Preventing Low Blood Sugar Levels
Here are some other tips to help you avoid low blood sugar levels:
- Eat all your meals and snacks on time and try not to skip any.
- Take the right amount of insulin.
- If you exercise longer or harder than usual, have an extra snack.
- Don’t take a hot bath or shower right after an insulin shot.
- Stick to your diabetes management plan.
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly, so you can tell if your blood sugars are running too low and your treatment plan needs adjustment.
- Carry something containing sugar with you at all times and take it right away if you have symptoms. Don’t wait to see if the symptoms will go away they may get worse!
Alcohol and drugs can cause major problems with your blood sugar levels, so avoiding them is another way to prevent diabetes problems. Drinking can be particularly dangerous even deadly for people with diabetes because it messes up the body’s ability to keep blood glucose in a normal range. This can cause a very rapid drop in blood glucose in people with diabetes. Drug or alcohol use is also dangerous because it may affect someone’s ability to sense low blood sugar levels.
Learning how to recognize the signs of low blood sugar levels and get them back to normal is an important part of caring for diabetes. Keeping track of your blood sugar levels and recording lows when they occur will help you and your diabetes health care team keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
Understanding The Processes Behind The Regulation Of Blood Glucose
20 April, 2004
VOL: 100, ISSUE: 16, PAGE NO: 56
Pat James, PhD, is senior lecturer in applied physiology
Roger McFadden, MSc, is senior lecturer in applied physiology both at the School of Health and Policy Studies, The University of Central England in Birmingham
Pat James, PhD, is senior lecturer in applied physiology
Glucose is one of the bodys principal fuels. It is an energy-rich monosaccharide sugar that is broken down in our cells to produce adenosine triphosphate. ATP is a small packet of chemical energy that powers the millions of biochemical reactions that take place in the body every second.
We obtain glucose from the food that we eat, predominantly starch-rich foods such as potatoes, rice, bread, and pasta. Starch is a polysaccharide that is broken down by digestive enzymes into individual glucose molecules.
In the small intestine, glucose is absorbed into the blood and travels to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The hepatocytes absorb much of the glucose and convert it into glycogen, an insoluble polymer of glucose.
This is stored in the liver and can be reconverted into glucose when blood-glucose levels fall. Other types of simple sugars in our diet such as fructose, sucrose and lactose are also fuels that contribute to the production of ATP.
If glucose levels fall to too low a concentration or rise too high then this situation can lead to the neurological processes in the brain being compromised.
Do You Have Insulin Resistance
How do you find out if youre insulin resistant? No one test will tell you, but if you have high blood sugar levels, high triglycerides , high LDL cholesterol, and low HDL cholesterol, your health care provider may determine you have insulin resistance.
Important note: Type 1 diabetes is different its thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction . People with type 1 diabetes dont make enough insulin and need to take it to survive.
Recommended Reading: Insulin Like Growth Factor 2
Effect Of Aerobic And Resistance Exercise Training On Glycemic Control
Meta-analyses on the effects of exercise have estimated that for people with type 2 diabetes, both aerobic and resistance exercise improve glycemic control to an extent comparable to some oral antidiabetic drugs. Exercise should theoretically be an attractive option for people who prefer not to use drugs, or wish to obtain additional blood glucose control benefits.
There is some evidence that both exercise duration and intensity affect HbA1c levels. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of at least 12 weeks in duration concluded that structured exercise training of more than 150 minutes of exercise per week resulted in greater HbA1c reductions , than those with less weekly exercise time . Another meta-analysis of aerobic exercise studies concluded that not only did higher exercise intensity tend to produce larger improvements in VO2max, but that exercise intensity predicted postintervention HbA1c better than exercise volume . Workouts were, on average, 49 minutes , with a mean of 3.4 sessions per week for 20 weeks. However, only one study included in the meta-analysis approached high-intensity at 75% of VO2max. In another meta-analysis for studies involving aerobic, resistance, and combined training, the overall reduction in HbA1c was 0.8% with the effect of exercise intensity being unclear.
