Throwing Away Your Needles And Lancets
Sharps bins and needle clippers are the safest way of disposing of your insulin needles and your lancets. A needle clipper removes the needle from your insulin pen, and is useful when youre out and about. How you get rid of your sharps bin depends on where you live. Your healthcare team should have information to help you get rid of your bin.
Regulation Of Insulin Secretion
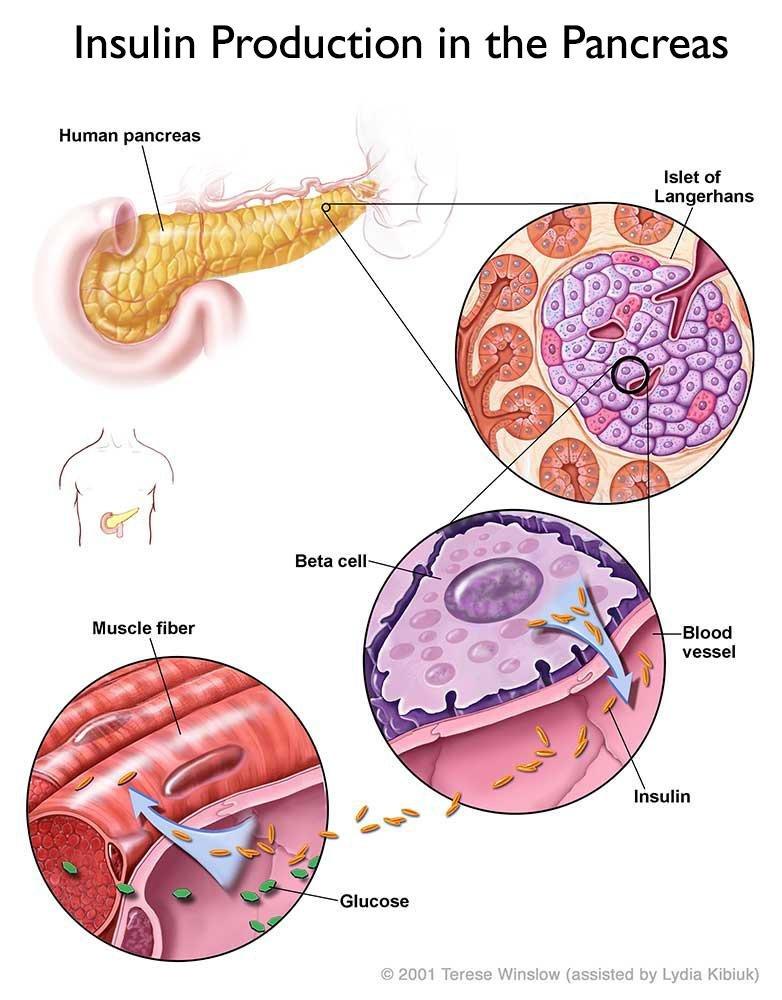
The physiology of insulin-producing cells is fundamental to understanding the regulation of insulin secretion. Insulin is a peptide hormone secreted by β cells of the pancreas. The human pancreas contains one to two million pancreatic islets housing different endocrine cells, primarily insulin-secreting β cells, glucagon-producing α cells, and somatostatin-secreting δ cells . Although islets compose only 1â2% of the human pancreas, they receive up to 10% of the total pancreatic blood supplies . Generally, insulin is released after ingesting glucose in a process named glucose-induced insulin stimulation. This process requires both the intracellular uptake and metabolic degradation of ingested glucose . In human β cells, glucose transporter 1 and GLUT3 are the prominent glucose transporters, whereas GLUT2 has been reported as a major glucose transporter in rodent . This difference could be attributed to the differences in Km values of different isoforms of glucose transporters .
The phosphorylation of glucose by the enzyme glucokinase is the first step in glucose metabolism. Glucose phosphorylation by GCK is related to insulin secretion therefore, GCK gene dysfunction or aberration leads to decreased glucose-mediated insulin release and glucose intolerance or diabetes . A major understanding of insulin secretion is derived from the research using rodent models, whereas few studies have been described in humans .
