Who Gets Type 2 Diabetes
What makes people more likely to develop type 2 diabetes? No one knows for sure. But experts have a few ideas about what puts a person at greater risk:
- Most people who have type 2 diabetes are overweight.
- People with family members who have diabetes get diabetes more often.
- People who are older than 10 are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than younger kids.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Sometimes people with type 2 diabetes take pills that help the insulin in their bodies work better. Some also need insulin shots or an insulin pump to control their diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes have to pay a little more attention to what they’re eating and doing than people who don’t have diabetes. They may need to:
- Eat a healthy diet, as determined by the care team.
- Get regular physical activity to achieve a healthy weight and allow insulin to work more effectively.
- Check their blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
- Get treatment for other health problems that can happen more often in people with type 2 diabetes, like high blood pressure or problems with the levels of fats in their blood.
- Have regular checkups with doctors and other people on their diabetes health care team so they can stay healthy and get treatment for any diabetes problems.
People with type 2 diabetes might have to eat smaller food portions and less salt or fat, too. Those who eat healthy foods, stay active, and get to a healthy weight may bring their blood sugar levels into a healthier range. Their doctors may even say they don’t need to take any medicines at all.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- Chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, or other signs of angina
- Loss of consciousness
Also call your provider if you have:
- Blood sugar levels that are higher than the goals you and your provider have set
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in your feet or legs
- Problems with your eyesight
- Sores or infections on your feet
- Frequent feelings of depression or anxiety
- Symptoms that your blood sugar is getting too low
- Symptoms that your blood sugar is too high
- Blood sugar readings that are below 70 mg/dL
You can treat early signs of hypoglycemia at home by drinking orange juice, eating sugar or candy, or by taking glucose tablets. If signs of hypoglycemia continue or your blood glucose level stays below 60 mg/dL , go to the emergency room.
Recommended Reading: Does Type 2 Diabetes Need Insulin
When The Blood Glucose Level Goes Down
- Blood sugar drops
- The pancreas detects the drop in blood sugar
- The pancreas switches on the output of glucagon into the blood
- Glucagon signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose
- The liver releases glucose into the bloodstream
- Blood glucose goes up to its normal set point and
- The pancreas detects the rise in blood sugar and switches off glucagon release.
What’s It Like For Teens With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes people who have diabetes feel different from their friends because they need to think about how they eat and how to control their blood sugar levels every day.
Some teens with diabetes want to deny that they even have it. They might hope that if they ignore diabetes, it will just go away. They may feel angry, depressed, or helpless, or think that their parents are constantly worrying about their diabetes management.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s normal to feel like your world has been turned upside down. Your diabetes care team is there to provide answers and support. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctors, dietitian, and other treatment professionals for advice and tips. It also can help to find support groups where you can talk about your feelings and find out how other teens cope.
Diabetes brings challenges, but teens who have it play sports, travel, date, go to school, and work just like their friends.
Read Also: Can A Diabetic Eat Chocolate
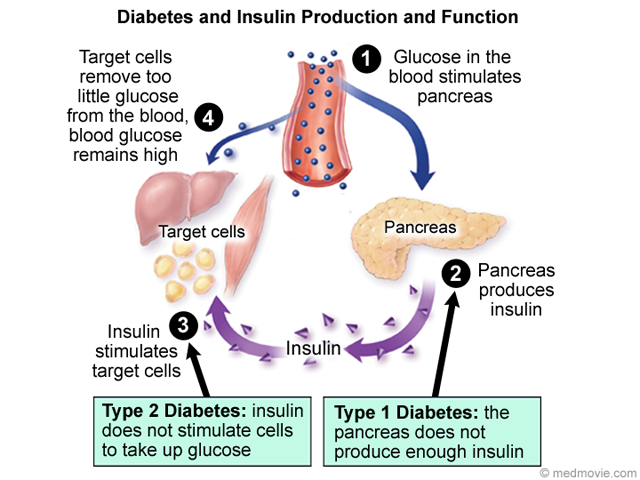
The Endocrine System And Diabetes
Diabetes affects how the body regulates blood glucose levels. Insulin helps to reduce levels of blood glucose whereas glucagons role is to increase blood glucose levels.
