What Causes Diabetes Mellitus
The main causes of this metabolic disorder are not known, though genetics, environmental factors, poor diet, obesity, medications, infections, and a sedentary lifestyle are regarded as some of the possible factors that can be associated with this condition.
There are mainly two types of diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes can be termed as an autoimmune disease, where bodys own immune system attacks and destroys the beta cells of the pancreas. What exactly triggers this autoimmune response is not known precisely, but genetics and environmental factors like viral infections are thought to be some of the important contributory factors.
Genetics can be another important cause, and a person has 10% probability of developing the disease, if a first degree relative of his or her has diabetes. In the case of a viral infection, the viral protein that enters the body resembles the beta cell protein. The immune system starts attacking both the beta cells and the virus, being unable to distinguish one from the other.
However, certain other factors can also play a significant role in the development of this metabolic disorder. T lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells, are responsible for producing the immune factors known as cytokines, that destroy the beta cells of the pancreas. Several proteins like glutamic acid, decarboxylase, insulin, and islet cell antigens act as autoantigens, and stimulate the autoimmune factors.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if youre not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
Diseases Of The Exocrine Pancreas
Damage of the pancreas must be extensive for diabetes to occur . The most common causes are pancreatitis, trauma, and carcinoma. Chronic pancreatitis can cause general inflammatory/fibrotic changes in the pancreas which can cause diabetes. Cystic fibrosis causes a well-recognized pancreatic exocrine function insufficiency, but the same thick, viscous secretions cause inflammation, obstruction, and destruction of small ducts in the pancreas, which can lead to insulin deficiency. Hemochromatosis has also been associated with impaired insulin secretion and diabetes.
You May Like: How To Reduce Side Effects Of Metformin
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
What Should I Expect If I Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
If you have diabetes, the most important thing you can do is keep your blood glucose level within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. In general, these targets are:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
You will need to closely follow a treatment plan, which will likely include following a customized diet plan, exercising 30 minutes five times a week, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and getting seven to nine hours of sleep a night. Always take your medications and insulin as instructed by your provider.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Withdrawal
Why Is My Blood Glucose Level High How Does This Happen
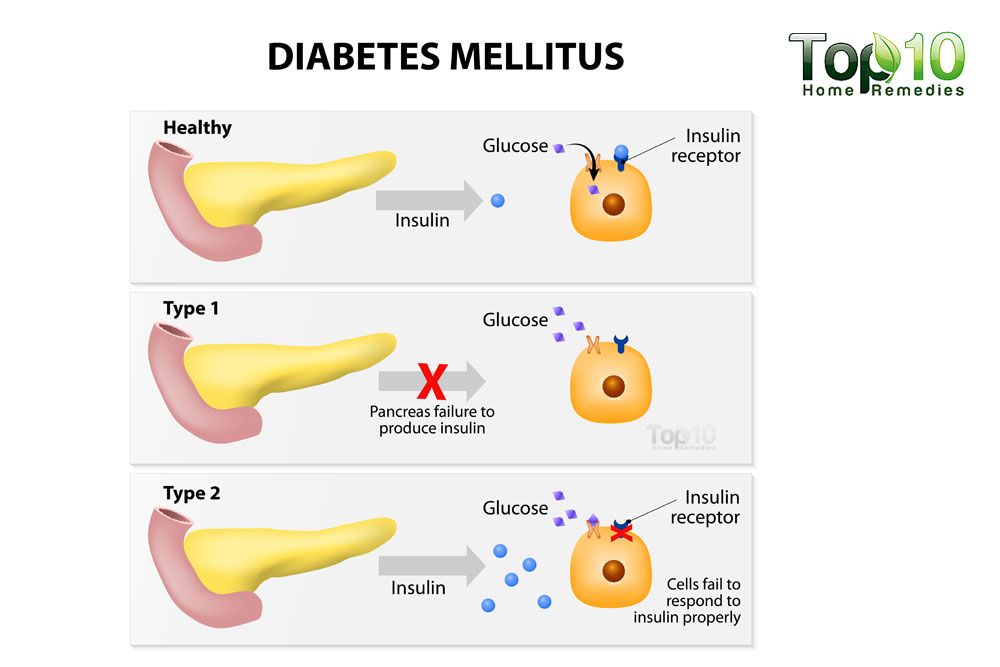
The process of digestion includes breaking down the food you eat into various different nutrient sources. When you eat carbohydrates , your body breaks this down into sugar . When glucose is in your bloodstream, it needs help a “key” to get into its final destination where it’s used, which is inside your body’s cells . This help or “key” is insulin.