What Are The Disadvantages Of Human Insulin
In high concentrations, human and animal insulin tends to clump when injected into the skin. This clumping can cause slow and sporadic absorption. In comparison, insulin analogs tend to clump less and are absorbed more predictably.
Human insulin tends to take effect slower than insulin analogs. Insulin analogs can start acting in as little as
Read Also: Insulin Like Growth Factor 2
Favorite Resource For Diabetes Education
If insulin resistance has led you to be diagnosed with diabetes or you want to be educated if that day comes, enroll in a program led by Joslin Diabetes Center experts. The 12-week Why Wait program is designed to help you meet your weight goals, which could improve your bodys sensitivity to insulin.
Human Insulin And Insulin Analogs
Until the
Human insulin is available in two forms:
- a regular or short-acting form
- an intermediate-acting form called neural protamine Hagedorn insulin.
Regular human insulin takes action within 15 to 30 minutes and peaks in 1 to 3 hours. The more you take, the quicker it starts working.
A fish protein called protamine or zinc is added to NPH insulin to slow its absorption. NPH insulin takes effect about 2 hours after injection and reaches its maximum effect after about 4 to 6 hours.
Nowadays, insulin analogs are also used to treat diabetes. Insulin analogs are made in the same way as human insulin but are genetically altered to change the way they act in your body.
Insulin analogs have a different chemical structure and lower your blood sugar
