Testing For Type 1 Diabetes
A simple blood test will let you know if you have diabetes. If youve gotten your blood sugar tested at a health fair or pharmacy, follow up at a clinic or doctors office to make sure the results are accurate.
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also be tested for autoantibodies that are often present with type 1 diabetes but not with type 2. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2.
How To Reverse Diabetes Naturally
May 30, 2018
According to the 2017 National Diabetes Statistics Report, over 30 million people living in the United States have diabetes. Thats almost 10 percent of the U.S. population. And diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States, causing, at least in part, over 250,000 deaths in 2015. Thats why its so important to take steps to reverse diabetes and the diabetes epidemic in America.
Type 2 diabetes is a dangerous disease that can lead to many other health conditions when its not managed properly, including kidney disease, blindness, leg and food amputations, nerve damage, and even death.
Type 2 diabetes is a completely preventable and reversible condition, and with diet and lifestyle changes, you can greatly reduce your chances of getting the disease or reverse the condition if youve already been diagnosed. If you are one of the millions of Americans struggling with diabetes symptoms, begin the steps to reverse diabetes naturally today. With my diabetic diet plan, suggested supplements and increased physical activity, you can quickly regain your health and reverse diabetes the natural way.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
People of all ages can develop type 1 diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make insulin or makes very little insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps blood sugar enter the cells in your body where it can be used for energy. Without insulin, blood sugar cant get into cells and builds up in the bloodstream. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and causes many of the symptoms and complications of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults, but it can develop at any age.
Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2approximately 5-10% of people with diabetes have type 1. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes, but it can be managed by following your doctors recommendations for living a healthy lifestyle, managing your blood sugar, getting regular health checkups, and getting diabetes self-management education and support.
Read Also: Is 10 Units Of Insulin A Lot
What Are Some Easy Ways You Can Prevent Heart Disease And Diabetes
Diet plays a large role in chronic disease prevention. For example, while eating a pint of ice cream every once in a while wonât necessarily increase your risk, routinely eating these types of unhealthy foods most likely will.
âStudies show that people who regularly eat more whole grains, vegetables, fruit, beans, and nutsand less red meat, processed meat, saturated fats, highly processed foods, and sugartend to have lower rates of both diabetes and heart disease,â she says.
Eating a predominantly plant-based diet is one key way to reduce your risk of chronic disease, as the foods tend to be higher in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Not to mention, plant-based foods also tend to be much lower in saturated fat.
âRed and processed meats, on the other hand, are high in saturated fat,â Ramsing says. âAnd eating too much can raise your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and even some cancers.â
On the contrary, substituting beans and lentils for red meat can help improve blood sugar levels, which is critical for diabetes prevention, as well as cholesterol and blood pressure levelstwo major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Ramsing suggests incorporating Meatless Monday into your weekly routine to help you reduce your consumption of meat while increasing your intake of plant-based foods.