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas, an organ located behind your stomach. Your pancreas releases insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin acts as the key that unlocks the cell wall door, which allows glucose to enter your bodys cells. Glucose provides the fuel or energy tissues and organs need to properly function.
If you have diabetes:
- Your pancreas doesnt make any insulin or enough insulin.
- Your pancreas makes insulin but your bodys cells dont respond to it and cant use it as it normally should.
If glucose cant get into your bodys cells, it stays in your bloodstream and your blood glucose level rises.
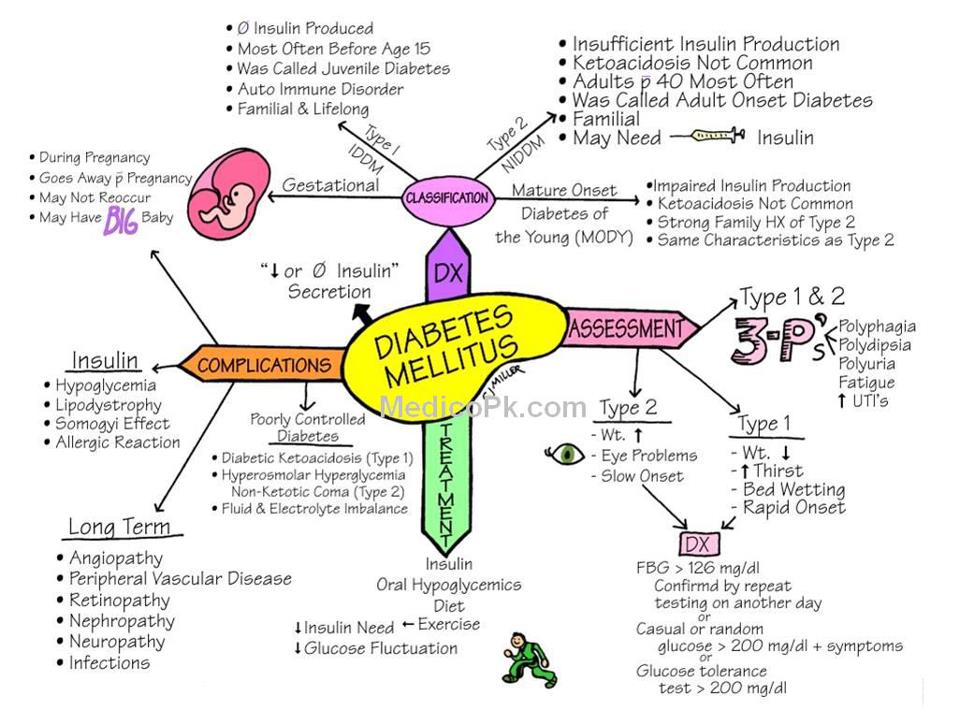
Risk Factors For Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus affects a variety of people of all races, ages and nations. It is unkown why some people develop type 1 diabetes.
It may be linked to environmental factors or a virus however it has been estabilished if there is a family history of type 1 diabetes then there is a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus are greater for some ethnicities, as mentioned before. Furthermore, those people who have a family history of type 2 diabetes, who are overweight or inactive also face a greater risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is often preceded by pre-diabetes .