The Basics Of High Blood Sugar
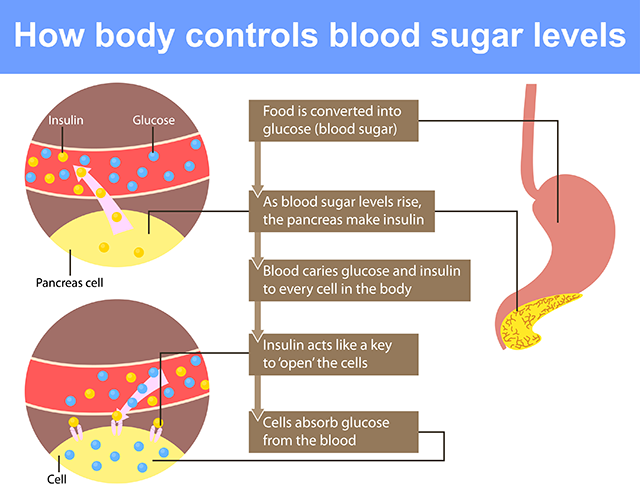
Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood sugar levels to rise higher than normal. This is also called hyperglycemia.
When you eat, your body breaks food down into sugar and sends it into the blood. Insulin then helps move the sugar from the blood into your cells. When sugar enters your cells, it is either used as fuel for energy right away or stored for later use. In a person with diabetes, there is a problem with insulin. But, not everyone with diabetes has the same problem.
There are different types of diabetestype 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes. If you have diabetestype 1, type 2 or gestationalyour body either doesn’t make enough insulin, can’t use the insulin well, or both.
Learn more about blood sugar Learn more about insulin
Also Check: Glipizide Vs Metformin
The Impact Of Brief High
Type 2 diabetes is a worldwide epidemic associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. The estimated lifetime risk of developing diabetes for a person born in the United States in 2000 is 32.8% for males and 38.5% for females. Diabetes increases morbidity and mortality due to heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, foot problems, and periodontal disease, and has a significant impact on quality of life. In 2010 it accounted for US$376 billion or 12% of the global health expenditure. This is approximately US$1330 per person per year.
Treatment goals for patients with diabetes include achieving and maintaining optimal blood glucose, blood pressure, and lipid levels in order to prevent or delay the progression of chronic complications. Exercise, along with diet and weight control, is considered essential for the prevention and management of diabetes. Epidemiological studies suggest that physical activity can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes by 30% to 50% in the general population. Exercise helps treat the glucose, blood pressure, and lipid abnormalities often found in people with diabetes, and assists with weight loss maintenance. In the United States, only 39% of adults with diabetes are active compared to 58% of those without the condition.
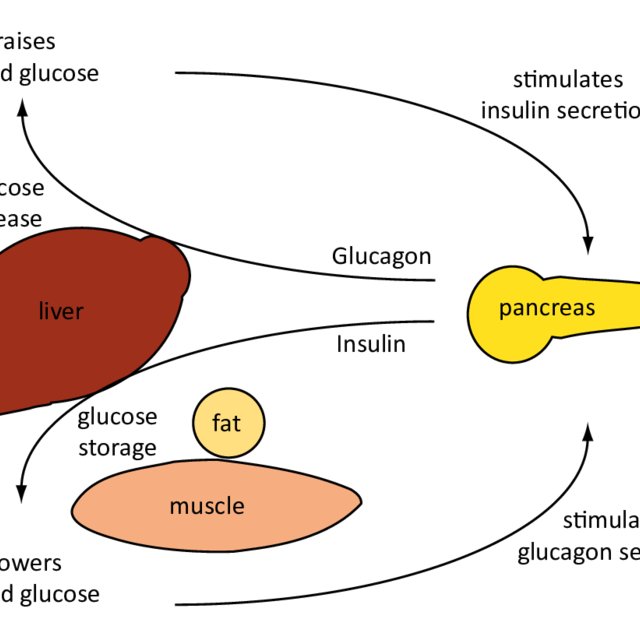
The Role Of Glucagon In Blood Glucose Control
The effect of glucagon is to make the liver release the glucose it has stored in its cells into the bloodstream, with the net effect of increasing blood glucose. Glucagon also induces the liver to make glucose out of building blocks obtained from other nutrients found in the body .
Our bodies desire blood glucose to be maintained between 70 mg/dl and 110 mg/dl . Below 70 is termed “hypoglycemia.” Above 110 can be normal if you have eaten within 2 to 3 hours. That is why your doctor wants to measure your blood glucose while you are fasting…it should be between 70 and 110. Even after you have eaten, however, your glucose should be below 180. Above 180 is termed “hyperglycemia” . If your 2 two blood sugar measurements above 200 after drinking a sugar-water drink , then you are diagnosed with diabetes.
