What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
So where does T1D come from? Why might it happen to your child?
Scientists have confirmed that there is a genetic component to T1D, but its not entirely clear how the disease is passed down, and there are many other factors at play.
Type 1 diabetes does run in families and many newly diagnosed individuals already have a family member living with type 1 diabetes, says Wisconsin endocrinologist Pollock. If one parent has type 1 diabetes, a child has a 5 percent chance of developing type 1 diabetes, compared to a 40 percent chance in the case of type 2 diabetes.
There are several genetic changes that can be tested for that are known to be more common in individuals with type 1 diabetes, adds Pollock, but many of these mutations or variations can be found in individuals without the disease, too.
The leading theories suggest individuals with some known genetic variations are at risk for type 1 diabetes and these individuals then have some non-genetic, potentially environmental change that occurs and triggers the onset in someone already at-risk.
Potential environmental triggers that initiate the onset of T1D could include:
- the flu or other serious illness
- trauma, in the form of death of a loved one or divorce
- dietary inflammation
While other family members may not have type 1 diabetes, they may have autoimmune diseases like hypothyroidism or Celiac disease, which indicates a genetic predisposition to developing an autoimmune disease.
Low Blood Sugar: What To Watch Out For
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes who:
- Take too much medication or insulin
- Are late eating a meal or snack
- Have increased physical activity
- Drink too much alcohol
Symptoms of low blood sugar include feeling weak, sweaty or clammy, confused, hungry and/or irritable. Sometimes people experience a fast heartbeat and some symptoms may make a person appear to be drunk. A severely low blood sugar can result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma or death especially when a low occurs during the night.
Low blood sugar affects many parts of the body, but the most frustrating part can be that hypoglycemia can happen anytime and anywhere even when you think you are closely following the plan for your diabetes care. If low blood sugar is severe, people may need to go to the hospital to help raise their glucose level or miss work due to the side effects.
It can happen during a date, during a business meeting, or even while driving, which is the most dangerous scenario if there is confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel. Its important to use your blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others safe. Frequent testing with your blood sugar meter and taking action when blood sugar is trending low can prevent a severe low and keep your life on track.
Signs That Blood Sugar Levels Are High
People with high blood sugar may:
- pee a lot. When blood sugar levels get too high, the kidneys flush out the extra glucose into your urine , which is why people who have high blood sugar levels need to pee more often and in larger amounts.
- drink a lot. Because you’re losing so much fluid from peeing so much, you can get very thirsty.
- lose weight. If there isn’t enough insulin to help the body use glucose, the body starts to break down your muscle and fat for energy and you lose weight.
- feel tired. Because the body can’t use glucose for energy properly, you may feel really tired.
High blood sugar levels don’t always cause these symptoms. Sometimes you can have high blood sugar levels without even knowing it. But if left untreated, they can cause serious health problems. That’s why it’s important to work with your parents and diabetes team to keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. This can mean checking your blood sugar levels a few times a day, even when you feel fine.
Page 2
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c Range
Different Levels And What They Mean
The ranges of safe levels of blood glucose depend on factors such as what time of day it is and when you last ate. Safe levels of blood sugar are high enough to supply your organs with the sugar they need, but low enough to prevent symptoms of hyperglycemia or complications of diabetes which follow the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases guides. Dangerous levels of blood glucose are outside of this range.
The target levels can also vary if you have diabetes. For example, if you are diabetic and are monitoring your blood sugar, you might get a reading of 65 mg/dl. That is considered to be mild hypoglycemia, and you would be wise to eat 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and retest your blood sugar in 15 minutes.;
If you were not diabetic, you probably would not know that your sugar was low because you would not test and because you would not symptoms, and you would not act.
That is fine because your body is capable, under normal circumstances, of raising your blood glucose to healthy levels when needed, even if you have not eaten. It is important to keep them in control to help prevent issues like heart disease or nerve damage.
Looking for the best prediabetes diet? Learn what foods are best to help you manage your prediabetes.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
You May Like: Normal A1c Level
Managing Your Familys Diabetes Attitude And Mental Health
Living with type 1 diabetes is a 24/7 job that neither you nor your child will ever do perfectly. Its important to keep that in mind!
Many people living with it describe type 1 diabetes as a juggling act, and the balls youre juggling constantly change. Maintaining a science project attitude can help tremendously in preventing guilt and burnout. Every high blood sugar is simply a learning opportunity, and every low blood sugar needs to be treated and then life goes on!
Know that children with type 1 diabetes can live long, healthy, full lives!