Recommended Reading: How To Keep Blood Sugar From Dropping
How Immunotherapy Could Stop And Prevent Type 1 Diabetes
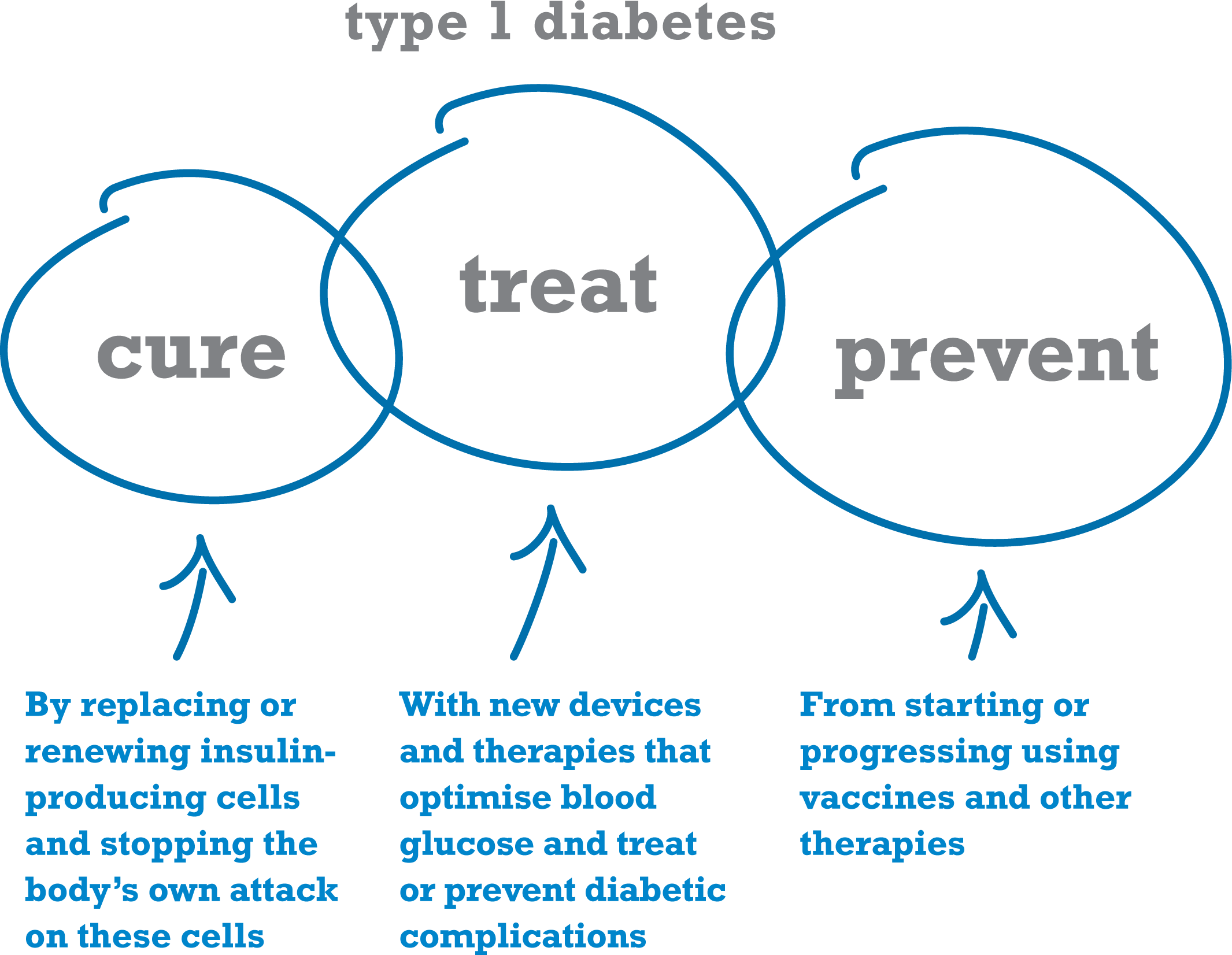
People with type 1 diabetes need lifelong treatments of daily insulin injections to manage their condition that still leave them at risk of long-term complications. Immunotherapy could one day become an insulin-free alternative to stop, prevent, and potentially cure this chronic disease.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are wrongly detected as foreign and destroyed by the immune system.
There is no cure once initiated, the disease will progress to complete destruction of the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, Pierre Vandepapelière, previous CEO of Imcyse, told me. This Belgian company is developing an innovative form of treatment that could change the way type 1 diabetes is treated.
Currently, the standard treatment for the disease consists of monitoring glucose levels and frequent insulin injections to keep healthy blood sugar levels. However, even with the best control measures, patients are still at risk of complications affecting the eyes, kidneys and nerves in the long term. Insulin treatment also carries the risk of inducing episodes of extremely low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, which can be life-threatening.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Metformin Lower Blood Glucose
How Long Do You Have To Take This Cocktail
Unfortunately, you have to take this cocktail for as long as you dont want Type 1 Diabetes or until theres a cure. Sonias son has gone off the cocktail multiple times, had markers return, and then gone back on the cocktail to remove the markers. Hes lucky in that hes been able to get rid of his markers every time they returned. I wish there was a one-time solution but I am willing to take a handful of pills multiple times a day to avoid a diagnosis of T1D.
