What Causes Insulin Resistance
Obesity , an inactive lifestyle, and a diet high in carbohydrates are the primary causes of insulin resistance. Some women develop insulin resistance while they are pregnant. This is called gestational diabetes. Certain diseases are associated with insulin resistance. That includes heart disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Certain risk factors are associated with insulin resistance, including:
- A family history of diabetes
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Race
- Age
- Hormones
- Smoking
How To Store Insulin
Proper insulin storage is important to ensure that the insulin stays effective.
Avoid exposing insulin products to extreme temperatures. Insulin is a protein and this makes it subject to degradation when temperatures are too hot or too cold. Additionally, keep insulin products away from direct sunlight as this can also cause a breakdown of the insulin.
Proper insulin storage is so important that the FDA recently took action to ensure that Insulin pens must always be dispensed in their original boxes so that instructions for the proper use and storage of insulin are always included. This means that your pharmacy is not allowed to give you just 2 insulin pens from a box of 6 pens.
Insulin that is not being used should be stored in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F , a safe distance away from the back and top of the refrigerator where cooling elements may cause the temperature to approach freezing.
The refrigerators butter compartment or produce drawer is typically a good option for insulin storage.
Update: A new study from 2021 shows that insulin stored at 77° to 98.6°F for four weeks showed the same stability as insulin stored at the currently recommended pharmaceutical protocols of 36° to 46°F until opened.
Any insulin vials or pen that are in use can be stored outside of the refrigerator at temperatures up to 86F or 30C .
The reason for storing in-use insulin at room temperature is that cold insulin can produce a more painful injection.
Muscle And Fat Storage
Insulin helps your muscles and fat cells store extra glucose so it doesnt overwhelm your bloodstream.
It signals your muscle and fat tissue cells to stop breaking down glucose to help stabilize your blood sugar level.
The cells then begin creating glycogen, the stored form of glucose. Glycogen provides your body with energy when your blood sugar level drops.
When your liver can hold no more glycogen, insulin triggers your fat cells to take in glucose. Its stored as triglycerides, a type of fat in your blood, that can be used for energy later.
Don’t Miss: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Does Insulin Work In The Body
Insulin works in different ways to control your blood sugar levels so that it doesnt reach too high or too low . When your blood sugar levels rise after taking a meal, the pancreas will release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin will then help your cells, liver, fat and muscle absorb the glucose from the blood. This will lead to a fall in blood glucose levels. In case of extra glucose, insulin will stimulate the muscle and liver to store it in the form of glycogen. Insulin can also lower blood glucose levels by limiting the production of glucose by the liver. In case your blood glucose falls because you havent eaten for hours, the stored glycogen will be broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream. This will help restore the blood glucose levels to normal. Without enough insulin in your body, your blood glucose may reach dangerous levels that could lead to serious health complications.
What Does Insulin Do In Case Of An Insulin Resistance
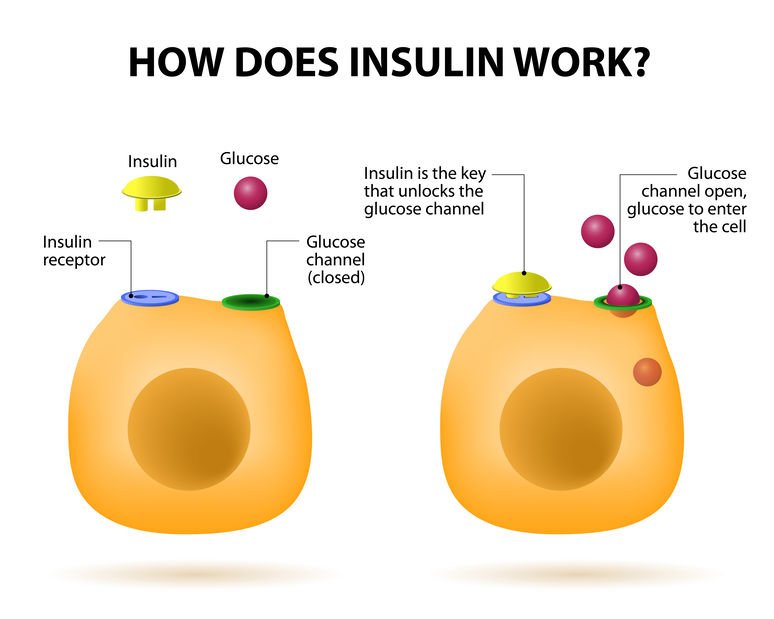
With insulin resistance, fat, muscle and liver cells cannot respond well to insulin. Therefore, glucose cannot be absorbed from the blood. This means that your body needs higher amount of insulin to help glucose get into the cells. To respond to the demand for insulin, the beta cells in the pancreas will respond by releasing more insulin. So long as there is enough insulin produced by the beta cells, the blood glucose levels will remain healthy. In case the beta cells fail to keep up with increased demand for insulin, it may lead to the risk of getting type 2 diabetes. This is because there will be excess glucose in the blood. Insulin resistance mostly affects people who do not exercise or are overweight.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What’s It Like For Teens With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes people who have diabetes feel different from their friends because they need to think about how they eat and how to control their blood sugar levels every day.