Some excellent resources and networking opportunities for families of T1D kids can be found here:
Normal Blood Sugar For Kids
The body gets most of its glucose by metabolizing the carbohydrates in food. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps move glucose out of the blood and into the cells, where it is used for energy, according to Kaiser Permanente. Through this process, insulin also lowers blood sugar. For people with diabetes, insulin function is impaired, leading to high blood sugar.
Glucose levels vary in both children and adults, depending on how long it has been since the last meal, drink or snack. According to Yale School of Medicine, a normal blood sugar for a child without diabetes should fall within the following ranges:
- Before breakfast : 70 to 120 mg/dL
- One to two hours after meals: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Before meals and at bedtime: 70 to 120 mg/dL
Blood glucose levels can be checked during your child’s regular doctor appointment. If blood sugar levels are elevated, the doctor may order additional blood and/or urine tests to determine whether your child has diabetes.
You May Like: Normal A1c Range For Diabetics
Eat Healthy Foods And Follow A Regular Eating Schedule
Following a healthy diet as recommended by your diabetes team, watching portion sizes, and not skipping meals can help to prevent side effects like low blood sugar that can occur while taking glipizide. Notify your healthcare providers if you are not able to eat because you are sick or because you will be having a surgery or procedure done.
Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
People with diabetes have difficulty creating or using enough insulin, which is the hormone that helps convert glucose into energy. Although there is no universal blood sugar chart for everyone with diabetes, clinical organizations like the ADA and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists offer guidelines on target blood sugar levels as a starting point.
Healthcare providers typically tailor normal blood sugar target ranges to an individual diabetes care plan. This includes considering your:
- Age
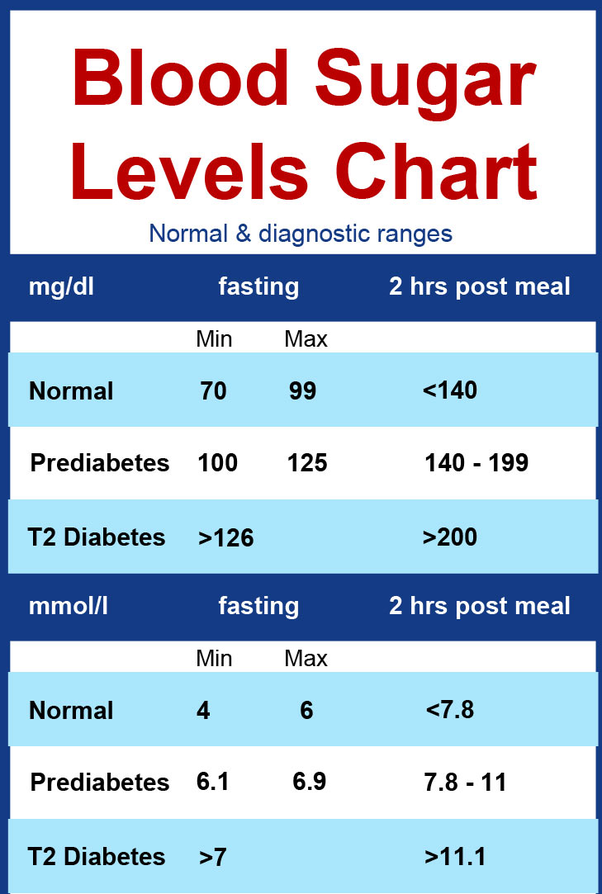
The normal blood sugar ;level for a healthy adult should be less than 126 mg/dL or 6 mmol/L before fasting and meals, and below 200mg/dL two hours after meals.
If you are diabetic, then you should consult with your doctor in order for appropriate blood sugar level targets to be set based on the severity of your condition, medications taken and overall health status.
The below information describes what normal blood sugar levels are prior to and after meals and what the recommended HbA1c levels are for those with and without diabetes.