What Does Insulin Do
Insulin is a hormone from the pancreas that allows sugar to enter the cells. Insulin also lowers the amount of sugar in the bloodstream. Without insulin, sugar is unable to enter the cells. This means that cells that make up muscles and other tissues will not be able to receive their main source of energy. People with type 1 diabetes may have a buildup of sugar in the bloodstream, causing life-threatening conditions.
Insulin Side Effects
Also Check: How Can Type 1 Diabetics Lose Weight
What Is The Life Expectancy For Someone With Type 1 Diabetes
Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association reported that people with type 1 diabetes live about 11 years less than average however, new research also suggests this differential can be reduced with good glycemic control. Most people with type 1 diabetes die from complications of type 1 diabetes such as heart disease or kidney disease. Thus, preventing complications and following a healthy lifestyle that prevents heart disease and controls blood sugar are the best things people with type 1 diabetes can do to live a long, healthy life.
Stem Cell Therapy To Prevent Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases affecting humans – the WHO estimates that around 350 million people have diabetes globally. Approximately 10% have type 1 diabetes – a disease that is often diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not make enough of the hormone insulin that keeps blood sugar levels in the normal range. People with type 1 diabetes must frequently take finger prick tests of their blood sugar level and receive multiple daily injections of insulin or wear an implanted insulin pump. While the cause of type 1 diabetes is not fully understood, the immune system plays a major role in causing the damage to the insulin producing cells in the pancreas. There is currently no prevention or cure for type 1 diabetes – but stem cells may be a promising new approach.
The role of stem cells
Stem cells are basic cells that have the capacity to multiply – either into specialized cells or to regenerate themselves. Cord blood stem cells are particularly unique because they not only have the capacity to develop into other cell types, but are also immune tolerant – that is they are less likely to provoke an immune response. They also contain greater numbers of regulatory T cells – a particular type of white blood cell that helps to keep the immune system in balance. This makes cord blood stem cells potentially useful for treating diseases where the immune system has ‘gone astray’ – such as type 1 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
Take Care Of Your Mental Health
A 2005 study found that depression may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, although more research is needed to determine how closely the two are connected.
If you need guidance, support, a calming voice, or a gentle reminder, pull up a couch and use one of these mental health apps to ease both your mind and your diabetes risk.
- Calm
How Type 1 Diabetes Works
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas creates little to no insulin for the body to convert sugar into energy. When this happens, sugar builds up in the bloodstream and can damage blood vessels throughout the body. Keeping blood sugar within a healthy range is crucial for type 1 diabetes, and people with type 1 diabetes will have to take insulin through injections or a pump.
Also Check: Low Or High Blood Sugar Symptoms
Does Exercise Affect Blood Sugar Levels
- Exercise is important for everyone, including people with type 1 diabetes.
- People with type 1 diabetes need to be careful to monitor their blood sugar before, during, and after exercise and have snacks with them in case blood sugar goes too low.
- When people exercise, the muscles use insulin to access blood sugar for fuel.
- This can lead to lower than expected blood sugar.
- Exercise also may trigger release of stored glucose from the liver. This can lead to higher than expected blood sugar. This is why it is important to check blood sugar, especially when beginning a new exercise program.
- People with type 1 diabetes may see their blood sugar go up or down with exercise.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes

If you have just been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes you are probably wondering, ‘why me?’
It is important to know it is not your fault that you have type 1 diabetes it is not caused by poor diet or an unhealthy lifestyle. In fact, it isnt caused by anything that you did or didnt do, and there was nothing you could have done to prevent it.