Some teens with diabetes want to deny that they even have it. They might hope that if they ignore diabetes, it will just go away. They may feel angry, depressed, or helpless, or think that their parents are constantly worrying about their diabetes management.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s normal to feel like your world has been turned upside down. Your diabetes care team is there to provide answers and support. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctors, dietitian, and other treatment professionals for advice and tips. It also can help to find support groups where you can talk about your feelings and find out how other teens cope.
Diabetes brings challenges, but teens who have it play sports, travel, date, go to school, and work just like their friends.
Where Can I Find Help Acquiring Or Paying For Insulin
The ADA has a dedicated page for helping people who need insulin get it, regardless of finances: .
JRDF has a page with a variety of links to organizations who also supply insulin assistance:
Recommended Reading: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Does Insulin Expire Storage Safety And How To Tell If Your Insulin Has Gone Bad
Being a pharmacist, I have often been asked if its safe to use expired insulin and how to tell if insulin has gone bad from exposure to heat or cold.
Medications have an expiration date because their stability cannot be guaranteed, based on clinical studies, past that date.
Taking a chance on eating an expired food product is one thing its quite another taking a chance on insulin that may not work at maximum capacity, and therefore may cause harm to your overall health.
The Dangers Of Taking Insulin When You Don’t Need It
Insulin is a crucial hormone which, among other functions, helps the body control blood sugar levels. Many people with diabetes need insulin injections to regulate their blood sugar, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 14.
Unfortunately, there are some misconceptions about insulin and some people even take it for purposes other than managing diabetes 1. This can have serious health consequences.
Recommended Reading: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Factors Influencing Insulin Biosynthesis And Release
Insulin secretion may be influenced by alterations in synthesis at the level of gene transcription, translation, and post-translational modification in the Golgi as well as by factors influencing insulin release from secretory granules. Longer-term modification may occur via influences on cell mass and differentiation. Given insulins pivotal role in glucose utilisation and metabolism, it is not surprising that glucose has multiple influences on insulin biosynthesis and secretion. However, other factors such as amino acids, fatty acids, acetylcholine, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide , glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide , glucagon-like peptide-1 , and several other agonists, together in combination, also influence these processes.
Physiology Of Insulin Secretion
Glucose is the principal stimulus for insulin secretion, though other macronutrients, hormones, humoral factors and neural input may modify this response. Insulin, together with its principal counter-regulatory hormone glucagon, regulates blood glucose concentrations. Pancreatic cells secrete 0.251.5 units of insulin per hour during the fasting state, sufficient to enable glucose insulin-dependent entry into cells. This level prevents uncontrolled hydrolysis of triglycerides and limits gluconeogenesis, thereby maintaining normal fasting blood glucose levels. Basal insulin secretion accounts for over 50% of total 24 hour insulin secretion. Following secretion of insulin into the portal venous system, 60% is subsequently removed by the liver so portal vein insulin concentrations reaching the liver approach triple that of the peripheral circulation. In healthy lean individuals circulating venous fasting insulin concentrations are about 315 mIU/L or 1890 pmol/L. Meal-related insulin secretion accounts for the remaining fraction of the total daily output.
Read Also: Where Is Glucagon Released From
What Are The Drawbacks To Insulin Treatment For Diabetes
The biggest issue with insulin right now is unaffordability. A box of rapid-acting insulin can cost $400 without insurance. As so many people continue to lose their health coverage, its becoming an enormous problem, Dr. Zilbermint says.
