When Is It Necessary To Call A Doctor If You Have Diabetes
- If you have diabetes and your blood sugar is 300 mg/dL or higher two times in a row for an unknown reason.
- If you have a low blood sugar that has not come up after three treatments, call your healthcare provider or 911.
- If you see a person with diabetes who appears confused, they may be having a low blood sugar episode. Left untreated, the low blood sugar could lead to a diabetic coma. If the person is still able to follow instructions, give him or her something to drink or eat and call for an ambulance or 911.
- If you see someone with diabetes become unresponsive, call 911.
If you do call 911, let the responders know that the person has diabetes if theyre not able to communicate. If you do have diabetes, you may want to wear a medical identification item like a bracelet or necklace.
When you are taken to a healthcare facility, providers will do a physical examination and take blood to determine levels of glucose, ketones and other substances.
What Is Severe Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can be mild, moderate, or severe based on the persons blood glucose and condition. Here are the levels:
- Level 1 hypoglycemia: Blood glucose is less than 70 mg/dL but is 54 mg/dL or higher.
- Level 2 hypoglycemia: Blood glucose is less than 54 mg/dL.
- Level 3 hypoglycemia: A person is unable to function because of mental or physical changes. They need help from another person. In this case, blood glucose is often below 40mg/dL.
Signs And Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
Each person’s reaction to low blood sugar is different. Learn your own signs and symptoms of when your blood sugar is low. Taking time to write these symptoms down may help you learn your own symptoms of when your blood sugar is low. From milder, more common indicators to most severe, signs and symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- Feeling shaky
- Color draining from the skin
- Feeling sleepy
- Feeling weak or having no energy
- Blurred/impaired vision
- Tingling or numbness in the lips, tongue or cheeks
- Headaches
- Nightmares or crying out during sleep
- Seizures
The only sure way to know whether you are experiencing low blood sugar is to check your blood sugar, if possible. If you are experiencing symptoms and you are unable to check your blood sugar for any reason, treat the hypoglycemia.
A low blood sugar level triggers the release of epinephrine , the fight-or-flight hormone. Epinephrine is what can cause the symptoms of hypoglycemia such as thumping heart, sweating, tingling and anxiety.
If the blood sugar level continues to drop, the brain does not get enough glucose and stops functioning as it should. This can lead to blurred vision, difficulty concentrating, confused thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and drowsiness. If blood sugar stays low for too long, starving the brain of glucose, it may lead to seizures, coma and very rarely death.
Read Also: Can You Take Too Much Metformin
Causes Of Low Blood Sugar
In people with diabetes, the main causes of low blood sugar are:
- taking too much diabetes medicine especially too much insulin, medicines called sulphonylureas or medicines called glinides
- skipping or delaying a meal
- eating less carbohydrate-containing food than usual, such as bread, cereals, pasta, potato and fruit
- exercise or activity, especially if it’s intense or unplanned
- binge drinking or drinking alcohol on an empty stomach
Sometimes there’s no obvious reason why low blood sugar happens.
Very occasionally, it can happen in people who don’t have diabetes – see section on low blood sugar without diabetes.
What Causes Low Blood Glucose In People With Diabetes
Low blood glucose levels can be a side effect of insulin or some other medicines that help your pancreas release insulin into your blood. Taking these can lower your blood glucose level.
Two types of diabetes pills can cause low blood glucose
- sulfonylureas, usually taken once or twice per day, which increase insulin over several hours
- meglitinides, taken before meals to promote a short-term increase in insulin
The following may also lower your blood glucose level
You May Like: What Is Normal A1c For Non Diabetic
What Happens When Your Blood Sugar Drops To Zero
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal. This may result in a variety of symptoms, including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Feelings of hunger, sweating, shakiness, or weakness may also be present.
How Do I Use An Emergency Glucagon Kit
Most often, an emergency glucagon kit contains a vial of powder , a syringe already filled with saline . Other kits may include an auto-injector, or a nasal spray .
To use a kit by injection, follow these steps:
Also Check: Metformin Dosage For Diabetes
What Are The Risk Factors For Diabetic Coma
While anyone who has diabetes is at risk for a diabetic coma, the causes depend on the type of diabetes:
- People with Type 1 diabetes have a greater chance of going into a diabetic coma as a result of diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. This is because people with Type 1 diabetes always need insulin and have a wider range in their blood glucose levels than people with Type 2 diabetes.
- People with Type 2 diabetes have a greater chance of going into a diabetic coma from diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome than from diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia.
Other risks that can lead to diabetic coma in anyone who has diabetes include:
- Surgery.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Dka
The symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis usually don’t develop all at once they usually come on slowly over several hours. People who have DKA may:
- feel really tired
- feel really thirsty or pee way more than usual
- have a dry mouth and signs of dehydration
These symptoms are caused by the high blood sugar levels that usually happen before someone develops DKA. If the person doesn’t get treatment, these signs of DKA can happen:
- abdominal pain
- unconsciousness
Don’t Miss: Nph Insulin Side Effects
Treating Low Blood Glucose If You Take Medicines That Slow Down Digestion
Some diabetes medicines slow down the digestion of carbohydrates to keep blood glucose levels from rising too high after you eat. If you develop low blood glucose while taking these medicines, you will need to take glucose tablets or glucose gel right away. Eating or drinking other sources of carbohydrates wont raise your blood glucose level quickly enough.