Recommended Reading: What Are The Effects Of Metformin
How Is Type1 Or Type2 Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosed
The definitive diagnosis of either type of diabetes is done through blood testing. The amount of sugar in the blood can be determined in several ways. First, a fasting blood sugar level can be determined. Fasting blood sugar levels under 100 mg/dL are considered normal, between 100 mg/dL and 126 mg/dL are considered borderline, and over 126 mg/dL are considered diabetic.
Other tests may include a glucose tolerance test or the A1c test. The glucose tolerance test measures the way the body responds after a sugar solution is introduced. A patient’s blood is tested at various intervals after drinking the sugar solution to determine if values are normal. The A1c test measures the sugar in the red blood cells over a three-month time span. It is not a method for diagnosis, but it is helpful for monitoring and controlling the disease.
Understanding Diabetes From Other Causes
In addition to type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, a small minority of people develop specific types of diabetes due to other causes. This includes:
- Monogenic diabetes syndromes, such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- Diseases of the exocrine pancreas, such as cystic fibrosis and pancreatitis
- Drug or chemical-induced diabetes, such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS or after organ transplantation
Because these types of diabetes are rare, they are often misdiagnosed as other types of diabetes. You can learn more about these types of diabetes in the Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes section in the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. If you think you might have one of these types, be sure to talk with your doctor.
Read Also: What Is Normal A1c Level For Nondiabetic
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss, blurred vision and extreme tiredness.
Type 2 symptoms appear gradually and are more subtle than those seen with type 1. This makes catching the onset of type 2 diabetes harder to recognize for early treatment. Symptoms include unexpected weight loss, blurred vision, feeling tired or sick more frequently, more frequent urination . Higher levels of thirst, frequent infections and slower healing of cuts and scrapes.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Lower Blood Sugar
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
What Are The Other Types Of Diabetes
Gestational diabetes
Diabetes can occur temporarily during pregnancy, and reports suggest that it occurs in 2% to 10% of all pregnancies. Significant hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to blood sugar elevation in genetically predisposed individuals. Blood sugar elevation during pregnancy is called gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually resolves once the baby is born. However, 35% to 60% of women with gestational diabetes will eventually develop type 2 diabetes over the next 10 to 20 years, especially in those who require insulin during pregnancy and those who remain overweight after their delivery. Women with gestational diabetes are usually asked to undergo an oral glucose tolerance test about six weeks after giving birth to determine if their diabetes has persisted beyond the pregnancy, or if any evidence is present that may be a clue to a risk for developing diabetes.
Secondary diabetes
“Secondary” diabetes refers to elevated blood sugar levels from another medical condition. Secondary diabetes may develop when the pancreatic tissue responsible for the production of insulin is destroyed by disease, such as chronic pancreatitis , trauma, or surgical removal of the pancreas.
Hormonal disturbances
Medications
Certain medications may worsen diabetes control, or “unmask” latent diabetes. This is seen most commonly when steroid medications are taken and also with medications used in the treatment of HIV infection .
Recommended Reading: Side Effects For Metformin
Causes Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 And Type 2
Diabetes mellitus is a condition, where the body cells fail to absorb or utilize glucose from the bloodstream, due to the insufficient production of insulin, or insulin resistance. Find out more about diabetes mellitus and its causes, through this HealthHearty write-up.
Diabetes mellitus is a condition, where the body cells fail to absorb or utilize glucose from the bloodstream, due to the insufficient production of insulin, or insulin resistance. Find out more about diabetes mellitus and its causes, through this HealthHearty write-up.
Diabetes mellitus or diabetes is a condition, where the body fails to produce enough insulin, or utilize this hormone properly. This impairs normal sugar or glucose metabolism. Insulin is a hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas.
The islets of Langerhans contains two types of cells alpha and beta cells, which are responsible for producing insulin. Insulin is required by the body for absorbing glucose from the bloodstream. The carbohydrates we consume are broken down into simpler molecules of glucose in the small intestine.