Pens and syringes are both injected under your skin with a small needle. The needle in pens tends to be smaller than the needle in syringes. Some pens use cartridges that you insert into the pen manually while others are prefilled and thrown away when empty.
Insulin pumps deliver insulin through a tube placed into the fatty layer under your skin, usually around your stomach or the back of your upper arm.
Never reuse syringes, needles, or pens. Its also important not to share them with other people. Doing so can increase your risk of contracting or transmitting a blood-borne illness such as hepatitis or HIV.
still debate on whether insulin analogs offer significant benefits.
Recommended Reading: D50 And Insulin For Hyperkalemia
Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by the body not responding effectively to insulin. This is termed insulin resistance. As a result the body is less able to take up glucose from the blood. In the earlier stages of type 2 diabetes, the body responds by producing more insulin than it would normally need to.
If type 2 diabetes develops over a number of years, the extra demands on the pancreas to produce insulin can lead to a loss of insulin producing cells as they wear out.
Depending on their level of insulin resistance, people with type 2 diabetes may also need to take insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
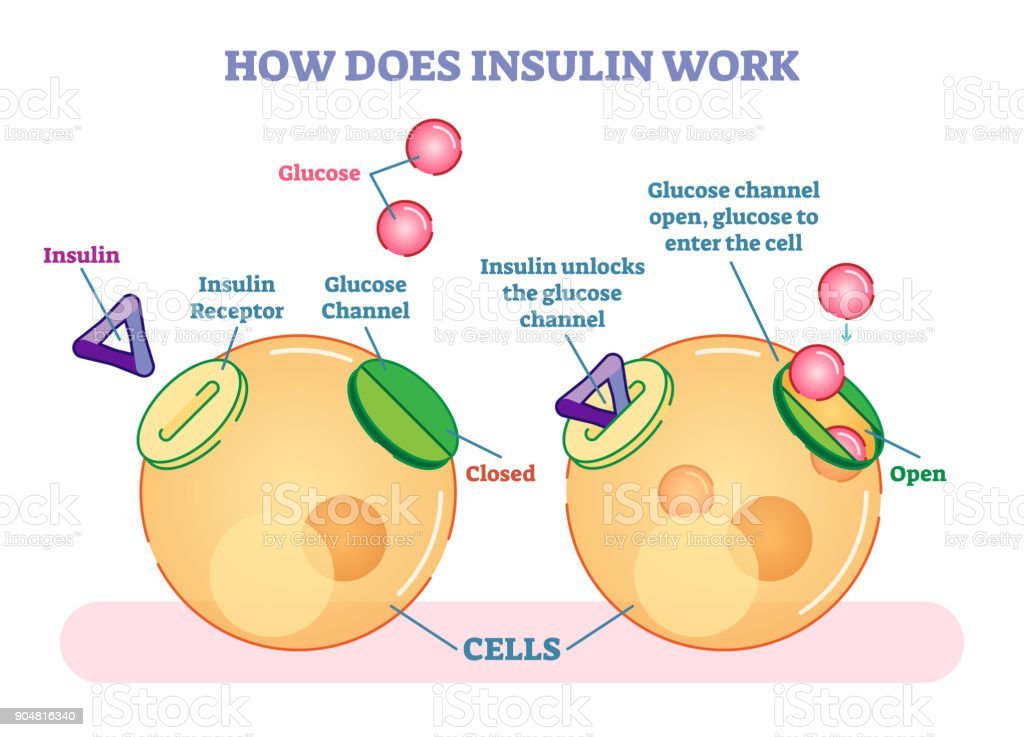
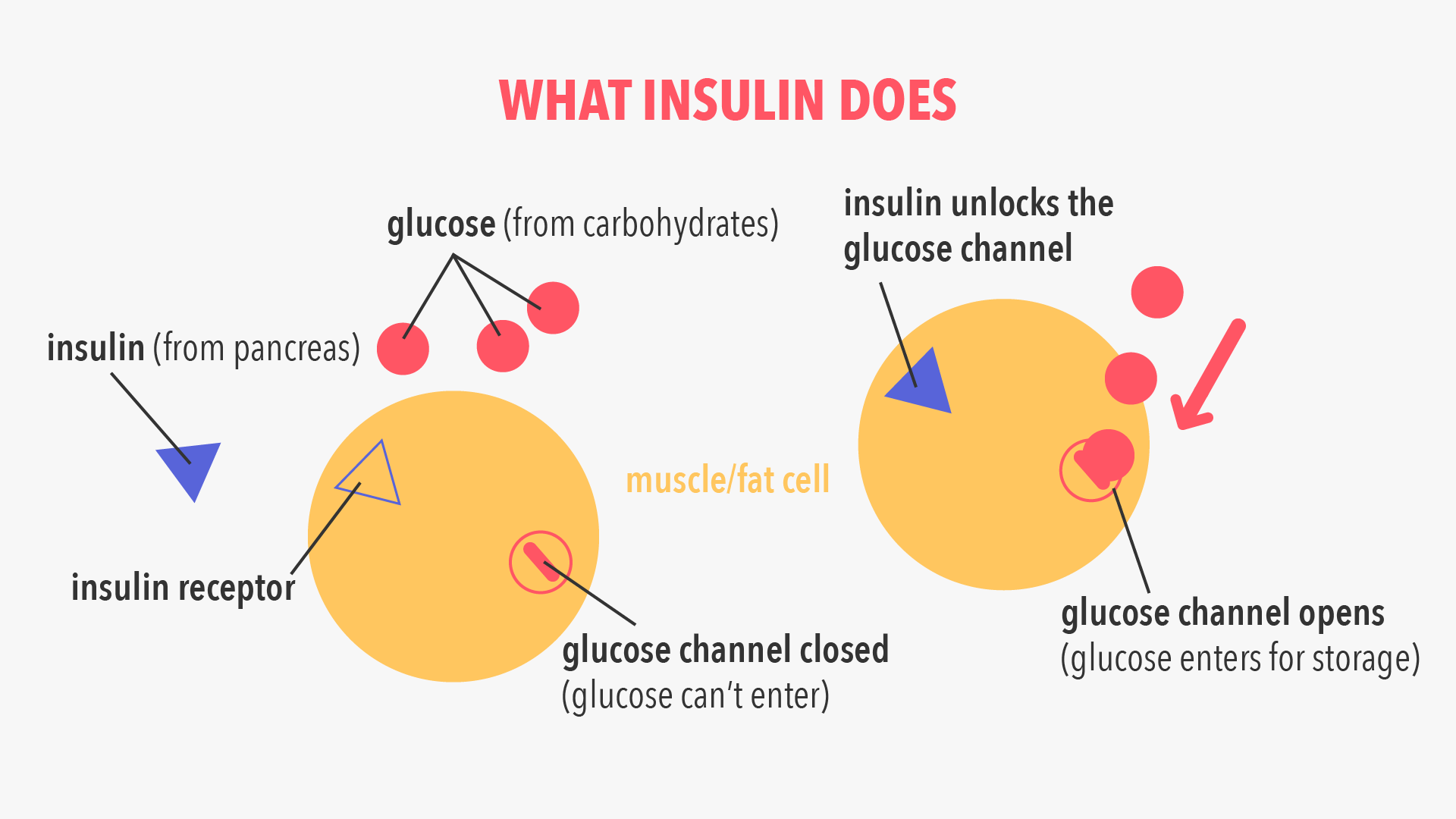
What Exactly Is Insulin
Is insulin a protein or a hormone?