Read Also: Sideffects Of Metformin
Glucose Metabolism During Moderate
Skeletal muscle is responsible for most of the uptake of glucose after a meal, and transport of glucose into the muscle is considered the limiting step in glucose disposal., Glucose transport occurs primarily by diffusion utilizing glucose transporter carrier proteins . Both exercise and insulin regulate glucose transport mainly by the translocation of the GLUT4 isoform from an intracellular compartment to the plasma membrane and transverse tubules., GLUT4 levels are considered an important determinant of insulin sensitivity,
At rest and postprandially, glucose uptake is insulin-dependent, with the major purpose being the replenishment of muscle glycogen stores. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation is generally impaired in type 2 diabetes. During exercise, muscle utilizes glucose made available by intramuscular glycogenolysis and by increased glucose uptake. Both aerobic and resistance exercises increase GLUT4 abundance and translocation, and hence blood glucose uptake by a pathway that is not dependent on insulin. Glucose uptake into contracting muscle is therefore normal even in the presence of type 2 diabetes.,, Following exercise, glucose uptake remains elevated with the contraction-mediated pathway remaining active for several hours.
How Insulin Works In The Body
Insulin is produced naturally in the body by the pancreas. The pancreas contains millions of beta cells, and these cells are responsible for making insulin. Whenever you eat food with carbohydrates, your beta cells release insulin so that other cells in the body can use the blood glucose it gets from food for energy. In a sense, insulin acts as a key, letting glucose into the cells.
Read Also: Metformin Withdrawal
Glucose : How Insulin And Glucagon Work
May 24, 2021
If you really want to understand how to manage your blood sugar levels, you should get to know your hormone functions.
âInsulin and glucagon are essential building blocks of human biology. If you’re monitoring your glucose levels for health and optimization reasons, it helps to know the nitty-gritty of the relationship these hormones have.
Our bodies work hard to continually keep our glucose in a tight rangeâonly a few teaspoons are found in the bloodstream at any time. Insulin and Glucagon are the two hormones that work as opposing forces to constantly regulate glucose levels.
When insulin and glucagon are working in perfect harmony, our blood sugar levels will stay nice and balanced. But what happens if they are not in sync? Letâs take a look at how these two hormones keep your blood sugar within healthy limits.
Aspartame And Your Health
These sweeteners don’t affect your blood sugar and are considered “free” foods if you have diabetes. Foods with fewer than 20 calories and 5 grams or less of carbohydrates don’t count on a diabetes exchange, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Obesity tends to travel with diabetes, and both conditions raise the risk for heart disease. Low- or no-calorie sweeteners may help with your weight loss efforts, Dr. Bernstein says. Aspartame is also completely digested into aspartic acid, phenylalanine and methanol in the upper small intestine, and then it is absorbed into the blood.
As such, aspartame does not disturb the balance of good and bad bacteria in your gut. It’s when these levels are out of whack that digestive issues can occur, according to the American Association of Diabetes Educators. That organization states that the safe limit for aspartame is 50 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. For a 150-pound adult, this translates to 3,409 milligrams of aspartame. A 12-ounce drink of aspartame-sweetened soda contains 200 milligrams.
However, there isn’t unanimous approval for aspartame. Dana Greene, RD, a dietitian in Brookline, Massachusetts, prefers that her diabetes patients use aspartame sparingly. “Use it in moderation and try to cut down or eliminate it over time,” she suggests. Her concern is that aspartame and other artificial sweeteners will whet a person’s appetite for more sweets.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Safe Dose Range
What Causes Hyperglycemia In People With Diabetes
- The dose of insulin or oral diabetes medication that you are taking is not the most helpful dose for your needs.
- Your body isnt using your natural insulin effectively .
- The amount of carbohydrates you are eating or drinking is not balanced with the amount of insulin your body is able to make or the amount of insulin you inject.
- You are less active than usual.
- Physical stress is affecting you.
- Emotional stress is affecting you.
- You are taking steroids for another condition.
- The dawn phenomenon is affecting you.
Other possible causes
- Pancreatic diseases such as pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and cystic fibrosis.
- Certain medications .
- Gestational diabetes, which happens in 4% of pregnancies, and is due to decreased insulin sensitivity.
- Surgery or trauma.
What Are The Symptoms Of Insulin Resistance And Prediabetes
Insulin resistance and prediabetes usually have no symptoms. Some people with prediabetes may have darkened skin in the armpit or on the back and sides of the neck, a condition called acanthosis nigricans. Many small skin growths called skin tags often appear in these same areas.
Even though blood glucose levels are not high enough to cause symptoms for most people, a few research studies have shown that some people with prediabetes may already have early changes in their eyes that can lead to retinopathy. This problem more often occurs in people with diabetes.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Glucaphage
Stress Increases Cortisol Which Affects Insulin Sensitivity
Youre overextended at work, theres a family crisis, and suddenly your blood sugar level is through the roof. Sound familiar? Stress definitely raises blood sugar levels, Dodell says. It increases cortisol, our fight-or-flight hormone. When cortisol goes up, it makes us less sensitive either to our bodys own insulin or to insulin injections.