A HbA1c test determines your average level of blood glucose over the past two to three months. Red blood cells have a lifespan of roughly three months, and a HbA1c blood test measures the amount of glucose that has bound to them during this period.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
You May Like: Non Diabetic A1c Levels
Blood Sugar Levels For Kids And Teens With Diabetes
Well-controlled blood sugars help children with diabetes grow and develop normally. Your doctor will help you figure out what levels are right for your child, since targets change as kids get older. Test your child’s blood sugar several times a day so you’ll know what you need to do to adjust it. Your goal is simple: Get it into the target range when it isn’t. What causes ups and downs? Food Growth and hormones Illness Stress and other emotions No one expects a growing child’s blood sugar levels to be normal all the time. And when your child enters puberty, his hormones could cause problems with blood sugars changing wildly. Remember, the numbers on the meter aren’t “good” or “bad” — they’re just numbers. They give you information about how to keep your child healthy. Since you or your child might not notice symptoms, testing is the best way to avoid dangerously high and low levels. Help kids learn to manage their diabetes on their own. Encourage good habits. Praise your child when he tests, regardless of the result. Don’t let him feel bad or blame him when his levels are out of range. Offer support to get him back on track.Continue reading >>
Do You Have To Fast For An A1c Blood Test
Unlike the fasting plasma glucose and the OGTT tests, there is no need to fast before having the A1C test. If A1C test results indicate a person has or might have diabetes, a healthcare provider might suggest one of these tests to confirm the results. Another test, the random plasma glucose test, which does not require fasting, can also be used. If the results are borderline or if the results of the different tests do not match, a doctor might suggest repeating the test in several weeks or months.;
Also Check: Does Diet Soda Affect Blood Sugar
Why Blood Glucose Levels Rise In Diabetes
The food we eat is converted to glucose and released into the bloodstream. Therefore, blood glucose levels are high after eating. As does the glucose generates, the body signals the pancreas to release insulin.
Insulin helps in the absorption of blood glucose by the body cells. As a result, the glucose from the blood is absorbed, and its level in the blood becomes normal again. Thus, together insulin and cell absorption helps in regulating blood glucose levels.
But in the case of diabetes, the body becomes insulin resistant, or there is insulin deficiency. Due to which the cell absorption of the blood glucose decreases. As a result, high blood glucose levels cause Diabetes. Over time, such high blood glucose levels can cause damage to nerves, kidneys, eyes, and heart.
Therefore if you have diabetes, it is essential to keep your blood glucose levels to some typical acceptable values. To help you understand blood glucose levels, a blood sugar level chart is the best option.
Summary
Blood glucose levels, if high, cause diabetes. Blood sugar level charts can help in regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose
Picture 1: Poke the side of the finger with the lancet
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
The Emotional And Mental Health Of A Diabetic Child:
A diabetic child also lives in the same environment as healthy children, but conditions are not the same since he/she has diabetes, so he/she has to take care of more than others.
Such a child seems to be very responsible and selective in their eating habits. It is so because they know that eating more sugar can be dangerous for them. That is not the case with other healthy children.
Moreover, diabetic children that are on insulin therapy are more fearless of needles and syringes. Sometimes they may face more unsatisfactory health conditions than others. They may be more affected by infections. All these circumstances pose severe concerns over the mental health of diabetic children.
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieving closer to normal blood sugar levels. If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person;without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.;
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Stopping Diabetes Medication
Signs Of Diabetes In Kids
It can be challenging to spot the signs of diabetes in children because they may not be able to communicate their symptoms to you. According to the Mayo Clinic, here are some signs to look out for:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination, especially within a short amount of time
- Extreme hunger, accompanied by weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Nausea and vomiting
Bed-wetting is another diabetes red flag, Cara Schrager, RDN, a certified diabetes educator at Harvard’s Joslin Diabetes Center, tells LIVESTRONG.com. Diabetes in children is typically diagnosed after they have been potty-trained, so “bed-wetting is a big giveaway,” she says. “If a child starts wetting the bed again, it’s important to bring it up with their pediatrician.”
Warning
Nausea and vomiting are particularly important signs to watch out for because they are symptoms of a rare but life-threatening diabetes complication called diabetic ketoacidosis .
Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
The NIDDK states that gestational diabetes is high blood sugar that occurs during pregnancy if you were not diabetic before getting pregnant. Healthy blood sugar during pregnancy can help lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later. It can also lower the risk of your baby being born prematurely, at a high birth weight, and having respiratory problems.
Blood sugar and insulin levels during the first trimester of pregnancy tend to be lower than usual, but they rise during the late second and early third trimesters. You can be diagnosed with an oral glucose tolerance test .;
These are the steps for the 2-step strategy.
- Drink a solution with 50 grams of glucose about the amount in 1 16-oz. bottle of a soft drink
- Get your blood drawn after 1 hour. IF the value is high, retest
- Fast overnight
- Drink a solution with 100 grams of glucose about the amount in 12 peanut butter cups
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1, 2, and 3 hours
Or, your doctor might use the 1-step strategy with a 2-hour OGTT:
- Fast overnight
- Drink a solution with 75 grams of glucose
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1 and 2 hours
These are some values to know from NIDKK related to gestational diabetes and healthy blood sugar in pregnancy.
| Time or Situation |
|---|
| Baseline: at least 105 mg/dl1 hour: at least 190 mg/dl2 hours: at least 165 mg/dl3 hours: at least 145 mg/dl |
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c Level

