Dopamine And The Glucose Effect
Glucose, or blood sugar, is the simplest of the carbohydrates. It is also essential for human survival. Glucose acts as the primary source of energy for every cell in the body, and the brain depends on it. An even supply of glucose keeps the brain functioning in a balanced way.
However, consuming too much added sugar may lead to increased irritability and peaks and drops in energy levels. Although the initial intake of sugar may feel positive, it will cause blood glucose levels to drop. It is this that affects the mind and body so dramatically.
For some people, however, sugar can be incredibly addictive. When a person consumes sugar, the mesolimbic dopamine system in the brain offers a reward, thereby increasing mood. The dopamine system starts working when feelings of pleasure approach.
Because these are added sugars, however, they are not beneficial to the body in any way. A high intake of these will mean chemical changes in the body. These occur to prevent overstimulation, so the body may crave more sugar on future occasions to achieve the same high mood.
The Link Between Anxiety And Glucose Levels
Stress can affect your blood sugars, though research tends to be mixed as to how. In some people, it appears to raise blood glucose levels, while in others it appears to lower them.
At least one has shown there may also be an association between glycemic control and mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression, particularly for men.
However, another study found that general anxiety didnt affect glycemic control, but diabetes-specific emotional stress did.
Other research has found that people with type 1 diabetes seem to be more susceptible to physical harm from stress while those with type 2 diabetes werent. Ones personality also seems to determine the effect to some extent as well.
Orthopaedic Trauma And Non
Karunakar et al., did a study to analyze the effect of stress hyperglycemia on infectious complications in orthopaedic trauma patients. They divided them into two subgroups based on mean serum glucose greater than 220 mg/dl 3.0 or greater) and concluded that mean perioperative glucose levels greater than 220 mg/dl were associated with a seven times higher risk of infection in orthopaedic trauma patients with no known history of diabetes mellitus .
Chen et al., carried out a prospective observational analysis of 1,257 consecutive patients with no history of diabetes who suffered hip fractures. They measured fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. They divided all the patients into stress hyperglycemia and non-hyperglycemia groups according to their FBG, and recorded incidence of acute myocardial infarction . Among the patients enrolled, the frequency of stress hyperglycemia was 47.89% and that of AMI was 9.31% and the occurrence of AMI in the SIH group was higher than in the non-hyperglycemia group. The authors concluded that SIH after hip fracture increased the risk of AMI .
Richards et al., studied the relationship of SIH and surgical site infections. They studied 790 patients with orthopaedics injuries who required operative intervention. They found that hyperglycemia with blood glucose levels 200mg/dl and HGI 1.76 was an independent risk factor for 30 day surgical-site infection in orthopaedic trauma patients without a history of diabetes .
You May Like: Is Instant Oatmeal Good For Diabetics
How Can I Help Prevent Hyperglycemia
- Exercise can help lower your blood sugar when it is high. It also can keep your blood sugar levels steady over time. Exercise for at least 30 minutes, 5 days a week. Work with your healthcare provider to create an exercise plan. Children should get at least 60 minutes of physical activity each day.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider how much you should weigh. A healthy weight can help you lower your blood sugar levels. Ask your provider to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight. Together you can set manageable weight loss goals.
- Follow your meal plan. A dietitian will help you make a meal plan to help lower your blood sugar level. You may need to decrease the amount of carbohydrates that you eat.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung damage. They can also make your blood sugar levels harder to control. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol. Alcohol can increase your blood sugar level. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor. Ask your healthcare provider if it is safe for you to drink alcohol. Also ask how much is safe for you to drink each day.
Recharge Your Batteries By Getting A Good Nights Sleep

Plenty of research shows that lack of adequate sleep can lead to emotional strain for example, a study published in the;Journal of Neuroscience shows that sleep deprivation is a contributing factor to anxiety disorders. Whats more, poor sleep may cause blood sugar levels to swing: In a large study published in;Diabetes Care,;people with type 2 diabetes who slept less than 4.5 hours per night had higher blood sugar levels than those who slept 6.5 to just over 7 hours a night. Sleeping too much was also associated with higher blood sugar. Getting enough sleep can help your diabetes management, Campbell says. If youre not sleeping well at night, discuss the matter with your doctor.
