Causes Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
An ulcer is an open sore or wound on the skin. Ulcers on the feet are particularly common in those who have diabetes. Complications from the disease such as poor circulation and loss of feeling in the feet due to diabetes-related nerve damage make it more likely for a wound to develop, and also harder to heal.
People with diabetes who use insulin, have diabetes-related kidney, eye or heart disease, or who are overweight, use alcohol or tobacco have an even higher risk of developing foot ulcers.
Management Of Systemic And Local Factors
Treatment of diabetic foot ulcers requires management of a number of systemic and local factors.
Precise diabetic control is, of course, vital, not only in achieving resolution of the current wound, but also in minimizing the risk of recurrence. Management of contributing systemic factors, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerotic heart disease, obesity, or renal insufficiency, is crucial. Management of arterial insufficiency, treatment of infection with appropriate antibiotics, offloading the area of the ulcer, and wound care are also essential.
References
Amin N, Doupis J. Diabetic foot disease: From the evaluation of the “foot at risk” to the novel diabetic ulcer treatment modalities. World J Diabetes. 2016 Apr 10. 7 :153-64. . .
Naves CC. The Diabetic Foot: A Historical Overview and Gaps in Current Treatment. Adv Wound Care . 2016 May 1. 5 :191-197. . .
Rice JB, Desai U, Cummings AK, Birnbaum HG, Skornicki M, Parsons NB. Burden of diabetic foot ulcers for Medicare and private insurers. Diabetes Care. 2014. 37 :651-8. .
Gentile AT, Berman SS, Reinke KR, Demas CP, Ihnat DH, Hughes JD, et al. A regional pedal ischemia scoring system for decision analysis in patients with heel ulceration. Am J Surg. 1998 Aug. 176:109-14. .
Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection . J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan. 59 :220-34.e1-2. . .
What It Means To Have A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that forms when skin tissue breaks down and exposes the layers underneath. These ulcers typically occur under the big toes and balls of the feet.
“Anyone with diabetes can develop foot ulcers, but some may be at higher risk than others,” says Barrett. “Those of Native American, African-American or Hispanic descent are at a greater risk for these ulcers. Older men, people who use insulin, and those who have kidney, eye or heart disease related to diabetes are also at a greater risk.”
Some common causes of diabetic foot ulcers include:
- Poor circulation
- Nerve damage.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Is A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- A diabetic foot ulcer is a sore on the bottom of your foot that occurs at some point in almost 25% of all diabetic patients throughout their life.
- The most common site for a diabetic ulcer is on your foot.
- Many of these people become hospitalized due to an infection or an ulcer, or related complications.
- Diabetes and blood flow disease has been called the number one cause of foot or leg amputation in the United States.
- Some patients who develop a full ulcer, if untreated, can progress to amputation. Those people with diabetes who do receive amputation are almost always preceded by diabetic foot ulceration.
- Research has shown that working with a podiatrist is one of the single best things to prevent your foot.
How Do Doctors Treat Diabetic Foot Ulcers
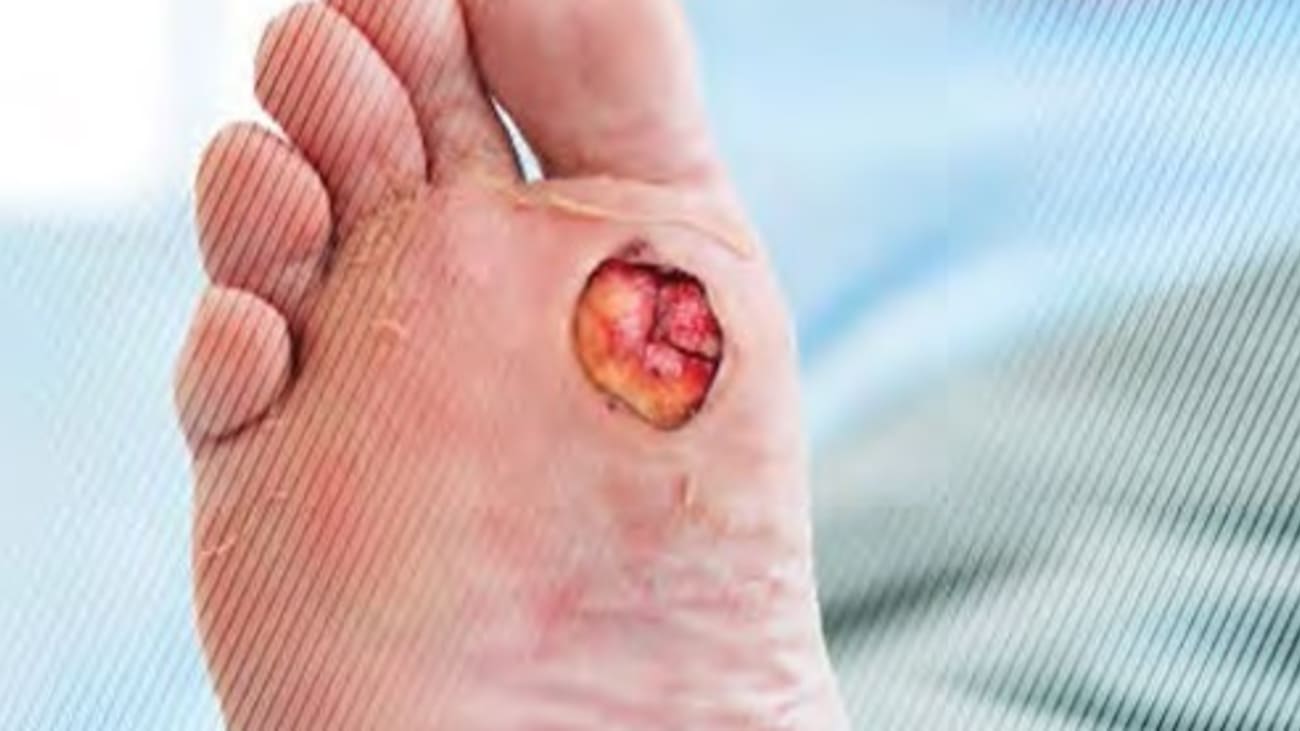