In case you didnt know, insulin is a hormone thats produced by the pancreas. In people who have diabetes, the pancreas has become damaged and therefore cannot properly produce this vital substance that the body needs.
Insulin is responsible for how the body processes sugar. The bodys cells need to have sugar for energy but this sugar cant enter them directly.
So, after you eat food and your blood sugar increases, cells in the pancreas release insulin into the bloodstream. This hormone attaches itself to cells and tells them to absorb sugar from the blood. But it also has some other interesting functions.
If your body has more sugar than your cells need, insulin will store the excess sugar in the liver. If your blood sugar becomes low, these reserves will be released. In this way, insulin helps to balance your blood sugar so that theyre within a normal range.
If you have diabetes, it basically means that your bodys not releasing the insulin that it needs. This results in cells of the body being starved for energy and seeking it from different sources, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
Also Check: Diabetes And Hypotension
The Liver Makes Sugar When You Need It
When youre not eating especially overnight or between meals, the body has to make its own sugar. The liver supplies sugar or glucose by turning glycogen into glucose in a process called glycogenolysis. The liver also can manufacture necessary sugar or glucose by harvesting amino acids, waste products and fat byproducts. This process is called gluconeogenesis.
The liver also makes another fuel, ketones, when sugar is in short supply.
When your bodys glycogen storage is running low, the body starts to conserve the sugar supplies for the organs that always require sugar. These include: the brain, red blood cells and parts of the kidney. To supplement the limited sugar supply, the liver makes alternative fuels called ketones from fats. This process is called ketogenesis. The hormone signal for ketogenesis to begin is a low level of insulin. Ketones are burned as fuel by muscle and other body organs. And the sugar is saved for the organs that need it.
The terms gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis and ketogenesis may seem like complicated concepts or words on a biology test. Take a moment to review the definitions and illustrations above. When you have diabetes, these processes can be thrown off balance, and if you fully understand what is happening, you can take steps to fix the problem.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Sometimes people with type 2 diabetes take pills that help the insulin in their bodies work better. Some also need insulin shots or an insulin pump to control their diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes have to pay a little more attention to what they’re eating and doing than people who don’t have diabetes. They may need to:
- Eat a healthy diet, as determined by the care team.
- Get regular physical activity to achieve a healthy weight and allow insulin to work more effectively.
- Check their blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
- Get treatment for other health problems that can happen more often in people with type 2 diabetes, like high blood pressure or problems with the levels of fats in their blood.
- Have regular checkups with doctors and other people on their diabetes health care team so they can stay healthy and get treatment for any diabetes problems.
People with type 2 diabetes might have to eat smaller food portions and less salt or fat, too. Those who eat healthy foods, stay active, and get to a healthy weight may bring their blood sugar levels into a healthier range. Their doctors may even say they don’t need to take any medicines at all.