RELATED: Why Sleep Matters When Youre Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Diabetic
There Are Several Ways To Self
One of;the most important tests people with diabetes use;is the daily finger prick, in which a drop of blood is placed on a test strip and inserted into a blood sugar meter to quickly get a blood sugar reading. People with diabetes often need to self-test their blood sugar to make sure its steady. However, there are other ways to self-test blood sugar, including continuous glucose monitors. More often used by people with type 1 diabetes, the devices use a small sensor wire that is inserted below the skins surface to continuously monitor glucose levels. The sensors need to be replaced every three to seven days, and people who use them typically still need to do finger-prick tests to make sure the devices are working correctly.
What Medications Can Raise Blood Sugar Levels
Many prescription medications and some OTC medications raise blood sugar levels, but this does not mean they can not be taken if they are needed. You must work with your doctor on the correct way to use them. Some prescription medicines that increase blood sugar levels are steroids, birth control pills, statins, drugs that treat mental health issues, medication for acne, and high doses of asthma medicines. Some OTC medicines that increase blood sugar levels include decongestants and cough syrups.
Read Also: How To Get Sugar Out Of Your Blood
Glucose Fuels The Brain
Although glucose so far sounds like a bad thing, you wouldnt be able to survive without it. In fact, one of the amazing facts about your brain;is that your noggin runs on glucose. According to Harvard Universitys Neuroscience Institute, the brain uses the most energy out of all the bodys organs, and so requires half of the bodys sugar. In addition, glucose is the primary source of energy used by our bodies, Zuckerbrot says. Once your body has used the energy it needs, glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, she says. If your body runs low on glucose, the pancreas will release its other hormone, glucagon. Glucagon induces the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, Zuckerbrot says.
Seek Support In Reducing Stress
Living with type 2 diabetes can be intrinsically stressful. Called diabetes burnout, overwhelm and fatigue caused by blood sugar testing, carb-counting, insulin administration, doctor visits, and other facets of diabetes management can negatively affect both physical and emotional health, according to the ADA.
Take advantage of your support circle. A family member, friend, or other source of support who will listen to you can make a big difference in the way you manage stress, Campbell says, adding, You can also talk to a counselor or join an online support community. The ADA recommends diabetes support groups as a way to connect with people who understand what youre going through and to share management and coping advice. Check out The ADA Mental Health Provider Referral Directory to find nearby groups that, when the pandemic is over, you can join in person.
RELATED: How Diabetes Support Groups Can Change Your Life
Don’t Miss: How To Pass Gestational Diabetes Test
Anxiety Over Diabetes Management
Managing your blood sugar and other aspects of your health when you have diabetes can be time consuming and stressful, and also contribute to anxiety.
For people with diabetes, monitoring blood sugar usually involves a home finger prick test. Fear of needles, as well as fear of the results, may lead to anxiety.
One study found that 33% of people with diabetes experience anxiety specific to the finger prick method of glucose testing. Thirty percent of people with diabetes in this same study had generalized anxiety related to their diabetes management.
Other areas of diabetes management may also lead to stress and anxiety. This includes monitoring potential symptoms of vision loss , nerve damage , slow-healing wounds on the feet or extremities, kidney damage, and more.
Blood Sugar Level Charts For People With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most non-pregnant adults with diabetes:
| Type of patient | A1c | Oral glucose test |
|---|---|---|
| Prediabetes |
Children, teens, and adolescents with diabetes should aim to keep within these ranges:
| Age | A1c |
|---|---|
| 6-12 years old | |
| 7.5% |
The A1c test looks at how good your blood glucose control has been over a period of 3 months. These values are a guide. Your doctor will provide you with a personal management plan.