Consistently rising costs have led some patients to ration their insulin, which can be dangerous and even deadly. The cost of testing strips is also an issue, and both have led to a black market in testing strips and insulin. Its illegal, says Dr. Zilbermint, but its happening.
Measurement Of Insulin And Insulin Resistance
There are a variety of approaches to the laboratory assessment of insulin resistance. Over the years the limited specificity of older radio-immunoassays that cross-react with proinsulin have reduced the credibility of measuring insulin resistance in clinical settings. Current assays have improved specificity and precision. A comprehensive review of insulin assays is beyond the scope of this review and the reader is encouraged to consult Sapin in this regard. Insulin resistance may be measured by looking directly at insulin mediated glucose uptake in the basal or post-stimulated state, by inference from the relative concentrations of glucose and insulin, or by looking at surrogate markers of insulin action.
Recommended Reading: Smoking And Insulin Resistance
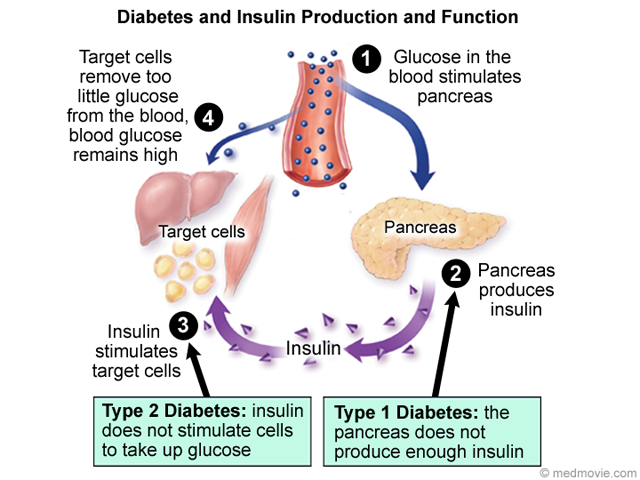
Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by the body not responding effectively to insulin. This is termed insulin resistance. As a result the body is less able to take up glucose from the blood. In the earlier stages of type 2 diabetes, the body responds by producing more insulin than it would normally need to.
If type 2 diabetes develops over a number of years, the extra demands on the pancreas to produce insulin can lead to a loss of insulin producing cells as they wear out.
Depending on their level of insulin resistance, people with type 2 diabetes may also need to take insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
The Basics Of High Blood Sugar
Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood sugar levels to rise higher than normal. This is also called hyperglycemia.
When you eat, your body breaks food down into sugar and sends it into the blood. Insulin then helps move the sugar from the blood into your cells. When sugar enters your cells, it is either used as fuel for energy right away or stored for later use. In a person with diabetes, there is a problem with insulin. But, not everyone with diabetes has the same problem.
There are different types of diabetestype 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes. If you have diabetestype 1, type 2 or gestationalyour body either doesn’t make enough insulin, can’t use the insulin well, or both.
Learn more about blood sugar Learn more about insulin
Read Also: Can You Use Insulin Straight From The Fridge
Who Needs To Take Insulin
Diabetes impairs insulin production by the pancreas and use of this essential hormone by the body. The condition causes high blood sugar levels.
However, not every person with type 2 diabetes will need to take insulin. People with type 1, on the other hand, will have to supplement their insulin supply for the rest of their lives.
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: Typically starts in childhood when a person does not produce enough insulin. Usually results from the bodys immune system attacking an otherwise healthy pancreas.
- Type 2 diabetes: Can develop at any age but 45 years is the average age of onset. Either the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or the bodys cells become resistant to its actions.
- Gestational diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and makes it harder for a womans body to respond to insulin. Typically stops after childbirth but increases a womans risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are usually lifelong conditions. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , more than 30 million people in the United States have diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common, accounting for
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Sometimes people with type 2 diabetes take pills that help the insulin in their bodies work better. Some also need insulin shots or an insulin pump to control their diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes have to pay a little more attention to what they’re eating and doing than people who don’t have diabetes. They may need to:
- Eat a healthy diet, as determined by the care team.
- Get regular physical activity to achieve a healthy weight and allow insulin to work more effectively.
- Check their blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
- Get treatment for other health problems that can happen more often in people with type 2 diabetes, like high blood pressure or problems with the levels of fats in their blood.