Read Also: Long Term Side Effects Of Insulin Use
Insulin And Blood Glucose Levels
Insulin helps control blood glucose levels by signaling the liver and muscle and fat cells to take in glucose from the blood. Insulin therefore helps cells to take in glucose to be used for energy.
If the body has sufficient energy, insulin signals the liver to take up glucose and store it as glycogen.
The liver can store up to around 5% of its mass as glycogen.
Some cells in the body can take glucose from the blood without insulin, but most cells do require insulin to be present.
Physiological Roles Of Insulin
The major purpose of insulin is to regulate the bodyâs energy supply by balancing micronutrient levels during the fed state . Insulin is critical for transporting intracellular glucose to insulin-dependent cells/tissues, such as liver, muscle, and adipose tissue. Any imbalance in exogenous energy supplies results in the breakdown of fats stored in adipose tissue and eventually accelerates insulin secretion. In the following sections, we discuss the major role of insulin in regulating several insulin-dependent tissue/organ functions.
Read Also: Does Low Blood Sugar Cause High Blood Pressure
Where Does Insulin Come From And What Does It Do
Insulin is probably a word youve heard a lot in relation to diabetes, but have you ever asked yourself, where does insulin come from? Have you wondered about what it does, and how were able to put it in vials for injection? Its true that insulin plays an important role in the body, so lets have a look at what insulin actually does, how it works, and answer the question where does insulin come from?
Why Is Insulin So Expensive
One of the problems encountered with insulin is its price tag. There are many reasons why diabetes medication is so expensive and more costly than it used to be.
Shockingly, 15 years ago a patient with diabetes would have to pay around $175 for a 20-milliliter vial of insulin, but today he or she would have to pay $1,478 for the same amount, as Stat News reports.
Why is this happening?
There are many reasons why insulin is still so expensive. Heres a rundown of some of them.
Read Also: Drug Interactions With Metformin
What Is Insulin Made Of
Insulin is made in different ways. You and your healthcare team will discuss which insulin you can take.
- Human insulin this is synthetic and made in a laboratory to be like insulin made in the body.
- Analogue insulin the insulin molecule is like a string of beads. Scientists have managed to alter the position of some of these beads to create genetically engineered insulin known as analogues.
- Animal insulin This isnt used much anymore, but some people find that insulin from animals works best for them. It is usually from a cow or pig.
Types Of Insulin Treatments
All types of insulin produce the same effect. They are used to mimic the natural increases and decreases of insulin levels in the body during the day. The makeup of different types of insulin affects how fast and how long they work.
The type of insulin youll be prescribed will vary depending on things like:
- your age
- how long it takes your body to absorb insulin
- how long insulin stays active in your system
| Insulin type | ||
|---|---|---|
| varied peaks | 10 to 16 hours | Taken twice a day, commonly 10 to 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner. This type is a combination of intermediate- and short-acting insulin. |
Talk with a doctor about the right insulin for you and your lifestyle.
You May Like: Glucophage Side Effects
Insulin Is Controlled By Three Companies
In the U.S., the production of insulin is produced by three companies who dominate over 90 percent of the worlds insulin market. These companies are Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
The Washington Post reports that over the last 20 years, both Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk have increased their prices on insulin 450 percent above inflation. The unfortunate reality is that most diabetes patients are vulnerable to drug company prices, as companies can set whatever price tag they want to on their drugs.
When The Blood Glucose Level Goes Down
- Blood sugar drops
- The pancreas detects the drop in blood sugar
- The pancreas switches on the output of glucagon into the blood
- Glucagon signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose
- The liver releases glucose into the bloodstream
- Blood glucose goes up to its normal set point and
- The pancreas detects the rise in blood sugar and switches off glucagon release.
Read Also: Walmart Insulin Otc
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
People who have type 2 diabetes may not know it because the symptoms aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Some people don’t have any symptoms at all.