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common complication of;that can occur because of diabetes. People with diabetes often have poor circulation and neuropathy which make foot wounds slow to heal and difficult to detect. If your doctor spots a DFU on your foot, there are several potential treatment options, depending on the severity of the wound. Your doctor may debride the wound by removing dead tissue. A bandage will usually be placed over the wound to keep the area moist and protect it from infection. Taking pressure off of the wound, by resting the foot and using cushions, braces, or orthotics, will help it heal. In very severe cases, surgery may be necessary. If you have a DFU, please seek the care of a podiatrist.;
Wound care is an important part in dealing with diabetes. If you have diabetes and a foot wound or would like more information about wound care for diabetics, consult with Cynthia Ferrelli, DPM from New York. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
What Is Wound Care?
Wound care is the practice of taking proper care of a wound. This can range from the smallest to the largest of wounds. While everyone can benefit from proper wound care, it is much more important for diabetics. Diabetics often suffer from poor blood circulation which causes wounds to heal much slower than they would in a non-diabetic.;
What Is the Importance of Wound Care?
How to Care for Wounds
Also Check: Diabetic Macaroni And Cheese
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Symptoms
Normally a wound or sore on the skin would cause pain. But the same loss of feeling in the feet that often contributes to the development of a diabetic foot ulcer means that theres often no pain associated with the ulcer. This can make it difficult for people to realize that an ulcer is even there in the early stages, when treatment is most effective.
Aside from pain, another sign to look for is discharge or drainage from the wound in the socks. Ulcers that have been present for some time and that have become infected may also cause an unpleasant odor.
Make Sure You Dont Have An Infection:
- This is an area where your podiatrist can work with an infectious disease doctor. If you have any redness around your wound or drainage from the center of your wound, you likely have an infection of the current. In the short term, it is essential to start taking antibiotics and to get antibiotic medication onto this site. This can be life-threatening if allowed to continue for lengthy periods of time without improving.
- If you have redness or drainage developing around your ulcer, dont waste any time, this is the single most urgent thing you can do, dont be someone who loses their leg because they waited one or two days too long.
Recommended Reading: Normal A1c Levels Non Diabetics
How Diabetic Foot Ulcers Are Treated
If you do develop a diabetic foot ulcer, your podiatrist will perform debridement of the wound. This means that the doctor will remove the dead skin and tissue from the ulcer to encourage the healing of the tissue. The podiatrist will then apply a dressing to it to prevent an infection. The physician can also perform off-loading to relieve pressure from your foot ulcers, whereby your foot may be placed in a special boot, brace, or cast as your ulcers heal.
New Wound Therapytopical Pure Oxygenappears Effective In Healing Food Ulcers
Investigators from Midwestern University invited 73 people who had diabetes, both type 1 and 2, to participate in a study to test this new treatment for diabetic foot ulcers.
