stock Photo
;What is fasting sugar ?
Fasting Blood Sugar is the level of sugar found in blood early in the morning , before consumption of any food.; Where post prandial sugar levels depend on the food that you consume , fasting blood sugars depend on various factors .
- Over all hepatic output of glucose; over night .
- The amount of glucose produced indirectly depends on Your evening snack and dinner , stress levels , and your over all blood sugar control.
So now that we know the reasons that attribute to fasting sugar , we can control the fasting blood sugar; by; keeping a watch on these causative factors. let us see in details about;how to reduce fasting blood sugar level during pregnancy.
Gestational Diabetes Risk Factors
Youâre more likely to get gestational diabetes if you:
- Were overweight before you got pregnant
- Are African-American, Asian, Hispanic, Alaska Native, Pacific Islander, or Native American
- Have blood sugar levels that are higher than they should be but not high enough to be diabetes
- Have a family member with diabetes
- Have had gestational diabetes before
- Have polycystic ovary syndrome or another health condition linked to problems with insulin
- Have given birth to a baby who was stillborn or had certain birth defects
- Are older than 25
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Delivery When You Have Gestational Diabetes
When planning for the baby’s arrival,; the doctor will access the size of the baby to determine if you can deliver vaginally. If you have been able to keep your blood glucose well- controlled, your baby’s weight is within an appropriate range, you don’t have any other pregnancy concerns such as high blood pressure, and you are not on medication, than your labor should proceed just as it would if you didn’t have gestational diabetes. Of course, your delivery team will monitor your blood sugar throughout.
If your baby is considered too large for you to deliver vaginally than you will likely be induced at weeks 38 or 39. You and your doctor may also decide that a cesarean section may be a better route for delivering the baby. Should blood sugar levels get too high during labor, the baby may release more insulin in response.;That increases the risk of the baby developing low blood glucose after birth so a C-section may be considered.
What Health Problems Could I Develop During Pregnancy Because Of My Diabetes
Pregnancy can worsen certain long-term diabetes problems, such as eye problems and kidney disease, especially if your blood glucose levels are too high.
You also have a greater chance of developing preeclampsia, sometimes called toxemia, which is when you develop high blood pressure and too much protein in your urine during the second half of pregnancy. Preeclampsia can cause serious or life-threatening problems for you and your baby. The only cure for preeclampsia is to give birth. If you have preeclampsia and have reached 37 weeks of pregnancy, your doctor may want to deliver your baby early. Before 37 weeks, you and your doctor may consider other options to help your baby develop as much as possible before he or she is born.
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Diabetes Insipidus
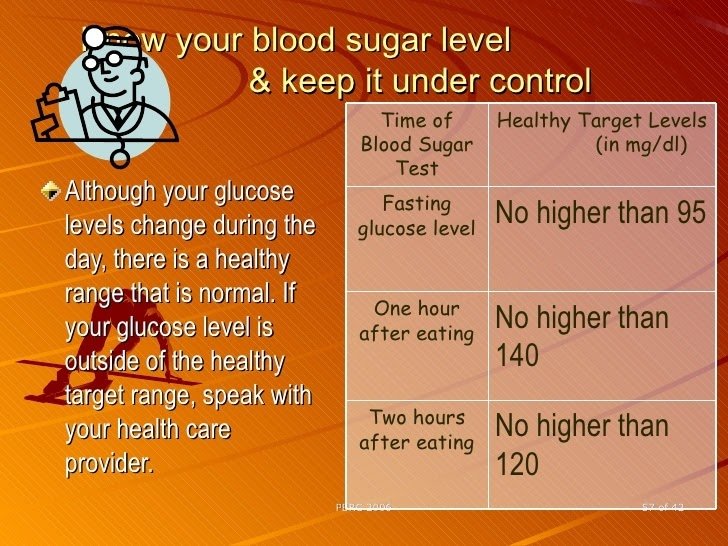
Target Blood Glucose Levels During Pregnancy
Recommended daily target blood glucose numbers for most pregnant women with diabetes are
- Before meals, at bedtime, and overnight: 90 or less
- 1 hour after eating: 130 to 140 or less
- 2 hours after eating: 120 or less3
Ask your doctor what targets are right for you. If you have type 1 diabetes, your targets may be higher so you dont develop low blood glucose, also called hypoglycemia.
Sleep Duration And Blood Glucose Control In Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Go to: To describe the relationship between objectively assessed sleep and blood glucose in a prospective cohort of women recently diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus . Women with GDM were enrolled immediately after attending a GDM education class. All patients were recruited during their first week of attempted dietary management of GDM. They were instructed on the use of a glucometer and on the principles of a GDM diet. Women wore an actigraph and completed a sleep log for 7 consecutive days. Glucose records were compared against the objective sleep data. Linear mixed model analysis was used to estimate the association of sleep duration on morning fasting and one-hour postprandial blood glucose concentrations. Thirty-seven participants provided data for 213 sleep-intervals that corresponded to at least one glucose reading. Sleep duration was negatively associated with fasting and one-hour postprandial blood glucose concentrations In analyses adjusted for age, gestational age and BMI, a one-hour increase in sleep time was associated with statistically significant reductions in fasting glucose as well as postprandial glucose concentrations . Short sleep durations are associated with worsened glucose control in women with gestational diabetes. Educating women on healthy sleep and screening for and treating sleep disorders during pregnancy may have a role in optimizing blood glucose control in gestational diabetes.Continue reading >>
Don’t Miss: A1c Cutoff