Ensuring A Long Life With Diabetes
Death is an unpleasant subject and no one wants to die of any disease. Hence, taking a certain precaution is a must as this can increase the life expectancy to a great extent. The following paragraphs deal with the subject as to how can you increase the life expectancy even if you suffer from a chronic condition like diabetes.
Hence, ensure a long life with diabetes by taking the following simple steps:
- The first and foremost thing which is of prime importance in diabetes is to maintain healthy and recommended levels of blood glucose.In this regard, the following should be kept in mind:
The most important consideration, while you try to manage type 1 diabetes in your child is to regularly monitor the level of blood sugar or blood glucose. The following prescribed range of blood glucose should be kept in mind:
- For a diabetic patient, the fasting blood sugar is under 126mg/dl or even higher.
- As per the American Diabetes Association, the normal blood sugar for a diabetic should be around 80-130mg/dl before the meals and around 200mg/dl a couple of hours after meals.
The recommended levels for type 2 diabetes include:
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Nondiabetic Person
What If Im Experiencing Hypoglycemic Episodes Even Though My Doctor Has Confirmed That Im Not Diabetic Or Prediabetic
If you have low blood sugar and dont have diabetes or prediabetes, it can be a sign of another serious health issue such as a tumor, hormone deficiency, kidney disorder, anorexia, or other eating disorder, all of which can cause dangerously low blood sugar.
Anorexia has the highest mortality of any psychiatric disorder, and the cause of death can be hypoglycemia, so take your illness seriously and seek help if you suspect your eating disorder may be progressing to the point where it is causing you to faint or experience other signs and symptoms of dangerously low blood sugar. The National Eating Disorders Association has resources on how to identify the signs that you may have an eating disorder, a hotline for help, as well as easily accessible information on everything from how to know when you need help to how to find quality treatment options in your zip code.
People who are not diabetic don’t spontaneously have hypoglycemia for no reason, explains Dr. Christofides. Its often an indication of another underlying issue, such as a hormone deficiency or eating disorder, so its important to schedule an appointment with your doctor to determine the cause in order to prevent complications.
Common causes of hypoglycemia in people without diabetes include:
- Pancreatic tumor
- Medication that inhibits the proper production of insulin
- Hepatitis or kidney disorders
- Hormone deficiencies
- Anorexia and other eating disorders
How Is Hypoglycemia Treated If I Lose Consciousness
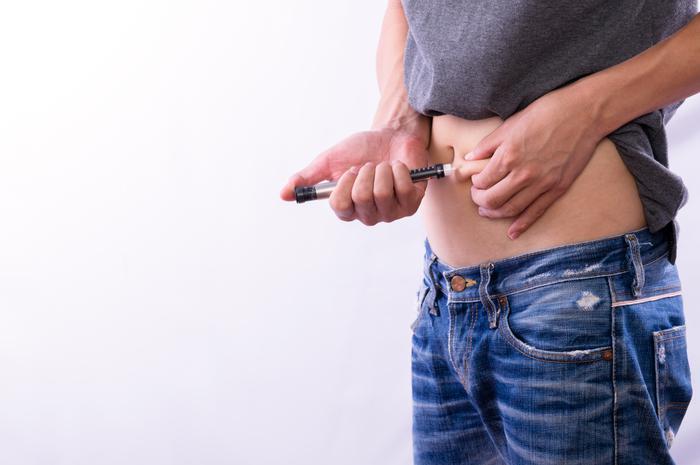

Severe blood sugar drops can cause you to pass out. This is more likely in people with type 1 diabetes but can also happen in people with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin. This can be a life-threatening. Its important to educate your family, friends, and even coworkers on how to administer a glucagon injection if you lose consciousness during a hypoglycemic episode. Glucagon is a hormone that stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose. Talk to your doctor to see if you need a prescription for a glucagon emergency kit.
The best way to avoid hypoglycemia is by following your treatment plan. A diabetes control plan to prevent hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes includes managing:
- diet
- medication
If one of these is off balance, hypoglycemia can occur.
The only way to know your blood sugar levels is to test your blood sugar. If you use insulin to control your blood sugar, you should check blood sugar levels four or more times per day. Your healthcare team will help you decide how often you should test.
If your blood sugar levels arent in the target range, work with your team to change your treatment plan. This will help you identify what actions might lower your blood sugar suddenly, such as skipping a meal or exercising more than usual. You shouldnt make any adjustments without notifying your doctor.
Read Also: Child Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Low Blood Sugar Tied To Death Risk In Hospitalized
Association was seen even if patient did not have diabetes
HealthDay Reporter
THURSDAY, Nov. 17, 2016 — Hospital patients with low blood sugar may be at increased risk for death, a new study from Israel suggests.