In people without diabetes, insulin and glucagon work together to keep blood glucose levels balanced.
In diabetes, the body either doesnt produce enough insulin or doesnt respond properly to insulin causing an imbalance between the effects of insulin and glucagon.
In type 1 diabetes , the body isnt able to produce enough insulin and so blood glucose becomes too high unless insulin is injected.
In type 2 diabetes , the body is unable to respond effectively to insulin, which can also result in higher than normal blood glucose levels. Medications for type 2 diabetes include those which help to increase insulin sensitivity, those which stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin and other medications which inhibit the release of glucagon.
Sites Of Insulin Action And Manifestations Of Insulin Resistance
The effects of insulin, insulin deficiency and insulin resistance vary according to the physiological function of the tissues and organs concerned, and their dependence on insulin for metabolic processes. Those tissues defined as insulin dependent, based on intracellular glucose transport, are principally adipose tissue and muscle. However, insulins actions are pleotropic and widespread, as are the manifestations of insulin resistance and the associated compensatory hyperinsulinaemia.
Read Also: Which Organ System Triggers Insulin Release
Sleep And Sleep Deprivation
Acute sleep deprivation in healthy young adults has been reported to raise fasting blood glucose concentrations in association with altered diurnal cortisol secretion and reduced heart rate variability. These effects suggest increased counter-regulatory hormone secretion via hyper-arousal with activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary adrenal axis. There is also accumulating evidence that chronic sleep deprivation may impact on insulin and insulin resistance. Recent epidemiological studies report that reduced sleep duration is associated with increased BMI. Sleep deprivation is associated with decreased plasma concentrations of leptin, the adipocyte peptide hormone regulating fat mass and appetite, and increased concentrations of ghrelin, which increases appetite. Growth hormone is secreted during slow wave sleep, sleep declines with age and growth hormone deficiency in adults has been associated with central adiposity and insulin resistance, but whether sleep deprivation acts through these mechanisms is not clearly established. Obstructive sleep apnoea , where sleep disturbance results from obstruction to breathing during sleep, is associated with impaired glucose tolerance independent of adiposity, and improves with continuous positive airway pressure treatment but whether this is due to resolution of hypoxia and hypercapnia, or to effects on sleep quality, is unclear.
Insulin And Fat Storage
As well as being involved in the regulation of blood glucose, insulin is also involved in how fat is used by the body. When the liver is has taken up its capacity of glycoge, insulin signals fat cells to take up glucose to be stored as triglycerides.
An additional effect of insulin is in inhibiting the breakdown of fats.
Read Also: What Candy Can Diabetics Eat
What Severe Complications Can Occur Because Of Rationing Or Running Out Of Insulin
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an emergency condition that results if you dont have enough insulin to regulate your blood sugar. DKA causes your body to break down fat for energy in the absence of insulin. This leads to a dangerous accumulation of acids known as ketones in your blood that can cause your brain to swell and your body to go into shock.
Signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
- Thirst or a very dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- High levels of ketones in your urine
- Fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain
- Difficulty breathing
- A fruity or acetone odor on your breath
- Confusion or acting drunk while sober
DKA is so common and can come on so quickly that it is the first sign of Type 1 diabetes in 20% of cases, and the way many type 1 diabetics are first diagnosed with the condition. If you go into diabetic ketoacidosis, dont try to hide it or make light of it. Treat it as the emergency it is and get to a hospital as soon as possible to recover. Ive had people tell me theyre tired of taking insulin, or that theyre rationing it due to cost. In type 1 diabetes, thats all it takes to end up in a life-threatening situation, says Dr. Zilbermint.
Another complication facing diabetics who use insulin is the potential for hyperglycemia, also known as insulin shock, which involves using too much insulin and causing your blood sugar to drop extremely low. This can cause coma, seizures, and heart attacks, says Dr. Powers.
How Do You Choose The Right Syringe For Injecting Insulin
Just as there are different sizes of syringes for administering insulin, there are also varying sizes of insulin needles. Shorter needles usually mean less sting when injecting. The downside is that the shallower the injection is, the longer it takes for the insulin to work. Your doctor will help you find the balance thats best for you.