Stress can be physical sustaining an injury, for example or mental, such as being beset with financial woes or marriage problems. Even positive changes to your daily routine a promotion at work or going on vacation can cause a sudden increase in blood sugar, he says.
The best ways to de-stress and get the hormones back under control? People often turn to food, which doesnt help, Grieger says. But we can learn new ways to manage stress. There are things you can do when youre right in the moment when tension at work suddenly makes you want to pull your hair out. Go for a five-minute walk or take 10 deep breaths to slow your breathing, she says. And there are regular habits you can develop, like establishing a daily exercise or meditation routine.
Regulation Of Blood Glucose
Regulation of glucose in the body is done autonomically and constantly throughout each minute of the day. Normal BG levels should be between 60 and 140 mg/dL in order to supply cells of the body with its required energy. Brain cells dont require insulin to drive glucose into neurons however, there must still be normal amounts available. Too little glucose, called hypoglycemia, starves cells, and too much glucose creates a sticky, paralyzing effect on cells. Euglycemia, or blood sugar within the normal range, is naturally ideal for the bodys functions. A delicate balance between hormones of the pancreas, intestines, brain, and even adrenals is required to maintain normal BG levels.
You May Like: Insulin-induced Hypoglycemia Test
Sleep And Sleep Deprivation
Acute sleep deprivation in healthy young adults has been reported to raise fasting blood glucose concentrations in association with altered diurnal cortisol secretion and reduced heart rate variability. These effects suggest increased counter-regulatory hormone secretion via hyper-arousal with activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary adrenal axis. There is also accumulating evidence that chronic sleep deprivation may impact on insulin and insulin resistance. Recent epidemiological studies report that reduced sleep duration is associated with increased BMI. Sleep deprivation is associated with decreased plasma concentrations of leptin, the adipocyte peptide hormone regulating fat mass and appetite, and increased concentrations of ghrelin, which increases appetite. Growth hormone is secreted during slow wave sleep, sleep declines with age and growth hormone deficiency in adults has been associated with central adiposity and insulin resistance, but whether sleep deprivation acts through these mechanisms is not clearly established. Obstructive sleep apnoea , where sleep disturbance results from obstruction to breathing during sleep, is associated with impaired glucose tolerance independent of adiposity, and improves with continuous positive airway pressure treatment but whether this is due to resolution of hypoxia and hypercapnia, or to effects on sleep quality, is unclear.
What Happens To My Blood Sugar Levels When Im Stressed
During stressful situations, epinephrine , glucagon, growth hormone and cortisol play a role in blood sugar levels. Stressful situations include infections, serious illness or significant emotion stress.
When stressed, the body prepares itself by ensuring that enough sugar or energy is readily available. Insulin levels fall, glucagon and epinephrine levels rise and more glucose is released from the liver. At the same time, growth hormone and cortisol levels rise, which causes body tissues to be less sensitive to insulin. As a result, more glucose is available in the blood stream.
When you have type 2 diabetes, low blood sugars from too much medication or insulin are a common cause of stress. The hormonal response to a low blood sugar includes a rapid release of epinephrine and glucagon, followed by a slower release of cortisol and growth hormone. These hormonal responses to the low blood sugar may last for 6-8 hours during that time the blood sugar may be difficult to control. The phenomena of a low blood sugar followed by a high blood sugar is called a rebound or Somogyi reaction.
When you have type 2 diabetes, stress may make your blood sugar go up and become more difficult to control and you may need to take higher doses of your diabetes medications or insulin.
During times of stress, individuals with diabetes, may have more difficulty controlling their blood sugars.
You May Like: Too Much Metformin
Mechanisms Of Insulin Resistance
Physiologically, at the whole body level, the actions of insulin are influenced by the interplay of other hormones. Insulin, though the dominant hormone driving metabolic processes in the fed state, acts in concert with growth hormone and IGF-1 growth hormone is secreted in response to insulin, among other stimuli, preventing insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Other counter-regulatory hormones include glucagon, glucocorticoids and catecholamines. These hormones drive metabolic processes in the fasting state. Glucagon promotes glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis. The ratio of insulin to glucagons determines the degree of phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of the relevant enzymes. Catecholamines promote lipolysis and glycogenolysis glucocorticoids promote muscle catabolism, gluconeogenesis and lipolysis. Excess secretion of these hormones may contribute to insulin resistance in particular settings, but does not account for the vast majority of insulin resistant states.