The study included nearly 3,000 patients with low blood sugar . Nearly 32 percent died by the end of the follow-up period.
For patients with moderate hypoglycemia, the risk of death was higher among those taking insulin than among those not taking insulin. For those with severe hypoglycemia, death risk was the same in both groups.
The reason for hospital admission had no effect on the association between blood sugar levels and death risk, according to the study.
It was published Nov. 17 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
“Hypoglycemia is common among hospitalized patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Our findings suggest that hypoglycemia, whether insulin-related or non-insulin related, is associated with short- and long-term mortality risk,” said senior study author Dr. Amit Akirov, from Rabin Medical Center in Israel.
“These data are a timely reminder that hypoglycemia of any cause carries the association with increased mortality,” Akirov said in a journal news release.
However, the study did not prove that low blood sugar causes death risk to rise.
Show Sources
What Are The Treatments For Hypoglycemia
Make an appointment with an endocrinologist if you feel like youre having episodes of hypoglycemia, even if youre not diabetic. Theyll talk you through treatment strategies, including:
- Adjusting your medications. You may need to change how often you take insulin or other medications, which medications youre on, how much you take, and when you take them.
- Working with a registered dietitian on a personalized meal plan that stabilizes blood sugar levels. Theres no one-size-fits-all hypoglycemia diet, but a nutritionist can help you figure out a consistent meal plan tailored to you, and teach you how to count carbohydrate grams to go along with your health and routine.
- Increasing and improving self-monitoring of your blood glucose levels. Knowing your blood glucose level throughout the daywhen you get up, before meals, and after meals etc.can help you keep it from getting too low.
- Limiting consumption of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol interferes with the way your body metabolizes glucose. If you’re prone to hypoglycemia, consider decreasing how much alcohol you consume.
- Glucose tablets . Make sure you always have glucose tablets on hand, whether at home, school, the office, or the gym. After taking the tablet, check your blood sugar. If its still low, take another tablet. If that doesnt help, check with your doctor.
You May Like: Diabetics Eat Bananas
How Can I Prevent Hypoglycemia
You may need to change what and when you eat to prevent low blood sugar levels. Follow the meal plan that you and the dietitian have planned. The following guidelines may help you keep your blood sugar levels under control.
- Eat 5 to 6 small meals each day instead of 3 large meals. Eat the same amount of carbohydrate at meals and snacks each day. Most people need about 3 to 4 servings of carbohydrate at meals and 1 to 2 servings for snacks. Do not skip meals. Carbohydrate counting can be used plan your meals. Ask your healthcare provider or dietitian for information about carbohydrate counting.
- Limit refined carbohydrates. Examples are white bread, pastries , regular sodas, syrups, and candy.
- Do not have drinks or foods that contain caffeine. Examples are coffee, tea, and certain types of sodas. Caffeine may cause you to have the same symptoms as hypoglycemia, and may cause you to feel worse.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol. Women should limit alcohol to 1 drink a day. Men should limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor. Do not drink alcohol on an empty stomach. Drink alcohol with meals to avoid hypoglycemia.
- Include protein foods and vegetables in your meals. Some foods that are high in protein include beef, pork, fish, poultry , beans, and nuts. Eat a variety of vegetables with your meals.
Questions A Caregivers Should Ask
As a family member, friend, or caregiver, you want to do your best to keep your loved one, friend, or patient safe from severe hypoglycemia. But knowing whats best can be overwhelming. Here are some questions to help you get started.
- What are my loved ones/friends/patients chances for severe hypoglycemia?
- How often should my loved one/friend/patient check their blood glucose?
- What should I do if there is no change after giving the glucagon?
- What would be the best food or drink to give my loved one/friend/patient once they wake up?
- Should I talk with a diabetes educator?
- How can I help treat their hypoglycemia?
Recommended Reading: Does Black Coffee Trigger Insulin
Does Everyone Have Symptoms From Hypoglycemia
Some people dont have symptoms or dont notice them. Healthcare providers call that situation hypoglycemia unawareness. People with such a challenge arent aware when they need to do something about their blood sugar. Theyre then more likely to have severe episodes and need medical help. People with hypoglycemia unawareness should check their blood sugar more often.
Can A Diabetic Coma Be Prevented
You can help yourself prevent a diabetic coma by taking steps to keep your blood sugar in the target ranges. Meeting with a Certified Diabetes Educator is an important part of understanding how to care for your diabetes. The CDE will help you be aware of symptoms for high and low blood sugar levels and how best to manage your condition.
It’s also important for your family, friends and coworkers to understand how to help you if you need help. Let them know about the symptoms of high and low blood sugar.
In terms of food and drink, here are some tips for preventing diabetic coma:
- Learn about foods that affect your blood sugar and the best meal plan for you.
- Dont skip meals.
- Keep treatment for a low blood sugar with you at all times .
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol.
- Ask your healthcare provider to prescribe a glucagon kit and teach a support person how to use it in case you ever have severe low blood sugar.
These are other recommendations to help you manage your blood glucose levels:
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/02/2020.
References
Also Check: Metformin / Sitagliptin Side Effects