You May Like: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
What Happens If I Have Too Little Insulin
People with diabetes have problems either making insulin, how that insulin works or both. The main two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although there are other more uncommon types.
People with type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin at all. This condition is caused when the beta cells that make insulin have been destroyed by antibodies , hence they are unable to produce insulin. With too little insulin, the body can no longer move glucose from the blood into the cells, causing high blood glucose levels. If the glucose level is high enough, excess glucose spills into the urine. This drags extra water into the urine causing more frequent urination and thirst. This leads to dehydration, which can cause confusion. In addition, with too little insulin, the cells cannot take in glucose for energy and other sources of energy are needed to provide this energy. This makes the body tired and can cause weight loss. If this continues, patients can become very ill. This is because the body attempts to make new energy from fat and causes acids to be produced as waste products. Ultimately, this can lead to coma and death if medical attention is not sought. People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin in order to survive.
What Is The Function Of The Pancreas
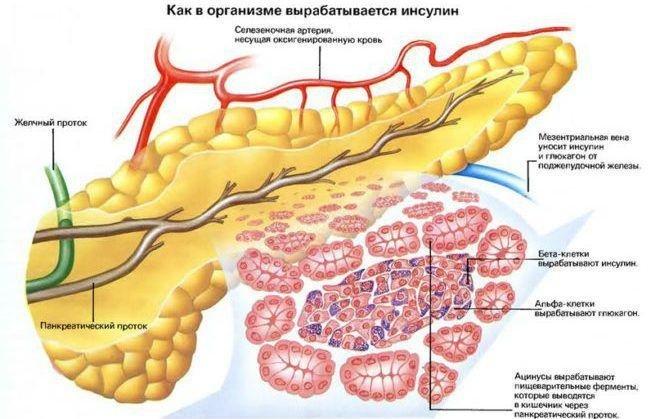
A pancreas that is functioning normally produces chemicals which are responsible for digesting food that we eat. The pancreas plays a role in two different systems, that is the exocrine system and the endocrine system. The exocrine tissue in the pancreas secretes an alkaline fluid that consists of several enzymes. These enzymes work by breaking down the food we eat into small particles that can be absorbed by the intestines.
Don’t Miss: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Physiological Role Of Insulin
Insulin is the pivotal hormone regulating cellular energy supply and macronutrient balance, directing anabolic processes of the fed state. Insulin is essential for the intra-cellular transport of glucose into insulin-dependent tissues such as muscle and adipose tissue. Signalling abundance of exogenous energy, adipose tissue fat breakdown is suppressed and its synthesis promoted. In muscle cells, glucose entry enables glycogen to be synthesised and stored, and for carbohydrates, rather than fatty acids to be utilised as the immediately available energy source for muscle contraction. Insulin therefore promotes glycogen and lipid synthesis in muscle cells, while suppressing lipolysis and gluconeogenesis from muscle amino acids. In the presence of an adequate supply of amino acids, insulin is anabolic in muscle.
Body Can Regain The Ability To Produce Insulin
Researchers have discovered that patients with type 1 diabetes can regain the ability to produce insulin. They showed that insulin-producing cells can recover outside the body.
Hand-picked beta cells from the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Photo: Oskar Skog, Uppsala University.
Type 1 diabetes is a serious disease that affects many children and adolescents. The disease causes the pancreas to stop producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
When blood sugar levels are too high, the smallest blood vessels in the body eventually become damaged. This can lead to serious health problems further down the line, including heart attacks, stroke, blindness, kidney failure and foot amputations.
Professor Knut Dahl-Jørgensen and doctoral student Lars Krogvold are leading a research project, , in which they want to ascertain among other things whether a virus in the pancreas might cause type 1 diabetes.
They have previously discovered viruses in hormone-producing cells, the so-called islets of Langerhans, in the pancreas. Now their research has generated some new and surprising results.
Lars Krogvold, doctoral student at the University of Oslo and paediatrician at Oslo University Hospital. Photo: Private
Don’t Miss: Metformin Max Dose Per Day
The Effects Of Insulin On The Body
Insulin is a natural hormone produced by your pancreas that controls how your body uses and stores blood sugar . Its like a key that allows glucose to enter cells throughout your body.