You May Like: Are Pumpkin Seeds Good For Diabetics
Can Surgery Cause Increased Blood Sugar In Non
-Any surgery acts as a physical stress for the body. -The body gears up for a speedy recovery and during this period, our body mobilizes energy i.e. glucose to overcome this stress. -Certain hormones too are released to overcome this stress. Among many others like cortisol, these hormones include insulin and glucagon, both of which work in combination to maintain our blood sugar levels within the normal range. -This increased mobilization of glucose as a stress response and increased release of hormones can result in an imbalance of sugar level and thus, increase blood sugars . -This is usually managed without medicines, as glucose levels come down within the normal range in a few hours to days. But, in case of diabetic patients insulin needs to be administered for controlling it.Continue reading >>
S To Find Out If Stress Is Affecting Your Blood Glucose Levels
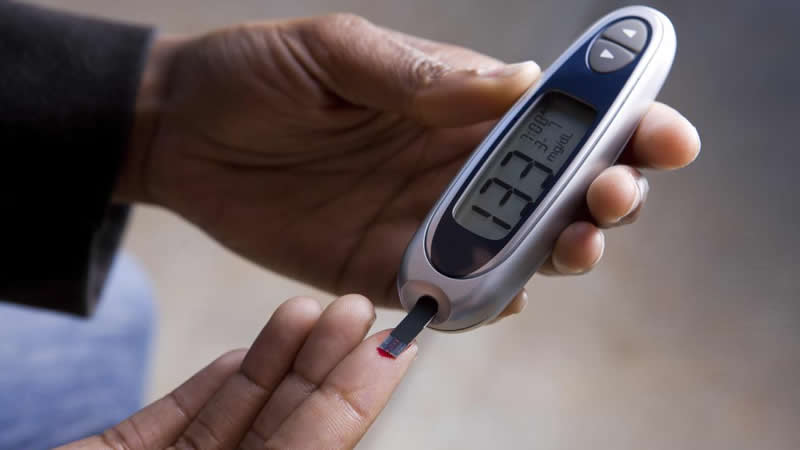
- Step 1. Rate your stress level from 1-10, where 1 indicates the lowest stress level and ; 10 the highest. Record the stress level along with situation and feelings in your logbook.
- Step 2. Test your blood glucose and record your result.
- Step 3. After a week or two, study your results to see if theres any pattern between your stress levels and your blood glucose levels.
Don’t Miss: When Administering Insulin What Would Be Most Appropriate
The Mental Vicious Circle
Beyond the pure physical impact of stress, theres a confounding mental element: If you are stressed out, your mental bandwidth to deal with complex tasks is reduced. You are less organized, energetic and motivated. So naturally, this impacts diabetes control. When people get stressed out, theyre more likely to eat heavy comfort foods, skip difficult tasks or medications, and to basically ignore their diabetes. This is even more significant when it comes to stresss first cousin: Depression.
Depressions negative effect on diabetes control is well-documented, and deadly serious.
Theres a big difference between being stressed or burnt out, and being clinically depressed, according to Dr. Bill Polonsky, founder of the Behavioral Diabetes Institute, in this article on mental health and diabetes.
Depression is a clinically diagnosed or diagnosable medical condition, whereas experiencing stress is not. He explains:
Still, everyday stress on its own can certainly derail your diabetes management, and research shows it can even weaken your immune system.
What To Do If You Have A Blood Sugar Spike
For those with diabetes, having a blood sugar spike can be dangerous because too much sugar in the blood passes into the urine. This triggers the body to filter out the fluid, which could lead to dehydration or a diabetic coma.
In the event that blood sugar levels spike because of stressors that cannot be managed, its vital to make managing your blood glucose a priority. You can do this by focusing on things you can control, such as your diet and exercise, checking your blood sugar regularly, and taking your medications as instructed by your physician.
Read Also: Can You Have Low Blood Sugar Without Diabetes
What Happens In Your Body When You Get Stressed
Stress hormones have a big role to play.