But when a person gets type 2 diabetes, he or she may:
- pee a lot because the body tries to get rid of the extra blood sugar by passing it out of the body in the urine
- drink a lot to make up for all that peeing
- feel tired all the time because the body can’t use sugar for energy properly
Also, people whose bodies are having problems using insulin or who are overweight may notice something called acanthosis nigricans. This can cause a dark ring around the neck that doesn’t wash off, as well as thick, dark, velvety skin under the arms, in between fingers and toes, between the legs, or on elbows and knees. This skin darkening can lighten over time with improvement in insulin resistance.
In addition, girls with insulin resistance may have polycystic ovary syndrome . In PCOS, the ovaries get bigger and develop fluid-filled sacs called cysts. Girls with this condition often have irregular periods or may stop having periods, and they might have excess facial and body hair.
Types Of Insulin Administration With Needles Pumps Pens And Why Insulin Is So Expensive
What does insulin do? Help your body turn food into energy, for starters. When you have diabetes, and youre either not producing insulin or your insulin function is off, all sorts of things can go wrong. From needles to pens to pumps to types of insulin, were here to empower you with clear answers to all your pressing questions.
In This Article:
Alvin Powers, MD, Mihail Zilbermint, MD, and Irl Hirsch, MD
Don’t Miss: Baked Sweet Potatoes For Diabetics
The History Of A Wonderful Thing We Call Insulin
Since the dawn of time, we have searched for ways to make life easier for us. The modern age has given us some amazing technological advanceswhat we would do without the internet, our iPhones or high-speed travel?
For many people, surviving life without these things sounds rough. However, if you have diabetes, no doubt youre also a big fan of one particular 20th-century discovery: insulin.
Before insulin was discovered in 1921, people with diabetes didnt live for long there wasnt much doctors could do for them. The most effective treatment was to put patients with diabetes on very strict diets with minimal carbohydrate intake. This could buy patients a few extra years but couldnt save them. Harsh diets sometimes even caused patients to die of starvation.
So how did this wonderful breakthrough blossom? Lets travel back a little more than 100 years ago.
In 1889, two German researchers, Oskar Minkowski and Joseph von Mering, found that when the pancreas gland was removed from dogs, the animals developed symptoms of diabetes and died soon afterward. This led to the idea that the pancreas was the site where pancreatic substances were produced.
Later experimenters narrowed this search to the islets of Langerhans . In 1910, Sir Edward Albert Sharpey-Shafer suggested only one chemical was missing from the pancreas in people with diabetes. He decided to call this chemical insulin, which comes for the Latin word insula, meaning island.
Last edited: August 31, 2020
Alternative Methods For Insulin Production
The second commercial method for insulin production is the two-chain method, in which the A chain and the B chain of insulin are produced separately and then fused . Here, these 2 polypeptides are cultured in bacteria in two different fermenters and then purified. The purified A and B chains are then incubated under oxidizing conditions to form the disulfide bonds that are present in human insulin37.
Also Check: Signs Of High A1c
Role Of Insulin In Body
Insulin has a significant role in the metabolism of the body. It mainly regulates the storage of sugar and fat. The body cells mainly depend on glucose for uptaking glucose from the blood for the utilization of energy. Insulin will adjust the bodys glucose level by giving a signal to the fat cells and muscles to take glucose available in the blood. This glucose can be converted to energy. If excess glucose or sufficient glucose needed to be converted to life, insulin signals the liver to absorb the glucose and turn it into glycogen, stored.
The human liver can store up to 5% of its mass as glycogen. Most of the cells need glucose to take insulin, but some can do it even without insulin. It is an anabolic hormone which helps in glycogenesis, glucose uptake, lipogenesis. It also helps in the protein synthesis of skeletal muscle and fat tissue through the tyrosine kinase receptor pathway. In addition to this, it is an essential factor in the optimization of plasma glucose homeostasis. It generally counteracts hormones like Glucagon, other Catabolic Hormones like growth Hormones, Glucocorticoid, and Epinephrine.