Insulin is a vital part of metabolism. Without it, your body would cease to function.
When you eat, your pancreas releases insulin to help your body make energy out of glucose, a type of sugar found in carbohydrates. It also helps you store energy.
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas is no longer able to produce insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas initially produces insulin, but the cells of your body are unable to make good use of the insulin. This is called insulin resistance.
Unmanaged diabetes allows glucose to build up in the blood rather than being distributed to cells or stored. This can wreak havoc with virtually every part of your body.
Blood tests can quickly indicate whether your glucose levels are too high or too low.
Complications of diabetes include kidney disease, nerve damage, heart problems, eye problems, and stomach problems.
People with type 1 diabetes need insulin therapy to live. Some people with type 2 diabetes must also take insulin therapy to control their blood sugar levels and avoid complications.
If you have diabetes, insulin therapy can do the job your pancreas cant. The following types of insulin are available:
Regulation And Mechanisms Of Insulin Secretion At The Cellular Level
Synthesis and secretion of insulin is regulated by both nutrient and non-nutrient secretagogues, in the context of environmental stimuli and the interplay of other hormones. Nutrient secretagogues such as glucose appear to trigger insulin secretion from the cell by increasing intracellular ATP and closing of K+-ATP channels as outlined above. Generation of cyclic AMP and other cellular energy intermediates is also augmented, further enhancing insulin release. Glucose does not require insulin action to enter the cell . Non-nutrient secretagogues may act via neural stimuli such as cholinergic and adrenergic pathways, or through peptide hormones and cationic amino acids.
Neural Stimuli
1. Cholinergic Transmission
It has been well recognised that vagus nerve stimulation results in pancreatic insulin secretion. This is thought to mediate the so-called cephalic phase of insulin secretion, occurring when food is seen, smelled or acutely ingested. Islet cell cholinergic muscarinic receptors activate phospholipase C, with subsequent intracellular events activating protein kinase C, phospholipase A2 and mobilizing intracellular calcium. Insulin secretion by these mechanisms does not occur in the fasting state or if blood glucose levels are low, but may augment the anabolic response to feeding.
2. Adrenergic Pathway
Peptide Hormones
Amino Acids
Schematic presentation of insulin secretory pathways. Adapted from references: & .
Footnotes: Figure Abbreviations
DAG = diacylglycerol
Recommended Reading: What Color Ribbon Is For Diabetes
The Primary Hormones That Are Produced By The Pancreas Include:
- Insulin this hormone works by allowing the bodys cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it as energy. This in turn helps to reduce high blood sugar levels.
- Gastrin gastrin hormone stimulates specific cells in the stomach that aids in digestion.
- Glucagon this hormone helps insulin to maintain a normal blood sugar level by stimulating the cells to release glucose when it is too low.
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide vasoactive intestinal peptide helps to control absorption and secretion of water from the intestines.
- Somatostatin in case other hormones such as glucagon and insulin are too high, the hormone somatostatin will be released to help maintain blood sugar.
Gurmar Powder Can Also Boost Insulin Production
Gurmar in sanskrit denotes Sugar Destroyer. Human and animal studies confirm that Gurmar helps to maintain sugar levels. It has astringent & hepatic stimulant properties that act on pancreas adrenal glands & digestive glands to maintain normal level of sugar in the blood Benefits : Has hypoglycemic properties. Supports healthy cholesterol levels. Helps maintain the metabolic activities of liver, kidney and spleen. Gurmar contains a substance that is gymnemic acid which helps decrease the absorption of sugar from the intestine. Gymnema sylvestre also increases the amount of insulin in the body and increase the growth of beta cells in pancreas. In fact gymnema sylvestre and diabetes were inseperable , Gurmar is used since 2000 years in India to treat diabetes
Chewing 10 tulsi leaves along with ginger can prepare pancreas for producing insulin
I picked this tip from a Book Diabetes Type -1 & 2 cure in 72 hours written by Dr. Biswaroop Roy Chowdhary who holds two Guiness world records on his name and also a inventor of HOBS wheel for Diabetes. What the Doctor recommends is as follows
Read Also: A1c Range For Non Diabetic