When youre experiencing physical or emotional stress, hormones are released that increase your blood sugar. Cortisol and adrenaline are other primary hormones involved.
This is a perfectly natural response. For example, if youre being chased by a barking dog or youre in a dangerous situation, you need these hormones to prepare your body for a fight or flight situation.
But when youre stressed, your body releases these hormones, even if there isnt a major physical threat involved.
The result? Higher blood pressure, increased heart rate and a rise in blood sugar.
The problem becomes more complicated.
If youre consistently under stress, your hormones and sugar will continue to surge.
Over time, this can put you at risk for:
- Heart disease
This is one reason why its so important to treat your stress and anxiety.
How Can Glucose Levels Influence Depression
There are a few reasons for poor glucose control resulting in higher prevalence of depression in both diabetic and healthy populations. Research has shown that diets high in added sugars or foods that ultimately raise your blood sugar are linked to depression and adverse mental health symptoms after several years. This informs us that diets high in added sugar impacts mental health on a long-term basis.
High dietary intake of added sugar has impacts on various metabolic processes that may result in the development of depression
- Excessive sugar intake can lead to inflammation in the body, which is correlated with higher risks of depression, along with varied high and low glucose levels that impacts fluctuations in our hormones. Hormone dysregulation can often have a negative effect on our moods and is linked to greater risk for depression over time.
Excess sugar intake can have an addictive like effect
- Diets high in added sugar can often impact our pleasure / reward chemical, dopamine, in the brain â resulting in an addictive effect that feeds a cycle of poor mood, depression, and desire for more sugar to improve those feelings.
Overall stress related to being diagnosed with and managing diabetes
Studies show a biological relationship related to a mechanism in the brain that predisposes diabetics to depression
Increased blood glucose levels have been associated with increasing the neurotransmitter Glutamate
Also Check: Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented
Dealing With Diabetes Can Cause Anxiety
Lets face it:;Controlling diabetes;is hard work. That in itself is enough to cause worry and stress. In fact, according to the;Centers for Disease Control, those with diabetes are 20 percent more likely to experience anxiety than those without the disease.
We understand this, and were dedicated to helping alleviate your worry by working together as a team to address any distressing issues.
Effect Of Long Stress On Blood Glucose Levels
It is important to be aware that repeated episodes of stress can cause serious changes in blood sugar levels, making it harder for diabetics to manage their condition and increasing the risk of hypoglycemia .
Constant stress will also cause adrenal fatigue leading to adrenal failure, which is why it is vital to remove stress from your life, especially if you have diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Does Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Blood Sugar
Scary Movies Work Stress And Trauma Of Any Kind All Cause Your Liver To Release Stored Glucose To Support Natural ‘fight Or Flight’ Responses
Last weekend I decided to stay up late and watch a scary movie. It had something to do with super-gross vampires who get their jollies by eating the flesh of unsuspecting hotel guests.
Anyway, after the final gut-wrenching, heart-pumping scene, I decided to check my blood sugar. Ill be darned it had risen about 200 mg/dL during the movie. With blood that sweet, I felt like the grand prize for any vampires that might happen to be lurking in my neighborhood.
As you may be aware, the liver serves as a storehouse for glucose, keeping it in a concentrated form called glycogen. The liver breaks down small amounts of glycogen all the time, releasing glucose into the bloodstream to nourish the brain, nerves, heart and other always active organs.
The livers release of glucose depends largely on the presence of certain hormones. Of all the hormones in the body, only insulin causes the liver to take sugar out of the bloodstream and store it in the form of glycogen. All the other hormonesincluding stress hormones, sex hormones, growth hormones and glucagoncause the liver to secrete glucose back into the bloodstream.
Anxious moments and nerve-racking situations happen to all of us. From speaking in public to test-taking to a simple visit to the doctor or dentist, many events elicit a stress hormone response that causes, among other things, a sharp blood sugar rise.