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
Don’t Miss: Cheese Diabetics Can Eat
Underlying Conditions And Possible Causes
Polyphagia is one of the most common symptoms of diabetes mellitus. It is associated with hyperthyroidism and endocrine diseases, e.g., , and it has also been noted in and other genetic conditions caused by chromosomal anomalies. It is only one of several diagnostic criteria for bulimia and is not by itself classified as an eating disorder. As a symptom of , it is sometimes termed megaphagia.
Knocking out receptors has been shown to cause hyperphagia.
According to the National Center for Biomedical Information, polyphagia is found in the following conditions:
- Chromosome 22q13 duplication syndrome
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
Recommended Reading: Maximum Metformin Dose
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Level Why Is This Important
Checking your blood glucose level is important because the results help guide decisions about what to eat, your physical activity and any needed medication and insulin adjustments or additions.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level is with a blood glucose meter. With this test, you prick the side of your finger, apply the drop of blood to a test strip, insert the strip into the meter and the meter will show your glucose level at that moment in time. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often youll need to check your glucose level.
What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
You May Like: Metformin Adverse Reactions
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Type 1 diabetes is a systemic disorder with diverse presentations and very high morbidity for this reason, the condition is best managed by an interprofessional team of healthcare professionals.
Type 1 diabetes is a serious disorder with very high morbidity and mortality. Over the long term, the vast majority of patients with this disorder will develop blindness, adverse cardiac events, end-stage renal disease, neuropathy, and in some cases, premature death. Data indicate that for those patients who manage to control their blood sugars without developing serious complications tend to have a good quality of life.
The key factor in preventing complications is patient compliance with their medications, follow up with the specialists and educators. At every patient encounter, the pharmacist, nurse, and clinicians should emphasize the importance of blood glucose control, long-term complications, and management goals. The patient should be encouraged to modify the lifestyle to reduce the risk of complications. In addition, all patients with diabetes should be made aware of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and ways of managing it. Patients should be educated about resources that are available and the benefits of joining support groups. A dietitian should educate the patient about foods that can be consumed, and the nurse should educate the patient on blood glucose monitoring at home.
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
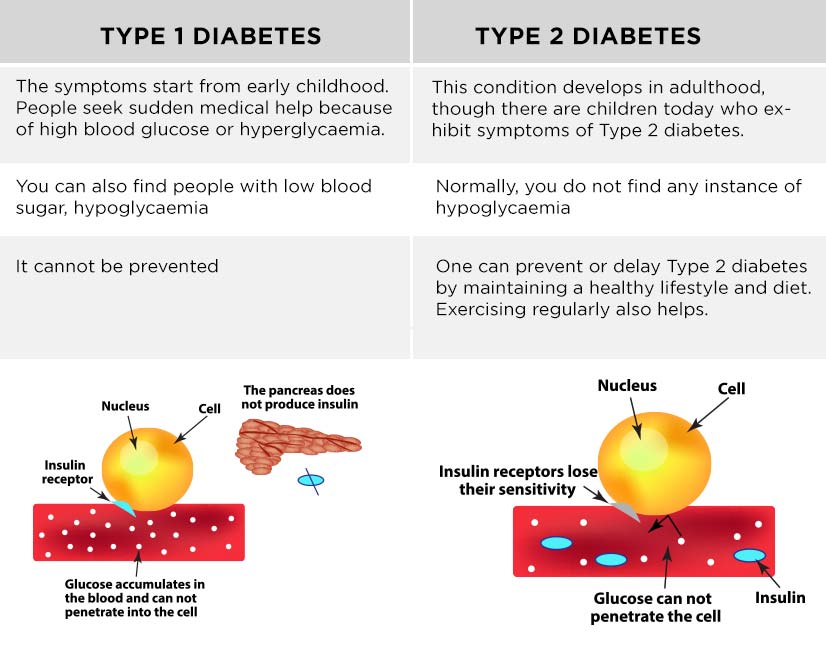
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
Don’t Miss: Orthostatic Hypotension Diabetes