- Have regular checkups with doctors and other people on their diabetes health care team so they can stay healthy and get treatment for any diabetes problems.
People with type 2 diabetes might have to eat smaller food portions and less salt or fat, too. Those who eat healthy foods, stay active, and get to a healthy weight may bring their blood sugar levels into a healthier range. Their doctors may even say they don’t need to take any medicines at all.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Diabetics Need Insulin Therapy Because They Can’t Make Their Own
Insulin therapy tries to mimic natural insulin secretion what happens automatically in non-diabetics.
The ultimate goal of insulin therapy is to mimic normal insulin levels. Unfortunately, current insulin replacement therapy can only approximate normal insulin levels. Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes ranges from one injection a day to multiple injections and using an insulin pump . The more frequent the insulin injections, the better the approximation of natural or normal insulin levels. Discuss with your medical provider the insulin regimen that is best for you.
Insulin Receptors And Insulin Binding
Insulin mediates its actions through binding to insulin receptors. The insulin receptor was first characterised in 1971. It consists of a heterotetramer consisting of 2 and 2 glycoprotein subunits linked by disulphide bonds and is located on the cell membrane. The gene coding for the insulin receptor is located on the short arm of chromosome 19. Insulin binds to the extracellular subunit, resulting in conformational change enabling ATP to bind to the intracellular component of the subunit. ATP binding in turn triggers phosphorylation of the subunit conferring tyrosine kinase activity. This enables tyrosine phosphorylation of intracellular substrate proteins known as insulin responsive substrates . The IRS can then bind other signalling molecules which mediate further cellular actions of insulin.
PI 3-kinase promotes the translocation of glucose transporter proteins, glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis, anti-lipolysis and the control of hepatic gluconeogenesis. PI 3-kinase acts via serine and threonine kinases such as Akt/protein kinase B , protein kinase C and PI dependent protein kinases1& 2 . The RAS pathway activates transcription factors and stimulates the growth promoting actions of insulin. Thus broadly, PI 3-kinase mediates insulins metabolic effects, e.g. cellular glucose uptake, while RAS significantly mediates insulins mitogenic effects, together with other less well described actions. These pathways are presented schematically in .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Purpose Of Metformin
Insulin Resistance Causes And Symptoms
One in three Americansincluding half of those age 60 and older1 have a silent blood sugar problem known as insulin resistance. Insulin resistance increases the risk for prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and a host of other serious health problems, including heart attacks, strokes2 and cancer.3
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, body fat and liver start resisting or ignoring the signal that the hormone insulin is trying to send outwhich is to grab glucose out of the bloodstream and put it into our cells. Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the bodys main source of fuel. We get glucose from grains, fruit, vegetables, dairy products, and drinks that bring break down into carbohydrates.
How Insulin Resistance Develops
While genetics, aging and ethnicity play roles in developing insulin sensitivity, the driving forces behind insulin resistance include excess body weight, too much belly fat, a lack of exercise, smoking, and even skimping on sleep.4
Signs and Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is usually triggered by a combination of factors linked to weight, age, genetics, being sedentary and smoking.
– You have additional signs of metabolic syndrome. According to the National Institutes of Health,7 in addition to a large waist, if you have three or more of the following, you likely have metabolic syndrome, which creates insulin resistance.