Read Also: Insulin Is Released From The Pancreas In Response To
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Who Is At Risk For Type 2 Diabetes
Many Americans are at risk for type 2 diabetes. Your chances of getting it depend on a combination of risk factors such as your genes and lifestyle. The risk factors include
- Having prediabetes, which means you have blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes
- Being overweight or having obesity
- Being age 45 or older
- A family history of diabetes
- Being African American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asian American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander
- Having acanthosis nigricans, a skin condition in which your skin becomes dark and thick, especially around your neck or armpits
- Smoking
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
Recommended Reading: Increase Blood Sugar Symptoms
What Types Of Diabetes Require Insulin
People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin to live. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your body has attacked your pancreas, destroying the cells that make insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, your pancreas makes insulin, but it doesnt work as it should. In some people with Type 2 diabetes, insulin may be needed to help glucose move from your bloodstream to your bodys cells where its needed for energy. You may or may not need insulin if you have gestational diabetes. If you are pregnant or have Type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider will check your blood glucose level, assess other risk factors and determine a treatment approach which may include a combination of lifestyle changes, oral medications and insulin. Each person is unique and so is your treatment plan.
You May Like: Greek Yogurt Diabetes
Is There A Type 1 Diabetes Diet
The basics of a type 1 diabetes diet include making sure carbohydrate intake is matched with insulin and choosing healthy options to maximize nutrition in each calorie. People with type 1 diabetes will find it is easiest to match carbohydrates to insulin if they follow a low-glycemic load diet, so that the impact of carbohydrates on blood sugar is slow and gradual. This also makes it easier to predict and match to required insulin.
Because weight gain can be a side effect of injecting insulin, a type 1 diabetes diet should be healthy and low in calories to help the person maintain or lose weight. Food lists of low-glycemic load options can help people learn what to include in their diet.
Recommended Reading: Alpha Cells Of Pancreas
Towards The Future: Prevention And Cure
Although the first goal of immunotherapy treatments for type 1 diabetes is to stop the progression of the disease in people who still have some insulin-producing cells, this technology has potential to go beyond that.
Immunotherapy could also prevent the development of type 1 diabetes in people known to be at risk. The risk of developing type 1 diabetes can be predicted 3 to 5 years before its onset, said Vandepapelière. It could therefore be possible to prevent the disease by halting this autoimmune process early. If conducted on a nationwide scale, this could possibly eradicate the disease.
Imcyse is contemplating testing the ability of its immunotherapy to prevent type 1 diabetes. To do so, it would have to implement a wide screening, particularly in children, to identify the subjects most at risk of developing the disease. This, however, would take considerable time. A longer study is needed to demonstrate the preventive efficacy, as with most vaccine developments, said Vandepapelière.
Further down the line, but already a tangible possibility, immunotherapy could be the key to the much-wanted cure for type 1 diabetes. In patients with established type 1 diabetes, an extinction of the autoimmune and inflammatory process could regenerate the beta cells, either spontaneously or after grafting beta cells, said Vandepapelière.
This article was originally published in January 2019 and has since been updated to reflect the latest developments.
Explore Related Topics:
Preventing Heart Disease And Stroke
Your heart health can be at greater risk if you have type 1 diabetes. If you’re overweight, smoke, and don’t control your blood sugar well, you could be two to four times more likely to develop cardiovascular disease than someone without type 1 diabetes is. Excess sugar in your blood can damage blood vessel walls. Controlling your blood sugar can reduce your risk for a heart attack or stroke from damaged blood vessels by more than 50 percent. Losing weight, not smoking, and keeping your blood pressure in check can all help, too.
Read Also: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
Every day we make choices that affect our health. Take these important five steps to make your lifestyle healthier and to start to prevent or reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and pre-diabetes:
Practical Approach To Pre

A practical approach to the management of islet autoantibody positivity starts with how islet autoantibody positivity is determined. This may occur through testing of islet autoantibodies in patients found to have a mildly elevated blood glucose found incidentally , hyperglycemia detected during an acute illness that resolves but in whom autoantibody testing was done, screening in the setting of multiple other autoimmune conditions, screening of family members of probands diagnosed with clinical type 1 diabetes as part of a research study, or population screening . After confirmation of either one or more islet autoantibodies , the patient should be counseled if possible and referred to centers participating in available research studies . If the patient does not qualify for any trials or does not wish to participate in a trial or research follow-up, the primary care provider, endocrinologist, or diabetologist should consider performing a hemoglobin A1c and/or random/fasting/post-prandial blood glucose self-monitoring. An OGTT may be done to detect early clinical diabetes .
Don’t Miss: Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat Bananas