They found that nearly 42% of those who were randomly assigned to receive the oxygen therapy experienced significant symptom relief, compared to just 13.5% of those who were treated with regular room air for 12 weeks.2
This new food ulcer therapy is called TWO2 for Topical Wound Oxygen home care therapy. The treatment involves placing an inflatable chamber, similar to a large stocking, over the wound, and then an oxygen generator fills the chamber with pure oxygen administered under pressure.2
As a result of the oxygen therapy, Dr. Frykberg says, “it stimulates production of collagen, growth factor, new blood vessels and increased ability to fight infection.”
Oxygen has long been viewed as crucial in the wound-healing process,3-7;the researchers say. ;For years, hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been studied intensely to heal foot ulcers and prevent amputation. But results remain inconsistent, the researchers say.
However, Dr. Frykberg and his colleagues say that the use of topically administered oxygen therapy has been hampered by studies that weren’t well designed and complicated by results that were inconsistent.8-10
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Are The Risks Of Failing To Seek Treatment For A Dfu
There are several risks for a diabetes patient who either fails to seek treatment or fails to be compliant with their physicians recommendations. These risks include limb amputation, infections such as sepsis, and critical tissue damage such as gangrene.;
When PAD is present in a diabetic person, it can lead to PAD. When the vessels begin to narrow, and the reduction of blood flow to the legs and feet starts, nerve damage can begin . If there is no blood flow and the nerves are damaged, the patient may not know that an ulcer exists. PAD can slow down the bodys natural ability to heal, which can lead to amputation of toes, feet, and sometimes the lower leg.;
Infections can easily set in when glucose levels are high. If a foot ulcer exists and glucose levels spike, the chance of infection escalates. If the infection is mild to moderate and cellulitis is present, it may be able to be treated on an outpatient basis. If the patient does not follow medical directions, the result can be sepsis .;
A patient that goes untreated is at risk for critical tissue damage, such as gangrene. If the damage does not halt with aggressive treatment measures, the chances of necrosis are substantial.;
What Makes Foot Ulcers So Serious
The soft tissue of the foot isnt like that on other parts of the body, so an infection can get to the muscle and bone very quickly. Infection and poor blood flow can lead to more serious complications, Dr. Scott says.
That infection is what ultimately can lead to amputation. For this reason, you need to see your doctor quickly if you suspect you have a foot ulcer.
Your doctor may order an X-ray, and possibly an MRI, if you have an ulcer that is worsening. This will show whether there is any infection in the bone.
If you do get a foot ulcer, you need to keep your sugars under control;and follow up regularly with your doctor.
Its important not to ever let a wound linger without treatment. As time passes, the chances of it healing decrease. Be sure to see your doctor right away. If you dont have a podiatrist, youll need to get one to help you keep tabs on your foot health, Dr. Scott says.
Don’t Miss: Can You Live A Long Life With Diabetes
Promising Treatments For The Healing Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The number of Canadians with #diabetes is rapidly increasing. According to the Canadian Diabetes Association, more than 20 Canadians are diagnosed with the disease every hour of every day.
#Diabetic foot ulcers are the most common chronic complication from diabetes, affecting four to 10 per cent of patients. DFUs can last a year or longer and can happen again in up to 70 per cent of people who have previously been affected. Patients are more likely to develop DFUs if they have had diabetes for a long time, have poorly controlled blood sugar, have foot injuries or infection, are older, or smoke. However, neuropathy, damage to the nerves, which may result in a lack of feeling in the feet, and peripheral artery disease, which;reduces the blood flow to the limbs, may be the most significant causes. Because of nerve damage and numbness, an individual with diabetes may not be aware that they have a sore or wound, leading to even minor injuries getting worse or becoming infected. Decreased blood flow caused by peripheral vascular disease may prevent healing once an injury occurs.
When DFUs become infected, the bone or skin can also become infected. ;This can lead to significant pain and suffering; poor quality of life for patients; amputation of a leg, foot, or toe; increased treatment and hospitalization costs and can even lead to death.
Off-Loading Devices
MORE: SOLVING THE MYSTERIES OF HEART SURGERY
Compression Therapy
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment
The first step in treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is to remove necrotic wound tissue from the wound. It is essential that the method of debridement utilized does not damage nerves, tendons, and blood vessels. Since many people with diabetes don’t feel pain from the wound site, health care practitioners can’t rely on the patient to let them know when sensitive areas are being examined. The debridement will:
- Reduce pressure on the ulcer.
- Stimulate wound healing.
- Allow the healthy underlying tissue to be examined.
- Help the wound to drain.