Health Conditions Related to Insulin Resistance
What Severe Complications Can Occur Because Of Rationing Or Running Out Of Insulin
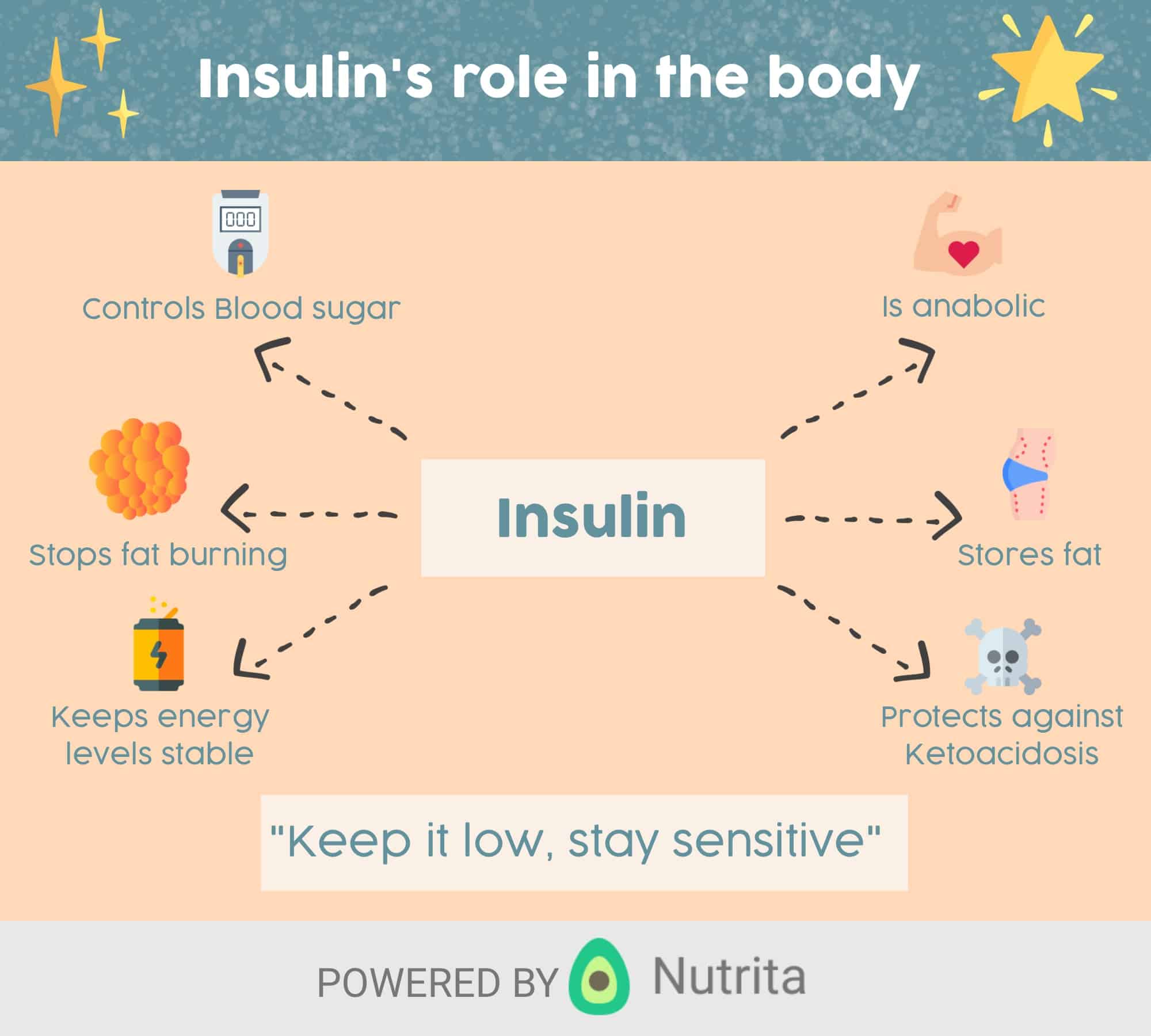
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an emergency condition that results if you dont have enough insulin to regulate your blood sugar. DKA causes your body to break down fat for energy in the absence of insulin. This leads to a dangerous accumulation of acids known as ketones in your blood that can cause your brain to swell and your body to go into shock.
Signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
- Thirst or a very dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- High levels of ketones in your urine
- Fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain
- Difficulty breathing
- A fruity or acetone odor on your breath
- Confusion or acting drunk while sober
DKA is so common and can come on so quickly that it is the first sign of Type 1 diabetes in 20% of cases, and the way many type 1 diabetics are first diagnosed with the condition. If you go into diabetic ketoacidosis, dont try to hide it or make light of it. Treat it as the emergency it is and get to a hospital as soon as possible to recover. Ive had people tell me theyre tired of taking insulin, or that theyre rationing it due to cost. In type 1 diabetes, thats all it takes to end up in a life-threatening situation, says Dr. Zilbermint.
Another complication facing diabetics who use insulin is the potential for hyperglycemia, also known as insulin shock, which involves using too much insulin and causing your blood sugar to drop extremely low. This can cause coma, seizures, and heart attacks, says Dr. Powers.
Also Check: What Happens If You Take Glipizide And Don T Eat