- Optimize the effectiveness of the wound dressing.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Healing Tips For Diabetic Wound Care And Ulcers Of The Foot
Patients with diabetes can be at risk for diabetic foot ulcers, infections, and complications from those infections. Diabetic foot ulcers or wounds put patients at a higher risk of hospitalization and need for surgery or amputation. In fact, according to the CDC, there are 130,000 hospitalizations a year for amputations in those with diabetes. Up to 11.8% of those with diabetes have a wound and many may go on to need surgery. This means that wound care for diabetic foot ulcers as well as prevention is of the utmost importance.
As physicians, we have to use our resources and work with patients in order to heal diabetic foot wounds to prevent such complications.; If a patient also has numbness in their feet, they may not feel a foot wound developing. Diabetic foot sores that start from a small scrap or cut can unknowingly form into a deep ulcer. Checking your feet and keeping your blood sugar
Whether you have diabetes or are caring for a loved one requiring foot diabetic wound treatment, Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists can effectively help your wound heal and prevent further complications. Here we will discuss diabetic foot care and how to minimize the traumatic consequences of ulcers.
How do we care for diabetic foot wounds and how does one clean a diabetic foot wound?;
For;proper wound care, clean the wound with saline, apply a topical gel or antibiotic ointment medication to the wound once a day, as recommended by your doctor.;
Preventing diabetic wounds
How Does Hbot Help Your Diabetic Wounds Heal
Oxygen can only make its way through the blood within red blood cells. Since the circulation problems associated with diabetes slow the movement of red blood cells, important tissues become deprived of oxygen.
Without enough oxygen, cells struggle to produce the energy they need to block bacteria, synthesize new collagen, or regenerate and repair after injury. This is why diabetic wound healing slows until it comes to a full stop. Inhaling the concentrated flow of oxygen provided through regular HBOT treatments makes it possible to overcome oxygen deficiencies and;stimulate a more effective healing process.;;
Overall, HBOT helps your diabetic wounds heal faster. It recruits white blood cells by providing the oxygen they need to effectively kill bacteria, reduce swelling, and allow the rapid reproduction of new blood vessels. When you commit to weekly treatments in an ongoing protocol, HBOT revitalizes the bodys healing process and renews tissues you thought may never recover.
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
Evaluation And Treatment Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot problems, such as ulcerations, infections, andgangrene, are the most common cause of hospitalization among diabeticpatients. Routine ulcer care, treatment of infections, amputations, andhospitalizations cost billions of dollars every year and place a tremendousburden on the health care system.
The average cost of healing a single ulcer is $8,000, that of an infectedulcer is $17,000, and that of a major amputation is $45,000. More than 80,000amputations are performed each year on diabetic patients in the United States,and 50% of the people with amputations will develop ulcerations andinfections in the contralateral limb within 18 months. An alarming 58% willhave a contralateral amputation 3-5 years after the first amputation. Inaddition, the 3-year mortality after a first amputation has been estimated ashigh as 20-50%, and these numbers have not changed much in the past 30 years,despite huge advances in the medical and surgical treatment of patients withdiabetes.
Why Are Diabetics Prone To Foot Ulcers And Other Chronic Wounds
Diabetic patients are more prone to developing chronic wounds for a few reasons. Two of the most influencing factors are nerve damage and blood circulation issues that are common among diabetic patients.
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, tends to occur in patients who have a longer history with diabetes because elevated blood glucose levels damage nerves over time. Neuropathy causes patients to experience reduced, or lack of, sensation in the areas affected.
Many patients can sustain trauma or develop an infection without realizing it because theyre unable to feel pain in the area. Further, neuropathy commonly affects the feet, so a wound on the bottom of the foot can escalate quickly because the patient cannot feel or see the wound easily.
Blood circulation issues also can increase the risk for developing chronic wounds, as well as making the wounds more prone to infection. High blood glucose levels cause the narrowing of blood vessels, which constricts blood supply, Estocado said. Adequate blood supply is essential to normal wound healing. The secondary effect of impaired blood supply is a decrease in white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting infection and maintaining a strong immune system.
You May Like: Normal A1c For Non Diabetics
Diabetic Wound Care: 6 Ways To Treat Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Neuropathic ulcers, often caused by diabetes, are slow to healeven more so as patients age, if they have longer-term diabetes, or if theyre smokers. Other factors that may stall healing include hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and abnormal blood sugar levels, often associated with diabetes.
Diabetic ulcers typically occur below the ankle at any site of pressure, friction, shear, or trauma. The wound is likely to be round, with margins often characterized by a periwound callus. The presence of diabetes increases the risk for infection.
Treating neuropathic/diabetic ulcers can be challenging, so be sure to take the following steps to simplify the process and help improve outcomes:

